Trading Performance BoostStrategies, Systems, and Mindset for Consistent Market Success
Trading performance is not improved by a single indicator, secret strategy, or occasional big win. A true trading performance boost comes from aligning knowledge, discipline, psychology, risk control, and execution into one structured process. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, the difference between average and exceptional performance lies in how consistently you apply proven principles over time. This comprehensive guide explains how traders can significantly improve their performance by focusing on the right areas that matter most.
Understanding Trading Performance
Trading performance is measured not just by profits, but by consistency, drawdown control, risk-adjusted returns, and emotional stability. Many traders judge success only by daily or weekly profits, which leads to impulsive decisions. High-performing traders instead focus on executing their plan correctly, knowing that profits are the byproduct of disciplined behavior. A performance boost begins when you shift from outcome-based thinking to process-based thinking.
Building a Strong Trading System
A trading system is the foundation of performance. It defines what to trade, when to trade, how much to trade, and when to exit. Without a system, trading becomes emotional and random. A robust system includes:
Clear entry criteria based on price action, indicators, or structure
Defined stop-loss placement to control downside risk
Logical profit targets or trailing exits
Rules for trade frequency and position sizing
Consistency in applying the same system allows traders to evaluate performance objectively and make data-driven improvements.
Risk Management as a Performance Multiplier
Risk management is the most powerful performance booster in trading. Even the best strategy fails without proper risk control. Successful traders typically risk 1–2% of capital per trade, ensuring survival during losing streaks. Key risk management principles include:
Maintaining a favorable risk-to-reward ratio
Avoiding over-leverage and revenge trading
Limiting correlated trades
Protecting capital during volatile or uncertain markets
When risk is controlled, confidence improves, emotions stabilize, and decision-making becomes clearer.
Psychology and Emotional Discipline
Trading psychology is often the biggest barrier to performance improvement. Fear, greed, impatience, and overconfidence cause traders to break rules. Emotional discipline means executing trades exactly as planned, regardless of recent wins or losses. Performance improves when traders:
Accept losses as a normal business expense
Avoid impulsive entries and exits
Detach self-worth from individual trades
Remain patient during low-opportunity periods
Mental resilience allows traders to stay focused during drawdowns and prevents emotional mistakes that erode profits.
The Power of Trade Journaling and Review
A detailed trading journal is an essential tool for performance enhancement. Journaling helps traders identify strengths, weaknesses, and recurring errors. A good journal records:
Entry and exit reasons
Market conditions
Emotional state during the trade
Outcome and lessons learned
Regular review of journal data allows traders to refine strategies, eliminate bad habits, and reinforce successful behaviors. Many professional traders attribute their performance breakthroughs to disciplined journaling.
Enhancing Execution and Timing
Execution quality significantly impacts trading performance. Slippage, delayed entries, and premature exits can reduce profitability even with a good strategy. Performance improves when traders:
Use limit orders where appropriate
Avoid chasing price movements
Trade during optimal market sessions
Focus on high-probability setups only
Improved execution reduces unnecessary losses and increases average trade efficiency.
Adapting to Market Conditions
Markets constantly change between trending, ranging, and volatile phases. A major performance boost comes from adapting strategies to current conditions instead of forcing trades. Skilled traders know when to:
Trade aggressively during clear trends
Reduce position size in choppy markets
Stay on the sidelines when conditions are unfavorable
Flexibility ensures capital protection and maintains long-term consistency.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Trading is a skill-based profession that requires ongoing learning. Performance improves when traders regularly refine their understanding of:
Market structure and price behavior
Advanced risk management techniques
Strategy optimization and backtesting
New tools and technologies
However, learning should be selective. Overloading with indicators or strategies often reduces clarity and performance.
Lifestyle and Performance Optimization
Trading performance is influenced by physical and mental health. Fatigue, stress, and poor lifestyle habits reduce decision-making quality. High-performing traders prioritize:
Adequate sleep and exercise
Structured daily routines
Breaks from screens and markets
Stress management practices
A healthy body and mind support focus, patience, and emotional control, directly improving trading outcomes.
Long-Term Consistency Over Short-Term Gains
The ultimate trading performance boost comes from thinking long-term. Sustainable success is built through small, repeatable edges applied consistently. Traders who focus on steady growth, capital preservation, and continuous improvement outperform those chasing quick profits. Compounding works in favor of disciplined traders who survive long enough to let probability play out.
Conclusion
A trading performance boost is not achieved overnight. It is the result of combining a solid trading system, strict risk management, emotional discipline, continuous review, and adaptive thinking. When traders focus on executing their plan flawlessly rather than predicting the market, performance naturally improves. In trading, mastery is not about being right all the time—it is about managing risk, controlling emotions, and staying consistent. Those who commit to this process unlock sustained profitability and long-term success in the markets.
