GOLD MARKET VOLATILITY - REALITY CHECK Noise is high around XAUUSD with headlines like “trillions wiped out” and “gold crashing”.
Let’s keep it factual.
Gold is volatile due to profit-booking after a historic rally, geo-political uncertainty, and US policy expectations.
This is correction + consolidation, not a confirmed crash.
💡 “Trillions wiped out” = notional intraday value swings, not permanent losses.
Key Levels to Watch (XAUUSD)
Resistance: 5250 – 5300
Support: 5080 – 5000 (major demand zone)
Below 5000: Only if volatility expands with strong volume
Key Takeaway for Traders 🎯
High volatility ≠ clear direction
Avoid revenge or blind trades
Let price settle → trade with risk control
🛑 Staying out is also a strategy
📊 Focus on Forex / Crypto / Indices if Gold is unstable
Risk management > FOMO
Chart Patterns
FORTIS Near Strong Support – Bounce PossibleFortis has corrected from the top and moved down into a strong support area.
This trendline has acted as support before, and once again price is reacting positively from here.
Selling pressure is slowing down and buyers are starting to step in.
As long as this support holds, a bounce towards the upper resistance zone looks possible.
If support breaks, then further downside can happen.
For now, this is an important level to watch.
Nestlé India – Strong Uptrend with Healthy ConsolidationNestlé India continues to respect a well-defined rising channel, showing clear strength in its overall structure. After a strong upward move, the stock has entered a brief consolidation phase, forming a tight range while holding above key support levels.
This kind of price behavior usually reflects healthy profit booking rather than weakness. Buyers are still in control as long as the price stays within the channel and above the recent support zone.
If the structure remains intact, the trend favors further upside in the coming sessions, with higher levels likely to be tested gradually.
Overall, the stock is showing stability, strength, and controlled pullbacks — all signs of a strong trending market.
XAUUSD (Gold) – 4H Chart Analysis (Short & Clear)XAUUSD (Gold) – 4H Chart Analysis (Short & Clear)
Market Structure
Overall strong uptrend intact (higher high–higher low).
Recent move shows sharp rally → profit booking / pullback.
Current price ~5127, bounced from below 5000 area.
Key Levels
Resistance:
5250–5280 (minor)
5450–5600 (major supply zone / previous top)
Support:
5050–5000 (important demand zone)
4850–4800 (strong swing support)
Price Action Insight
Big red candles after top = healthy correction, not trend reversal yet.
Last candle shows rejection from lows → buyers still active.
As long as 5000 holds, bias remains bullish.
Buy-side View
Buy on dip near 5050–5000 with confirmation.
Safer buy if market reclaims & holds above 5200.
Targets (short-term): 5250 → 5400
Targets (swing): 5500–5600
Bearish Scenario (Only if)
Clean 4H close below 4950 → deeper correction possible
Downside then: 4850 → 4700
Conclusion
📈 Trend = Bullish
🔁 Phase = Pullback / consolidation
🧠 Best strategy = Buy dips, avoid panic selling
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingBest Practices for Retail Traders
1. Start with Buying Options
Risk is limited.
2. Prefer ATM or Slight ITM
Better stability, realistic probability.
3. Avoid Holding Overnight
Unless you understand IV, theta, and event risk.
4. Track Implied Volatility
Buy when IV is low, sell when IV is high.
5. Use a Trading Plan
Entry levels
Stop loss
Target
Position size
6. Don’t Chase Cheap OTM Options
They expire worthless most of the time.
Part 5 Advance Option Trading Strategies Risks in Option Trading
Options offer high rewards, but also involve risks if not used carefully.
1. For Option Buyers
High time decay (theta loss daily)
Need strong, fast movement
2. For Option Sellers
Unlimited risk (if naked selling)
High margin requirement
Volatility spikes kill profits
3. Liquidity Risk
Wide bid-ask spreads reduce profit potential.
4. Event Risk
News announcements can cause unpredictable moves.
Advance Trade Setup - KSCLKaveri Seed Company Ltd
BSE : 532899
NSE : KSCL
💡 Liked the idea?
Then don’t forget to Boost 🚀 it!
