IRFC 1 Day View 📊 Daily Pivot Levels (1-Day TF)
Pivot (daily equilibrium): ~ ₹115.3 – bias above this = short-term bullish; below = bearish.
📈 Resistance Levels (Upside)
R1: ~ ₹117.0–₹117.1 — first daily resistance.
R2: ~ ₹119.9–₹120.0 — secondary resistance zone.
R3: ~ ₹121.6–₹122.0+ — stronger upside barrier.
📉 Support Levels (Downside)
S1: ~ ₹112.5–₹112.6 — first support around recent lows.
S2: ~ ₹110.8–₹111.0 — next support zone below.
S3: ~ ₹107.9–₹108.0 — deeper support zone from pivot analysis.
🔁 Technical Bias Notes (Daily Timeframe)
Current daily RSI and momentum indicators show bearish to neutral bias, with price often trading below short-term moving averages — sellers have slight edge unless price clears key resistances.
Stochastic and oscillators have shown oversold pressures at times, so short-term bounce near support zones (₹110–₹112) is possible if momentum shifts.
Trade Management
Part 2 Technical Analysis Vs Institution Option TradingDirectional Strategies- Long Call: Bet on price going up.
- Long Put: Bet on price going down.
- Covered Call: Sell call on stock you own, generate income.
Volatility Strategies- Straddle: Buy call and put at same strike, profit from big moves.
- Strangle: Buy call and put at different strikes, profit from big moves.
Income Strategies- Credit Spreads: Sell options to collect premium.
- Iron Condor: Sell call and put spreads, profit from low volatility.
Hedging Strategies- Protective Put: Buy put on stock you own, limit downside.
- Collar: Buy put, sell call on stock you own, limit risk.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Types of Option Traders Use
1. In-the-Money (ITM) Options
High intrinsic value, costlier, but more stable.
2. At-the-Money (ATM) Options
Strike price closest to spot price; very popular for intraday.
3. Out-of-the-Money (OTM) Options
Cheap but time-decay heavy. High risk, high reward.
Premium Chart Pattern Limitations
No Guarantees: Patterns only indicate probabilities, not certainties.
False Signals: Markets can generate fake breakouts or pattern failures.
Subjectivity: Interpretation can vary among traders.
Context Matters: Patterns work best with trend confirmation and other technical indicators like RSI, MACD, and moving averages.
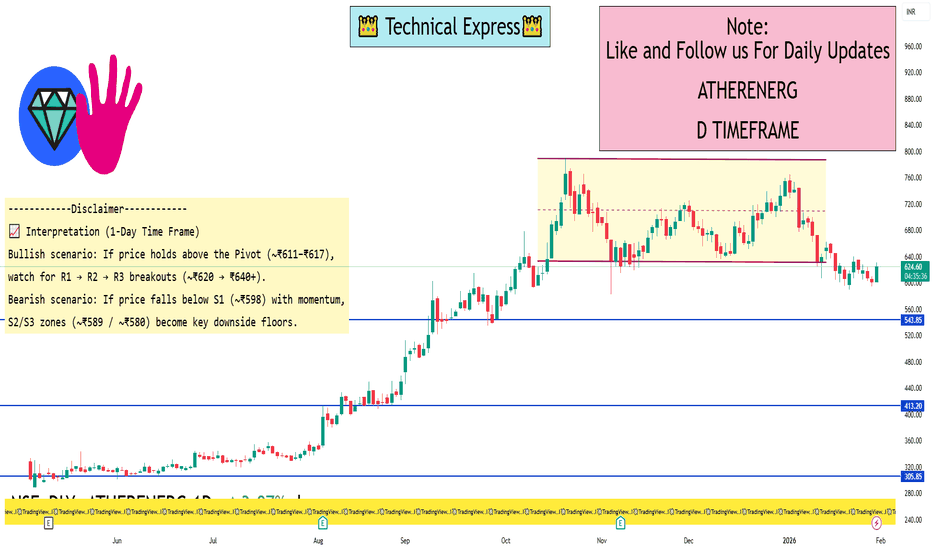
ATHERENERG 1 Day View 📌 Live Price Snapshot
Current Price (approx): ~₹620–₹630 range in recent sessions (market data can vary intraday).
