Price Action Trading in Indian Stocks1. What Is Price Action Trading?
Price Action Trading is a trading approach where decisions are made purely from price movement, without relying heavily on indicators. Traders study candlestick patterns, support–resistance levels, market structure, and volume behavior to understand the psychology of buyers and sellers.
In the Indian stock market—where news flow, operator activity, and institutional orders can cause sharp moves—price action works exceptionally well because price reflects everything: fundamentals, sentiment, and liquidity.
Price action traders believe:
“Indicators lag, price leads.”
Instead of predicting, they react to what price is doing right now.
2. Why Price Action Works Well in Indian Markets
Indian markets (NSE & BSE) have unique characteristics:
Strong institutional participation (FIIs & DIIs)
Frequent gap-up and gap-down openings
Sharp intraday volatility
Operator-driven moves in midcaps and smallcaps
Price action helps traders:
Read smart money footprints
Trade without confusion from multiple indicators
Adapt quickly to changing market conditions
Trade effectively in cash, futures, and options
Because price action is time-frame independent, it works for:
Intraday traders
Swing traders
Positional traders
3. Core Components of Price Action Trading
a) Candlestick Structure
Every candle tells a story:
Body → Strength of buyers or sellers
Wicks (shadows) → Rejection or absorption
Close location → Who is in control
Important Indian-market-friendly candles:
Strong bullish/bearish candles
Rejection candles near key levels
Inside candles before breakout
Wide-range candles during news or result days
b) Support and Resistance (Demand & Supply Zones)
Support and resistance are zones, not exact lines.
In Indian stocks:
Previous day high/low
Weekly and monthly levels
Pre-market highs/lows
Round numbers (₹100, ₹500, ₹1000)
These levels often act as:
Entry zones
Stop-loss placement areas
Profit booking zones
Institutions accumulate near support and distribute near resistance.
c) Market Structure
Market structure tells you trend direction:
Higher Highs & Higher Lows → Uptrend
Lower Highs & Lower Lows → Downtrend
Sideways → Range-bound market
Price action traders avoid fighting the trend and instead:
Buy pullbacks in uptrends
Sell rallies in downtrends
Trade breakouts from ranges
In Indian indices like NIFTY and BANKNIFTY, structure reading is critical due to high derivative activity.
4. Key Price Action Patterns Used in Indian Stocks
a) Breakout and Retest
Very popular in NSE stocks:
Price breaks a key resistance
Pulls back to test the level
Continues in the breakout direction
Works well in:
High-volume stocks
Result breakouts
Consolidation phases
b) Rejection at Key Levels
Long upper wick near resistance or long lower wick near support signals rejection.
Common during:
Market opening
Important news days
Index expiry sessions
c) Range Trading
Indian markets often consolidate:
Buy near range low
Sell near range high
Avoid trading mid-range
This works best when:
Volatility is low
No major news is expected
5. Role of Volume in Price Action
Price without volume is incomplete.
In Indian stocks:
High volume + breakout = genuine move
Low volume breakout = trap
Volume spikes near support/resistance indicate institutional activity
Volume confirms:
Strength of trend
Validity of breakouts
Exhaustion points
6. Time Frames Used in Indian Price Action Trading
Different traders use different time frames:
Trading Style Common Time Frames
Intraday 5-min, 15-min
Swing 1-hour, Daily
Positional Daily, Weekly
Top-down analysis is preferred:
Weekly → Daily → Intraday
This avoids trading against higher-time-frame trends.
7. Risk Management in Price Action Trading
Risk management is the backbone of success.
Indian traders often fail not due to bad analysis, but due to:
Overtrading
No stop-loss
Emotional decisions
Price action allows logical stop-loss placement:
Below support
Above resistance
Beyond rejection candle
Common rule:
Risk only 1–2% of capital per trade
Risk–reward minimum 1:2
Capital protection is more important than profits.
