AMBUJACEM 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Price Context
The stock has recently traded around ₹510 – ₹536 after earnings‑related volatility.
The 52‑week range is roughly ₹455 (low) to ₹625 (high).
🔁 1‑Week Technical Levels (approx)
Key resistance (levels where sellers may step in):
₹542‑₹545: Near recent pivotal resistance zone.
₹552‑₹558: Secondary resistance cluster short‑term.
Key support (levels where buyers may defend):
₹527‑₹528: Initial support within the week.
₹521‑₹516: Next support zone if the dip extends.
₹500 – ₹495: Stronger longer‑term support if selling intensifies.
📉 Short‑Term Trend & Signal
Technical aggregators rate the stock as weak/neutral to bearish on the 1‑week timeframe — meaning downside risks currently outweigh upside signal.
Price below recent pivot and moving averages suggests bearish short‑term momentum absent close above resistance.
📌 Practical Swing Levels (Simple Guide)
Bullish trigger zone: closing above ₹545‑₹550 on weekly closes could make higher levels nearer ₹560+ possible.
Bearish trigger zone: closing below ₹520 may open path toward ₹500 and deeper.
Harmonic Patterns
Advanced Technical Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide1. Principles of Advanced Technical Analysis
At its core, technical analysis is based on three main principles:
Price Discounts Everything: All information — news, fundamentals, market sentiment — is reflected in the price. Advanced TA accepts this as a foundation, emphasizing price action over external factors.
Price Moves in Trends: Markets trend in three ways — uptrend, downtrend, and sideways. Advanced analysis focuses on identifying the start and end of these trends with precision using sophisticated tools.
History Repeats Itself: Patterns, behaviors, and psychology tend to repeat due to human nature. Advanced TA uses pattern recognition and statistical methods to capitalize on these repetitive behaviors.
Advanced TA combines these principles with quantitative methods and behavioral insights to increase accuracy.
2. Advanced Chart Patterns
While basic patterns include head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, advanced patterns are more nuanced:
Harmonic Patterns: These patterns, like the Gartley, Butterfly, Bat, and Crab, use Fibonacci ratios to identify precise reversal zones. Unlike basic patterns, harmonic patterns offer a mathematically-defined framework for entry and exit.
Elliott Wave Theory: Developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott, this theory identifies recurring waves in price movement — impulsive (trend-following) and corrective (counter-trend) waves. Advanced traders use Elliott Wave to forecast multi-timeframe trends and market cycles.
Market Profile: This tool analyzes the distribution of traded volume at different price levels to identify value areas, points of control, and price acceptance zones. Market Profile is highly useful for intraday and institutional trading strategies.
3. Advanced Technical Indicators
Beyond moving averages and RSI, advanced traders rely on more sophisticated indicators:
Ichimoku Kinko Hyo: Often called the “one-glance indicator,” it provides support, resistance, trend direction, and momentum in one chart. The Kumo (cloud) identifies trend strength and potential reversals.
Fibonacci Extensions & Retracements: Advanced traders use Fibonacci levels not just for retracements, but for projecting price targets and stop-loss levels. Confluences with other indicators improve accuracy.
MACD with Histogram Divergence: While the basic MACD identifies trend and momentum, analyzing divergences between MACD and price uncovers early reversal signals.
Volume-based Indicators: Tools like On-Balance Volume (OBV), Chaikin Money Flow (CMF), and Volume Price Trend (VPT) help identify accumulation or distribution phases, indicating potential breakouts or breakdowns.
Adaptive Indicators: Indicators like Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) and Kaufman’s Efficiency Ratio adjust to market volatility, providing a more responsive approach than static indicators.
4. Multi-Timeframe Analysis
Advanced traders rarely rely on a single timeframe. Multi-timeframe analysis involves examining multiple chart intervals — from monthly to intraday — to identify trends and align trades with higher-probability setups. Key principles include:
Top-Down Approach: Start with a higher timeframe to identify the major trend, then use lower timeframes to refine entries and exits.
Timeframe Confluence: Trades are stronger when multiple timeframes agree on trend direction, support/resistance, and momentum.
Fractal Patterns: Price movements repeat across timeframes, allowing traders to anticipate behavior in smaller or larger scales using fractal analysis.
5. Advanced Price Action Techniques
Price action analysis is the study of raw price behavior without relying heavily on indicators. Advanced techniques include:
Order Flow Analysis: Examining the flow of buy and sell orders in real-time markets to understand institutional activity and anticipate price moves.
Candlestick Confluence: Combining multiple candlestick patterns across higher and lower timeframes to validate reversals or continuation signals.
Support/Resistance with Precision: Using historical highs/lows, pivot points, Fibonacci levels, and volume clusters to identify high-probability zones for entries and exits.
Trend Exhaustion Signals: Recognizing signs of overextension, like long wicks, shrinking volume, or divergence in oscillators, to anticipate reversals.
6. Quantitative and Statistical Methods
Professional technical analysis increasingly incorporates quantitative methods:
Statistical Indicators: Bollinger Bands, Standard Deviation Channels, and Keltner Channels help identify volatility, mean reversion, and breakout points.