📊 Daily Levels (1 Day Time Frame)
📍 Pivot & Key Levels
(Based on most recent technical calculations from current price action)
Central Pivot (PP): ~ ₹611–₹617
Resistance Levels:
R1: ~ ₹620–₹630
R2: ~ ₹632–₹643
R3: ~ ₹653–₹654
Support Levels:
S1: ~ ₹606–₹598
S2: ~ ₹594–₹589
S3: ~ ₹582–₹576
(Daily pivot and S/R are based on previous session ranges)
🧠 Notes
These levels are typically used for intraday or very short‑term trading and shift daily based on price action. Harsh deviations can occur on high volatility.
Always check a live chart or broker feed for minute‑by‑minute exact pivot/S/R values — the ones here are approximate based on latest calculated pivot data.
Price data is subject to real‑time movement and can differ slightly if markets are open.
ULTRACEMCO 1 Week View 📍 Current trading range (approx)
• Stock is trading near ~₹12,600-₹12,800 on NSE right now.
📊 Weekly Pivot Levels (1-Week Timeframe)
🔹 Resistance Levels
1. Major Resistance 3 (R3): ~₹13,190
2. Resistance 2 (R2): ~₹12,872
3. Resistance 1 (R1): ~₹12,621
➡️ If price closes above ₹12,620-12,630 on weekly close, momentum could pick up toward ₹12,870-₹13,190.
🔸 Support Levels
1. Support 1 (S1): ~₹12,051
2. Support 2 (S2): ~₹11,732
3. Support 3 (S3): ~₹11,481
➡️ Key weekly support is around ₹12,050-₹12,000 — break below this zone can accelerate downside toward ₹11,730-₹11,480.
🔁 Weekly Range Expectation
📍 Upside range: ₹12,620 → ₹12,870 → ₹13,190
📍 Downside range: ₹12,050 → ₹11,732 → ₹11,480
This gives an approximate weekly trading range of ~₹11,480 to ₹13,190 if volatility expands.
IIFL 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Price Snapshot
IIFL Finance share price: ~₹560–₹565 on NSE (today’s range) — with highs around ₹565 and lows near ₹540.45 earlier in today’s session.
📈 Weekly Support & Resistance (Key Levels)
These levels are derived from weekly pivot and longer‑term technical distribution — useful for swing/weekly traders:
🔹 Major Weekly Pivot Zone
Weekly Central Pivot (CPR): ~₹562–₹564 — this zone acts as the pivot around which weekly direction may tilt.
🔹 Weekly Resistance Levels
R1: ~₹613–₹616 — first major resistance if price rallies above current.
R2: ~₹650–₹672 — next higher resistance zone aligned with recent 52‑week highs.
R3: ~₹705+ — extended bullish breakout target.
🔻 Weekly Support Levels
S1: ~₹470–₹472 — first major support if selling accelerates.
S2: ~₹418–₹420 — secondary support from larger weekly pivots.
S3: ~₹326–₹330 — lowest weekly pivot support (deep correction scenario).
🧠 What this means (Weekly Macro View)
📍 Bullish Scenario
If price closes above the pivot zone (~₹562–564) on weekly charts, look for upside momentum toward ₹613–₹650 next.
📉 Bearish Scenario
A weekly close below ~₹470–₹472 could open deeper correction toward ₹418–₹380 support cluster.
Intraday Trading vs. Swing TradingIntroduction
Trading styles define how a trader interacts with the market—time horizon, risk appetite, capital usage, psychology, and even lifestyle. Among all styles, intraday trading and swing trading are the two most popular for active traders, especially in equity, derivatives, forex, and crypto markets.
While both aim to profit from price movements, they differ sharply in time frame, strategy, stress level, and skill requirements. Choosing the right one is less about returns and more about who you are as a trader.
1. Intraday Trading: Overview
Intraday trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. All positions are squared off before the market closes, eliminating overnight risk.
Key Characteristics
Holding period: Minutes to hours
Positions: Open and closed within the same day
Leverage: High (especially in derivatives)
Frequency: Multiple trades per day
Objective: Capture small price movements
Instruments Commonly Traded
Index futures & options (Nifty, Bank Nifty)
Highly liquid stocks
Forex pairs
Cryptocurrencies (24×7 markets)
2. Swing Trading: Overview
Swing trading aims to capture medium-term price “swings” over several days to weeks. Traders hold positions overnight and sometimes through volatile sessions.