8. Psychology and Discipline
Price action trading requires:
Patience to wait for setup
Discipline to follow rules
Emotional control during drawdowns
Indian markets test psychology due to:
Sudden news
Operator traps
False breakouts
Successful traders accept:
Losses are part of the game
Not every day is a trading day
Consistency beats jackpot trades
9. Price Action vs Indicator-Based Trading
Price Action Indicator Trading
Direct market reading Derived data
Faster decisions Lagging signals
Clean charts Cluttered charts
Requires screen time Easier for beginners
Many Indian traders eventually move from indicators to price action for clarity and confidence.
10. Common Mistakes Indian Traders Make
Trading without key levels
Ignoring higher time frames
Entering late due to fear of missing out (FOMO)
Overleveraging in F&O
Not journaling trades
Price action rewards process, not excitement.
11. Final Thoughts
Price Action Trading is not a shortcut or holy grail. It is a skill built through observation, screen time, and discipline. In the Indian stock market—where volatility, institutional flow, and sentiment play a major role—price action provides a reliable and flexible framework.
A trader who masters price action:
Trades with confidence
Avoids unnecessary indicators
Understands market psychology
Focuses on probability, not prediction
Price is truth. Learn to read it, and the market speaks clearly.
Trendbreak
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingBenefits
- Leverage: Control more with less capital.
- Limited Risk: Buyers risk only premium.
- Flexibility: Strategies for any market view.
- Hedging: Protect portfolios.
Risks- Time Decay: Options lose value over time.
- Volatility Risk: Sensitive to volatility changes.
- Loss of Premium: Buyers risk losing premium.
- Complexity: Strategies can be complex.
Part 2 Institutional Vs. Technical AnalysisGamma Scalping
Involves hedging delta during fast markets.
Mostly used by institutions.
Put-Call Ratio (PCR)
Extreme PCR < 0.7 → oversold.
PCR > 1.3 → overbought.
Helps identify reversal zones.
Impact of News
Options react instantly to news.
High IV before news, low IV after.
BIRLACORPN 1 Month View 📌 Current price range (recent NSE close): ~₹1,020–₹1,060 area over the past few weeks.
📊 Monthly Support & Resistance Zones (Key Levels)
🛑 Resistance Levels
Immediate Resistance: ~₹1,055–₹1,074
– This zone has shown repeated short-term highs around this range.
Next Upside Layer: ~₹1,085–₹1,110
– Price may face selling pressure if it approaches this zone.
Higher Level Breakout Target: ~₹1,220–₹1,250+
– Longer-term structure resistance from earlier higher levels in 2025.
🧱 Support Levels
Primary Support: ~₹1,017–₹1,031
– Near recent lows seen multiple times in late Jan/early Feb.
Secondary Support: ~₹1,000–₹989
– A psychologically important round number zone.
Lower Support: ~₹970 and below
– Weakness beyond this may lead to more downside.
📈 Trend & Momentum (1-Month)
Moving averages (20/50/100/200) are above current prices, indicating the recent trend is neutral to slightly bearish/sideways in the short term (price below short & mid MAs).
Oscillators like RSI are mid-range (not deeply oversold nor overbought), suggesting no strong immediate reversal signal.
TradingView technicals show the 1-month technical rating is currently on a sell bias, implying sellers dominate this timeframe.
📌 1-Month Price Action Summary
📉 Sideways / Mild Downtrend:
Price has traded mostly between ~₹1000–₹1075 without a decisive breakout.
Break above ₹1,075–₹1,085 could attract short covering and push towards next resistance (~₹1,120+).
A drop below ₹1,000 may accelerate weakness and test lower support (~₹970–₹950).
BSE 1 Week View 📊 📅 Weekly Pivot & Key Levels (Updated)
Pivot Point: ~ ₹2,821.5 – central level for weekly sentiment.
🔼 Weekly Resistance Levels
R1: ~ ₹2,847.8 — first weekly resistance.
R2: ~ ₹2,866.3 — secondary resistance.
R3: ~ ₹2,892.6 — higher resistance zone.
🔽 Weekly Support Levels
S1: ~ ₹2,803.0 — short-term weekly support.
S2: ~ ₹2,776.7 — deeper weekly support.