Harmonic Patterns
Backtest Your Strategies NowWhy It’s Possible, Powerful, and Essential for Modern Trading
In today’s fast-evolving financial markets, traders no longer need to rely solely on intuition, hindsight, or scattered trial-and-error to evaluate their ideas. Backtesting trading strategies is now not only possible but essential, thanks to the availability of historical market data, advanced platforms, and computational tools. Backtesting allows traders and investors to simulate how a trading strategy would have performed in the past, using real historical price movements, before risking actual capital. This process has transformed trading from a largely discretionary activity into a disciplined, data-driven profession.
What Is Backtesting?
Backtesting is the process of applying a predefined trading strategy to historical market data to measure its performance. The strategy may involve rules based on technical indicators, price action, options structures, or even fundamental signals. By running these rules on past data, traders can evaluate key metrics such as profitability, drawdowns, win rate, risk-to-reward ratio, and consistency.
In simple terms, backtesting answers a crucial question: “If I had traded this strategy in the past, how would it have performed?” While past performance does not guarantee future results, it provides valuable insights into how a strategy behaves under different market conditions.
Why Backtesting Is Now Easily Possible
Backtesting has become widely accessible due to several technological and structural developments:
Availability of Historical Data
Stock prices, index data, futures, and options chains are now available for years or even decades. Many platforms provide intraday, daily, and weekly data, making it easier to test strategies across multiple timeframes.
Advanced Trading Platforms
Modern charting and trading platforms allow traders to visually replay historical markets, apply indicators, and test rule-based strategies. Algorithmic trading software enables fully automated backtesting with thousands of trades executed in seconds.
Increased Computing Power
Even retail traders now have access to powerful computers and cloud-based tools that can process large datasets quickly. This makes complex strategy testing feasible without institutional-level infrastructure.
Rise of Quantitative and Systematic Trading
The growing popularity of systematic trading has pushed the development of user-friendly backtesting tools. Traders can code strategies or use built-in strategy testers without deep programming knowledge.
Benefits of Backtesting Your Strategy
Backtesting offers several critical advantages that directly impact trading success:
Confidence and Discipline
When traders know their strategy has worked historically, they are more likely to follow it with discipline. This reduces emotional decision-making driven by fear or greed.
Understanding Risk
Backtesting highlights the maximum drawdowns and losing streaks a strategy may experience. This prepares traders mentally and financially for real-world execution.
Strategy Optimization
By analyzing results, traders can refine entry rules, exit conditions, stop-loss placement, and position sizing. Small adjustments can significantly improve long-term performance.
Market Condition Awareness
Backtesting reveals how a strategy performs in trending markets, range-bound conditions, high volatility, or low liquidity environments. This helps traders decide when to apply or avoid a strategy.
Backtesting Across Different Trading Styles
Backtesting is not limited to one type of trading. It is applicable across multiple approaches:
Equity Trading: Testing moving average crossovers, breakout systems, or mean reversion strategies.
Options Trading: Evaluating strategies such as covered calls, iron condors, straddles, or directional option buying during specific volatility regimes.
Intraday Trading: Analyzing scalping or momentum strategies using minute-level data.
Swing and Positional Trading: Testing multi-day or multi-week setups based on technical or hybrid indicators.
For options traders especially, backtesting helps understand how time decay, implied volatility, and strike selection affect profitability over time.
Limitations and Risks of Backtesting
While backtesting is powerful, it must be approached with caution.
Overfitting
One of the biggest risks is over-optimizing a strategy to fit past data perfectly. A strategy that looks flawless in historical testing may fail in live markets because it is too specific to past conditions.
Data Quality Issues
Inaccurate or incomplete data can distort results. Corporate actions, missing candles, or incorrect option pricing can lead to misleading conclusions.
Ignoring Execution Costs
Real trading involves brokerage fees, slippage, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity constraints. If these are not factored into backtests, results may appear unrealistically profitable.
Market Evolution
Markets evolve due to regulations, technology, and participant behavior. A strategy that worked ten years ago may not perform the same way today.
Best Practices for Effective Backtesting
To make backtesting meaningful and reliable, traders should follow certain best practices:
Use out-of-sample testing, where a strategy is tested on unseen data.
Incorporate realistic transaction costs and slippage.
Test across multiple market cycles, including bull, bear, and sideways phases.
Focus on robustness rather than perfection—a good strategy works reasonably well under varied conditions.
Combine backtesting with forward testing or paper trading before going live.
Backtesting as a Trader’s Edge
In the modern trading environment, backtesting is no longer optional—it is a competitive necessity. Traders who backtest operate with evidence rather than assumptions. They understand their strategies deeply, including strengths, weaknesses, and risk exposure. This knowledge builds patience, consistency, and long-term sustainability.