Correlation Analysis: Examining how assets or indices move in relation to each other to hedge or amplify trades.
Backtesting and Algorithmic Validation: Advanced traders validate strategies using historical data, Monte Carlo simulations, and statistical models to measure risk and probability of success.
7. Risk Management and Trade Psychology
Advanced technical analysis is incomplete without rigorous risk management:
Position Sizing: Using volatility, ATR, or percentage-based methods to determine trade size.
Stop-Loss Placement: Placing stops beyond key support/resistance, volatility levels, or pattern invalidation points.
Reward-to-Risk Optimization: Targeting trades with at least a 2:1 or 3:1 reward-to-risk ratio ensures long-term profitability.
Psychological Discipline: Advanced traders maintain emotional control, avoid overtrading, and adhere strictly to plan-based trading.
8. Integration with Fundamental and Sentiment Analysis
Though TA focuses on price, advanced practitioners often combine it with fundamental and sentiment insights:
Macro Events: Interest rates, earnings, or geopolitical developments can amplify technical setups.
Market Sentiment Indicators: Commitment of Traders (COT) reports, VIX index, and news sentiment can provide context to technical signals.
Confluence Approach: Trades with alignment between technical setups, fundamental catalysts, and market sentiment tend to have the highest probability.
9. Algorithmic and Machine Learning Approaches
Modern advanced technical analysis increasingly incorporates algorithmic trading and AI:
Pattern Recognition AI: Machine learning models can detect complex chart patterns faster and more accurately than humans.
Predictive Analytics: Using historical price, volume, and alternative data to predict probabilities of trend continuation or reversal.
Automated Execution: Advanced traders often use bots and automated scripts to execute trades when conditions are met, reducing emotional bias and ensuring precision.
10. Key Takeaways
Advanced technical analysis is more than chart reading; it is an integrated science of price, volume, momentum, and psychology. Key principles for mastery include:
Understanding multi-timeframe trends.
Combining advanced indicators, harmonic patterns, and Elliott Wave.
Using quantitative validation and backtesting for strategy reliability.
Integrating price action with institutional order flow and sentiment data.
Implementing strict risk management and psychological discipline.
By combining these tools, techniques, and analytical frameworks, traders can increase the probability of success, adapt to changing market conditions, and make informed decisions beyond simple guesswork. Advanced technical analysis is not about finding “guaranteed” trades but about stacking probabilities in your favor.
VTL 1 Day View 📍 Latest Price Context (Daily Close)
Approx. share price: ~₹432 – ₹433 on NSE (close of last session).
Today’s range (recent session): High ~₹468, Low ~₹407.45.
52-week range: Low ~₹361.10, High ~₹539.90.
📊 Key Daily Levels (1-Day Time Frame)
🔑 Pivot & Intraday Levels
(Based on pivot point calculations for the daily session)
Central Pivot (Daily): ~₹412.33 – baseline pivot for directional bias.
📈 Resistance Levels
R1 ~₹418 – ₹423 – first near-term resistance zone.
R2 ~₹423 – ₹429 – next resistance above pivot.
R3 ~₹429 – ₹446 (or higher intraday) – notable upper resistance zone if price strengthens.
👉 Bullish scenario: Daily close above ~₹429-₹435 could trigger further upside momentum toward higher resistance zones (based on recent highs).
📉 Support Levels
S1 ~₹407 – ₹410 – short-term support near today’s low zone.
S2 ~₹401 – ₹405 – secondary support if price declines below S1.
S3 ~₹396 – ₹399 – deeper support on a pullback.
👉 Bearish scenario: A daily close below ~₹401-₹396 may open further decline toward lower support clusters.
📌 Simple Interpretation (Daily TF)
📍 Above Pivot (~₹412): Slightly bullish / range control.
📍 Holding Support (~₹407 – ₹401): Helps limit downside.
📍 Break above ~₹429: Potential for continuation to next resistance area.
📍 Break below ~₹396: Bearish momentum intensifies.
⚠️ Notes
Levels are based on standard pivot and support/resistance derivations — actual intraday price action may vary with market volatility.
For live charts and real-time plotting, it’s best to check TradingView, your broker’s charting tool, or other live market platforms.
AUROPHARMA 1 Month View📌 Current Price Context
Last traded / current price: ~₹1,207–₹1,208 on NSE.
📊 Key Technical Levels (1-Month View)
🔹 Pivot Point
Pivot (daily): ~₹1,200 – centre of recent price action.
📈 Resistance Levels
R1: ~₹1,226–₹1,228 — first meaningful resistance above current price.
R2: ~₹1,245–₹1,247 — higher resistance zone from classic pivot analysis.
R3: ~₹1,271–₹1,275+ — extended resistance from upper pivot range.
These resistances correspond to areas where price has previously found sellers or consolidation over the last few weeks.
📉 Support Levels
S1: ~₹1,181–₹1,182 — first support just below pivot region.