S3: ~ ₹2,758.2 — strong weekly support zone.
📍 These pivot points are calculated dynamically from recent price action and widely used by traders to map out where the stock may find buying or selling pressure within the weekly timeframe.
📌 How to Interpret This (Weekly Sentiment Guide)
Bullish Weekly View
Weekly closes above the pivot (~₹2,821) suggest strength.
Above R1 (~₹2,848) opens room toward R2 (~₹2,866) and potentially R3 (~₹2,892).
Bearish Weekly View
Fails to hold above pivot or breaks below S1 (~₹2,803) may signal more downside.
Deeper weakness if price closes below S2 (~₹2,777) and S3 (~₹2,758).
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingGreeks – The Heart of Option Pricing
The Greeks show how the option premium behaves:
Delta
Measures price change vs underlying.
Call delta: 0 to +1
Put delta: 0 to –1
Theta
Time decay.
Biggest enemy of buyers, friend of sellers.
Gamma
Rate of change of Delta.
High gamma = rapid premium movement.
Vega
Impact of volatility on premium.
Rho
Impact of interest rates (minor in India).
Part 5 Advance Option Trading Option Chain
Displays strike-wise premiums, open interest, volume, Greeks.
Traders read it to predict support/resistance and market structure.
Open Interest (OI)
Shows number of active contracts.
High call OI → resistance.
High put OI → support.
OI change indicates market sentiment shift.
Volume in Options
Measures trading activity at a price.
High volume = strong interest = better reliability.
Useful for volume profile and market structure analysis.
Part 2 Institutional Option Trading Vs. Techncal AnalysisTwo Types of Options
Call Option (CE): Right to buy at a chosen price.
Put Option (PE): Right to sell at a chosen price.
Strike Price
The fixed price at which you can buy/sell.
Example: Nifty 22,000 CE = option to buy Nifty at 22,000.
Premium
The price of the option contract.
Paid by the buyer, received by the seller (writer).
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingHedging with Options
Options are widely used for risk management.
Examples:
Buying put options to protect long equity portfolios
Using collars to limit upside and downside
Index puts for market crash protection
Hedging reduces returns slightly but protects capital, which is crucial for long-term survival.
Part 1 Technical Vs. Institutional Why Trade Options?
Option trading is preferred because it offers:
Leverage – Control large positions with small capital
Hedging – Protect portfolios against losses
Income Generation – Through option selling
Flexibility – Profit in bullish, bearish, and sideways markets
Defined Risk Strategies – With spreads and hedges
Part 1 Intraday Mater Class Introduction to Option Trading
Option trading is a derivative-based trading approach that allows traders and investors to profit from price movements, volatility, time decay, and even stagnant markets. Unlike equity trading—where profits depend largely on buying low and selling high—options provide multiple ways to make money, manage risk, and hedge portfolios.
An option is a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time period. The seller (writer) of the option has the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises it.
Options are widely traded in global markets and are extremely popular in India through NSE’s F&O segment, particularly in Index options (NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, FINNIFTY, SENSEX) and stock options.
Part 1 Technical Vs. Institutional Option Trading Key Components of Option Trading- Underlying Asset: The security (stock, index, etc.) the option is based on.
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiry Date: The last day the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price of the option contract.
- Call Option: Right to buy the underlying asset.
- Put Option: Right to sell the underlying asset.
AMBUJACEM 1 Month View 📈 1-Month Price Range (Most Recent Data)
📊 Last Traded Price:
• Around ₹510.15 – ₹510.20 as of 30 Jan 2026 close.
🔥 1-Month Highest Price:
• ₹573.10 – observed in early January 2026.
❄️ 1-Month Lowest Price:
• ₹507.90 – recent intra-month low.
➡️ Typical Trading Range Over Last Month:
• High: ~₹573
• Low: ~₹508
• Average: ~₹545 area (approx).
📊 Current Daily Range (Latest Session)
As of the latest session:
• Day’s High: ~₹536.05
• Day’s Low: ~₹507.90
• Close / Last Price: ~₹510.15.