Comments are Most Welcome
Techincal Setup Details
LTP 818.00
VRVP
RSI
LinReg
VRVP :
The Visible Range Volume Profile (VRVP) indicator, often referred to as VPVR, displays trading volume by price rather than time, specifically for the visible chart area. The Value Area High (VAH) is the upper boundary of the price range where a significant percentage (default 70%) of volume occurs, acting as a crucial resistance or support level.
Significance of VAH:
Resistance : When prices are below or approaching the VAH, it often acts as resistance, signaling a potential pullback.
Support : In an upward trend, a breakthrough above the VAH can signal a continuation, turning the former VAH into support.
Trading VAH with VRVP:
Range Trading : If the price is within the VAH (Value area High) & VAL (Value area Low), it suggests a range-bound market. Sellers often enter near the VAH.
Trend Identification : A price moving well above the VAH indicates strong bullish sentiment, while price staying below the VAH suggests bearish sentiment.
RSI :
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator ranging from 0 to 100 that measures the speed and change of price movements to identify overbought (>70) or oversold (<30) conditions. It helps traders detect potential trend reversals or corrections.
Linear Regression Channel :
The Linear Regression Indicator (LRI) is a technical analysis tool that fits a straight line, known as the "least squares regression," to a specific number of price bars (e.g., closing prices) to identify the current trend. It plots the final, predicted value of this regression line, acting as a responsive, noise-filtering alternative to moving averages that indicates where price "should" be
Purpose: Identifies trend direction, potential reversals, and acts as dynamic support/resistance
I've extended the Indicator/Lines on the Right so that when the actual reversal happens, it easy to go with the flow, will be a Helping hand.
In the Current Scenario # KSCL
VAH is @ 740
Price has Broken LinReg Lower Deviation # Channel Broken, which means we can expect further weakness
RSI is @ 30 odd with Bearish signal still ON
Why this idea is Titled as ADVANCE TRADE SETUP, because we must understand that further weakness is expected & we also need to know well in advance whats the BEST possible price to enter for a Decent RR Ratio
LTP stands @ 818
once its below 760 mark, start adding in tranches till 690 Levels
There is one important point that needs to be highlighted.
KSCL operates in the seed business, which is largely driven by the monsoon cycle.
If you look at its balance sheet, you’ll notice a clear revenue swing around June, and historically, the stock price also reacts during the March–June quarter.
As of now, we are nearing the end of January.
Till mid-March, we may get opportunities to accumulate the stock near the above-mentioned best buy zone.
Once the position is in place, the idea is to hold for an upswing, which could range between 40% to 80%, and possibly more.
Stop-loss (closing basis):
• ₹620 / ₹590
Important Note:
This idea is being shared well in advance.
All price levels mentioned are assumptions and expectations, meant only for guidance.
Actual prices may vary by ±10% to 15%.
Members are advised to act based on real-time market behavior and their own judgment.
Plan patiently. Execute with discipline.
For more insights & trade ideas,
📲 Visit my profile and hit Follow
Warm regards,
Naresh G
SEBI Registered Research Analyst
💬 Comment below if you want me to analyse any stock for you 🔍
If You Want to Catch the Bottom, First Wait for RSI.To Do Nothing.
Right now, staying out is already a win.
The market is moving fast, noisy, and uncomfortable. Both buyers and sellers are getting trapped — not because direction is unclear, but because the market has not finished its process yet.
This is a moment to stay calm and observe, not to force a trade.
Observe how price begins to slow down.
Observe how selling pressure fades.
Note:
Stay focused on RSI behavior. When price decelerates and RSI shows clear convergence / stabilization, that’s when it makes sense to start thinking about potential long ideas — not before.
Until then, observation comes first.
Sometimes, doing nothing is the most disciplined decision you can make.
