HINDZINC 1 Day Time Frame 📍 Current price context
• The stock has been trading around ~₹580-₹595 recently on NSE/BSE.
📊 1-Day (Daily) Key Levels
Daily Pivot & Main Zones (Approximate)
• Pivot Point (PP): ~₹591–₹592
• Central Pivot Range (CPR): ~₹589–₹592
Resistance (Upside) Levels
R1: ~₹599–₹600
R2: ~₹604–₹605
R3: ~₹613–₹615
(Above these, psychological/short-term supply could appear)
Support (Downside) Levels
S1: ~₹585–₹586
S2: ~₹577–₹578
S3: ~₹572–₹574
(Below these, downside momentum may strengthen)
📈 Intraday Trading Zones (Traders View)
From recent pivot based intraday ideas:
Upper intraday resistance: ~₹705–₹713 zone
Support zones: ~₹685, ~₹672–₹673, ~₹665 levels
(Note: These were generated when the stock was trading higher, so adjust relative to latest price levels)
🧠 Quick Interpretation
✅ Above daily pivot (~₹591–₹592) suggests short-term bullish bias.
⚠️ Below major support (~₹577) could open short-term further weakness.
💡 Resistance cluster (~₹600–₹615) will likely be tested if buyers return.
Community ideas
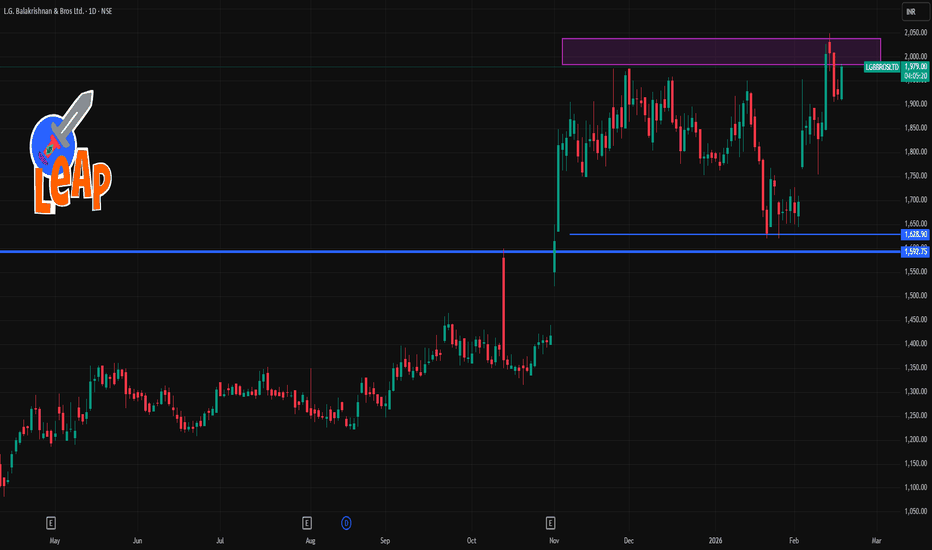
LGBBROSLTD 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Most recent price (approx): ~₹1,918–₹1,980 range (varies by data source & session)
🔹 Daily Pivot & Key Levels (Fibonacci / Standard)
Upside / Resistance (sell/target zones):
R1: ~₹1,983 – ₹1,987
R2: ~₹2,007 – ₹2,070
R3: ~₹2,139+ (higher resistance)
(These come from Fibonacci/volume S/R calculations)
Central Reference:
Daily Pivot: ~₹1,943 – ₹1,946 (midpoint bias for the day)
Downside / Support (buy/stop loss zones):
S1: ~₹1,889 – ₹1,905
S2: ~₹1,846 – ₹1,879
S3: ~₹1,777 – ₹1,780 (deeper support zone)
(Important zones if price weakens)
📊 What These Levels Mean (1-Day TF)
1. Above the pivot (~₹1,940) — intraday bias leans bullish (buyers in control).
2. Key resistance near ₹2,000–₹2,070 — breaking above can extend upwards momentum.
3. Support around ₹1,880–₹1,905 — crucial daily support; a break below may signal intraday weakness.
4. Lower support near ₹1,770–₹1,780 — last major zone before broader sell-off risk.
These levels are commonly used by day traders for entry, profit targets and stop placements.
MAHABANK 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Current Price
MAHABANK is trading around ₹65 – ₹67.1 on NSE, close to its 52-week high (~₹67.7).
📊 1-Month Timeframe Levels (Support & Resistance)
Pivot & Classic Levels (Daily/1-Month Reference)
(Useful for short-to-medium trend bias)
R3: ~₹67.5 - ₹67.7
R2: ~₹66.6
R1: ~₹66.0
Pivot: ~₹65.1
S1: ~₹64.8 - ₹64.6
S2: ~₹64.2
S3: ~₹63.1 - ₹63.7
These pivot/support/resistance levels are based on classic pivot calculations for recent price ranges.
Key Levels to Watch in the Month
📈 Bullish Breakout Zone: Above ₹66.6 – ₹67.7 — if price convincingly closes above this range on monthly candlesticks, it signals continuation to new highs.
📉 Immediate Support Zone: ₹64.8 – ₹63.1 — a breakdown below this could signal deeper pullback or range-loss.
📍 Pivot Base (~₹65.1) — short-term trend pivot area; staying above suggests bullish bias persists on this timeframe.
📌 Summary (1-Month Outlook)
🟢 Bullish if:
Price holds above pivot ~₹65.1 and climbs above R2/R3 (~₹66.6 – ₹67.7) ⇒ strength into higher levels.
⚠️ Neutral / Consolidation if:
Stays between ₹64.8–₹66.0, indicating range-bound price action.
🔴 Bearish risk if:
Breaks below support cluster ₹64.2 / ₹63.1, which could weaken the uptrend.
Digital Asset ETFs & Institutional Crypto Flows1. What Are Digital Asset ETFs?
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are pooled investment vehicles that trade like stocks on exchanges and aim to track the performance of an underlying asset or index. Digital asset ETFs are ETFs that provide exposure to cryptocurrencies—such as Bitcoin and Ethereum—or crypto-related products without requiring investors to hold the digital assets directly.
These products typically take two forms:
Spot-Backed ETFs:
These hold the underlying cryptocurrency (e.g., BTC or ETH) in custody and reflect the spot price of the asset.
Other Crypto ETPs (Exchange-Traded Products):
These may include baskets of multiple digital assets, futures-based exposures, or wider themed funds including NFTs, DeFi tokens, stablecoins, and blockchain infrastructure assets.
For institutions, ETFs are a familiar and regulated way to access digital assets without the need for direct wallet custody, complex key management, or decentralized exchange interactions. ETFs also provide traditional regulatory safeguards and reporting standards.
In the U.S., the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in 2024 was a watershed—setting a precedent for other spot and multi-asset products, including recent moves toward Ethereum spot ETFs. This regulatory clarity has accelerated launches and institutional adoption.
2. Why ETFs Matter for Institutional Investors
Institutional investors—such as pension funds, asset managers, mutual funds, insurers, hedge funds, and family offices—typically require:
Regulatory clarity
Custody and settlement safeguards
Liquidity
Familiar investment vehicles
Digital asset ETFs deliver on all of these fronts:
a. Regulated Exposure
ETFs trade on regulated exchanges and comply with securities laws, reducing counterparty risk relative to direct crypto exchange trading.
b. Liquidity and Market Depth
Large institutional capital, when invested through ETFs, adds liquidity to crypto markets as equivalents of spot crypto holdings are created or redeemed in the ETF ecosystem. This aligns more capital with market-making and deepens order books.
c. Portfolio Integration
Institutions can treat digital assets like any other asset class in portfolio construction. For example, they can use strategic allocations for diversification, risk-adjusted returns, or inflation hedging.
d. Tax Efficiency
ETF structures—especially those that allow in-kind creations/redemptions—can help institutions rebalance without triggering capital gains taxes, a significant benefit relative to outright spot trades.
Thanks to these features, ETFs have become the dominant on-ramp for institutional crypto exposure—far more than unregulated OTC markets or direct custody for many large investors.
3. Institutional Crypto Flows: The Data
Institutional flows into digital asset ETFs and funds have surged in recent years, signaling a shift from niche experimentation to mainstream portfolio inclusion:
a. Massive ETF Inflows
Record inflows into global crypto ETFs reached $5.95 billion in a single week in October 2025, driven largely by Bitcoin but also Ether, Solana, and XRP.