📌 Key Takeaways
Ambuja Cements’ share price traded between ~₹508 and ₹573 over the past 1 month.
The latest closing levels are near the lower end of that range (~₹510 area), reflecting recent downward movement.
This gives you a clear 1-month context of where support (near ~₹508) and resistance (near ~₹570+) have been.
Part 4 Institutional VS. Technical1. Delta
Measures how much the premium changes with a ₹1 move in the underlying.
Call delta: +0.0 to +1.0
Put delta: –0.0 to –1.0
High delta = faster premium movement.
2. Gamma
Measures how fast delta changes. Used to evaluate momentum and risk.
3. Theta
Measures time decay—how much premium decreases as expiration approaches.
Sellers benefit from theta.
Buyers lose value daily.
4. Vega
Measures sensitivity to implied volatility (IV).
Higher IV → higher premium.
5. Rho
Impact of interest rates (less important for short-term traders).
PFC 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Live Context (Daily)
📊 Approx Live Price: ~₹377‑₹379 (today’s trading range: ₹376 – ₹384) on NSE intraday quotes.
📈 Daily Pivot / Support & Resistance (Reliable Levels)
🔹 Pivot / Reference Zone
Central Pivot (CPR) ~ ₹386.8 area — key reference point for bias (above = bullish bias; below = bearish).
🚀 Resistance Levels (Upside)
R1 ~ ₹390–₹392 — initial resistance near current zone.
R2 ~ ₹394–₹398 — next supply zone.
R3 ~ ₹402–₹406 — stronger resistance on daily view.
Above ₹400 reinforces bullish structure and opens potential next targets up if breakout sustains.
🛑 Support Levels (Downside)
S1 ~ ₹382–₹386 — near‑term support zone (first buyer interest).
S2 ~ ₹378–₹381 — lower support region on daily pivots.
S3 ~ ₹370–₹376 — deeper support zone if price weakens.
Daily bias turns bearish if price closes clearly below the S2/S3 range (~₹378–₹376).
🔎 Quick Technical Bias Notes
Since current price (~₹377‑₹379) is below the pivot/CPR (~₹387), short‑term bias leans slightly bearish to neutral unless bulls reclaim pivot with volume.
A daily close above ~₹398‑₹400 could shift view bullish toward ~₹402+ and beyond.
Part 1 Institutional VS. Technical
Key Components of Options- Underlying Asset: The security (stock, index, etc.) the option is based on.
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiry Date: The last day the option can be exercised.
- Premium: The price of the option contract.
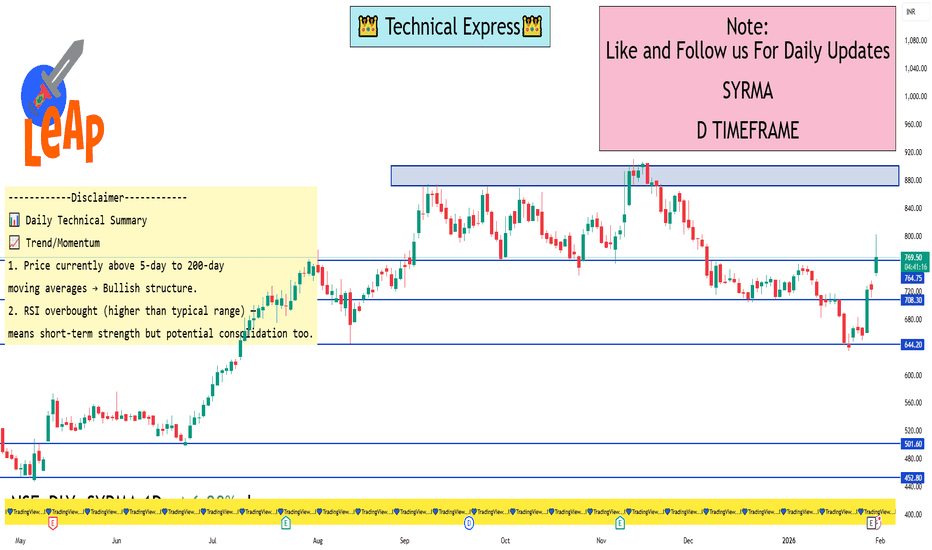
SYRMA 1 Day View 📍 Current Price (approx): ~₹760–₹770 (up strongly with gap‑up & volatility today) — trading above most MA’s signalling strong bullish bias.