S2: ~₹1,155–₹1,156 — secondary support from recent swing lows.
S3: ~₹1,136–₹1,138 — deeper support area if market weakens further.
These support zones align with recent range lows and moving average clusters over a monthly period.
📊 Moving Averages & Trend
20-day / 50-day / 100-day EMAs and SMAs are currently around ₹1,164–₹1,192 range — near price but showing neutral-to-slightly bullish bias on daily charts.
Price trading above most short and mid-term moving averages suggests short-term strength if levels hold.
📈 Oscillators / Momentum (Short-term indication)
RSI near mid-to-bullish levels (~58–68) indicating no extreme overbought condition yet.
Momentum suggests neutral-to-slightly uptrend in the recent 1-month timeframe.
📍 Summary (1-Month Technical View)
Bullish breakout zone:
• Above ~₹1,226 → may accelerate toward ₹1,245 / ₹1,270+
Key neutral range:
• ₹1,181–₹1,226 — consolidation band to watch intra-month
Bearish trigger (pullback):
• Below ~₹1,155 → risk of deeper test of ₹1,136+ support
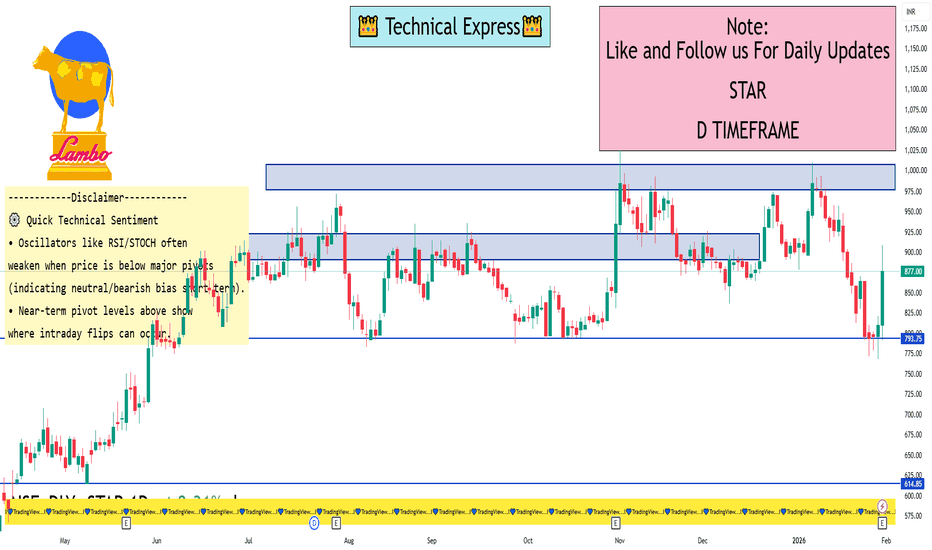
STAR 1 Day View 📌 Live Price Snapshot
• Current price: ~₹877.00 on NSE (Last traded)
• Today’s range: ₹791 – ₹908.40
• 52-Week range: ₹513.05 – ₹1,025.00
📊 Daily Pivot & Key Levels (1-Day Timeframe)
These are approximate pivot, support and resistance levels based on the most recent pivot analysis published today:
📍 Pivot Point
Central Pivot: ~ ₹850.8
🛑 Resistance Levels
R1: ~ ₹868.1
R2: ~ ₹891.0
R3: ~ ₹908.3
(These are short-term upside barriers where price may slow/reverse)
🟩 Support Levels
S1: ~ ₹827.9
S2: ~ ₹810.6
S3: ~ ₹787.7
(These are immediate downside zones where price could find buying interest)
📌 How to Use These Levels Today
✔ Bullish view:
• Above Pivot ₹850.8 → watch for closing above R1 (~₹868) to strengthen upside bias.
• Breaking and holding above R2 (~₹891) could extend toward R3 (~₹908).
✔ Bearish/Range view:
• Failure below Pivot ₹850.8 or S1 (~₹827.9) increases odds of deeper correction toward S2/S3.
• Intraday rejections at R1/R2 can signal short-term sellers.
ACC 1 Month View 📈 1-Month Key Price Range
🔹 1-Month High: ~₹1,779 (late Jan 2026)
🔹 1-Month Low: ~₹1,626 (recent session low)
➡️ So the current 1-month trading range is roughly:
👉 ₹1,626 – ₹1,779
🔥 Short-Term Support & Resistance Levels
Support (Downside)
• S1: ~₹1,626 — recent intra-day low and current 52-week low area.
• S2: ~₹1,600 — psychological/support near multi-session lows (below recent range).
• S3: ~₹1,570 … deeper support if the range breaks down.
Resistance (Upside)
• R1: ~₹1,670–₹1,680 — immediate resistance around recent price reaction zone.
• R2: ~₹1,720 — short-term resistance near 20–30 day moving averages.
• R3: ~₹1,760–₹1,780 — recent 1-month highs.