By Q3 2025, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs had attracted over $118 billion of institutional inflows, with some flagship products commanding significant market share.
b. Asset Under Management (AUM) Growth
Bitcoin ETFs alone have reached triple-digit billions in assets under management, reflecting broad institutional uptake.
Ethereum ETFs have also seen strong growth, with multi-billion-dollar inflows in 2025, highlighting diversification beyond Bitcoin.
c. Institutional Allocations
Surveys indicate widespread institutional involvement:
Roughly 86% of institutions either hold or plan to allocate to digital assets.
Allocations to digital assets are climbing, with projections expecting institutional crypto portfolio shares to triple within a few years as infrastructure and regulatory frameworks deepen.
d. Volatility and Two-Way Flows
Flows into and out of ETFs are dynamic—reflecting portfolio rebalancing rather than pure speculation. Institutions adjust exposures based on macro conditions, risk tolerance, and relative valuations.
Despite this, the broader trend remains long-term upward as digital assets mature and institutional acceptance grows.
4. What Drives Institutional Capital Inflows?
Several factors explain why institutions are increasingly allocating capital to digital assets:
a. Regulatory Certainty
Clear rules around ETF launches, custody standards, and reporting reduce legal and compliance barriers. For example, streamlined SEC processes have lowered barriers for new crypto ETFs.
b. Macro Conditions
Uncertain macroeconomic environments—such as inflation concerns, currency debasement fears, and traditional asset volatility—push institutions to consider uncorrelated or diversifying assets like Bitcoin and Ether.
c. Liquidity and Safety
Regulated ETFs offer high liquidity and custodial safety, prerequisites for large institutional allocations.
d. Strategic Portfolio Roles
Institutional investment teams increasingly view Bitcoin as a long-term store of value or inflation hedge, while Ether’s utility in DeFi and staking enhances its institutional appeal.
e. Yield and Staking
Some institutions seek crypto exposures that generate yield—especially Ether, via staking—further diversifying return profiles.
f. Operational Maturity
Custody infrastructure, audit standards, and investment platforms have matured, making institutional participation more feasible.
5. Impact on the Crypto Ecosystem
Institutional flows via ETFs and funds have profound effects:
a. Reduced Volatility
A larger institutional presence can dampen short-term price swings through deeper liquidity and sophisticated market making.
b. Price Support
Large inflows have coincided with BTC and ETH price rallies, partly due to ETF demand reducing available supply and increasing buy pressure.
c. Broader Market Legitimacy
Institutional capital validates crypto as a serious asset class and encourages other regulated products and services—such as tokenised bonds, tokenised funds, and broader blockchain-based financial instruments.
d. Integration with Traditional Finance
As digital asset ETFs grow, they act as bridges between traditional capital markets and crypto networks, facilitating increased participation by entities like pension funds, insurance companies, and mutual funds.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Despite strong institutional trends, challenges remain:
a. Regulatory Uncertainty
While progress has been significant, regulatory environments differ globally, and uncertainties remain in some jurisdictions.
b. Market Cycles and Outflows
Institutions react to macro environments; in some periods, large outflows occur as funds rebalance or macro priorities shift. Recent reports highlighted $1.7 billion in net outflows in early 2026—even as long-term flows stay net positive.
c. Education and Risk Management
Institutional risk teams must understand crypto risk profiles, custody models, and operational safeguards.
d. Liquidity in Altcoins
While Bitcoin and Ethereum dominate, institutional flows into other tokens are more fragmented and speculative, requiring careful due diligence.
7. The Future of Institutional Crypto Flows
Looking forward, key trends include:
Expansion of ETF Types: More products covering broader digital assets or thematic baskets.
Global Institutional Adoption: Institutions outside the U.S. and Europe are increasingly participating.
Hybrid Models: Tokenised traditional assets (Treasuries, money markets) on blockchain rails.
Increased Role in Portfolios: Strategic allocations to digital assets as part of diversified long-term strategies.
Conclusion
Digital asset ETFs have fast become the primary conduit for institutional capital into cryptocurrency markets. They provide regulated, liquid, and familiar exposure to digital assets, helping bridge the gap between traditional finance and blockchain-native markets. Institutional flows—while dynamic—show a clear upward trend, driven by regulatory clarity, macroeconomic conditions, and growing confidence in crypto’s utility as a strategic portfolio component. As infrastructure continues to mature and ETFs proliferate, institutional participation is likely to deepen, further embedding digital assets into the fabric of global finance.
Stablecoin Adoption & RegulationWhat Are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are digital tokens issued on blockchain networks that maintain a consistent value relative to a reference asset. The most common types include:
Fiat-backed stablecoins – Backed 1:1 by reserves of fiat currency or cash equivalents held by a centralized issuer. Examples include Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC).
Crypto-collateralized stablecoins – Backed by other cryptocurrencies and often overcollateralized to absorb volatility. Dai (DAI) is a well-known example.
Algorithmic stablecoins – Maintain their peg through algorithmic supply adjustments rather than collateral. Some have failed dramatically, leading to increased regulatory attention.
Stablecoins operate primarily on blockchains such as Ethereum, enabling programmable financial services through smart contracts.
Drivers of Stablecoin Adoption
1. Trading & Liquidity
Stablecoins first gained traction in crypto trading. Exchanges use them as a substitute for fiat currency, enabling traders to move funds quickly between assets without withdrawing to a bank account. USDT and USDC are widely used as base trading pairs, improving market liquidity and efficiency.
2. Cross-Border Payments
Traditional international transfers are slow and expensive. Stablecoins enable near-instant global transactions at lower cost. In emerging markets with unstable currencies, individuals use dollar-pegged stablecoins to preserve value and facilitate remittances.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi platforms rely heavily on stablecoins for lending, borrowing, and yield farming. Stablecoins function as the core settlement layer for decentralized exchanges and liquidity pools, enhancing capital efficiency.
4. Corporate & Institutional Adoption
Major fintech firms and payment processors have integrated stablecoins into their infrastructure. For example, PayPal launched its own stablecoin, signaling growing mainstream acceptance. Institutional investors also use stablecoins for settlement and treasury management.
5. Financial Inclusion
Stablecoins provide access to digital dollar savings for people without access to traditional banking. A smartphone and internet connection are often sufficient to store and transfer value.
Growth of the Stablecoin Market
Since 2020, stablecoin market capitalization has expanded dramatically, reaching hundreds of billions of dollars. Transaction volumes frequently exceed those of major card networks in certain periods, highlighting their growing role in digital commerce.
USDT remains the largest by market capitalization, while USDC is often viewed as more regulated and transparent. DAI represents decentralized alternatives, emphasizing crypto-backed collateral models.
This expansion has drawn the attention of regulators concerned about systemic risk, consumer protection, and monetary sovereignty.
Regulatory Concerns
Governments and central banks worldwide are evaluating stablecoins due to several risks:
1. Reserve Transparency
Fiat-backed stablecoins must maintain sufficient reserves to honor redemptions. Questions about reserve composition—such as exposure to commercial paper or other risky assets—have prompted demands for audits and disclosure requirements.
2. Systemic Risk
If stablecoins grow large enough, a sudden loss of confidence could trigger a “run,” similar to money market fund crises. This could affect broader financial markets.
3. Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Because stablecoins can move across borders quickly, regulators emphasize compliance with Know-Your-Customer (KYC) and AML laws.
4. Consumer Protection
Users need clarity regarding redemption rights, reserve backing, and operational risks.
5. Monetary Policy Impact
Widespread adoption of dollar-pegged stablecoins in foreign economies may reduce demand for local currencies, affecting monetary sovereignty.
Regulatory Approaches Around the World
United States
In the U.S., regulators have debated whether stablecoins should be treated as bank deposits, securities, or payment instruments. Legislative proposals aim to require issuers to hold high-quality liquid assets and obtain banking licenses. Oversight discussions involve agencies such as the Treasury Department and financial regulators.
European Union
The EU implemented the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, establishing licensing requirements, reserve standards, and consumer protections for stablecoin issuers. MiCA represents one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks globally.
Asia
Countries such as Singapore and Japan have introduced licensing regimes requiring reserve segregation and strict compliance standards. Meanwhile, China has banned private stablecoins while promoting its central bank digital currency (CBDC).
Stablecoins vs. CBDCs
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are government-issued digital currencies. Unlike private stablecoins, CBDCs represent direct liabilities of central banks.
