Technical Analysis MasteryA Complete Guide to Reading, Timing, and Trading Financial Markets
Technical analysis mastery is the art and science of interpreting market price behavior to make informed trading and investment decisions. Unlike fundamental analysis, which focuses on financial statements, economic indicators, and business performance, technical analysis concentrates on price, volume, and time. The core belief behind technical analysis is that all known information—fundamental, economic, political, and psychological—is already reflected in the market price. By mastering technical analysis, traders aim to identify trends, anticipate reversals, and optimize entry and exit points with greater precision.
Foundations of Technical Analysis
At the heart of technical analysis lie three classical assumptions. First, the market discounts everything, meaning price reflects all available information. Second, prices move in trends, and once a trend is established, it tends to continue rather than reverse abruptly. Third, history tends to repeat itself, as market participants often react in similar ways under similar circumstances due to human psychology. These principles form the philosophical backbone of all technical tools and strategies.
Mastery begins with understanding price charts, as they visually represent market behavior. The most commonly used charts are line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. Among these, candlestick charts are widely favored because they convey more information, such as open, high, low, and close prices, along with market sentiment. Each candlestick tells a story about the battle between buyers and sellers within a specific time period.
Trend Analysis and Market Structure
Trend identification is a cornerstone of technical analysis mastery. Trends are broadly classified into uptrends, downtrends, and sideways (range-bound) markets. An uptrend is characterized by higher highs and higher lows, while a downtrend shows lower highs and lower lows. Sideways markets reflect consolidation, where price moves within a defined range.
Understanding market structure—such as swing highs, swing lows, breakouts, and pullbacks—helps traders align with the dominant trend. The famous saying, “The trend is your friend,” emphasizes that trading in the direction of the prevailing trend significantly increases the probability of success. Mastery involves not only spotting trends early but also knowing when a trend is weakening or transitioning into another phase.
Support, Resistance, and Key Price Levels
Support and resistance are among the most powerful and widely used concepts in technical analysis. Support refers to a price level where buying interest is strong enough to prevent further decline, while resistance is a level where selling pressure halts upward movement. These levels often act as psychological barriers due to collective trader behavior.
As traders gain mastery, they learn that support and resistance are not exact lines but zones. Former resistance can become new support after a breakout, and vice versa. Identifying these levels across multiple timeframes adds robustness to analysis and helps in setting realistic targets and stop-loss levels.
Indicators and Oscillators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations derived from price and volume data. They help traders interpret market conditions more objectively. Indicators generally fall into two categories: trend-following indicators and momentum oscillators.
Trend-following indicators, such as moving averages and the Average Directional Index (ADX), help identify the direction and strength of a trend. Moving averages smooth price data and act as dynamic support or resistance levels. Momentum oscillators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic Oscillator, and MACD, help determine whether a market is overbought or oversold.
True mastery does not come from using many indicators but from understanding a few deeply. Overloading charts with indicators often leads to confusion and conflicting signals. Skilled analysts use indicators as confirmation tools rather than primary decision-makers.
Volume Analysis and Market Participation
Volume is the fuel behind price movement. Analyzing volume provides insight into the strength or weakness of a price move. Rising prices accompanied by increasing volume suggest strong buying interest, while price increases on declining volume may indicate a lack of conviction.
Volume analysis also helps in identifying breakout validity, accumulation, and distribution phases. Tools such as volume moving averages, On-Balance Volume (OBV), and Volume Profile enhance a trader’s ability to understand market participation. Mastery involves recognizing when “smart money” is entering or exiting the market.
Chart Patterns and Price Action
Chart patterns represent recurring formations created by price movement over time. Common patterns include head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, triangles, flags, and wedges. These patterns reflect shifts in supply and demand dynamics and often signal trend continuation or reversal.
Price action trading, a refined form of technical analysis, focuses on raw price behavior without heavy reliance on indicators. Candlestick patterns like doji, engulfing patterns, hammers, and shooting stars offer clues about market sentiment and potential turning points. Mastery in price action requires patience, screen time, and an understanding of context rather than isolated signals.
Risk Management and Trading Psychology
No level of technical analysis mastery is complete without strong risk management. Even the best technical setups can fail. Successful traders focus on probability and consistency, not certainty. This involves defining risk per trade, using stop-loss orders, maintaining favorable risk–reward ratios, and managing position size.