Ultimately, backtesting bridges the gap between theory and reality. It transforms ideas into validated strategies and replaces hope with probability. While it cannot eliminate risk or guarantee success, it significantly improves decision-making quality. For traders serious about longevity and growth, the message is clear: backtest your strategies now—because today, it’s not only possible, it’s indispensable.
Option Buying vs Option Selling: Comparative Guide for TradersUnderstanding Option Buying
Option buying is the more popular and intuitive approach, especially among beginners. When you buy an option, you purchase the right but not the obligation to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before or on expiry.
The biggest attraction of option buying is limited risk. The maximum loss is restricted to the premium paid. This makes it psychologically comfortable, especially in volatile markets. If the market moves sharply in your favor, the reward can be many times the premium invested.
However, option buying comes with a hidden enemy: time decay (Theta). Every passing day reduces the value of the option, even if the market does nothing. For an option buyer to profit, the price must move quickly and significantly in the expected direction. Direction alone is not enough; timing and volatility expansion are equally critical.
Option buying works best during:
Strong trending markets
Breakouts from consolidation
High volatility expansion phases
Event-based trades (results, policy announcements)
Despite its appeal, option buying has a low probability of success. Many trades result in partial or total premium loss due to slow market movement, sideways action, or volatility contraction.
Understanding Option Selling
Option selling is often referred to as premium trading. When you sell an option, you receive the premium upfront and take on the obligation to buy or sell the underlying if exercised.
The biggest advantage of option selling is that it benefits from time decay. Every day that passes works in favor of the seller. Even if the market moves slightly against the position, the decay in option value can still generate profit. This makes option selling a high-probability strategy, especially in range-bound or low-volatility markets.
However, option selling comes with unlimited or very high risk, depending on the structure. A naked call seller faces unlimited upside risk, while a naked put seller faces large downside risk. This is why option selling requires:
High margin
Strong risk management
Discipline and experience
Professional traders often use hedged strategies such as spreads, iron condors, or strangles with protection to manage risk.
Option selling works best during:
Sideways markets
Low to moderate volatility
Expiry weeks
Mean-reverting conditions
Risk and Reward Comparison
The most critical difference between option buying and selling lies in the risk–reward equation.
Option Buying
Risk: Limited (premium paid)
Reward: Unlimited or large
Probability: Low
Emotional challenge: Frequent small losses
Option Selling
Risk: High or unlimited (if unhedged)
Reward: Limited (premium received)
Probability: High
Emotional challenge: Occasional large losses
Option buyers often experience a series of small losses waiting for one big winning trade. Option sellers enjoy frequent small profits but must be prepared for rare but severe drawdowns.
Capital and Margin Requirements
Option buying is capital-efficient. Traders can participate with small capital because only the premium is paid upfront. This makes it attractive for retail traders.
Option selling requires significantly higher capital due to margin requirements imposed by exchanges. Hedged strategies reduce margin but still require more capital than buying options. As a result, option selling is typically favored by institutional and professional traders.
Role of Volatility
Volatility plays opposite roles in buying and selling.
Option buyers benefit from rising volatility. An increase in implied volatility raises option premiums, even if price movement is moderate.
Option sellers benefit from falling or stable volatility. When implied volatility contracts, option premiums erode faster.
Ignoring volatility is one of the biggest mistakes retail traders make, especially when buying options at already inflated premiums.
Psychological Differences
Option buying demands patience and emotional resilience. Losing streaks are common, and traders must avoid overtrading to recover losses.
Option selling requires discipline and risk awareness. Overconfidence during long winning streaks can lead to oversized positions and catastrophic losses. Successful sellers respect risk more than reward.
Which Is Better: Buying or Selling?
There is no universal answer. The choice depends on:
Market conditions
Trader experience
Capital size
Risk tolerance
Trading style
Beginners often start with option buying due to limited risk. As experience grows, many traders transition toward option selling or hybrid strategies that combine both.
Conclusion
Option buying and option selling are two sides of the same coin, yet they represent completely different philosophies of trading. Option buying focuses on direction and momentum, offering high reward with low probability. Option selling focuses on time decay and probability, offering consistent income with higher risk exposure.
A mature options trader does not choose one over the other permanently. Instead, they adapt—buying options during explosive trends and selling options during quiet, range-bound markets. Mastery comes not from preference, but from understanding when each approach offers the highest edge.
In options trading, success is not about being bullish or bearish—it is about being strategically aligned with time, volatility, and probability.