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Resistance Breakout in MTARTECH
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
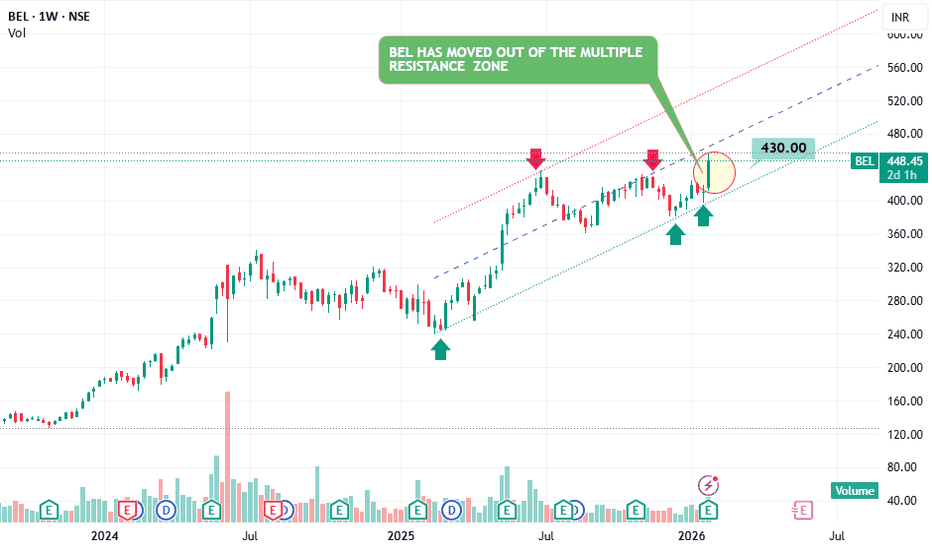
BEL (Bharat Electronics) – Bullish Technical SetupBEL is showing strong bullish structure across timeframes:
✅ Weekly Chart View
Stock is forming a Higher High + Higher Low (HH-HL) pattern
This confirms uptrend intact and buyers are consistently defending dips
Indicates trend continuation strength
✅ Daily Chart View
BEL has moved out of a multiple resistance zone
Breakout is supported by good volume, which adds confirmation and reduces chances of fake breakout
This breakout suggests fresh momentum and potential for next leg up
📌 What to watch next
Retest of breakout zone (if it happens) should act as support
Continuation will be stronger if price sustains above breakout with higher volumes on green candles
⚠️ Invalidation / Caution
If price falls back below the breakout zone, it can turn into a bull trap / false breakout
XAUUSD – H2 Technical AnalysisXAUUSD – H2 Technical Outlook: Short-Term Sell Pressure as Liquidity Gets Cleared | Lana ✨
Gold is showing signs of short-term weakness after an aggressive upside expansion. Price action suggests the market may continue to move lower in the near term, not as a trend reversal, but as a liquidity-driven correction within a broader bullish structure.
At this stage, the focus shifts from continuation to how price behaves while liquidity is being taken below structure.
📈 Market Structure & Price Behavior
The recent vertical rally has left the market overextended, making a corrective phase technically healthy.
Price has broken below short-term support and is now trading under a descending corrective trendline, signaling short-term bearish pressure.
This type of structure often develops when the market needs to clean buy-side positions before rebuilding for the next leg.
While the higher-timeframe trend remains bullish, the intraday bias has shifted to corrective / bearish until liquidity objectives are met.
🔍 Key Liquidity Zones on the Chart
Short-term sell zone: the descending trendline near current price As long as price reacts below this trendline, rallies are more likely to be sold.
Scalping buy liquidity: around 5050–5070 This area may generate temporary bounces, but reactions here should be treated as short-term only.
Key bullish order block: 4825 – 4830 A critical zone where stronger buyer participation may appear if the sell-off extends.
Major swing liquidity zone: 4613 – 4625 This is a high-confidence liquidity pocket where the market could complete a deeper correction and reset the broader bullish structure.
🎯 Trading Scenarios
Primary scenario – Continuation of the pullback: As long as price remains below the descending trendline, gold may continue to move lower to sweep liquidity below recent lows. This favors sell-on-rallies rather than buying strength.
Secondary scenario – Temporary reaction: Short-term bounces may occur around the 5050–5070 area, but without structural reclaim, these moves are more likely corrective than trend-changing.
Structural defense scenario: If price reaches the 4825–4830 or 4613–4625 zones, watch closely for signs of stabilization and absorption, which would signal that the liquidity objective has been completed.
🧠 Lana’s View
This move lower is best seen as liquidity cleanup, not panic selling. Lana stays patient during corrective phases, avoiding early longs and waiting for price to reach clear liquidity zones before reassessing bullish continuation.
✨ Let the market take what it needs, then look for structure to rebuild.