📊 1-Month Technical Context
📉 Over the past 30 days, ACC has been in a modest downtrend/weak range, with 1-month returns in negative territory and prices sliding from the upper ₹1,700s toward mid-₹1,600s.
Technical indicators also point toward bearish/neutral momentum in the short term (e.g., RSI weak, MACD bearish) — aligning with the recent price pressures.
[SeoVereign] BITCOIN BULLISH Outlook – January 31, 2025Bitcoin is currently deciding its next move around the recent daily low of 80,700 USDT.
At this point, there are three main scenarios that could unfold for Bitcoin. First, it does not break below 80,700 USDT and continues to rise. Second, it breaks below 80,700 USDT but forms a whipsaw movement, fully recovers the decline, and reverses upward. Third, it breaks below 80,700 USDT and leads to a major decline.
Since we are traders, we must determine which of these three scenarios will prove to be correct.
It would be ideal if we could clearly choose one of the three options above. However, a market perspective is rarely something that can be decisively concluded in a black-or-white manner.
Therefore, rather than selecting one of the three scenarios, I will describe my subjective view in a narrative form.
First, I believe that in the short term, Bitcoin could rise without breaking below 80,700 USDT. However, if that happens, I do not expect the upward trend to last very long.
The reason is that historically, when Bitcoin transitions from a major downtrend to an uptrend, it has often broken below the previous low through a whipsaw to stop out long positions before reversing.
This may differ in smaller trends, but in larger timeframes, a double bottom without a whipsaw (where the right bottom is higher than the left) has, in my experience and research, rarely resulted in a meaningful major trend reversal.
Therefore, if the price rises immediately from the current level, I plan to take profits relatively quickly, as indicated on the chart.
On the other hand, if Bitcoin breaks below 80,700 USDT, two possibilities emerge. It could form a whipsaw and then transition into a major bull trend, or it could enter what many would call a “season-ending” level of significant decline. Which of these becomes reality can only be determined by observing the chart structure after some time has passed following the actual breakdown below 80,700 USDT.
Predicting the distant future in advance may be possible for some, but I consider it nearly impossible.
That is why, even though I predicted a rise in my previous idea and currently hold a long position, I did not allocate a large size. Compared to my usual trades, the position is very small, because my level of conviction was not high before placing the bet.
Although it is still early 2026, this moment could turn out to be the most difficult trading environment to predict this year. As I always say, everything is hardest at the beginning. Investing is the same. Capturing the initial turning point from decline to rise is extremely difficult and painful. However, once this phase passes and the next trend forms, reading the market becomes much easier.
The reason I maintain a high win rate is that I do not rashly predict the distant future. If you wait, there are often moments when the chart provides clues about the next move. I simply wait until then. The longer you wait, the more evidence accumulates, and predicting the next move becomes significantly easier.
If Bitcoin breaks below 80,700 USDT, I will update my view in this idea or share a new post.
Another point I would like to mention is that significant movements are occurring across the broader market.
If a book is ever written about the history of silver, January 31 may be recorded as one of its historic days. As of now, silver is showing a drop of over 20% in a single day. Alongside the U.S. market, the commodities market is experiencing enormous volatility. While the exact cause requires further research, what is certain is that asset “rebalancing” is taking place.
For some time, crypto has been thoroughly neglected by the market. While other assets continued their rallies, crypto alone remained in decline. The reason is simple. The crypto market lacked attractiveness, and capital did not flow into it. However, crypto is now at relatively low price levels, while other assets are forming price ranges near their highs.
I believe there is a high probability that funds liquidated from assets positioned at high levels will eventually flow into the crypto market. If crypto continues to decline, it may mean that investors are temporarily holding that capital on the sidelines. In other words, commodities are likely to show weakness or move sideways, while crypto is likely to show strength or move sideways.
Even I am currently holding a substantial amount of cash while waiting for opportunities to increase my spot crypto allocation.
As mentioned in this post, crypto’s direction will soon be determined. When that moment comes, I will decide whether to purchase spot or wait a little longer.
In summary, in the short term, I plan to accumulate long exposure based on this idea. The size of the position will be adjusted over time as the market becomes clearer. For now, since information is limited and multiple directions remain open, I am buying only a small amount. Technically, I am basing this on the Shark Pattern, and from a macro perspective, on the market rebalancing discussed above.
Accordingly, I have set a short-term target around 89,308 USDT.
If the movement becomes clearer or the analysis requires updating, I will add to this post or return with a new one.
Thank you for reading.
DAILY FOREX SCAN Session – 22 30 01 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
Gold Market Shows Volatile Swings as Buyers and Sellers Clash(Educational)
At market open, Gold demonstrated strong bullish momentum, opening with a clear upside gap and quickly moving toward key highs. Early buying enthusiasm met significant selling pressure, causing prices to drop sharply. Buyers re-entered near lower zones, triggering a rebound, but renewed selling capped gains and pushed prices back down. The session has been marked by aggressive and fast swings, reflecting an active battle between buyers and sellers. Support is observed at lower zones, while resistance forms at recent highs and supply areas. Price action remains unstable, alternating between bullish and bearish phases, emphasizing the need for caution and disciplined observation. Traders should closely monitor these critical zones, as they highlight short-term momentum shifts, reversal potential, and areas where market control alternates. Overall, Gold continues to show a dynamic structure with rapid swings, requiring careful attention to market reactions and active participation from both sides. Volatility remains high, offering both opportunities and risks, making it important to follow price behavior and adjust strategies accordingly.