Equally important is trading psychology. Fear, greed, overconfidence, and hesitation can undermine even the most accurate analysis. Master traders develop discipline, emotional control, and the ability to follow a trading plan without deviation. Technical mastery is as much about mindset as it is about charts.
Multi-Timeframe Analysis and Strategy Integration
Advanced technical analysis incorporates multi-timeframe analysis, where traders analyze higher timeframes to identify the primary trend and lower timeframes for precise entries and exits. This approach aligns short-term trades with long-term market direction, improving accuracy.
Technical analysis mastery also involves integrating strategies—such as trend following, breakout trading, mean reversion, and swing trading—based on market conditions. There is no single strategy that works in all environments; adaptability is a hallmark of mastery.
Conclusion
Technical analysis mastery is a continuous learning journey rather than a destination. It combines chart reading, indicator interpretation, pattern recognition, volume analysis, risk management, and psychological discipline into a cohesive skill set. Over time, with consistent practice and reflection, traders develop an intuitive understanding of market behavior.
Ultimately, mastery means simplifying complexity—seeing clarity where others see chaos—and making decisions based on logic, probability, and discipline rather than emotion. In dynamic financial markets, technical analysis mastery empowers traders to navigate uncertainty with confidence and precision.
Harmonic Patterns
XAUUSD 1H Price Correction After Strong Rejection at 4550On the 1H chart, XAUUSD is showing a price correction after a sharp sell-off from the 4550 supply area. The rejection from this level clearly highlighted selling pressure from higher timeframes and caused a shift in short-term price structure, with gold unable to hold above higher price levels.
Following the decline, price found support and created a new 1H demand area near 4273, where buyers became active and selling momentum eased. This zone is now acting as a short-term support base. While price remains above 4270, the risk of immediate further downside stays low, and the market may move sideways or attempt a recovery.
From a structure point of view, gold is trying to build a higher low, which opens the possibility of a short-term price rebalance towards nearby liquidity. With stronger session participation and sustained volume, price can move towards the 4330–4380 range, which matches earlier intraday reactions and acts as the first resistance area.
Above this range, 4430 remains a key higher-timeframe level. This zone has seen multiple past reactions and supply presence, making it important for judging whether the correction continues or sellers step back in.
This view is shared for educational purposes only, based on price action and demand–supply behaviour. Always look for confirmation and follow proper risk management.
#NIFTY Intraday Support and Resistance Levels - 05/01/2026A gap-up opening near the 26,500 zone is expected in Nifty, indicating continuation of the recent bullish momentum. The index has moved strongly from lower levels and is currently holding above the 26,250 support, which keeps the short-term trend positive. As long as Nifty sustains above this level, buying interest is likely to remain intact.
On the upside, a decisive hold above 26,550 will open the gates for further upside expansion. In this scenario, fresh long positions can be considered with upside targets placed around 26,650, 26,700, and 26,750+. Any minor dip toward the 26,250–26,300 zone may act as a healthy pullback and provide a buying opportunity, as this area is now turning into a strong demand zone.
On the downside, if the index fails to sustain above 26,250 and slips below this support, short-term profit booking can be expected. A breakdown below 26,250 may drag Nifty toward 26,150, 26,100, and 26,000 levels. Until such a breakdown occurs, the overall bias remains buy-on-dips, with traders advised to trail stop losses and book partial profits at higher levels.
NIFTY- Intraday Levels - 5th Jan 2026* Approx levels Consider +/- buffer in levels*
If NIFTY sustain above 26431/53 then 26510/18 above this more bullish above this wait
If NIFTY sustain below 26257 then 26197/190 then 26161/146/41 below this more bearish then more levels marked on chart
My view :-
"My viewpoint, offered purely for analytical consideration, The trading thesis is: Nifty (bearish tactical approach: sell on rise)
Will be a red candle today? Will it form a top for tomorrows expiry?
This analysis is highly speculative and is not guaranteed to be accurate; therefore, the implementation of stringent risk controls is non-negotiable for mitigating trade risk."
Consider some buffer points in above levels.
Please do your due diligence before trading or investment.
**Disclaimer -
I am not a SEBI registered analyst or advisor. I does not represent or endorse the accuracy or reliability of any information, conversation, or content. Stock trading is inherently risky and the users agree to assume complete and full responsibility for the outcomes of all trading decisions that they make, including but not limited to loss of capital. None of these communications should be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities, nor advice to do so. The users understands and acknowledges that there is a very high risk involved in trading securities. By using this information, the user agrees that use of this information is entirely at their own risk.