🔁 Pivot & Key Levels (Daily Time‑Frame)
📌 Standard Daily Pivot Levels
🟡 Pivot Point: ~₹736–₹737 — central level for trend bias
🟢 Resistance 1 (R1): ~₹748–₹749
🟢 Resistance 2 (R2): ~₹761–₹762
🟢 Resistance 3 (R3): ~₹773–₹774
🔴 Support 1 (S1): ~₹698–₹700
🔴 Support 2 (S2): ~₹689–₹690
🔴 Support 3 (S3): ~₹685–₹686
👉 Interpretation: Trading above pivot & R1 suggests buyers are in control today. R2/R3 are key upside obstacles. S1/S2/S3 are important support zones in case of pullbacks.
🔑 Key Levels to Watch (for Today / Daily)
✅ Bullish breakout continuation levels:
Short‑term upside: ~₹748 → ₹762 → ₹774 (R1/ R2/ R3)
⚠️ Pullback / support levels:
Initial support: ~₹700–₹698 (S1)
Next support: ~₹690–₹686 (S2 / S3)
📊 Bias reference: Price above pivot → bullish bias today. A break below pivot could soften momentum.
🧠 How to Use These Levels
Bullish scenario:
Hold above ₹748 → higher targets: ₹761 / ₹773+.
Conservative traders:
Watch support at ₹700 / ₹690 for dips as potential trend continuation entry/stop‑loss areas.
Risk control:
If price drops below pivot (~₹737) decisively, momentum may weaken intraday.
Part 5 Best Trading Strategies Simple Example to Understand
Scenario
Nifty at 21500
You expect it to go to 21650.
Call Option Buy
Buy 21500 CE
If Nifty moves up → premium increases → profit
If Nifty falls → premium collapses → loss
Put Option Buy
Not useful in this scenario
Option Seller’s View
If seller expects market to remain sideways:
Seller sells 21600 CE
Seller sells 21400 PE
Both sides decay → seller profits
ULTRACEMCO 1 Day View 📊 Current Price (approx)
• ULTRACEMCO is trading around ₹12,620–₹12,770 on NSE in today’s session based on multiple live price feeds.
📈 Daily Support & Resistance Levels – NSE (Pivot-based)
📌 Daily Pivot & Range (classic pivot levels):
Resistance 3 (R3): ~ ₹13,101
Resistance 2 (R2): ~ ₹12,963
Resistance 1 (R1): ~ ₹12,776
Pivot Point (PP): ~ ₹12,638
Support 1 (S1): ~ ₹12,451
Support 2 (S2): ~ ₹12,313
Support 3 (S3): ~ ₹12,126
👉 Key intraday reference:
• If price holds above Pivot ~₹12,638, bulls may target the R1–R3 zone.
• A break below S1/S2 could open downside to ₹12,313–₹12,126 S3.
🔁 Alternate Daily Support / Resistance (Pivot Speed)
• R1: ~ ₹12,521
• R2: ~ ₹12,673
• R3: ~ ₹12,792
• Support 1: ~ ₹12,250
(Different pivot provider with slightly variation — good as corroborative levels)
📊 Short-Term Support & Resistance (Alternative)
• Daily Support (Munafasutra): ~ ₹12,264–₹12,265
• Daily Resistance: ~ ₹12,499–₹12,500
(These can be useful for tighter intraday stops)
📌 What This Means for 1D Trading
Bullish above:
• ₹12,638 Pivot — key to stay above for bullish bias today.
• Above ₹12,776–₹12,963 — adds confidence for breakout toward ₹13,101 R3.
Bearish below:
• Below ₹12,451 S1 — risk to ₹12,313–₹12,126 S3.
• Sustained close below Pivot may signal short-term pressure.