BTCUSD Demand Zone in Focus After Strong Bearish MoveBTCUSD is currently trading after a strong bearish move, where price broke below the earlier sideways structure with high selling momentum. The market clearly respected a downward trend, forming lower highs and showing consistent selling pressure. The resistance area around 89,800–90,400 worked as a strong selling zone, where price faced rejection and sellers regained control, leading to a sharp fall.
After this decline, price has now reached a major demand zone near 83,500–84,000. This area is supported by earlier buying activity and base formation, making it an important support level. The present reaction from this zone indicates that sellers are slowing down and buyers are trying to hold price. As long as BTCUSD stays above this demand, short-term stability or a corrective move can be seen.
The risk area below demand shows where downside pressure may increase if support breaks. A clear move below this zone would strengthen the bearish trend further. For now, price is consolidating near support, and volatility is expected around these levels. Overall market bias remains cautious, with bearish control still active, but short-term recovery chances remain while demand holds.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Trading involves risk and uncertainty.
GOLD MARKET VOLATILITY - REALITY CHECK Noise is high around XAUUSD with headlines like “trillions wiped out” and “gold crashing”.
Let’s keep it factual.
Gold is volatile due to profit-booking after a historic rally, geo-political uncertainty, and US policy expectations.
This is correction + consolidation, not a confirmed crash.
💡 “Trillions wiped out” = notional intraday value swings, not permanent losses.
Key Levels to Watch (XAUUSD)
Resistance: 5250 – 5300
Support: 5080 – 5000 (major demand zone)
Below 5000: Only if volatility expands with strong volume
Key Takeaway for Traders 🎯
High volatility ≠ clear direction
Avoid revenge or blind trades
Let price settle → trade with risk control
🛑 Staying out is also a strategy
📊 Focus on Forex / Crypto / Indices if Gold is unstable
Risk management > FOMO
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingBest Practices for Retail Traders
1. Start with Buying Options
Risk is limited.
2. Prefer ATM or Slight ITM
Better stability, realistic probability.
3. Avoid Holding Overnight
Unless you understand IV, theta, and event risk.
4. Track Implied Volatility
Buy when IV is low, sell when IV is high.
5. Use a Trading Plan
Entry levels
Stop loss
Target
Position size
6. Don’t Chase Cheap OTM Options
They expire worthless most of the time.
Part 4 Institutional VS. Technical1. Delta
Measures how much the premium changes with a ₹1 move in the underlying.
Call delta: +0.0 to +1.0
Put delta: –0.0 to –1.0
High delta = faster premium movement.
2. Gamma
Measures how fast delta changes. Used to evaluate momentum and risk.
3. Theta
Measures time decay—how much premium decreases as expiration approaches.
Sellers benefit from theta.
Buyers lose value daily.
4. Vega
Measures sensitivity to implied volatility (IV).
Higher IV → higher premium.
5. Rho
Impact of interest rates (less important for short-term traders).
INDIANB 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Current Price Context (as of latest trading)
Indian Bank is trading near ₹910–₹920 levels on NSE.
📈 1‑Month Key Resistance Levels (Upside)
These are the levels where price may face selling pressure or reversal if bulls weaken:
R1 — ₹918–₹920 — immediate resistance area just above current trade.
R2 — ₹927–₹930 — secondary resistance zone.
R3 — ₹935–₹940 — further upside resistance zone for continuation moves.
Summary: Immediate upside capped around ~₹918–₹930. Break and close above this band can signal stronger bullish continuation.
📉 1‑Month Key Support Levels (Downside)
Important levels that can act as rebound zones on pullbacks:
S1 — ~₹880–₹885 — first meaningful support near recent swing lows.
S2 — ~₹860–₹865 — secondary support from broader short‑term structure.
S3 — ~₹830–₹835 — major zone where bigger trend buyers may step in.
Summary: Minor supports start ~₹880, stronger support cluster around ~₹860‑₹835.
📊 Pivot / Neutral Reference
Pivot around ~₹907–₹910 — current central reference area.
Price above pivot suggests bullish bias, below could tilt neutral to bearish within the month.
📌 Interpretation For 1‑Month View
Bullish scenario:
Holds above ₹900–₹910 pivot → targeting ₹927–₹940 zone.
Neutral / consolidation:
Trading between ₹880–₹910.
Bearish risk:
Break below ₹860–₹845 could open deeper correction toward ₹830.
PFC 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Live Context (Daily)
📊 Approx Live Price: ~₹377‑₹379 (today’s trading range: ₹376 – ₹384) on NSE intraday quotes.