Key differences:
Issuer: Stablecoins are privately issued; CBDCs are state-issued.
Regulation: Stablecoins face regulatory oversight; CBDCs are sovereign instruments.
Innovation speed: Private stablecoins evolve faster due to market competition.
Some policymakers view CBDCs as a safer alternative, while others see stablecoins as complementary innovations in a diversified digital financial ecosystem.
Benefits of Clear Regulation
Clear regulatory frameworks can:
Enhance consumer confidence
Attract institutional capital
Reduce systemic risks
Encourage innovation within legal boundaries
Well-designed regulation balances innovation with risk management, preventing market abuses while supporting responsible growth.
Challenges Ahead
Despite progress, challenges remain:
Harmonizing global regulations to prevent regulatory arbitrage.
Ensuring interoperability between stablecoins and traditional financial systems.
Managing cybersecurity and operational risks.
Addressing concerns about privacy and surveillance.
Moreover, decentralized stablecoins raise unique legal questions because they lack a centralized issuer to regulate.
Future Outlook
Stablecoins are increasingly integrated into global finance. Their role may expand in:
Cross-border trade settlements
E-commerce payments
Tokenized asset markets
Web3 ecosystems
Collaboration between regulators, central banks, fintech firms, and blockchain developers will shape their trajectory. If effectively regulated, stablecoins could become foundational infrastructure for digital finance.
Conclusion
Stablecoin adoption reflects demand for digital assets that combine blockchain efficiency with price stability. Their utility in trading, payments, and DeFi has driven rapid growth. However, this expansion has raised regulatory concerns related to reserve backing, systemic risk, AML compliance, and monetary policy.
Global regulators are moving toward structured oversight frameworks, with regions like the EU leading through comprehensive legislation. As regulation evolves, stablecoins are likely to mature into a more secure and integrated component of the financial system.
The future of stablecoins will depend on achieving the right balance between innovation and regulation—ensuring stability without stifling technological progress.
Ethereum & Smart-Contract Token MarketsIntroduction
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin and a team of co-founders. While Bitcoin introduced the concept of digital scarcity and peer-to-peer money, Ethereum expanded blockchain technology by enabling programmable applications through smart contracts. This innovation transformed blockchain from a payment system into a global computational platform and laid the foundation for modern token markets.
Smart-contract token markets are digital ecosystems where tokens—created and managed by smart contracts—are issued, traded, governed, and utilized. These markets power decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), gaming economies, and much more.
1. Ethereum Architecture and Smart Contracts
Ethereum operates as a distributed ledger maintained by thousands of nodes worldwide. Unlike Bitcoin’s relatively limited scripting language, Ethereum introduced the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a Turing-complete environment capable of executing complex code.
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They automatically enforce rules once predefined conditions are met. Because they run on a decentralized network, they are:
Transparent
Immutable (once deployed)
Trust-minimized
Permissionless
Developers typically write smart contracts in Solidity, Ethereum’s primary programming language. Once deployed, these contracts can manage digital assets, enforce agreements, and create tokens without relying on centralized intermediaries.
2. Token Standards: ERC-20, ERC-721, and Beyond
Ethereum’s token economy is built on standardized contract interfaces known as Ethereum Request for Comments (ERC). These standards ensure compatibility across wallets, exchanges, and applications.
ERC-20: Fungible Tokens
ERC-20 defines a common set of rules for fungible tokens (tokens that are interchangeable and identical in value). Examples include governance tokens, stablecoins, and utility tokens.
The ERC-20 standard enabled:
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) (2017 boom)
Decentralized exchanges
Stablecoins like USD Coin
Governance tokens in DeFi protocols
ERC-20 tokens are the backbone of Ethereum’s financial ecosystem.
ERC-721: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
ERC-721 introduced non-fungible tokens—unique digital assets representing ownership of art, collectibles, or virtual land.
NFTs gained global attention through collections like CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club. Unlike ERC-20 tokens, each NFT has distinct metadata and ownership history recorded on-chain.
ERC-1155: Multi-Token Standard
ERC-1155 allows a single smart contract to manage multiple token types (both fungible and non-fungible). This standard is particularly useful in gaming ecosystems where assets vary in type and rarity.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to financial applications built on Ethereum that operate without centralized institutions. Key components include:
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap
Lending protocols
Yield farming platforms
Synthetic assets
In DeFi markets:
Users provide liquidity to pools.
Smart contracts automatically match trades.
Liquidity providers earn fees.
Governance tokens grant voting rights.
DeFi token markets are algorithmic and transparent. Prices are often determined by automated market maker (AMM) models instead of traditional order books.
4. Market Mechanics and Tokenomics
Smart-contract token markets rely on programmable economic incentives known as tokenomics. Tokenomics includes:
Supply limits
Inflation schedules
Burn mechanisms
Staking rewards
Governance rights
For example, some tokens use deflationary models where a portion of transaction fees is burned, reducing total supply over time. Others incentivize network security via staking.
Ethereum itself transitioned from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in 2022 through “The Merge.” This significantly reduced energy consumption and altered ETH issuance dynamics, making the token more economically efficient.
5. Market Participants
Smart-contract token markets involve several categories of participants:
Retail Users
Individual investors, traders, NFT collectors, gamers.
Developers
Build decentralized applications (dApps), protocols, and token contracts.
Liquidity Providers
Supply tokens to AMMs and earn fees.
Validators
Stake ETH to secure the network under Proof-of-Stake.
DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations govern protocols collectively via token voting.
6. Advantages of Smart-Contract Token Markets
Permissionless Access
Anyone with a wallet can participate.
Transparency
All transactions are publicly verifiable.
Programmability
Complex financial logic is automated.
Interoperability
Tokens can integrate seamlessly across DeFi protocols.
Global Liquidity
24/7 markets without borders.
7. Risks and Challenges
Despite innovation, Ethereum token markets face risks:
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Bugs can lead to exploits and loss of funds.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments are still defining crypto asset classifications.
Market Volatility
Token prices can fluctuate dramatically.
Scalability Constraints
High gas fees during congestion can limit participation.
Ethereum addresses scalability via:
Layer 2 solutions (rollups)
Sharding roadmap
Optimistic and zero-knowledge proofs
8. Token Launch Models
Token markets often begin with structured distribution mechanisms:
ICO (Initial Coin Offering)
IDO (Initial DEX Offering)
Airdrops
Liquidity mining
Airdrops reward early users with governance tokens, decentralizing ownership.
9. NFTs and Digital Ownership
NFT markets extend beyond art:
Gaming assets
Virtual real estate
Identity credentials
Intellectual property rights
Smart contracts ensure provable ownership and programmable royalties for creators.
10. Ethereum’s Role in the Broader Crypto Economy
Ethereum functions as the infrastructure layer for Web3. It supports:
DeFi
NFTs
DAOs
Stablecoins
Tokenized real-world assets
ETH serves dual roles:
Native currency for gas fees
Economic security asset via staking
Because most tokens are built on Ethereum or EVM-compatible chains, Ethereum acts as the settlement layer of decentralized finance.
11. Future Outlook
The evolution of Ethereum token markets will likely involve:
Increased institutional participation
Improved regulatory clarity
Expansion of tokenized real-world assets
Growth of Layer 2 ecosystems
Enhanced privacy technologies
The integration of traditional finance with smart-contract infrastructure could reshape capital markets, supply chains, intellectual property systems, and digital identity frameworks.
Conclusion
Ethereum fundamentally transformed blockchain technology by introducing smart contracts and enabling tokenized economies. Smart-contract token markets represent programmable, decentralized financial and ownership systems operating without traditional intermediaries. Through standards like ERC-20 and ERC-721, Ethereum has created interoperable digital asset ecosystems powering DeFi, NFTs, and governance models.
While challenges remain—including security, regulation, and scalability—the continued development of Ethereum and its ecosystem positions it as a central infrastructure layer for the decentralized digital economy. Smart-contract token markets are not merely speculative instruments; they are programmable economic systems that may redefine how value is created, transferred, and governed in the 21st century.
Bitcoin Price Action and Macro Correlations1. Introduction: Bitcoin as a Macro Asset
Since its launch in 2009, Bitcoin has evolved from a niche cryptographic experiment into a globally traded macro asset. In its early years, price movements were largely driven by internal crypto dynamics—exchange adoption, mining cycles, and retail speculation. Today, Bitcoin trades alongside equities, bonds, commodities, and currencies, reacting to interest rates, liquidity conditions, inflation expectations, and geopolitical shocks.