Key Characteristics
Holding period: 2 days to several weeks
Positions: Carried overnight
Leverage: Low to moderate
Frequency: Few trades per month
Objective: Capture trend segments
Instruments Commonly Traded
Stocks (cash market)
Futures (with hedging)
ETFs
Crypto & commodities
3. Time Frame and Market Engagement
Intraday Trading
Requires constant screen time
Most active during:
Market open (first 60–90 minutes)
Major news events
High-volume periods
Traders must react instantly to price action
Swing Trading
Less screen dependency
Analysis typically done:
After market hours
On weekends
Execution may take only a few minutes per day
Bottom line:
Intraday trading is time-intensive. Swing trading is time-efficient.
4. Risk Profile and Volatility Exposure
Intraday Trading Risks
Sudden spikes and fake breakouts
Slippage during high volatility
Overtrading
Emotional decision-making
Brokerage & transaction costs
However, intraday traders avoid:
Overnight gap risk
Unexpected global events while holding positions
Swing Trading Risks
Overnight gaps due to:
Earnings announcements
Global cues
Geopolitical events
Wider stop losses
Longer drawdown periods
Risk difference:
Intraday risk is intense but short-lived.
Swing trading risk is slower but persistent.
5. Capital Requirements and Cost Structure
Intraday Trading
Lower capital due to leverage
Higher costs because of:
Frequent trades
Brokerage, STT, exchange fees
Profitability depends heavily on cost control
Swing Trading
Higher capital preferred
Lower transaction costs
Better reward-to-risk ratios over time
Important insight:
Many intraday traders are profitable before costs but lose after expenses. Swing traders are less affected by this trap.
6. Strategy and Technical Approach
Intraday Trading Strategies
Scalping
VWAP trading
Opening range breakout
Momentum trading
Option gamma plays
Indicators used:
VWAP
RSI (short period)
EMA (5, 9, 20)
Volume profile
Order flow
Swing Trading Strategies
Trend following
Pullback entries
Breakout retests
Mean reversion
Sector rotation
Indicators used:
Daily & weekly moving averages
MACD
RSI (14-period)
Support & resistance
Fibonacci retracements
7. Psychological Demands
Intraday Trading Psychology
High stress
Quick decision-making
Requires emotional detachment
Prone to revenge trading
Mental fatigue is common
Swing Trading Psychology
Requires patience
Comfort with open P&L swings
Discipline to hold winners
Less emotional noise
Reality check:
Most traders fail in intraday trading due to psychological overload, not lack of strategy.
8. Lifestyle Compatibility
Intraday Trading Suits:
Full-time traders
People who enjoy fast decision cycles
Those who thrive under pressure
Traders with disciplined routines
Swing Trading Suits:
Working professionals
Business owners
Part-time traders
People who value flexibility
9. Profit Potential and Consistency
Intraday Trading
Potential for daily income
Compounding possible
High variance in results
Small mistakes can erase weeks of gains
Swing Trading
Slower but steadier growth
Larger profits per trade
Easier to maintain consistency
Better for long-term capital growth
Key truth:
Consistency is easier in swing trading than intraday trading.
10. Which One Should You Choose?
Ask yourself these questions:
Can I sit in front of the screen for hours daily?
Can I handle rapid losses without emotional reactions?
Do I prefer fast action or structured planning?
Is trading my primary income source?
Choose Intraday Trading if:
You can give full-time attention
You have strict discipline
You enjoy short-term action
You accept higher stress
Choose Swing Trading if:
You want work-life balance
You prefer analytical planning
You are building capital steadily
You want lower psychological pressure
Conclusion
Intraday trading and swing trading are not “better” or “worse”—they are different tools for different personalities.
Intraday trading rewards speed, focus, and emotional control
Swing trading rewards patience, structure, and consistency
Most successful traders eventually migrate toward swing trading as their capital and experience grow, while a small elite excels in intraday trading through strict discipline and process-driven execution.
The best approach is not choosing the most exciting style—but the one you can execute flawlessly, repeatedly, and calmly.
MARUTI 1 Month View 📌 Current Market Snapshot (Daily)
Current approximate price:
📍 ~₹14,480–₹14,900 range (varying slightly between NSE/BSE live feeds).
Daily trading range:
• Low: ~₹14,350
• High: ~₹14,870**
52-Week Range:
• Low: ~₹11,059
• High: ~₹17,370 +
📈 1-Month Key Levels (Support & Resistance)
🔁 Resistance Levels (Upside)
R1: ~₹15,300–₹15,400 — immediate supply / pivot resistance on the 1-month timeframe.
R2: ~₹15,730–₹15,800 — next resistance zone (near shorter moving averages).
R3: ~₹16,150–₹16,170 — higher resistance and lower trading range top.
Near term major resistance: Above ~₹16,650–₹16,830 could signal a breakout continuation to higher 1-month highs.