Profitable Option StrategiesStructured Approaches to Consistent Returns
Options trading is often seen as complex and risky, but when used strategically, it can become a powerful tool for generating consistent and controlled profits. Profitable option strategies are not about predicting markets perfectly; instead, they focus on probability, risk management, and disciplined execution. Successful traders select strategies based on market conditions such as direction, volatility, and time decay, rather than relying on a single approach. Below is a comprehensive explanation of the most effective and widely used profitable option strategies, along with the mindset required to apply them successfully.
Understanding the Foundation of Profitable Option Trading
Before applying any strategy, it is essential to understand that options derive value from four key factors: price movement, time, volatility, and interest rates. Profitable strategies are designed to benefit from one or more of these factors while controlling losses. Most professional traders prioritize capital preservation and consistent returns over aggressive profit-seeking. They focus on defined-risk strategies, high-probability setups, and position sizing.
Another critical element is market context. Options behave differently in trending markets, range-bound markets, and highly volatile environments. A strategy that works well in one condition may fail in another. Therefore, adaptability is a core principle of profitable options trading.
1. Covered Call Strategy
The covered call is one of the simplest and most profitable strategies for investors who already own stocks. In this strategy, the trader holds shares of a stock and sells a call option against those shares. The premium received provides immediate income and acts as a buffer against small declines in price.
This strategy is most profitable in sideways to mildly bullish markets. The maximum profit is limited but predictable, making it ideal for conservative traders. The main advantage is consistent income generation, especially in stable stocks with good liquidity. The primary risk is opportunity loss if the stock rallies sharply beyond the strike price.
2. Cash-Secured Put Strategy
The cash-secured put is a popular strategy for traders who want to acquire quality stocks at lower prices or earn premium income. In this approach, a trader sells a put option while keeping enough cash to buy the stock if assigned.
This strategy works best in neutral to moderately bullish markets. If the stock stays above the strike price, the trader keeps the premium as profit. If the stock falls below the strike, the trader buys the stock at an effective discounted price. Over time, this strategy can generate steady income while building a portfolio of fundamentally strong stocks.
3. Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread is a defined-risk, directional strategy used when a trader expects moderate upside movement. It involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling another call at a higher strike price with the same expiry.
This strategy reduces cost compared to buying a naked call and limits risk to the net premium paid. While the profit potential is capped, the probability of success is higher, and capital efficiency is improved. It is suitable for traders who want controlled exposure to bullish moves without excessive risk.
4. Bear Put Spread
The bear put spread is the bearish counterpart of the bull call spread. It is used when a trader expects moderate downside movement. The strategy involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling a put at a lower strike price.
This approach offers limited risk and limited reward, making it ideal during weak or declining markets. It is more cost-effective than buying a naked put and benefits from directional movement while managing volatility exposure.
5. Iron Condor Strategy
The iron condor is one of the most popular income-generating strategies among professional option traders. It involves selling an out-of-the-money call spread and an out-of-the-money put spread simultaneously.
This strategy profits when the underlying asset stays within a defined price range until expiry. It benefits from time decay and declining volatility. Iron condors are best applied in range-bound markets and on indices or highly liquid stocks. The key to profitability lies in proper strike selection, risk management, and avoiding high-impact event days.
6. Credit Spread Strategies
Credit spreads, including bull put spreads and bear call spreads, are probability-based strategies that generate income by selling options with limited risk. The trader receives a net premium upfront, and profit is realized if the option expires worthless.
These strategies work well in stable markets and are widely used due to their favorable risk-to-reward ratio. Successful traders focus on high-probability setups, typically selling options with lower delta values to increase the chance of success.
7. Calendar Spread Strategy
Calendar spreads involve buying a longer-term option and selling a shorter-term option at the same strike price. This strategy profits from time decay differences and changes in volatility.
Calendar spreads are effective in low-volatility environments where traders expect minimal price movement in the short term. They require precise timing and an understanding of implied volatility behavior. When used correctly, they can generate consistent returns with controlled risk.
8. Straddle and Strangle Adjustments
While buying straddles and strangles is generally expensive due to high volatility costs, selling adjusted versions can be profitable for experienced traders. These strategies are used when volatility is expected to fall after a major event.
Profitable application requires careful risk control, hedging techniques, and strict stop-loss rules. These strategies are more advanced and best suited for traders with experience in volatility analysis.
Risk Management: The Core of Profitability
No option strategy is profitable without proper risk management. Successful traders limit risk per trade, diversify strategies, and avoid overleveraging. Defined-risk strategies are preferred, especially for retail traders. Position sizing, stop-loss rules, and discipline play a larger role than strategy selection alone.
Another important factor is emotional control. Options trading demands patience, consistency, and the ability to accept small losses. Chasing profits or revenge trading often leads to large drawdowns.