XAUUSD 30 MIN T/F ANALYSIS---
📊 Market Structure Explanation (Gold – 30 Min)
The price show heavy selling so we can measure recent top supply and copy it
after retesting we can measure from retesting top and past previous supply and match current supply so supply will be completed --
🔍 What the market can do next:
Scenario 1 – Pullback / Reversal (Needs Confirmation):
For any meaningful reversal to occur, the market must first show clear bullish candlestick confirmation.
This includes patterns such as:
bullish engulfing candles
Strong rejection wicks (lower shadows)
morning star formations
Consecutive bullish closes
Short lower-wick rejection candles showing bullish pressure
Without these bullish structures, any upside move should be treated as a temporary pullback, not a reversal.
Scenario 2 – Continuation:
If sellers stay strong and bullish confirmation does not appear, price can break down this zone and continue lower with another impulsive bearish move.
Scenario 3 – Range formation:
Market may form a small sideways structure near this level before choosing a clear direction.
🧭 Summary:
The trend is bullish, but price is at a sensitive support zone.
Reversal is only valid if bullish candlestick patterns and bullish pressure appear.
Otherwise, the structure favors continuation or short-term consolidation before the next move.
MTAR Tech – Monthly Chart View (Breakout Note)MTAR Tech – Monthly Chart View (Breakout Note) 📈
MTRA Tech has moved out of its horizontal consolidation channel on the monthly timeframe, indicating a potential trend reversal / fresh bullish phase.
✅ Key Highlight:
Horizontal range breakout confirmed on monthly chart
Volume expansion during breakout adds strong credibility, showing institutional participation and genuine buying interest
📌 What it means technically:
Earlier, price was time-wise consolidating (sideways range = accumulation zone)
Now breakout suggests buyers have taken control
If price holds above the breakout zone, it can act as a new support in coming months
🎯 Bullish continuation signs to watch:
Monthly close sustained above the channel top
Next 1–2 months should show higher high – higher low structure
Volume should remain above average on up candles
⚠️ Risk / invalidation:
If price slips back inside the channel, it becomes a false breakout trap
Gold 4900/4hJust like silver, i see gold coming down to check 5000 levels or maybe 4900. Logic is simple too bullish too soon, without forming base. 8 continuous green candles on 1D, now finally a red doji and today broke that doji. So there might be some fake bullishness.
Be vigilant but remember everything is possible.
#All this is my view not a financial advise.
Silver Down to 90/4hAlthough we saw a good correction here, around -10% today. Somewhat somewhere i see silver moving further down to 90 levels (might come to check the old channel).
Well we could also see some buying here as it is bottom of its yellow channel(current), just to trap people in fomo bullishness.
My long term view is, I am still bullish, year end 200$+. But right now dont go all in, keep risk management and money management tight. Remember, Anything can happen.
#My views not a financial advice.
INDIANB 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Current Price Context (as of latest trading)
Indian Bank is trading near ₹910–₹920 levels on NSE.
📈 1‑Month Key Resistance Levels (Upside)
These are the levels where price may face selling pressure or reversal if bulls weaken:
R1 — ₹918–₹920 — immediate resistance area just above current trade.
R2 — ₹927–₹930 — secondary resistance zone.
R3 — ₹935–₹940 — further upside resistance zone for continuation moves.
Summary: Immediate upside capped around ~₹918–₹930. Break and close above this band can signal stronger bullish continuation.
📉 1‑Month Key Support Levels (Downside)
Important levels that can act as rebound zones on pullbacks:
S1 — ~₹880–₹885 — first meaningful support near recent swing lows.
S2 — ~₹860–₹865 — secondary support from broader short‑term structure.
S3 — ~₹830–₹835 — major zone where bigger trend buyers may step in.
Summary: Minor supports start ~₹880, stronger support cluster around ~₹860‑₹835.
📊 Pivot / Neutral Reference
Pivot around ~₹907–₹910 — current central reference area.
Price above pivot suggests bullish bias, below could tilt neutral to bearish within the month.
📌 Interpretation For 1‑Month View
Bullish scenario:
Holds above ₹900–₹910 pivot → targeting ₹927–₹940 zone.
Neutral / consolidation:
Trading between ₹880–₹910.
Bearish risk:
Break below ₹860–₹845 could open deeper correction toward ₹830.