Understanding Bitcoin price action now requires a macro lens. While it retains unique structural features (fixed supply, halving cycles, decentralized architecture), its behavior increasingly reflects global capital flows and monetary policy regimes.
2. Bitcoin and Global Liquidity
One of the strongest macro correlations observed since 2020 is between Bitcoin and global liquidity expansion.
When central banks—especially the Federal Reserve—expand balance sheets through quantitative easing (QE), financial conditions loosen. Excess liquidity flows into risk assets. During the 2020–2021 pandemic response, unprecedented monetary stimulus coincided with Bitcoin’s surge from under $10,000 to over $60,000.
Key mechanism:
QE increases bank reserves.
Yields compress.
Investors seek higher returns.
Capital rotates into equities, tech stocks, and Bitcoin.
Conversely, during quantitative tightening (QT), liquidity drains from markets. In 2022, aggressive rate hikes and balance sheet reduction correlated with Bitcoin’s drawdown from ~$69,000 to below $20,000.
Bitcoin often behaves like a “liquidity thermometer” — highly sensitive to marginal changes in global dollar availability.
3. Correlation with Equity Markets
A major structural shift occurred around 2020: Bitcoin’s increasing correlation with growth equities, particularly the NASDAQ-100.
Historically, Bitcoin was marketed as “digital gold” — an uncorrelated hedge. However, during 2020–2022, rolling 90-day correlations between Bitcoin and Nasdaq frequently exceeded 0.6–0.8, indicating strong alignment.
Why?
Both are duration-sensitive assets.
Both benefit from low interest rates.
Both attract speculative and institutional flows.
When real yields rise:
Growth stock valuations compress.
Bitcoin, which produces no cash flow, also de-rates.
This dynamic became evident during 2022 when tightening monetary policy caused simultaneous declines in tech stocks and crypto.
However, correlations are cyclical—not permanent. During certain risk-off episodes, Bitcoin has temporarily decoupled, especially during crypto-specific crises.
4. Bitcoin vs. Gold: Hedge or Risk Asset?
Bitcoin is frequently compared with Gold as a store of value and inflation hedge. Both assets share scarcity narratives:
Gold: Physically scarce, mined.
Bitcoin: Digitally scarce, capped at 21 million coins.
Yet their macro behaviors differ.
Gold typically:
Performs well during geopolitical stress.
Benefits from declining real yields.
Acts as a defensive allocation.
Bitcoin often:
Trades with high beta to risk.
Amplifies liquidity cycles.
Experiences sharper drawdowns.
In 2022, gold remained relatively stable while Bitcoin collapsed, challenging the inflation-hedge thesis in the short term. However, in longer structural cycles—especially during currency debasement fears—Bitcoin narrative alignment with gold strengthens.
Bitcoin may function less as “digital gold” and more as a high-volatility monetary hedge tied to liquidity expansion phases.
5. Interest Rates and Real Yields
One of the most important macro variables influencing Bitcoin is real yields (nominal yields minus inflation expectations).
When real yields rise:
Opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets increases.
The dollar strengthens.
Bitcoin faces headwinds.
When real yields fall:
Risk appetite improves.
The dollar weakens.
Bitcoin often rallies.
Bitcoin’s sensitivity to rate expectations became especially clear during policy pivots by the Federal Reserve in 2023–2024. Even small changes in forward guidance triggered sharp price reactions.
Bitcoin behaves similarly to long-duration tech stocks:
Future adoption narrative = “long duration.”
Sensitive to discount rate shifts.
Thus, macro traders increasingly watch treasury markets as closely as blockchain metrics.
6. Dollar Strength (DXY) Inverse Correlation
Bitcoin often exhibits an inverse relationship with the U.S. dollar index (DXY).
Mechanism:
Strong dollar = tighter global financial conditions.
Weaker dollar = easier liquidity and capital inflows to risk assets.
Because Bitcoin trades globally but is primarily priced in USD, dollar strength affects:
Emerging market demand.
Cross-border capital flows.
Speculative appetite.
Major Bitcoin rallies frequently coincide with periods of dollar weakness, while strong DXY environments suppress crypto momentum.
7. Inflation Narratives vs. Reality
Bitcoin’s inflation-hedge thesis gained popularity during 2020–2021 when consumer prices accelerated globally. However, price action revealed nuance.
Short-term:
Bitcoin rose alongside inflation fears (2020–2021).
But fell sharply during peak inflation in 2022.
Why?
Markets trade expectations, not current data. When inflation rises but central banks remain accommodative, Bitcoin benefits. When inflation forces aggressive tightening, Bitcoin suffers.
Thus, Bitcoin correlates more strongly with liquidity conditions than with inflation levels themselves.
8. Halving Cycles vs. Macro Cycles
Bitcoin’s internal supply mechanics add a unique dimension to macro analysis.
Every four years, mining rewards are cut in half (“halving”), reducing new supply issuance. Historically, halvings in 2012, 2016, 2020, and 2024 preceded major bull cycles.
However, as Bitcoin matures:
Supply shocks are predictable.
Institutional participation increases.
Macro liquidity may dominate over issuance mechanics.
Future cycles may depend more on global monetary conditions than purely on programmed scarcity. If halving aligns with liquidity expansion, bull markets can accelerate. If it aligns with tightening, impact may be muted.
9. Institutionalization and ETF Impact
The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs marked a structural shift. Institutional inflows link Bitcoin more tightly to traditional portfolio allocation frameworks.
Effects:
Greater integration into risk-on/risk-off flows.
Increased sensitivity to equity volatility.
Enhanced correlation during macro shocks.
As asset managers treat Bitcoin as a portfolio satellite allocation, its macro beta rises. Over time, however, deeper liquidity may reduce volatility amplitude.
10. Geopolitics and Safe-Haven Debate
During geopolitical stress—wars, banking crises, capital controls—Bitcoin occasionally experiences localized surges in demand.
Examples include:
Banking instability episodes.
Currency crises in emerging markets.
Capital flight scenarios.
However, global panic events often trigger liquidity-driven selloffs first, with Bitcoin dropping alongside equities before stabilizing.
Bitcoin’s safe-haven status is therefore situational rather than consistent.
11. Structural Evolution: From Retail Speculation to Macro Instrument
Bitcoin price action has transitioned through phases:
2010–2016: Retail-dominated, halving-driven cycles.
2017–2019: Speculative mania and crypto-native boom/bust.
2020–present: Macro-integrated, institutionally influenced asset.
Today, Bitcoin reacts to:
CPI prints.
Central bank meetings.
Treasury yield moves.
Dollar index swings.
It trades 24/7, often acting as a real-time sentiment gauge before equity markets open.
12. Conclusion: A Hybrid Asset Class
Bitcoin now occupies a hybrid position:
Part monetary experiment.
Part high-beta tech proxy.
Part liquidity barometer.
Part digital scarcity asset.
Its strongest consistent macro correlation has been with global liquidity and real rates. Equity correlation remains cyclical but significant. Gold correlation is narrative-driven and less stable.
As adoption deepens and macro regimes shift—from tightening to easing cycles—Bitcoin’s price action will likely remain highly sensitive to central bank policy and dollar liquidity.
In essence, Bitcoin no longer trades in isolation. It trades at the intersection of monetary policy, global capital flows, and technological adoption cycles. Understanding it requires blending on-chain analysis with macroeconomics—a convergence that defines modern crypto market structure.
Commodities Supercycle (Base Metals, Energy)What Is a Commodities Supercycle?
A commodities supercycle is a prolonged period—often 10 to 20+ years—during which prices of raw materials rise significantly above their long-term trend, driven by structural (not just cyclical) demand shifts. These episodes typically involve base metals (like copper, iron ore, nickel, aluminum) and energy commodities (oil, natural gas, coal), and are associated with industrialization waves, geopolitical realignments, or major technological transitions.
Unlike normal commodity cycles—tied to business expansions and recessions—supercycles are powered by deep, global transformations: urbanization, electrification, war reconstruction, or green energy transitions. They reshape trade patterns, capital flows, inflation trends, and geopolitical power balances.
Historical Commodity Supercycles
1. Late 19th Century Industrialization (1890s–1910s)
This early supercycle was driven by the industrial expansion of the United States and Germany. Massive railway construction, steel production, and coal consumption fueled rising demand for iron ore and energy resources. Urban growth and mechanization caused sustained commodity price strength.