Thank you.
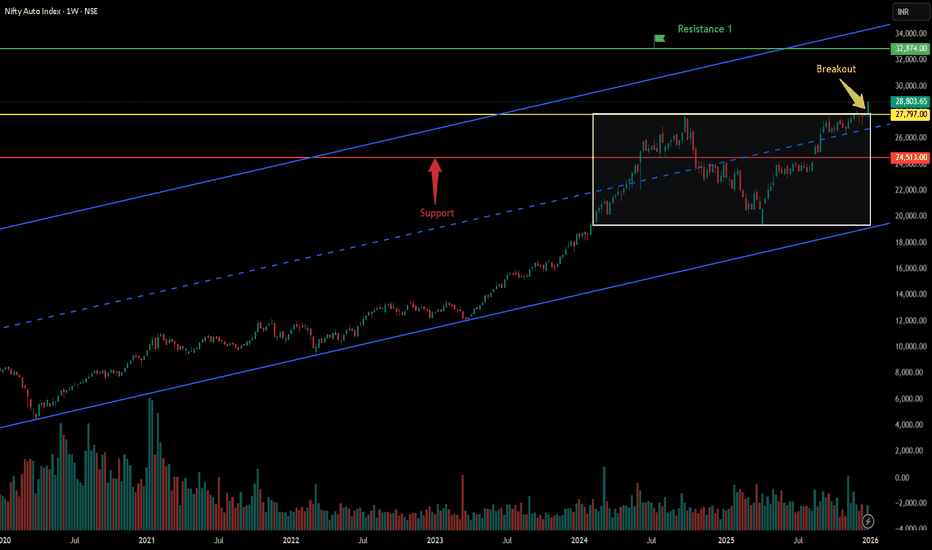
Breakout in Nifty Auto...Chart is self explanatory. Levels of breakout, possible up-moves (where index may find resistances) and support (close below which, setup will be invalidated) are clearly defined.
Disclaimer: This is for demonstration and educational purpose only. This is not buying or selling recommendations. I am not SEBI registered. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trade.
Breakout in CSB Bank Ltd...Chart is self explanatory. Levels of breakout, possible up-moves (where stock may find resistances) and support (close below which, setup will be invalidated) are clearly defined.
Disclaimer: This is for demonstration and educational purpose only. This is not buying or selling recommendations. I am not SEBI registered. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trade.
XAUUSD/GOLD WEEKLY SELL PROJECTION 04.01.26Price was moving inside a parallel uptrend channel
That channel is clearly broken, which is the first early warning of trend weakness
After the break, price failed to continue higher → bullish momentum exhausted
2️⃣ Major Reversal Patterns
Double Top Formation
Price tested the same resistance zone twice
Both tops were rejected strongly
This confirms buyers are unable to push price higher
M Pattern Confirmation
After the second top, price breaks below the neckline
This confirms trend reversal
3️⃣ Candlestick Confirmation (Very Strong)
At the resistance zone:
Evening Star (Triple Candlestick Pattern) → Classic reversal signal
Bearish Engulfing Candle → Sellers completely overpower buyers
These patterns together give a high-probability SELL confirmation
4️⃣ Resistance Zones
Resistance R2 → Major rejection zone (double top area)
Resistance R1 → Previous supply zone
Price respected resistance and obeyed the trendline → SELL zone
5️⃣ Entry Logic (SELL)
Sell after:
Trendline break
Double top confirmation
Bearish engulfing close
This is a swing low sell setup
6️⃣ Targets & Risk Management
Support S1 → First target / partial booking zone
Support S2 → Final target
Risk : Reward = 1 : 2
IDBI BANK LTD ANALYSISTHIS IS MY CHART OF THE WEEK PICK
FOR LEARNING PURPOSE
IDBI BANK- The current price of IDBI is 114.73 rupees
I am going to buy this stock because of the reasons as follows-
1. It has given a breakout of last 11 year resistance with some good volume and looks great.
2. This stock has seen some great buying from mid 2022 to March 2024. Then it went for some time and price correction which was needed.
This stock has been in my watchlist from last weeks.
I am personally more aggressive on Banks as they are holding really well.