Conclusion
Profitable option strategies are not about finding a single “best” method but about selecting the right strategy for the right market condition. Covered calls and cash-secured puts offer steady income, spreads provide controlled directional exposure, and neutral strategies like iron condors capitalize on time decay. Long-term success in options trading comes from combining strategy knowledge with discipline, risk management, and continuous learning. When applied correctly, options can become a reliable and flexible tool for building consistent trading profits over time.
NMDC LTD ANALYSISTHIS IS MY CHART OF THE WEEK PICK
FOR LEARNING PURPOSE
NMDC LTD- The current price of NMDC is 82.61 rupees
I am going to buy this stock because of the reasons as follows-
1. It has given a breakout of last 1.5 year resistance with some good volume and looks great.
2. This stock has seen some great buying in 2023. I bought this stock in 2023 and played some good move. It has got time and price correction which was required.
3. It is showing better relative strength as it stood strong in volatile times including last few weeks.
4. The risk and reward is favourable.
5. The stock is one of the outperformers in this market. The structure is great as of now. It has also outperformed it's sector in very short term but it was more of a lagging stock in mid term and probably it will show better strength in coming days.
6. Another good part- The overall sector has shown some decent strength and have good momentum.
I am expecting more from this in coming weeks.
I will buy it with minimum target of 35-40% and then will trail after that.
My SL is at 71.89 rupees.
I will be managing my risk.
BTCUSD Shows Stability After Drop, Buyers ReturningBTCUSD earlier saw a strong fall and then reached a clear demand area. From this zone, selling pressure started to reduce. Recent candles suggest sellers are losing control and buyers are slowly coming back into the market. Price is now holding above this support, which is a positive sign.
The market is no longer forming lower lows and price behaviour looks more stable. This indicates the decline may be ending and a recovery phase could begin. Buyers are entering cautiously, which often comes before a steady upward move.
As long as BTCUSD remains above the demand zone, the structure stays positive. If support holds, price can move higher step by step. The next important area to watch is around 90k, where price may react again due to past resistance.
Risk stays limited below the support near 85.5k. Holding above this level keeps the outlook in favour of buyers, with improving strength visible on the chart.
TCS Bullish ViewTata Consultancy Services (TCS) is a global **IT services** and consulting company and the flagship technology arm of the Tata Group. It is one of the world’s largest IT outsourcing and digital transformation companies.
## Basic overview
- Full name: Tata Consultancy Services Limited (TCS), founded in 1968 as part of Tata Sons.
- Nature of business: IT services, consulting, and business solutions provider serving large enterprises worldwide.
- Group: Part of the Tata Group, India’s largest industrial conglomerate.
## Services and solutions
- Offers application development & maintenance, consulting, cloud & infrastructure services, analytics, cybersecurity, and business process outsourcing (BPO).
- Provides industry platforms and products like TCS BaNCS (banking/financial), Cognix, Quartz, MasterCraft, and others for domain‑specific solutions.
## Scale and global presence
- Workforce of about 6–6.1 lakh employees (associates) across more than 46–55 countries, making it one of the largest IT employers globally.
- Operates via a global network delivery model with over 200 service delivery centers and offices across North America, Europe, India, and Asia‑Pacific.
## Financial and market position
- Recognised as India’s largest IT outsourcing company and a leading global IT services brand.
- First listed Indian IT company to cross US$100 billion market capitalization, reflecting strong profitability and investor confidence.
## Strategic focus
- Focus areas include digital transformation, cloud, AI, automation, data & analytics, cybersecurity, and industry‑specific platforms.
- Positions itself as a long‑term transformation partner, building “perpetually adaptive enterprises” by rapidly applying and scaling new technologies for clients.
If you want, a next step can be a short stock‑focused brief (business moat, client profile, margins, risks) specifically from an investor’s point of view.
Hindustan Copper Bullish View Target Near 1k in next 24 MonthsHindustan Copper Limited is a government-owned company in India that works across the entire **copper** value chain, from mining to refining. It is considered the country’s only vertically integrated producer of primary refined copper.
thanks
TATA Investment Downside Projection Till Blue POC near 550Tata Investment Corporation Limited (TICL) is a listed investment holding company of the Tata group that primarily invests long term in equities and related securities across sectors in India. It behaves economically like a diversified holding / quasi‑mutual fund vehicle, with income mainly from dividends, interest, and profit on sale of investments.
## Basic profile
- **Type**: Publicly listed, non‑banking investment company of the Tata group, originally promoted by Tata Sons in 1937 and listed in 1959.
- **Business**: Long‑term investing in equity shares, debt, and equity‑related instruments of Tata group and non‑Tata companies across many industries.
- **Income sources**: Dividend income, interest income, and capital gains from sale of investments.
## Portfolio and assets
- TICL holds a diversified portfolio spread over dozens of companies covering sectors such as banks, FMCG, IT, auto, power, infrastructure, metals, and more.