Key characteristics:
Infrastructure expansion (railroads, factories)
Rising steel and coal demand
Rapid industrialization
The cycle was interrupted by World War I and later economic volatility.
2. Post–World War II Reconstruction (1940s–1960s)
After World War II, Europe and Japan underwent large-scale rebuilding. Programs like the Marshall Plan accelerated construction, infrastructure development, and industrial revival.
This period saw:
Strong steel and copper demand
Expanding oil consumption
Large infrastructure investment
The rise of automobile culture in the United States also boosted petroleum demand, reinforcing the energy component of the supercycle.
3. The China-Led Supercycle (2000–2014)
The most recent and widely discussed supercycle was driven by China’s rapid industrialization and urbanization after its entry into the World Trade Organization in 2001.
China consumed:
Over 50% of global iron ore
Massive quantities of copper and aluminum
Growing oil imports
Between 2000 and 2008, prices of oil, copper, and iron ore surged dramatically. Oil reached nearly $150 per barrel in 2008. Mining companies expanded aggressively, investing billions in new capacity.
However, after 2014:
China’s growth slowed
Commodity supply caught up
Prices collapsed (2014–2016 downturn)
This marked the end of that supercycle phase.
Key Drivers of a Commodities Supercycle
1. Structural Demand Shifts
A supercycle begins when a large economy (or group of economies) undergoes transformation:
Industrialization
Urbanization
Electrification
Military buildup
Energy transition
For example, China’s shift from agrarian to industrial society required steel, cement, and copper at unprecedented levels.
2. Supply Constraints
Commodity supply is relatively inelastic in the short and medium term. Developing new mines or oil fields can take 5–15 years.
During supercycles:
Underinvestment in previous years limits supply
Environmental and regulatory barriers slow expansion
Geopolitical risks disrupt output
This mismatch between rapid demand growth and slow supply response pushes prices higher for extended periods.
3. Financialization of Commodities
Since the 2000s, commodities became an asset class. Institutional investors, hedge funds, and ETFs increased participation, amplifying price trends. While financial flows do not create a supercycle alone, they can intensify price movements.
Base Metals in a Supercycle
Base metals are central to supercycles because they are foundational to infrastructure and industry.
Copper
Often called “Dr. Copper” because it signals economic health. It is critical for:
Electrical wiring
Construction
Renewable energy systems
Energy transition policies significantly increase copper intensity per unit of GDP.
Iron Ore
Used in steel production—essential for buildings, bridges, ships, and machinery.
Nickel
Important for stainless steel and increasingly for electric vehicle batteries.
Aluminum
Lightweight metal used in transport, packaging, and aerospace.
During supercycles, base metal prices rise as infrastructure and industrial production surge.
Energy in a Supercycle
Energy commodities often experience even more volatility than metals.
Oil
Oil demand grows with transportation, petrochemicals, and industrial activity. Supercycles often coincide with:
Rising vehicle ownership
Expanding global trade
Military conflicts
Natural Gas
Used for power generation and industrial heating. LNG trade expansion has globalized gas markets.
Coal
Though declining in some regions due to climate policies, coal remains critical in emerging markets.
Energy supercycles can also be triggered by supply disruptions (e.g., geopolitical tensions or OPEC production decisions).
Inflation and Macroeconomic Effects
Commodity supercycles often generate:
Higher global inflation
Trade surpluses for exporting nations
Fiscal windfalls for resource-rich countries
Countries like Australia, Brazil, Canada, and Russia tend to benefit from rising commodity prices. Conversely, commodity-importing nations may face inflationary pressures.
Central banks must respond carefully. The 2000s commodity boom contributed to inflation concerns prior to the 2008 financial crisis.
Are We in a New Supercycle?
Some analysts argue that a new supercycle began around 2020–2022, driven by:
1. Energy Transition
Decarbonization requires enormous metal inputs:
Copper for grids
Nickel and lithium for batteries
Aluminum for lightweight transport
Electric vehicles require significantly more copper than internal combustion cars.
2. Underinvestment in Fossil Fuels
After the 2014 oil crash and ESG pressures, investment in oil and gas declined. Limited new supply could tighten markets.
3. Geopolitical Fragmentation
Supply chain reshoring, sanctions, and trade fragmentation may increase commodity intensity and raise costs.
4. Infrastructure Stimulus
Government spending in the United States, Europe, and Asia on infrastructure and clean energy may boost demand.
However, skeptics argue:
China’s growth has slowed structurally.
Renewable energy could eventually reduce fossil fuel demand.
Technological innovation may improve material efficiency.
Thus, whether the world is entering a sustained supercycle remains debated.
Risks That End Supercycles
Commodity supercycles typically end when:
Supply finally catches up
New mines, oil fields, and refining capacity enter production.
Demand slows
Economic slowdown or structural shifts.
Technological substitution
New materials replace old ones.
Energy efficiency reduces consumption.
Policy shifts
Environmental regulations.
Carbon pricing.
Trade changes.
The 2014 downturn in commodities occurred after massive mining investment met slowing Chinese demand.
Conclusion
A commodities supercycle is not simply a temporary price spike—it is a deep, structural transformation in global demand and supply patterns that reshapes economies and geopolitics.
Historically, supercycles have been linked to:
Industrial revolutions
War reconstruction
Rapid urbanization
Economic globalization
Base metals and energy commodities lie at the center of these cycles because they underpin infrastructure, industry, and development.
Today, the debate revolves around whether the green energy transition and geopolitical realignment will trigger a new supercycle. If so, it could redefine global trade, inflation dynamics, and resource politics for decades to come.
Understanding commodity supercycles is crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses, as their effects ripple across currencies, stock markets, emerging economies, and global stability.
Energy Sector Momentum (Oil, Gas Trades)Understanding Energy Sector Momentum
Momentum in financial markets refers to the tendency of assets to continue moving in the same direction—upward or downward—over a certain period due to persistent buying or selling pressure. In the energy sector, this typically manifests through:
Rising crude oil prices (WTI and Brent benchmarks)
Strength in natural gas futures
Outperformance of oil & gas equities
Increased capital flows into energy ETFs
Higher volatility and trading volume
Because energy commodities are foundational to global economic activity, price trends often reinforce themselves once they begin.
Oil Market Momentum
Key Benchmarks
The two major global crude benchmarks are:
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) – U.S. benchmark priced at Cushing, Oklahoma
Brent Crude (Brent) – International benchmark tied to North Sea production
Momentum in oil typically begins when:
Supply constraints emerge
OPEC+ production cuts
Geopolitical disruptions
Sanctions on major producers
Demand strengthens
Global economic expansion
Increased travel and industrial production
Seasonal demand spikes
Inventory draws accelerate
Falling crude stockpiles
Tight refining capacity
When oil breaks through key technical levels (such as long-term moving averages or resistance zones), institutional traders often add long positions, accelerating price momentum.
Role of OPEC and Geopolitics
The energy market is uniquely sensitive to political risk.
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its extended group OPEC+ often influence price momentum through coordinated production decisions. When OPEC cuts supply during tight market conditions, it amplifies bullish momentum. Conversely, unexpected production increases can reverse trends sharply.
Geopolitical flashpoints in major producing regions—Middle East conflicts, Russia-related supply shocks, or sanctions regimes—frequently trigger rapid upward momentum due to perceived supply risk premiums.
Natural Gas Momentum
Natural gas trades exhibit even greater volatility than oil. Unlike crude, gas markets are more regional due to transportation limitations.
In the U.S., pricing centers around Henry Hub, while globally, liquefied natural gas (LNG) trade has expanded international pricing influence.
Gas momentum often builds from:
Extreme weather (cold winters or hot summers)
LNG export demand surges
Storage deficits
Production slowdowns
Because natural gas is heavily used for power generation and heating, weather-driven demand can create explosive price trends. Short squeezes are common due to large speculative positioning in futures markets.
Energy Equities and Sector Rotation
When oil and gas prices trend higher, capital typically rotates into energy stocks. Major integrated oil companies, exploration & production firms, and oilfield service providers benefit directly from higher commodity prices.
Examples of global energy giants include:
ExxonMobil
Chevron Corporation
Saudi Aramco
Momentum investors often use ETFs to gain exposure, such as:
Energy Select Sector SPDR Fund (XLE)
Energy sector momentum frequently coincides with:
Rising inflation expectations
A strong U.S. dollar environment (though sometimes inverse)
Late-cycle economic expansion
Sector rotation strategies often favor energy when inflation is persistent and commodities outperform growth stocks.