🔽 Support Levels (Downside)
S1: ~₹14,440–₹14,480 — immediate downside support cluster.
S2: ~₹14,000 — psychological and lower short-term support.
S3: ~₹13,570–₹13,600 — deeper support if weak momentum continues.
🔄 Pivot Reference
Pivot (central reference): ~₹14,867–₹14,900 area — if price closes above this regularly, short-term bias could tilt up; below it suggests bearish control in the 1-month context.
📊 1-Month Price Behavior & Interpretation
✔ The stock has pulled back significantly from recent peak levels near ₹16.8k–₹17.3k seen earlier in January/December.
✔ Currently trading below most short-term moving averages (20 DMA / 50 DMA) — indicating short-term bearish pressure.
✔ Near-term price action will focus on whether ₹14.4k support holds; breach below that could expose deeper pullbacks toward ₹14.0k–₹13.6k.
Why Chart Patterns Matter ?Chart patterns reflect real-time battle between buyers and sellers. Every high, low, candle close, and wick communicates intentions of institutions, retail traders, and algos.
For traders, chart patterns help in:
Identifying trend direction
Spotting reversal before confirmation
Planning entries, stop-loss, and take-profit zones
Understanding supply–demand imbalance
Filtering noise in volatile markets
Because patterns repeat across timeframes and markets (stocks, options, forex, crypto), they become reliable tools — especially when aligned with volume spikes and market structure breaks.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading How Institutions Trade Options
Institutions use:
Delta hedging
Gamma scalping
Volatility Arbitrage
Neutral strategies
They focus more on:
Probability
Volatility cycles
Liquidity zones
Mean reversion
Understanding institutional behavior helps traders make better decisions, especially when reading volume profiles and OI shifts.
PHOENIXLTD 1 Week Time Frame📌 Current weekly reference price: ~₹1,730–₹1,740 on NSE (updated latest).
📊 Weekly Pivot & Key Levels (Most Recent)
▶️ Weekly Pivot Point
Weekly Pivot (Standard): ₹1,768.93 (central reference for the week)
📈 Weekly Resistance Levels
(Upside levels where price may face selling pressure)
1. R1: ~₹1,818.67 – first major resistance zone this week
2. R2: ~₹1,910.83 – secondary resistance on extended upside
3. R3: ~₹1,960.57 – deep stretch resistance if bullish momentum builds
Interpretation:
A weekly close above ₹1,818–₹1,820 would suggest strength and bullish continuation into higher zones.
Strong upside momentum could target tier‑2 and tier‑3 resistance levels above ₹1,900.
📉 Weekly Support Levels
(Key downside levels where price may find buying interest)
1. S1: ~₹1,676.77 – immediate support if price dips from current levels
2. S2: ~₹1,627.03 – deeper zone of support below S1
3. S3: ~₹1,534.87 – medium‑term support zone, stronger base area
Interpretation:
If price confirms a break below weekly support ₹1,676–₹1,680, it increases the likelihood of further correction toward ₹1,627 and then ~₹1,535.
📌 Summary — Weekly Price Action Framework
Bullish Scenario (weekly view):
Price sustains above pivot ~₹1,768–₹1,770
Breaks ₹1,818–₹1,820 weekly resistance
➡️ Upside target zones: ₹1,910 → ₹1,960+
Bearish/Neutral Scenario (weekly view):
Weekly close below ₹1,676–₹1,680 support
➡️ Downside zones: ₹1,627 → ₹1,535
Nifty 50 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Level (approx)
Nifty 50 ~ 25,200–25,350 area as of the last trading sessions (January 27–28, 2026).
📈 Key Weekly Levels to Watch
🔹 Immediate Resistance
1. ~25,300–25,350 — short‑term upside barrier (recent highs around these levels).
2. ~25,500–25,700+ — next major resistance zone (from prior weekly technical analysis, a breakout above ~26,100 historically signalled stronger bullish control).
🔻 Support Zones
1. ~24,900–25,000 — key short‑term support defended in recent sessions and noted by traders as a pivot area.
2. ~24,500–24,700 — broader weekly support zone (buffer from intermediate trend lines / moving averages).
3. ~24,200–24,300 — deeper weekly support; breach here could imply stronger correction risk.
📌 Weekly Trading Range (Probable)
Based on recent technical ranges and previous weekly outlooks:
➡️ Bullish bias above ~25,000 with resistance towards 25,500–25,700+.