- As of 31 March 2025, total asset value is around ₹35,100 crore, reflecting the marked‑to‑market value of its investment portfolio.
## Market information
- The company trades on NSE/BSE with ticker **TATAINVEST**, and is classified as a mid‑cap with market cap around ₹33,000–36,000 crore in 2025.
- Recent data (July 2025) shows a share price around ₹6,620 on NSE, with a high P/E (~107x) and P/B just above 1x, implying rich earnings valuation but low premium to book.
## Recent developments
- The board and shareholders have approved a **1:10 stock split**, changing face value from ₹10 to ₹1, with record date 14 October 2025.
- The stock showed sharp moves in 2025, including strong rallies linked to value unlocking expectations from Tata group financial entities like Tata Capital’s IPO where TICL holds a stake.
## Strategic role in Tata group
- Historically, TICL was created to provide risk capital to emerging entrepreneurs and projects, often taking minority equity stakes and supporting long‑term industrial development.
- TICL co‑promoted Tata Asset Management Company (Tata Mutual Fund) and holds a strategic minority stake there, complementing its role as a long‑term **investment** platform within the group.
If you share your intent (long‑term investing, listing‑play, Tata group exposure, etc.), a more tailored view on valuation, risks, and position sizing can be outlined.
thanks
Litecoin Super potential toward $300?Real Silver is Up +180% YTD 2025 & Digital Silver ( CRYPTOCAP:LTC ) is Down -44% YTD 2025
That Gap is Getting Impossible to Ignore.
When Real Silver is Pumping Hard but Digital Silver is Sleeping, it Usually Doesn’t Last Forever.
If the Rotation Happens in 2026, CRYPTOCAP:LTC at $250–$300 is Very Realistic.
Now Litecoin has One Job: Prove it Truly is Digital Silver.
NFA & DYOR
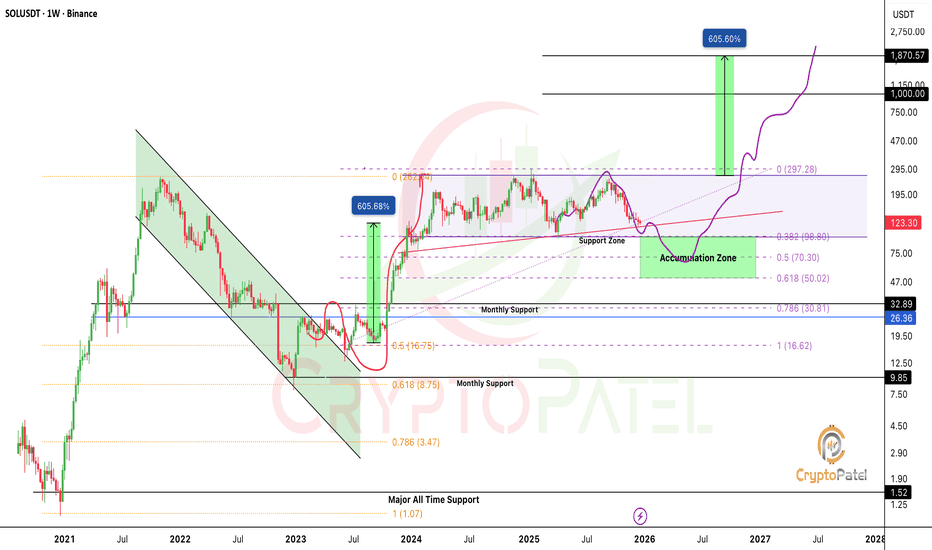
Will SOLANA potentila to $1000?Many people are emotionally attached to Solana and the $1,000 target and that may be possible long term.
But markets never move straight up.
Corrections are part of every cycle, and CRYPTOCAP:SOL is currently in a correction phase.
If the $120 support breaks, I’m expecting SOL to drop below $100.
A move under $100 could offer a strong long-term accumulation opportunity.
My accumulation zone: $98 – $50
Long-term outlook: $500 – $1,000
Crypto is highly volatile and risky.
Always DYOR, manage risk properly, and this is not financial advice (NFA).
$FLOW CRASH ALERT – WHAT JUST HAPPENED?AMEX:FLOW just got destroyed, dropping over 52% in 24 hours.