Macro Drivers of Momentum
1. Inflation
Oil is a key component of inflation. When inflation accelerates, investors hedge by buying real assets, including crude oil and energy stocks. This creates a self-reinforcing feedback loop.
2. Interest Rates
Higher rates can initially pressure equities, but energy companies with strong cash flows and low debt can outperform in high-rate environments.
3. Global Growth
China, as the world’s largest energy importer, plays a major role. Strong Chinese industrial data often sparks upward momentum in crude markets.
Technical Factors
Momentum in oil and gas trades is also highly technical.
Traders watch:
50-day and 200-day moving averages
Breakouts above multi-month resistance
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Commitment of Traders (COT) positioning
When crude oil forms a sustained uptrend, algorithmic trading systems and commodity trading advisors (CTAs) add long exposure, magnifying price moves.
Volatility and Risk
Energy momentum is powerful but unstable.
Oil markets have historically experienced extreme cycles:
Supply glut collapses
Demand destruction during recessions
Rapid price spikes during geopolitical crises
Leverage in futures markets amplifies both gains and losses. Options activity also increases significantly during momentum phases.
Structural Shifts in Energy Markets
The long-term energy landscape is evolving.
Renewable energy expansion, electric vehicle adoption, and ESG investing trends have influenced capital allocation. However, underinvestment in traditional oil & gas infrastructure over the past decade has periodically created supply tightness—supporting bullish momentum cycles.
Even during energy transition narratives, oil and gas remain essential to transportation, petrochemicals, aviation, and heavy industry.
Momentum Cycle Phases
Energy momentum typically unfolds in stages:
Accumulation Phase
Smart money begins buying undervalued assets.
Sentiment is neutral or bearish.
Breakout Phase
Prices breach resistance levels.
Media coverage increases.
Institutional flows accelerate.
Acceleration Phase
Retail participation increases.
Volatility spikes.
Energy becomes top-performing sector.
Exhaustion Phase
Overbought technical readings.
Speculative excess.
Potential reversal catalysts emerge.
Recognizing which phase the market is in is critical for traders.
Capital Flow Dynamics
When oil prices rise sharply:
Sovereign wealth funds tied to oil-producing nations accumulate capital.
Energy companies generate excess free cash flow.
Share buybacks and dividend increases support equity prices.
During strong momentum cycles, energy stocks often outperform broader indices such as the S&P 500, particularly when technology stocks underperform.
The Psychological Component
Energy trades are highly sentiment-driven.
Bullish momentum often feeds on narratives such as:
“Supply crisis”
“Underinvestment”
“Supercycle”
Bearish momentum emerges from:
Recession fears
Demand destruction
Oversupply
Positioning imbalances can lead to rapid squeezes in either direction.
Conclusion
Momentum in the oil and gas sector is a powerful force shaped by macroeconomics, geopolitics, technical factors, and capital flows. Crude oil benchmarks like West Texas Intermediate and Brent Crude, along with natural gas pricing at Henry Hub, serve as the foundation for global energy trade dynamics.
Energy sector momentum often reflects broader inflationary and economic trends. When supply tightens or demand accelerates, oil and gas prices can enter strong upward cycles that spill into equities and derivatives markets. Conversely, economic slowdowns or production surges can rapidly reverse gains.
Green Tech & Renewable Energy Equities🌞 Solar Energy Equities
Solar energy companies form one of the largest segments of renewable energy equities. These firms manufacture photovoltaic (PV) panels, inverters, mounting systems, and provide installation and project development services.
Major publicly traded solar players include:
First Solar – A U.S.-based manufacturer known for thin-film solar modules.
Enphase Energy – Specializes in microinverters and solar energy management systems.
Sunrun – Focused on residential solar installation and leasing models.
Solar equities tend to benefit from declining panel costs, supportive government subsidies, and rising electricity demand. However, they can be volatile due to policy shifts, supply chain constraints, and fluctuating commodity prices such as silicon.
💨 Wind Energy Companies
Wind energy equities include manufacturers of turbines, project developers, and operators of wind farms. Wind power has become one of the most cost-effective sources of new electricity generation globally.
Key companies include:
Vestas Wind Systems – A global leader in wind turbine manufacturing.
Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy – A major supplier of offshore and onshore turbines.
Ørsted – A pioneer in offshore wind farm development.
Wind energy stocks are influenced by infrastructure investment cycles, power purchase agreements (PPAs), and technological advancements that improve turbine efficiency.
🔋 Energy Storage & Battery Technology
Renewable energy intermittency makes storage solutions essential. Battery companies and storage technology providers are therefore critical to the green transition.
Important players include:
Tesla, Inc. – Beyond EVs, Tesla produces large-scale battery storage systems like Powerwall and Megapack.
CATL – One of the world’s largest EV battery producers.
Fluence Energy – Specializes in grid-scale storage solutions.
Battery equities are closely linked to lithium, cobalt, and nickel markets, as well as EV demand growth. As battery chemistry evolves, companies that innovate may gain significant competitive advantages.
🚗 Electric Vehicle (EV) & Clean Transport Stocks
Transport electrification is a central pillar of decarbonization. EV-related equities include automakers, battery suppliers, charging infrastructure firms, and software developers.
Prominent companies:
Tesla, Inc. – Dominates the global EV market.
BYD – A leading EV and battery producer.
ChargePoint – Operates EV charging networks.
EV stocks can be growth-oriented and volatile, often reflecting consumer adoption rates, regulatory incentives, and global competition.
🌊 Hydropower & Other Renewables
Beyond solar and wind, renewable equities include companies operating hydroelectric dams, geothermal plants, biomass facilities, and emerging marine energy technologies.
Examples include:
Brookfield Renewable Partners – Operates hydro, wind, solar, and storage assets globally.
Ormat Technologies – A leading geothermal energy producer.
These assets often provide stable, long-term cash flows due to regulated pricing structures and long-term contracts.
📊 Investment Vehicles: ETFs & Funds
For diversified exposure, investors often choose renewable energy exchange-traded funds (ETFs) rather than individual stocks.
Popular examples:
iShares Global Clean Energy ETF
Invesco Solar ETF
ARK Innovation ETF (includes clean tech exposure)
ETFs reduce company-specific risk while providing access to the broader green transition theme.
📈 Growth Drivers of Green Energy Equities
Several structural forces support long-term growth:
Government Policy & Incentives – Climate legislation, carbon pricing, and subsidies accelerate adoption.
Corporate ESG Commitments – Companies aim to achieve net-zero emissions.
Technological Innovation – Falling costs in solar panels and batteries.
Energy Security Concerns – Countries reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Investor Demand for Sustainable Assets – ESG-focused portfolios continue expanding.
Major legislation such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act has significantly boosted investment in domestic clean energy manufacturing and infrastructure.
⚠️ Risks & Volatility
Despite strong long-term potential, green energy equities carry risks:
Policy reversals or subsidy cuts
Supply chain disruptions
Commodity price volatility
High capital expenditure requirements
Interest rate sensitivity (many projects are debt-financed)
Renewable energy stocks often behave like growth equities, making them sensitive to rising interest rates and market sentiment shifts.
🌍 Global Market Landscape
China, the United States, and the European Union dominate renewable energy investment and manufacturing. Emerging markets are also rapidly expanding solar and wind capacity due to declining costs.
Developing economies, particularly in Asia and Africa, may become key growth regions as electrification and infrastructure expand.
💡 Long-Term Outlook
The global energy transition is expected to span decades. According to international energy agencies, trillions of dollars in investment will be required to meet climate targets. This creates significant opportunity for renewable energy equities, particularly those with strong balance sheets, scalable technologies, and competitive advantages.
However, investors should approach the sector with a long-term perspective, understanding that volatility is common. Diversification across subsectors—solar, wind, storage, EVs, and grid infrastructure—can mitigate risk.
Conclusion
Green tech and renewable energy equities represent a dynamic and evolving investment landscape. From solar panels and offshore wind farms to electric vehicles and grid-scale batteries, these companies are reshaping the global energy system. While risks remain, structural growth drivers such as decarbonization policies, technological progress, and rising energy demand position the sector as a key pillar of future economic development.
For investors seeking exposure to sustainability, innovation, and long-term megatrends, renewable energy equities offer both opportunity and responsibility—supporting not only financial returns but also the transition to a cleaner, more resilient global economy.