➡️ Bearish/mixed bias if breaks below ~24,900, with support down to 24,500 and 24,200 zones.
⚠️ Important Notes
These levels are technical references used by traders — not investment advice.
Weekly support/resistance can shift quickly with strong market moves or macro events (especially around global policy news or earnings).
Always use stop losses and proper risk management if trading off these levels.
TATAELXSI 1 Week View 📊 Current context
The stock price is in the range of around ₹5,350–₹5,450 (as of last close).
📈 1‑Week Technical Levels
These are typical support/resistance values used by short‑term traders (daily/weekly pivots & swing levels):
🧭 Weekly Support
1. ~₹5,270–₹5,280 — first major weekly support zone.
2. ~₹5,106–₹5,110 — secondary support before lower breakdown risk.
3. ~₹4,700 area — strong downside zone (52‑week low area).
🚧 Weekly Resistance
1. ~₹5,618–₹5,620 — initial weekly resistance level.
2. ~₹5,950–₹6,000 — higher breakout zone for bullish momentum.
3. Above ₹6,300 — strong breakout continuation level.
These weekly levels are useful for planning trades across the next 5–7 sessions — gains above initial resistance suggest near‑term strength, while breaks below support indicate further weakness.
🔁 Daily Pivot Levels (for intraday / short swing)
Pivot Point: ~₹5,400–₹5,407
Support†: ~₹5,355 → ₹5,295 → ₹5,250
Resistance†: ~₹5,460 → ₹5,505 → ₹5,565 (higher targets)
These pivot levels help define day‑to‑day trading range within the week.
LUPIN 1 Day View 📊 Current Market Snapshot (Latest Available Close)
Price: ~₹2,137.20 (NSE) — price range on the most recent session was ₹2,130.30–₹2,178.00.
Previous Close: ₹2,163.20.
52‑week range: ₹1,795.20 low ~ ₹2,226.30 high.
📈 Daily Pivot & Key Levels (Short‑Term Technical)
🔁 Pivot (Reference Level)
Pivot point: ~₹2,166–₹2,160 zone — this is the central level that often defines bull/bear bias intraday.
🔼 Resistance (Upside Levels)
R1: ~₹2,185–₹2,189 — immediate upside barrier.
R2: ~₹2,206–₹2,208 — next medium resistance.
R3: ~₹2,227–₹2,238 — stronger resistance zone (intraday to short‑term).
🔽 Support (Downside Levels)
S1: ~₹2,143–₹2,119 — initial support from recent pivot structures.
S2: ~₹2,124–₹2,100 — mid downside support.
S3: ~₹2,102–₹2,071 — deeper support if bearish momentum accelerates.
🧠 How to Use These Levels Today
Bullish view: Stay above pivot (~₹2,160–₹2,166) for upside bias toward R1→R2.
Neutral/Range: Between S1 and R1 suggests consolidation — trade bounces within this zone.
Bearish breakdown: A close below S2/S3 can indicate deeper correction — watch S2 as key risk cutoff.
(These are not buy/sell recommendations, just short‑term technical reference points.)
AXISBANK 1 Month View📈 Current Context
As of late January 2026, Axis Bank’s stock is trading around ₹1,300 – ₹1,340 range amid strong recent earnings and price momentum.
📊 1-Month Key Levels (Daily/Short-Term Range)
🔼 Resistance (Upside)
1. ₹1,340 – ₹1,350 – Near recent high/resistance zone (short-term cap)
2. ₹1,355 – ₹1,365 – Next resistance cluster above recent highs
3. ₹1,370 + – Broader higher breakout zone if strong bullish continuation occurs
Note: Weekly/short weekly resistance zones are around ₹1,317-₹1,320 and then ₹1,340-₹1,350.
🔽 Support (Downside)
1. ₹1,280 – ₹1,285 – Immediate support near recent pivot lows
2. ₹1,270 – ₹1,275 – Secondary support zone tracked by moving averages
3. ₹1,260 – ₹1,265 – Broader channel support if price weakens further
🧭 Interpretation for a 1-Month View
Bullish scenario: A sustained break and close above ₹1,350 could extend momentum toward ₹1,365+ in the coming weeks.
Bearish scenario: A break below ₹1,270 might open the path toward ₹1,250 – ₹1,260 support cluster.
Neutral/Range: In sideways conditions, expect most trading between roughly ₹1,270 – ₹1,350.
HINDALCO 1 Month View 📌 Current Price Snapshot
Approximate recent price: ₹961–₹975 on NSE.
52-week range: ₹546.45 (low) to ~₹985 (high).