3. It is showing better relative strength as it stood strong in volatile times including last few weeks.
4. The risk and reward is favourable.
5. The stock is one of the outperformers in this market. The structure is great as of now. It has also outperformed it's sector in very short term but it was more of a lagging stock in long term and probably it will show better strength in coming days.
6. Another good part- The overall sector has shown some decent strength and have good momentum.
I am expecting more from this in coming weeks.
I will buy it with minimum target of 35-40% and then will trail after that.
My SL is at 100 rupees.
I will be managing my risk.
2026 XAUUSD/GOLD YEARLY ANALYSISXAUUSD / GOLD – 2026 Yearly Buy Plan
With Entry, Stop Loss & Targets
🔹 Market Bias
Gold (XAUUSD) is bullish for 2026 based on:
Global economic uncertainty
Central bank gold accumulation
Expected US interest-rate cuts
Strong long-term bullish structure on the daily chart
🔹 Buy Zones (Entries)
✅ Major Buy Zone (Best Risk–Reward)
Entry: 3,250 – 3,300
This zone is near:
Golden Fibonacci retracement
Yearly swing low
Strong institutional demand area
👉 Suitable for positional & long-term investors
✅ First Confirmation Buy
Entry: 3,950 – 4,050
Buy only if price holds above support and shows bullish candles
👉 Suitable for safe swing traders
🔴 Stop Loss (Risk Control)
🛑 Stop Loss Placement
Stop Loss: Below 3,150
Reason:
Break of yearly structure
Bullish view invalid below this level
📌 Risk should be 1–2% per trade, not more.
🎯 Take Profit Targets (2026)
🎯 Target 1
4,800 – 5,000
Partial profit booking recommended (30–40%)
🎯 Target 2
5,800 – 6,000
Trail stop loss to cost or profit
🎯 Target 3 (Long-Term Extreme Target)
7,500 – 7,800
Only for patient positional holders
🔹 Trade Management Plan
Buy only on pullbacks, not at highs
Book partial profits at each target
Move stop loss gradually as price moves up
Avoid over-leverage
Force Motors Ltd - Breakout Setup, Move is ON...#FORCEMOT trading above Resistance of 21123
Next Resistance is at 30646
Support is at 14435
Here are previous charts:
Chart is self explanatory. Levels of breakout, possible up-moves (where stock may find resistances) and support (close below which, setup will be invalidated) are clearly defined.
Disclaimer: This is for demonstration and educational purpose only. This is not buying or selling recommendations. I am not SEBI registered. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trade.
Laurus Labs Limited - Breakout Setup, Move is ON...#LAURUSLABS trading above Resistance of 1091
Next Resistance is at 1512
Support is at 806
Here are previous charts:
Chart is self explanatory. Levels of breakout, possible up-moves (where stock may find resistances) and support (close below which, setup will be invalidated) are clearly defined.
Disclaimer: This is for demonstration and educational purpose only. This is not buying or selling recommendations. I am not SEBI registered. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trade.
$XRP Price Forecast | Is $10 Possible?CRYPTOCAP:XRP Is Currently Retesting A Breakout That Took Nearly 8 Years To Form — A Rare, High-Timeframe, Cycle-Level Structure That Typically Precedes Major Market Expansions.
The Last Time This Exact Structure Appeared (2017), XRP Delivered An Extraordinary 40,000% (400x) Move Following The Breakout.
Current High-Timeframe Technical Structure:
✅ Multi-Year Descending Structure Broken
✅ ~57% Corrective Pullback From Recent ATH
✅ Price Holding Within The $2–$1.50 Demand Zone
✅ Strong Macro Support Identified At $1–$0.80
As Long As Price Respects This Support Region, The Primary Technical Projection Remains $8–$10 XRP Over The Cycle, Based On Measured Move And Historical Structure Behavior.
Why Expect Only 5x–10x From Here?
The Previous Multi-Year XRP Breakout Resulted In A 400x (40,000%) Expansion.
Historically, Large Bases Lead To Large Moves — Not Modest Returns.
From A Purely Structural Perspective, A Move Toward $10–$20 Cannot Be Ruled Out In The Next Market Cycle If The Breakout Holds And Momentum Confirms.
Disclaimer:
This Analysis Is For Educational Purposes Only And Does Not Constitute Financial Advice. Technical Analysis Is Probabilistic, Not Predictive. Always Apply Proper Risk Management And Conduct Your Own Research.
Part 9 Trading Master Class Real-World Example (NIFTY)
Suppose NIFTY is at 24,500.