📈 Daily Pivot / Support & Resistance (Reliable Levels)
🔹 Pivot / Reference Zone
Central Pivot (CPR) ~ ₹386.8 area — key reference point for bias (above = bullish bias; below = bearish).
🚀 Resistance Levels (Upside)
R1 ~ ₹390–₹392 — initial resistance near current zone.
R2 ~ ₹394–₹398 — next supply zone.
R3 ~ ₹402–₹406 — stronger resistance on daily view.
Above ₹400 reinforces bullish structure and opens potential next targets up if breakout sustains.
🛑 Support Levels (Downside)
S1 ~ ₹382–₹386 — near‑term support zone (first buyer interest).
S2 ~ ₹378–₹381 — lower support region on daily pivots.
S3 ~ ₹370–₹376 — deeper support zone if price weakens.
Daily bias turns bearish if price closes clearly below the S2/S3 range (~₹378–₹376).
🔎 Quick Technical Bias Notes
Since current price (~₹377‑₹379) is below the pivot/CPR (~₹387), short‑term bias leans slightly bearish to neutral unless bulls reclaim pivot with volume.
A daily close above ~₹398‑₹400 could shift view bullish toward ~₹402+ and beyond.
Part 2 Institutional VS. TechnicalWhat Are Options?
Options are derivative contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset—such as stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, or ETFs. There are two basic types of options:
1. Call Option
A call option gives you the right to buy the underlying asset at a fixed price (called the strike price) within a specified period.
Traders buy calls when they expect price to rise.
Profit increases as the underlying price moves above the strike price.
2. Put Option
A put option gives you the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price within a specified period.
Traders buy puts when they expect price to fall.
Profit increases as the underlying price moves below the strike price.
Every option has two key components:
Strike Price: The price at which the asset can be bought/sold.
Expiration Date: When the option becomes invalid.
Part 1 Institutional VS. Technical
Key Components of Options- Underlying Asset: The security (stock, index, etc.) the option is based on.
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiry Date: The last day the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price of the option contract.
SAMMAANCAP 1 Month Time Frame 📈 Current Snapshot (as reference)
Last traded / recent price around ~₹147 – ₹151 on NSE (varies with intraday moves).
52‑week range: ~₹97 – ₹192.9.
🔑 1‑Month Key Levels – NSE Pivot, Support & Resistance
Monthly Pivot Levels (short‑term framework):
These come from pivot analysis that captures intermediate trend areas over the past sessions — useful for 1‑month traders.
📍 Pivot Reference (Monthly)
Pivot (central reference): ~₹146‑₹147
This is the main gravity level — above it suggests bullish bias; below implies bearish bias in the short term.
🛑 Resistance Levels (Upside)
These are zones where price may face selling pressure if it rallies:
R1: ~₹155 – ₹157
R2: ~₹164 – ₹165
R3: ~₹173 – ₹175
Resistance areas represent possible profit‑taking or reversal zones near recent reaction highs.
🧱 Support Levels (Downside)
These levels may act as demand zones if price corrects:
S1: ~₹137 – ₹138
S2: ~₹128 – ₹130
S3: ~₹120 – ₹122
Below S1, sellers may dominate, with deeper support closer to S3 in an extended correction.
⚠️ Note
These levels are derived from pivot and technical data (not financial advice). Market news/events (e.g., legal developments, earnings) can quickly shift short‑term trend dynamics, so use stops and risk management if trading.
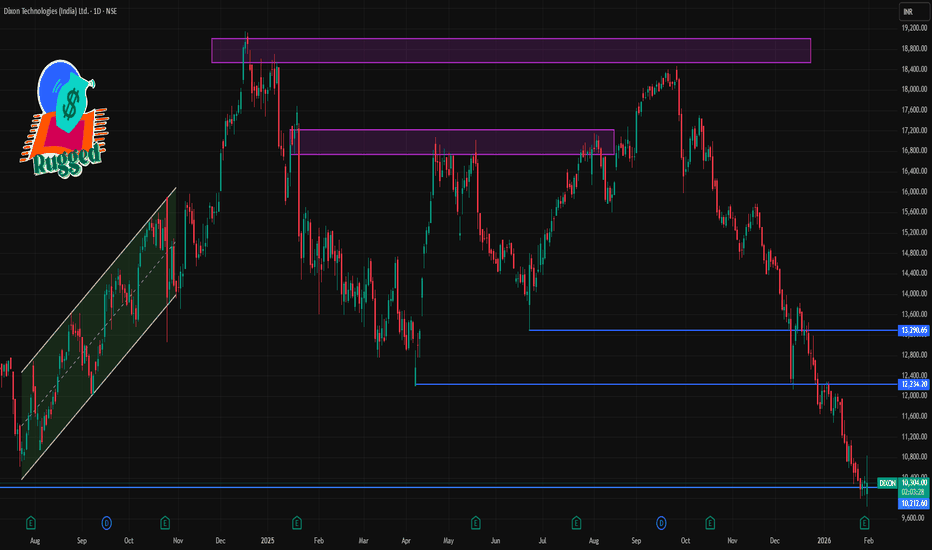
DIXON 1 Day Time Frame 📊 Current Price Snapshot (Daily)
Latest traded price: ~₹10,300 – ₹10,460 approx on NSE/BSE (mid-day range).