Price action
High: $0.174
Low: $0.079
Current: ~$0.10
Major Red Flags Today:
🔹 Upbit & Bithumb Suspended Deposits and Withdrawals
🔹 South Korea’s DAXA Issued a Trading Risk Warning
🔹 Flow Foundation confirmed they are investigating a potential security incident on the Flow network
What On-Chain Data Shows:
🔹 Top 100 holders Reduced Holdings by ~2.79M FLOW
🔹 No Smart Money Accumulation signal
🔹 Heavy Selling by Public Wallets During Peak Hours
🔹 ~1.69M FLOW moved to Exchanges (Selling Pressure)
🔹 Late buyers Jumped in During the Crash, Not Before
Market Behavior:
🔹 Panic selling dominated
🔹 Whales appear to have distributed near highs
🔹 Some wallets aggressively bought the dip amid fear
🔹 Reports of a large whale dumping on DEXs
Uncertainty Remains:
🔹 Cause of the “security incident” is still unclear
🔹 CEX suspensions increase fear and volatility
🔹 Short-term sentiment remains extremely bearish
This Move Was Driven by Fear, Uncertainty, and Heavy Selling Pressure. Until Clarity Comes from the Flow Foundation, Risk Remains Very high.
Investors are Waiting for clear Answers from Flow Blockchain
Trade Carefully. Volatility is Brutal Right Now.
NFA & DYOR
XAUUSD (H4) – Trading Rising ChannelLana focuses on pullback buys for the week ahead 💛
Weekly overview
Primary trend (H4): Strong bullish structure, price is respecting a clean ascending channel
Current state: Price is trading near ATH and Fibonacci extensions → short-term reactions are possible
Weekly strategy: No FOMO. Lana prefers buying pullbacks at value zones, not chasing highs
Market context
Recent comments from the U.S. highlight strong economic growth and confidence in trade policies. While such statements can influence USD sentiment, gold at year-end is often driven more by liquidity conditions and technical structure than headlines.
With holiday liquidity thinning out, price movements can become sharper and less predictable. That’s why this week Lana stays disciplined and trades strictly based on structure and key levels.
Technical view based on the chart (H4)
On the H4 timeframe, gold is moving smoothly within a rising channel, consistently forming higher lows. The strong impulse leg has already completed its psychological breakout phase, and price is now hovering near the upper area of the channel.
Key points:
Fibonacci extension zones near the top act as psychological resistance, where temporary pullbacks are normal.
The best opportunities remain inside the channel, around value and liquidity zones.
Key levels Lana is watching this week Primary buy zone – Value Area (VL)
Buy: 4482 – 4485
This is a value zone within the rising channel. If price pulls back here and holds structure, continuation to the upside becomes more likely.
Safer buy zone – POC (Volume Profile)
Buy: 4419 – 4422
This POC zone shows heavy prior accumulation. If volatility increases or price corrects deeper, this area offers a more conservative buy opportunity.
Psychological resistance to respect
4603 – 4607: Fibonacci extension & psychological barrier At this zone, a short-term rejection or liquidity grab is possible before the next directional move.
Weekly trading plan (Lana’s approach)
Buy only on pullbacks into planned zones, with confirmation on lower timeframes.
Avoid chasing price near ATH or psychological resistance.
Reduce position size and manage risk carefully during low-liquidity holiday sessions.
Lana’s note 🌿
The trend is strong, but discipline at the entry is everything. If price doesn’t return to my zones, I’m happy to stay patient and wait.
This is Lana’s personal market view, not financial advice. Always manage your own risk. 💛
Part 3 Learn Institutional Trading What Is an Option?
An option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, on or before a specified date called the expiry date. The seller (or writer) of the option has the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise the option.
Options are traded on various underlying assets, including stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, and ETFs. The price paid by the buyer to acquire this right is known as the option premium.
Part 2 Ride The Big Moves Option Trading in Practice
Successful option trading requires more than theoretical knowledge. Traders must combine:
Technical analysis to identify price trends and support–resistance levels.
Volatility analysis to choose the right strategies.
Market awareness, including events like earnings, economic data, and policy announcements.
Psychological discipline to handle losses and avoid impulsive decisions.
Part 1 Ride The Big Moves 1. Hedging
Investors use options to protect their portfolios from adverse price movements. For example, buying a put option on a stock you own acts like insurance against a price fall.
2. Speculation
Options allow traders to speculate on market direction with relatively low capital. A small move in the underlying can lead to a large percentage gain in the option premium.
3. Income Generation
By selling options (such as covered calls), traders can generate regular income in sideways or mildly trending markets.
4. Flexibility and Leverage
Options provide leverage, enabling traders to control a large position with a smaller investment compared to buying the underlying asset outright.
Part 1 Intraday Master Class Key Terminologies in Options
Understanding options requires familiarity with certain core concepts:
Strike Price: The price at which the option can be exercised.
Premium: The price paid for the option.
Expiry: The date on which the option contract expires.
Intrinsic Value: The immediate value of an option if exercised now.
Time Value: The portion of the premium attributable to the remaining time until expiry.