If you expect a big move → Long Straddle
Buy 24,500 call + 24,500 put
High debit, but profits in big move.
If expecting sideways → Iron Condor
Sell 24,700 CE
Buy 24,900 CE
Sell 24,300 PE
Buy 24,100 PE
High probability, low risk.
If moderately bullish → Bull Put Spread
Sell 24,300 PE
Buy 24,100 PE
Credit strategy with limited risk.
Part 6 Learn Institutional Trading Which Strategy to Use When?
Below is a quick guide:
Market View Best Strategies
Highly bullish Ratio backspread, bull call, synthetic long
Moderately bullish Bull call/put spread, covered call, diagonal spread
Bearish Bear put spread, ratio put backspread, synthetic short
Sideways Iron condor, butterfly, calendar spread
High volatility expected Long straddle, long strangle, ratio spreads
Low volatility expected Short straddle, short strangle, iron butterfly
BNB Price Forecast 2026 | Is $10K/BNB Possible? | Analysis By CPBNB has shown strong price action recently. After bouncing from the $500 support zone, price moved higher, broke the previous all-time high, and successfully cleared the $700 resistance, which is now acting as a strong support area.
Currently, BNB is consolidating around the $800 level, suggesting the market is digesting the recent move.
Technical Overview
Multi-year ascending trendline: Still intact, indicating long-term bullish structure.
Major support zone: $500–$800
This range has acted as an accumulation area during previous pullbacks.
Current structure: Sideways consolidation near $800 after a strong breakout.
Possible Scenarios
Bullish continuation:
If BNB holds above $800 and breaks higher with volume, continuation toward higher levels is possible.
Pullback scenario:
If price drops below $800, a retest of $700–$500 could occur. Historically, this zone has provided strong demand and may attract long-term buyers.
Long-Term Perspective (Cycle-Based)
Bull market target (speculative): Around $3,000
Macro cycle projections (high risk & speculative): $10,000–$20,000
These levels are not predictions, but potential zones based on historical cycles, trend strength, and broader market conditions.
Key Takeaway
The overall structure remains bullish as long as price stays above major support levels. Consolidations and pullbacks within an uptrend are normal and often help reset the market before the next move.
This is an educational analysis only. Not financial advice.
Always manage risk and do your own research (DYOR).
Candle PatternsWhy Candle Patterns Matter in Trading
Candlestick patterns matter because they provide:
1. Early trend reversal signals
Before a trend changes, buyers and sellers show hesitation, exhaustion, or aggression. Candles capture these emotions early.
2. Clarity of market sentiment
You can quickly understand whether bulls or bears are in control.
3. Entry and exit confirmation
Combined with chart patterns, market structure, and volume profile, candle patterns significantly improve precision.
4. Risk management
Certain patterns provide tight stop-loss areas—like wicks, rejection levels, and candle lows/highs.
5. Works across markets
Whether it’s stocks, forex, crypto, commodities, or index trading, candle patterns behave the same because human psychology is universal.
CUB 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Latest Price Context
Current price: Around ₹284–₹290 on NSE (varies by source/time) — markets fluctuate intra‑day.
📈 1‑Month Resistance Levels
These are areas where price often faces supply (selling) pressure:
Resistance Approx. Level (INR) Notes
R1 ~₹290–₹292 Near current cluster resistance.
R2 ~₹295–₹297 Resistance near recent highs & 52‑week top.
R3 ~₹300–₹305 Psychological / upper range breakout.
👉 Break above ₹295–₹300 with volume could indicate strength in the 1‑month trend.
📉 1‑Month Support Levels
Key levels where demand may absorb selling:
Support Approx. Level (INR) Notes
S1 ~₹282–₹285 Near short‑term support.
S2 ~₹278–₹280 Next downside cushion.
S3 ~₹274–₹276 Lower range support in recent weeks.
👉 A sustained close below ~₹278–₹280 may signal deeper pullbacks.
⚠️ Notes
These levels are approximate and based on recent publicly available technical data.
Prices move continuously — intraday pricing may vary within the day.
For live dynamic charts, always check your trading platform or a reliable live chart (e.g., TradingView / NSE site).
SJVN 1 Week Time Frame 📈 Current Price Context
SJVN is trading around ~₹73–₹83 recently (data varies by source/time — approximate current market level) with volatility around that band.