Kross cmp 224 by Daily Chart view since listedKross cmp 224 by Daily Chart view since listed
- Support Zone 187 to 206 Price Band
- Resistance Zone 222 to 239 Price Band
- Bullish Rounding Bottoms followed by Cup & Handle
- Falling Resistance Trendline Breakout seems in progress
- Resistance Zone Breakout anticipated by steady attempts
- Volumes flat yet closely synced with average traded quantity
Cloud Computing and SemiconductorsWhat Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). Instead of owning and maintaining physical hardware, individuals and organizations rent computing resources from providers and pay only for what they use.
Major cloud providers include:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft (Azure)
Google (Google Cloud)
These companies operate massive data centers filled with servers that handle billions of requests daily.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
On-Demand Self-Service – Users can provision computing power instantly.
Broad Network Access – Services are available over the internet.
Resource Pooling – Multiple users share the same infrastructure.
Rapid Elasticity – Resources scale up or down automatically.
Measured Service – Users pay based on consumption.
Types of Cloud Computing
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Provides virtualized computing resources (e.g., virtual machines).
Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Offers development environments and tools.
Software as a Service (SaaS) – Delivers applications through browsers (e.g., email, collaboration tools).
Cloud computing enables businesses to reduce capital costs, increase flexibility, improve disaster recovery, and innovate faster.
What Are Semiconductors?
Semiconductors are materials—most commonly silicon—that have electrical conductivity between conductors (like copper) and insulators (like glass). This unique property allows them to control electrical current precisely, making them ideal for building electronic components such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs).
A semiconductor chip (also called a microchip) contains millions or even billions of tiny transistors etched onto a silicon wafer. These transistors act as switches that process and store information in binary form (0s and 1s).
Key Components Built from Semiconductors
Central Processing Units (CPUs) – The brain of a computer.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) – Designed for parallel processing and AI.
Memory chips (RAM and storage)
Networking chips
AI accelerators
Major semiconductor companies include:
Intel
NVIDIA
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC)
Samsung Electronics
Semiconductor manufacturing is one of the most complex industrial processes in the world, involving photolithography, extreme precision engineering, and billion-dollar fabrication plants (fabs).
The Relationship Between Cloud Computing and Semiconductors
Cloud computing depends entirely on semiconductor technology. Every cloud service runs on physical servers housed in data centers, and those servers are powered by semiconductor chips.
1. Data Centers and Chips
Data centers contain thousands or even millions of servers. Each server contains:
CPUs (often from Intel or custom chips designed by cloud companies)
GPUs (from NVIDIA for AI workloads)
Memory chips
Networking processors
Without advanced semiconductor chips, cloud providers could not offer scalable, high-performance computing.
2. Artificial Intelligence and High-Performance Chips
The rapid growth of AI has strengthened the connection between cloud computing and semiconductors. AI models require massive computational power for training and inference. GPUs and AI accelerators, such as those produced by NVIDIA, are essential in powering AI services offered in the cloud.
Cloud platforms provide AI tools as services, but behind the scenes, these tools rely on billions of transistors working together on specialized chips.
3. Custom Silicon and Cloud Innovation
Major cloud companies are now designing their own chips to optimize performance and reduce costs:
AWS designs custom processors (e.g., Graviton series).
Google develops Tensor Processing Units (TPUs).
Microsoft invests in AI-focused silicon.
This shift shows how cloud companies increasingly depend on semiconductor innovation to stay competitive.
Economic Importance
Both industries are central to the global economy.
Cloud Computing Market
Cloud computing has become a multi-trillion-dollar industry. It supports digital transformation, remote work, e-commerce, streaming, online education, and enterprise IT systems. Startups and large corporations alike rely on cloud infrastructure.
Semiconductor Industry
Semiconductors are critical to nearly every modern device: smartphones, cars, medical equipment, industrial machines, and cloud servers. Global chip shortages in recent years demonstrated how essential semiconductors are to supply chains worldwide.
Countries view semiconductor manufacturing as strategically important. Governments in the United States, China, South Korea, Taiwan, and Europe invest heavily in chip production to secure technological independence.
Challenges Facing Both Industries
1. Supply Chain Complexity
Semiconductor production depends on global supply chains. A single chip may be designed in the United States, fabricated in Taiwan, packaged in Southeast Asia, and assembled into servers worldwide. Disruptions—such as pandemics or geopolitical tensions—can impact cloud services.
2. Energy Consumption
Cloud data centers consume vast amounts of electricity. Advanced semiconductor chips are designed to improve energy efficiency, but the overall demand for computing power continues to rise.
Sustainability has become a major focus, with cloud providers investing in renewable energy sources.
3. Technological Limits
As transistors shrink to nanometer scales, physical and engineering challenges increase. Moore’s Law—the observation that transistor density doubles approximately every two years—has slowed, making innovation more complex and expensive.
Future Trends
1. AI-Centric Computing
AI workloads will drive demand for specialized semiconductors and expanded cloud infrastructure. Advanced AI models require faster chips, more memory bandwidth, and optimized data center architectures.
2. Edge Computing
Instead of processing everything in centralized data centers, some computing is moving closer to users (at the “edge”). This requires new semiconductor designs for smaller, distributed systems.
3. Quantum and Advanced Materials
Future computing may rely on quantum processors or new materials beyond silicon. Though still experimental, these technologies could redefine both cloud and semiconductor industries.
4. Integration and Customization
Cloud providers will continue designing custom chips tailored for specific workloads, such as AI training, data analytics, or security encryption. This vertical integration strengthens the bond between hardware and cloud software.
Conclusion
Cloud computing and semiconductors form a powerful technological partnership. Semiconductors provide the physical building blocks—transistors, chips, processors—that enable data centers to operate. Cloud computing transforms that hardware into flexible, scalable services accessible from anywhere in the world.
As digital transformation accelerates, the demand for cloud services continues to grow. At the same time, semiconductor innovation pushes the boundaries of computing performance, efficiency, and intelligence. Advances in AI, custom silicon, and next-generation materials will further deepen the relationship between these two industries.
In essence, cloud computing represents the service layer of modern digital infrastructure, while semiconductors represent the hardware foundation. Neither can function without the other. Together, they power the connected world and shape the future of technology, economics, and global development.
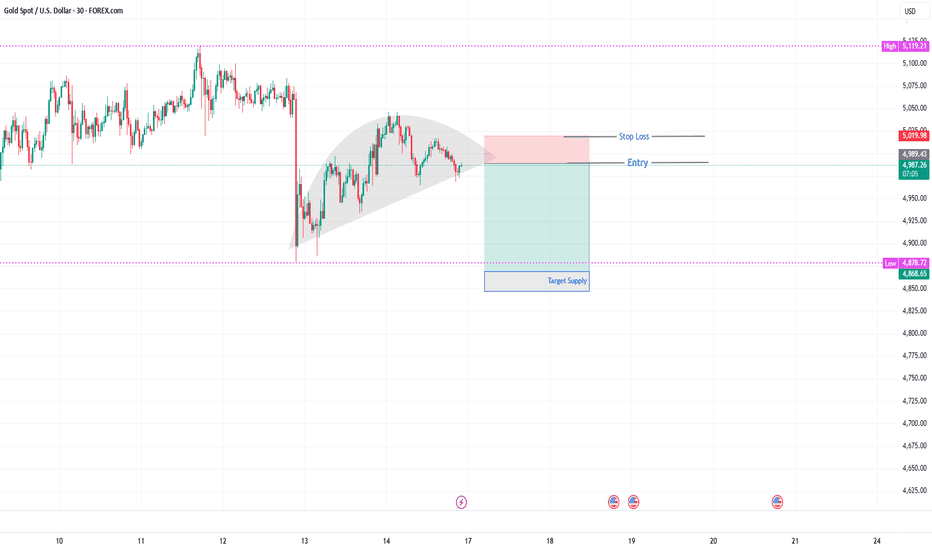
FOREX "PAIRS IN PLAY" Session 34 17 02 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
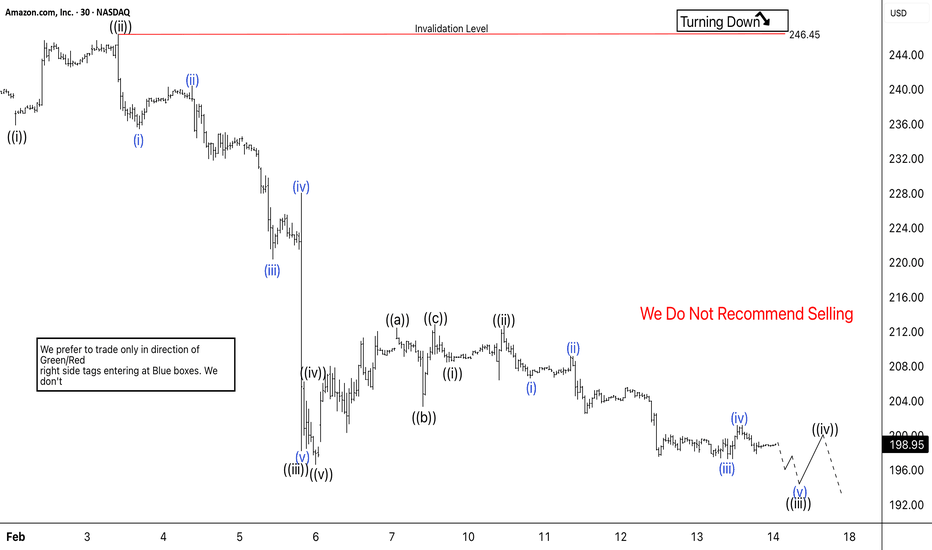
Elliott Wave Analysis: AMZN Resumes Downtrend as Wave 5 Decline Amazon completes wave 4 bounce and turns lower toward Fibonacci downside targets.