Today’s price range: ₹9,835 (low) – ₹10,843 (high).
52-week range: ₹9,835 – ₹18,471.
Bias: The stock remains below key short-term averages (e.g., 20/50/100-day EMAs), indicating a bearish daily trend until price successfully closes above resistance levels.
📈 Daily Pivot & Technical Levels (1-Day Time Frame)
🔹 Pivot Point (Daily Centre)
• Pivot: ~₹10,276 – ₹10,496 (central reference for today’s bias)
🚧 Resistance Levels (Upside)
1. R1: ~₹10,496 – ₹10,500 (1st resistance zone)
2. R2: ~₹10,656 – ₹10,660 (daily push-back region)
3. R3: ~₹10,876 – ₹10,880 (higher barrier)
👉 A sustained daily close above ~₹10,500–₹10,650 is needed to reduce near-term bearish momentum.
📉 Support Levels (Downside)
1. S1: ~₹10,116 – ₹10,120 (initial support)
2. S2: ~₹9,896 – ₹9,900 (secondary cushion)
3. S3: ~₹9,736 – ₹9,740 (deeper support)
👉 Breach of ₹9,900 and then ₹9,740 could expand downside risk on the daily chart.
💡 Quick Trading Reference — Today
Bullish bias resume only if price closes above:
✔️ ₹10,500 (initial breakout)
✔️ ₹10,650+ (confirmation of relief rally)
Bearish pressure sustained while below these:
⏬ ₹10,116 → first downside target
⏬ ₹9,896 – ₹9,740 → strong support zones
VEDL 1 Day Time Frame 📊 Key Daily Price Levels (NSE)
(Current price context — road-tested from multiple live feeds)
⛳ Pivot & Intraday Reference (Daily pivot is the key bias level)
• Daily Pivot: ~₹685 – ₹719 region (major pivot range varies by source)
📈 Resistances (Upside Levels)
• R1: ~₹725 – ₹730 zone — initial resistance for bulls today
• R2: ~₹738 – ₹751 — stronger barrier area where sellers may step in
• R3: ~₹760 – ₹803 (higher overhead zone) — breakout target if momentum is strong
📉 Supports (Downside / Bounce Zones)
• Immediate Support: ~₹700 – ₹710 (near today’s intraday low mid-range)
• Next Support: ~₹689 – ₹690 (lower circuit boundary / near recent low)
• Deeper Support Zones: ₹665-₹660 cluster — a demand zone if price slips further
📌 What Today’s Price Action Looks Like
• Currently trading in a wide intraday range ~₹695–₹755 today on NSE — volatile with a broadened circuit range of ₹689.75 (LC) to ₹842.95 (UC).
• The stock has been in strong short-term uptrend, but faces selling pressure near upper resistances — this suggests cautious profit-booking near R1-R2 unless breakout with volume confirms strength.
📊 Technical Indicator Context (Daily)
⚡ RSI/oscillators on some providers show overbought conditions on short timeframe, indicating possible pullbacks if resistance holds.
Key Levels to Use for Stops/Entries:
Stop-loss (for long trades): below ₹689 (intraday structural support).
Aggressive breakout entry: above ₹738-₹750 (for momentum play).
Support test entry: near ₹700-₹690 (with tight stop).
The Global IPO Market1. What Is an IPO & Why It Matters
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time by listing on a stock exchange. It allows companies to raise capital from a broad investor base, provides liquidity to early investors and employees, and increases visibility and credibility. In return, public markets demand transparency, regulatory compliance, and ongoing disclosure.
IPOs serve as a crucial mechanism in global finance for capital formation, enabling companies to fund expansion, repay debt, invest in research and development, and pursue acquisitions. For investors, IPOs can offer growth opportunities—especially if the company scales rapidly post‑listing.
2. How the Global IPO Market Works
Key Participants
Issuing Company (Issuer): Seeks capital through a public listing.
Underwriters/Investment Banks: Advise on pricing, structure the deal, and sell shares to institutional and retail investors.
Stock Exchanges: Provide the platform for listing (e.g., NYSE, Nasdaq, HKEX).
Regulators: Oversee disclosure and compliance (e.g., SEC in the U.S.).
Investors: Institutional (mutual funds, hedge funds) and retail investors who buy shares.
Process Overview
Preparation: Financial audits, governance structures, and prospectus creation.
Due Diligence: Underwriters evaluate company financials and market potential.
Marketing (Roadshow): Presenting the investment case to potential investors.
Pricing: Shares are priced based on demand and valuation metrics.
Listing: Shares begin trading publicly, often with first‑day “pop” or volatility.
The success of an IPO depends on market conditions, investor appetite, sector momentum, and broader economic trends.