📊 1-Month Technical Levels (Support & Resistance)
🔁 Pivot & Balanced Level
Pivot Level: ~₹954 – ₹963 (central zone where trend bias often flips)
📈 Resistance Levels (Upside Barriers)
1. R1: ~₹959 – ₹960 — first key resistance above current pivot.
2. R2: ~₹969 – ₹970 — near recent short-term highs.
3. R3: ~₹975 – ₹980+ — upper resistance and psychological round number area.
💡 Above ~₹980: breakout build-up zone toward recent swing highs (~₹985).
📉 Support Levels (Downside Floors)
1. S1: ~₹944 – ₹945 — first major support zone.
2. S2: ~₹938 – ₹940 — next lower support within recent range.
3. S3: ~₹929 – ₹932 — deeper support if price slides further.
4. Lower structural zone: ~₹907 – ₹921 — broader support band from longer-term pivots.
📅 Trend & Market Context (1-Month)
Momentum: RSI around mid-60s suggesting moderately bullish momentum without being overbought.
Moving averages: Price trading above major short & mid-term averages (20/50 DMA), indicating bullish bias on the monthly view.
Volatility: ATR indicates normal volatility — not extreme swings.
Interpretation:
✔ Stays bullish above ~₹944–₹945 support.
✔ Upside can extend to ~₹969–₹980 if momentum persists.
⚠ A break below ~₹932 could signal deeper pullbacks toward ~₹907 area.
Candle Patterns in Technical AnalysisCandle patterns are formations created by Japanese candlesticks on a chart, indicating market sentiment and potential price movements. Here are some common ones:
Bullish Patterns- Hammer: Indicates potential reversal from bearish to bullish.
- Bullish Engulfing: Indicates reversal from bearish to bullish.
- Morning Star: Indicates reversal from bearish to bullish.
Bearish Patterns- Shooting Star: Indicates potential reversal from bullish to bearish.
- Bearish Engulfing: Indicates reversal from bullish to bearish.
- Evening Star: Indicates reversal from bullish to bearish.
Indecision Patterns- Doji: Indicates indecision in market.
- Spinning Top: Indicates indecision.
Chart Patterns in Technical AnalysisChart patterns are formations created by price movements on a chart, helping traders predict future price movements. Here are some common ones:
Reversal Patterns- Head and Shoulders: Indicates a reversal from bullish to bearish.
- Inverse Head and Shoulders: Indicates a reversal from bearish to bullish.
- Double Top: Bearish reversal pattern.
- Double Bottom: Bullish reversal pattern.
Continuation Patterns- Triangle: Can be bullish or bearish, indicates continuation.
- Pennant: Indicates continuation of trend.
- Flag: Indicates continuation of trend.
Other Patterns- Cup and Handle: Bullish pattern indicating continuation.
- Wedge: Can indicate reversal or continuation.
Part 1 Intrday Institutional Trading Role of Institutions & Smart Money in Options
Institutions dominate the option markets.
They control the market using:
Delta hedging
Gamma scalping
Liquidity creation
Option selling walls
Volume absorption
Understanding their footprints helps predict:
Support zones
Resistance zones
Directional bias
Volatility behavior
Part 3 Technical Analysis VS. Institutional Option TradingHow Option Pricing Works
Option pricing is influenced by market structure, volatility, liquidity, and hedging flows.
Three components determine premium:
Intrinsic Value
For Call Option:
Max(Spot price – Strike price, 0)
For Put Option:
Max(Strike price – Spot price, 0)
Time Value
Extra value based on:
Time left to expiry
Volatility
Market expectations
Demand & supply
As expiry approaches:
Time value decays → Premium decreases
This is called theta decay.
Implied Volatility (IV)
IV measures the market’s expectation of future movement.
High IV → High premiums
Low IV → Low premiums
Events that cause IV spikes:
Budget announcements
RBI policy decisions
Elections
Global news
Understanding IV is essential for timing entry, especially for option sellers.
Part 1 Technical Analysis VS. Institutional Option Trading Introduction to Option Trading
Options are financial derivatives—meaning their value is derived from an underlying asset such as:
Stocks (e.g., TCS, HDFC Bank)
Indices (Nifty, Bank Nifty, SENSEX)
Commodities (Gold, Silver, Crude)
Currencies (USD/INR, EUR/INR)
An option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price before a specific date.
There are two major types of options:
Call Option → Right to buy
Put Option → Right to sell
You pay a small amount called premium to obtain this right.