Option Trading Strategies Participants in Option Trading
Option trading involves two main participants:
Option Buyers: They pay a premium and have limited risk (the premium paid) with potentially unlimited or substantial profit.
Option Sellers (Writers): They receive the premium and have limited profit potential but can face significant or even unlimited risk, depending on the strategy.
Infy - Analysis caution alert Bullish Levels -Above 1679/94 above this bullish then then around 1754 above this wait
Bearish levels :- if sustain below 1630/30 below this bearish then 1608/1599 bearish this more bearish then 1585 to 1530 last hope more level marked on chart
**Consider some Points buffer in above levels
**Disclaimer -
I am not a SEBI registered analyst or advisor. I does not represent or endorse the accuracy or reliability of any information, conversation, or content. Stock trading is inherently risky and the users agree to assume complete and full responsibility for the outcomes of all trading decisions that they make, including but not limited to loss of capital. None of these communications should be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities, nor advice to do so. The users understands and acknowledges that there is a very high risk involved in trading securities. By using this information, the user agrees that use of this information is entirely at their own risk.
Thank you.
HINDCOPPER 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Current Price (Reference)
The stock is trading near ~₹475–₹480 on NSE/BSE (Dec 2025 close).
📊 Key Levels for ~1‑Month Time Frame
🔵 Bullish / Resistance Levels
These are potential upside barriers where price may slow or reverse:
1. ~₹490–₹495 — Near recent pivot resistance zone.
2. ~₹500–₹505 — Mid‑term resistance zone (psychological/technical).
3. ~₹525–₹530 — Extended upside if momentum remains strong.
Interpretation: If price sustains above ₹490–₹495, it may attempt to test ₹500–₹530. A breakout above these zones could fuel further bullish sentiment.
🔴 Bearish / Support Levels
Important floors where buyers may step in on dips:
1. ~₹452–₹455 — Near immediate support (recent pivot low).
2. ~₹428–₹430 — Secondary support zone.
3. ~₹415–₹420 — Major support; breach could signal deeper correction.
Interpretation: If the stock drops below ₹452–₹455, watch for holds around ₹428–₹430, then ₹415–₹420. A failure to hold these levels could lead to broader consolidation.
🧠 How to Use These Levels
Range traders might look to take profit near resistance zones and buy near established supports.
Breakouts above ₹500 with volume could open room toward the ₹525–₹530 area.
Downside breaks under ~₹452 might see a pullback toward ₹428 and lower supports.
JWL 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Live / Current Price (Market Close)
📍 JWL closed around ₹347.5 (↑ ~2% on the day) on 26 Dec 2025 — this is the latest pricing reference.
📊 Intraday / 1‑Day Technical Levels
🔥 Key Pivot & Levels for Today
(Used for quick intraday setup — support and resistance for 1‑day horizon)
Daily Pivot Points (Classic)
Pivot: ~ ₹335‑340 (approx balance area)
Immediate Support 1: ₹334‑336
Support 2: ₹320‑322
Support 3: ₹308‑310
Resistance 1: ₹359‑360
Resistance 2: ₹371‑372
Resistance 3: ₹384‑385
📌 Interpretation for intraday traders:
Bulls need sustained strength above ~₹360 to test higher resistance zones.
Bears find strength if price drops below ~₹334‑₹330 — watch for deeper support at ~₹320 and ₹308.
🧠 Intraday Range (Recent Trading)
Today’s low: ~ ₹332‑333
Today’s high: ~ ₹358
So the realized intraday range today was roughly ₹332 to ₹358.
BANDHANBNK 1 Day Time Frame 📍 Current Price Snapshot
Current Price/Last Close: ~₹147–₹150 range intraday recently.
Day’s Range (recent session): ~₹144.95 (Low) to ~₹150.50 (High).
📈 Daily Support & Resistance Levels
📌 Support Levels (Buy Zones)
🟩 S1: ~₹145–₹146 — first support zone (near recent low).
🟩 S2: ~₹142–₹143 — secondary support zone.
🟩 S3: ~₹140–₹141 — strong support cluster from volume profile.
📌 Resistance Levels (Supply Zones)
🔴 R1: ~₹149–₹150 — near‑term resistance (price has struggled around here).
🔴 R2: ~₹151–₹153 — next resistance above R1.
🔴 R3: ~₹153.5–₹155 — extended resistance zone.
📉 Trend / Technical Sentiment
Daily technical indicators show neutral to slightly bearish bias overall.
Moving averages on daily are mostly above current price (suggesting resistance near ~₹152–₹155).
📌 How to Use These Levels Today
Bullish scenario:
➡️ Break & hold above ₹150–₹151 with volume → next upside towards ₹153–₹155.
Bearish scenario:
➡️ Failure near ₹150 and break of ₹145 → next support around ₹142–₹140.