3. Current Trends in the Global IPO Market (2025)
Overall Market Health
After years of caution driven by geopolitical tensions, interest rate uncertainty, and volatility, 2025 saw a stabilizing and resilient global IPO market. According to data from EY’s Global IPO Trends, there were approximately 1,293 IPOs raising US$171.8 billion globally in 2025, signaling renewed confidence and a shift toward higher‑quality offerings.
This continues a trend of recovery following slow periods in 2022–24. While not yet at the frothy peaks of the 2021 boom, IPO markets are showing strength characterized by larger deal sizes and selective investor interest in standout companies.
Volume vs. Proceeds
Data indicates that while the number of IPOs hasn’t surged dramatically, total capital raised is increasing—reflecting a shift toward larger, more established issuers deciding to go public rather than many small firms. This is a key metric of market maturity and investor selectivity.
Cross‑Border Listings
Companies increasingly choose to list on foreign exchanges—a trend especially evident in the U.S. This can enhance liquidity and broaden the investor base. Cross‑border IPOs reached multi‑decade highs in 2025, highlighting globalization within equity capital markets.
Sector Focus
Major IPO activity is concentrated in sectors that attract investor interest, such as:
Technology & AI: Companies tied to digital transformation.
Fintech: Financial technology firms tapping broader capital markets.
Healthcare & Life Sciences: Biotech and life science companies.
Industrials & Consumer Goods: Established firms with strong growth plans.
4. Regional Dynamics
Asia‑Pacific
Asia continues to be a powerhouse in IPO activity.
Greater China (including Hong Kong and mainland China) has emerged as a dominant source of IPO proceeds, capturing around one‑third of global capital raised in the first half of 2025.
Hong Kong Exchange (HKEX) has enjoyed strong listings in 2025, with companies raising significant capital — reflecting confidence in Asia’s public markets.
India has also shown strong IPO volume and improvement in fundraising, trending toward record years and ranking among the top global IPO markets.
This reflects broader economic growth in the region, deepening equity markets, and policy frameworks aimed at attracting listings.
United States
The U.S. traditionally leads global IPO markets in capital raised thanks to large tech and growth company listings:
The U.S. recorded strong IPO volumes in early to mid‑2025—the highest since 2021 in some quarters.
Some of the most anticipated potential IPOs (e.g., SpaceX) could redefine market scale if they materialize.
However, intermittent challenges like regulatory slowdowns (e.g., government shutdowns affecting the SEC) have occasionally slowed the pace of launches.
Europe
Europe’s IPO market remains smaller relative to Asia and the U.S. but showed record momentum at the start of 2026 with major industrial and defense listings.
Emerging Markets
Latin America, the Middle East, and other emerging regions see sporadic but noteworthy IPOs, with firms choosing international listings to access deeper capital pools.
5. Major Recent IPOs & Signals
2026 Activity Indicators
Even in early 2026, new signs of life include:
PicPay’s Nasdaq IPO marking a return of Brazilian companies to public markets after a multi‑year break.
Agibank’s planned U.S. IPO underlining fintech interest from Latin America.
Busy Ming’s successful Hong Kong IPO showing continued appeal of Asian listings.
These signals reflect a nuanced landscape where IPOs are widely spread across sectors and geographies.
6. Challenges Facing the IPO Market
Despite improvements, the global IPO market faces several persistent challenges:
Market Volatility & Economic Uncertainty
Global macroeconomic uncertainty—driven by tariffs, interest rate shifts, and geopolitical tensions—has made companies more cautious about listing timing.
Regulatory & Compliance Pressures
Companies face rising compliance costs and investor demands for transparency and ESG (environmental, social, governance) disclosures—both prerequisites for modern listings.
Investor Selectivity
Investors increasingly focus on firm quality, profitability pathways, and sustainability of growth. Firms with weak fundamentals or unclear growth prospects often delay or cancel IPO plans.
Valuation Concerns
High valuation expectations by private companies sometimes misalign with market realities, leading to postponed listings or sub‑par performances post‑IPO.
7. The Future Outlook
The outlook for the global IPO market remains cautiously optimistic, with several key forces shaping its trajectory:
Strong Pipelines
Many large private companies (especially in tech, fintech, and biotech) remain IPO candidates. As markets stabilize, these firms may enter public markets—potentially providing a meaningful uplift to aggregate proceeds.
Innovation & New Sectors
New sectors like AI, green tech, and biotech are attracting investors and may lead to new high‑value IPOs.
Geographic Shifts
Asia’s increasing share and cross‑border listings suggest a more balanced global IPO market, reducing reliance on single regions.
Economic Policies
If monetary easing continues and geopolitical tensions reduce, IPO markets are likely to see further expansion in both number and value of offerings.
8. Conclusion
The global IPO market in the mid‑2020s has shifted from the uncertainty of the early 2020s to a phase of resilience and cautious expansion. While market volatility and external economic pressures remain challenges, structural improvements, stronger investor sentiment, and megadeals in promising sectors suggest a maturing market with significant future capital formation potential.
Whether for young innovators or established industrial firms, the IPO remains a central pillar of global capital markets—connecting companies with investors and driving growth across regions and industries.