📌 Practical Weekly Trading Levels
Bullish Scenario (Price Structure)
Bullish threshold: Break & hold above ₹77–₹80 (weekly close)
Next upside zone: ₹83+ weekly resistance
Targets: ~₹83 → ₹88+ if bullish momentum continues
Bearish Scenario
Bearish invalidation: Failure below ₹69
Next lower supports: ~₹65, then ~₹62
Neutral / Range
Between ₹71–₹77 → consolidative range, price may oscillate with low conviction.
🧠 Summary (1-Week Bias)
Short-term bias: Neutral to slightly bearish — price stuck in range with sellers dominant if it stays under key zone ~₹77-₹80.
Bullish trigger: Weekly close above ¥80
Bearish trigger: Weekly close below ₹69-71
ADANIENT 1 Week Time Frame 📌 Current Price (approx): ~₹2,225-₹2,280 (showing slight variation in live feeds)
📊 Weekly Pivot / Key Levels
Resistance (Upside)
R1: ~₹2,289-₹2,298
R2: ~₹2,298-₹2,314
R3: ~₹2,314-₹2,320+
Pivot: ~₹2,274-₹2,280
Support (Downside)
S1: ~₹2,264-₹2,249
S2: ~₹2,240-₹2,227
S3: ~₹2,216-₹2,200
📈 Weekly Trading Range Expectation
✔ Bullish Break: Clear weekly close above ~₹2,298-₹2,314 would validate bullish momentum and open room toward higher resistance (~₹2,320+).
✔ Bearish Breakdown: Weekly close below ~₹2,227-₹2,216 suggests deeper corrective action toward lower supports.
📌 Trading Implications This Week
Bullish scenario:
Hold above pivot (~₹2,274-₹2,280)
Push through R1/R2 (~₹2,289-₹2,298) and target R3 (~₹2,314+)
Bearish scenario:
Failure to hold pivot/support zone (~₹2,240-₹2,227)
Risk to S2-S3 (~₹2,216 and below)
ITC 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Price (Live / Most Recent)
Approx. ₹350.05 (recent trade / live quote from latest session; price has been under pressure recently due to tax impact sell-offs)
📈 Daily Price Action (1D)
Recent Day’s Range:
Day Low: ~₹345.25
Day High: ~₹360.00
Daily trading has been volatile and downward-biased.
52-Week Range:
Low: ~₹345.25
High: ~₹471.50
(This helps frame where current price sits relative to yearly extremes.)
📍 What This Means for Trading (1-Day Frame)
Bullish scenario:
A sustained close above ₹403–₹406 may unlock upside toward ₹410+.
Bearish scenario:
Failure to hold ₹345–₹350 could expose deeper supports around ₹375–₹385 or lower.
AVNT Why This Zone Matters?📌 1. Pattern Overview
AVNT is trading inside a descending channel after a strong selloff.
This structure shows sellers still control the trend with lower highs, but the range is compressing which often leads to a sharp expansion once price leaves the channel.
Price is sitting in the decision zone of the channel, where breakouts and breakdowns usually move fast.
The next daily close here can decide whether this is a base forming or just another lower high before continuation.
📉 2. Key Levels
Support
0.36 — current base and near-term demand; losing this shifts control back to sellers
0.30 — next major support and likely downside magnet if 0.36 breaks
Resistance
0.428 — reclaim level; a daily close above this is the first sign the market is changing character
0.490 — major supply; clearing this confirms strength and opens room for a larger move
📈 3. Market Outlook
Higher time frame remains bearish, so the default bias stays defensive until price proves acceptance above resistance.
Momentum shifts bullish only after a daily close above 0.428 and a clean retest hold.
Institutions typically wait for that confirmation because it signals real demand, not just a short-lived bounce.
🧭 4. Trade Scenarios
🟢 Bullish Scenario
Entry trigger: Daily close above 0.428, then retest holds as support
First target: 0.490
Second target: 0.60
Reasoning: Break and hold flips structure, traps shorts, and often accelerates into the next supply zone
🔻 Bearish Scenario
Breakdown trigger: Daily close below 0.36
Target: 0.30 first, then 0.22 if weakness continues
Why this happens: Losing the base removes support and price typically searches the next demand pocket
⚠️ 5. Final Note
Don’t chase the first move. Let the daily candle close confirm direction, then look for the retest.
If you want more clean, level-based breakdowns like this, follow me for daily analysis.