Amazon (AMZN) has resumed its decline after completing a corrective bounce. The stock formed a three-swing recovery in red wave 4 following the earlier three-wave drop from the peak at 247.77. The bounce remained corrective and failed to change the bearish trend. After finishing wave 4, price turned lower again and started a new impulsive move. The decline is now progressing in wave 5 and is developing as a clear five-wave structure. This confirms sellers remain in control and the larger downside sequence continues.
In the near term, the current leg lower should extend toward the 1.236 external retracement of wave 4 near 192.96. This area represents the first downside target. However, the bearish momentum suggests the move can stretch further. The next potential objective stands near 187.17 if selling pressure continues. Rallies are expected to remain corrective and should fail below the wave 4 pivot. Therefore, buying at current levels is not recommended. The market still favors selling bounces while the structure stays bearish.
Overall, AMZN remains in a downward trend. The Elliott Wave structure supports additional weakness in the short term as wave 5 continues to unfold
Fresh Nifty Analysis for Feb 17-20, 2026Wrap up:-
Nifty is now in wave 3 of major wave c, in which inner wave 1 is completed at 25641 and wave 2 is in progress which is making a wxy corrected pattern of which wave w is completed at 25685, wave x is completed at 25372 and wave y is also completed at 25730. Therefore, inner wave 2 of major wave 3 is completed at 25730.
What I’m Watching for Feb 17-20, 2026 🔍
If nifty breaks and sustains below 25593, low risk entry range is 25593-25645 for a Probable target i.e. 25247-25102 with a stoploss of 25731.
Disclaimer: Sharing my personal market view — only for educational purpose not financial advice.
"Don't predict the market. Decode them."
PNB — Rotation Before ExpansionCMP: 124.9
On the higher timeframe, the structural low near 40 marked the end of the long distribution phase. Since then, price has been printing higher highs and higher lows — classic trend transition.
On the daily, the recent pullback into the 119–120 zone held cleanly. That area now acts as demand. The sharp bounce from that pocket signals accumulation, not relief.
Short-term averages are turning up.
Momentum is rebuilding above reclaimed support.
Supply near 130–136 is being tested again.
Trade Framework
Bias: Upside continuation
Key Support: 118 (structural invalidation on closing basis)
Primary Objective: 136
Above 136, the expansion leg opens toward 150+.
As long as 118 holds, dips are absorption — not weakness.
The structure favors higher prices.
Risk defined.
Trend aligned.
AUROPHARMA — Compression Before ExpansionCMP: 1,208
The stock has spent months rotating between 1,150–1,250.
Supply has been absorbed multiple times without breakdown.
Higher lows are forming quietly above the 1,160–1,170 support cluster.
Short-term averages are turning up.
Momentum is rebuilding.
This is not a breakout yet — it’s positioning before one.
The longer a stock compresses under resistance, the stronger the expansion once it clears.
Trade Structure
Bias: Bullish
Stop-loss: 1,150 (structural invalidation)
Upside Objectives:
• 1,300 — first expansion zone
• 1,400 — prior supply pocket
• 1,600 — measured move extension
As long as 1,150 holds on a closing basis, the risk-reward favors upside rotation.
This is accumulation energy.
When it releases, it won’t be subtle.
#AUROPHARMA #SwingTrade #MarketStructure #BreakoutSetup #PriceAction #NSEStocks #TradingView
NIFTY 50 — Coiled for ExpansionCMP: 25,692
The panic leg is done.
The base is forming above the 200 DMA cluster (25,520–25,600).
Price has absorbed supply and is now building higher lows on the daily frame.
Short-term averages are turning up.
Volatility has compressed after the flush.
This is how accumulation phases look before expansion.
---
The Setup
The index is holding structure above reclaimed support while refusing to break lower.
Failed breakdown → shift in control.
Now it’s about acceptance and follow-through.
Trade Framework
Bias: Bullish continuation
Stop-loss: 25,400 (structural invalidation)
Target: 27,000
As long as price holds above the 25,400 pivot, the probability favors upside rotation toward the prior value high zone.
This is not a bounce call.
This is a positioning call.
Risk defined.
Upside asymmetric.
#NIFTY50 #IndexTrading #MarketStructure #SwingSetup #PriceAction #TradingView
GIFTNIFTY Intra-Swing Level Analysis for 17th FEB 2026GIFTNIFTY Intra-Swing Level Analysis for 17th FEB 2026
🚀Follow & Compare NIFTY spot Post for Taking Trade
👇🏼Screenshot of NIFTY Spot All-day(16th FEB 2026) in 5 min TF with perodical update.
━━━━━━━━━₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹━━━━━━━━
⚪Weekly PCR Analysis:
17 Feb 2026 EXP. Weekly Basis =>
Put OI:41,97,932, Call OI: 39,70,386, PCR: 1.06. Trend Strength: 🟠Neutral. Sentiment: Positive
Intraday Change in Weekly Basis Data =>
PPut OI Change: 111,90,371, Call OI Change: 11,48,263, Change OI PCR: 1.04 Trend Strength: 🟠Neutral.
━━━━━━━━━₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹━━━━━━━━
💥Level Interpretation / description:
L#1: If the candle crossed & stays above the “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Bullish bias.
L#2: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLB#1 & UBTgt
L#3: If the candle stays above “Sell Gen” but below “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Sidewise. Aggressive Traders can take Long position near “Sell Gen” either retesting or crossed from Below & vice-versa i.e. can take Short position near “Buy Gen” either retesting or crossed downward from Above.
L#4: If the candle crossed & stays below the “Sell Gen”, it is treated / considered a Bearish bias.
L#5: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLS#1 & USTgt
HZB (Buy side) & HZS (Sell side) => Hurdle Zone,
*** Specialty of “HZB#1, HZB#2 HZS#1 & HZS#2” is Sidewise (behaviour in Nature)
Rest Plotted and Mentioned on Chart
Color code Used:
Green =. Positive bias.
Red =. Negative bias.
RED in Between Green means Trend Finder / Momentum Change
/ CYCLE Change and Vice Versa.
Notice One thing: HOW LEVELS are Working.
Use any Momentum Indicator / Oscillator or as you "USED to" to Take entry.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⚠️ DISCLAIMER:
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments. I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
"🔔As HARD EARNED MONEY IS YOUR's, So DECISION SHOULD HAVE TO BE YOUR's".
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
❇️ Follow notification about periodical View
💥 Do Comment for Stock WEEKLY Level Analysis.🚀
📊 Do you agree with this view?
✈️ HIT THE PLANE ICON if this technical observation resonates with you. It will Motivate me.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💡 If You LOOKING any CHART & want for Level and ANALYZE?
Share your desired stock names in the comments below! I will try to analyze the chart Levels, patterns and share my technical view (so far my Knowledge).
If Viewers think It can identify meaningful setups. Looking forward to hearing from all of you — let's keep this discussion going and help each other make better trading decisions.________________^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^_________________