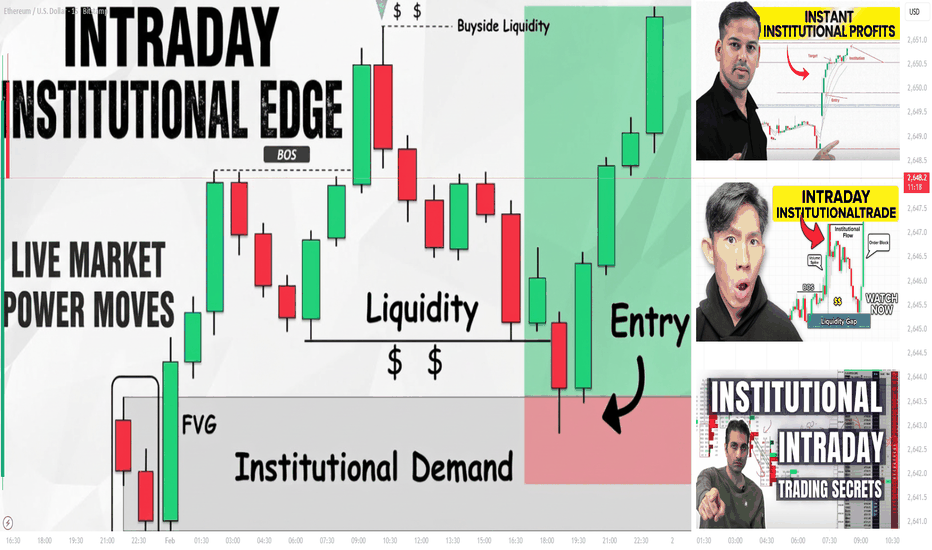
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingHow Beginners Should Start?
✔ Step-by-Step:
Start with understanding futures & spot movement
Trade small lots
Focus on ATM & ITM
Avoid expiry day
Avoid illiquid stocks
Study Greeks
Backtest simple strategies
Track OI & volume data
Start with debit spreads instead of naked options
Never sell naked options without hedge
Trendlinebounce
Part 3 Institutional Trading VS. Technical AnalysisWhat Are Options? — The Foundation
Options are derivative contracts whose price is derived from an underlying asset like:
Stocks
Indices (Nifty, Bank Nifty)
Commodities
Currencies
An option is a contract between a buyer and a seller that gives special rights to the buyer.
✔ In simple words:
An option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying at a fixed price before a fixed date.
This fixed price = Strike Price
This fixed date = Expiry Date
Options are of two types: Call & Put.
Part 2 Institutional Option Trading VS. Technical Analysis⭐ Types of Options
Two main types:
Call Options (CE)
A call gives you the right to buy.
You buy a call when you expect the market to go up.
If the price rises, your call premium increases.
You can sell the call later and book profit.
You are not required to buy the stock — you only trade the premium.
Put Options (PE)
A put gives you the right to sell.
You buy a put when you expect the market to fall.
If the price falls, your put premium increases.
You sell the put later to book profit.
No obligation to actually sell the stock.
Part 1 Institutional Option Trading VS. Technical Analysis ⭐ 1. What Are Options?
Options are contracts, not shares.
They give you a right, not an obligation, to buy or sell something.
That “something” is usually a stock, index, commodity, or currency.
Options have an expiry date — they lose value as time passes.
Options are part of a bigger market called derivatives.
They derive their value from the underlying asset (like Nifty, Bank Nifty, stocks).
An option is like a reservation — you pay a small price to control a large position.
This small price is called premium.
Because premium is small, options give leverage — small money, big impact.
Options can be used to hedge, speculate, or generate income.
Part 2 Institutional Trading VS. Technical AnalysisMoneyness of Options
Moneyness describes the relationship between the spot price and strike price.
1. In-the-Money (ITM)
Call: Spot > Strike
Put: Spot < Strike
2. At-the-Money (ATM)
Spot ≈ Strike
3. Out-of-the-Money (OTM)
Call: Spot < Strike
Put: Spot > Strike
ITM options have intrinsic value; OTM options are purely speculative.
Part 3 Institutional Option Trading VS. Technical AnalysisBest Practices for Option Traders
1. Use a strategy, not impulses
Enter with logic, not emotion.
2. Risk Management
Never risk more than 1–2% of capital per trade.
3. Understand Volatility
Most retail losses come from ignoring IV.
4. Avoid Illiquid Options
Always trade high-volume strikes.
5. Prefer spreads over naked positions
Spreads reduce both risk and margin.
6. Don’t hold losing trades
Cut loss quickly; small loss is a big victory.
Best Sectors For DIP Buying: Long-Term Investor + Smart TraderUnderstanding DIP Buying at a Sector Level
Sector-based DIP buying works better than stock-only dip buying because:
Sector corrections are often cyclical, not permanent
Money rotates between sectors, not out of markets forever
Institutions buy sectors in phases, not randomly
The goal is to buy quality sectors during pessimism, not hype.
1. Banking & Financial Services
Why banks are prime DIP-buying candidates
Banking is one of the most cyclical sectors in any economy. Corrections often occur due to:
Interest rate uncertainty
Rising NPAs fears
Credit cycle slowdowns
Regulatory tightening
Yet banks are the backbone of economic growth.
Why dips happen
Rate hikes compress short-term margins
Liquidity fears create panic
Temporary credit slowdown
Why dips are opportunities
Strong banks adapt faster to rate cycles
Loan growth rebounds with GDP recovery
Financialization keeps expanding
Best for DIP buying
Large private banks
Strong PSU banks post-cleanup
NBFCs with diversified loan books
📌 DIP logic: When fear peaks, banks trade below historical valuations—this is where institutions quietly accumulate.
2. Information Technology (IT & Tech Services)
Why IT corrects sharply
IT is highly sensitive to:
US recession fears
Dollar volatility
Global tech spending cuts
This makes IT stocks fall fast and deep.
Why it’s a classic DIP sector
Global outsourcing demand never disappears
Cost-cutting cycles actually increase outsourcing
Digital transformation is structural, not optional
Common dip triggers
Weak quarterly guidance
Margin compression
Hiring slowdown
Why recovery is powerful
Currency tailwinds kick in
Deal pipelines revive suddenly
Valuations re-rate quickly
📌 DIP logic: IT rarely dies—it pauses. Dips usually reflect timing issues, not broken business models.
3. Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
Why pharma is defensive but volatile
Pharma behaves oddly:
Defensive during crises
Volatile due to regulations and approvals
Why dips occur
USFDA warnings
Price erosion in generics
R&D failures
Why it’s great for DIP buying
Healthcare demand is non-cyclical
Aging population supports long-term growth
Innovation cycles create rebounds
Ideal DIP scenarios
Regulatory scare without long-term damage
Temporary margin pressure
Currency-driven corrections
📌 DIP logic: Fear-driven pharma sell-offs often overshoot reality, creating value zones.
4. Capital Goods & Infrastructure
Why this sector crashes hard
Capital goods depend on:
Government spending
Private capex cycles
Interest rate environment
When capex slows, this sector gets punished brutally.
Why dips are golden
Infrastructure cycles last many years
Order books provide long visibility
Government-led spending revives demand
Dip triggers
Election uncertainty
Fiscal deficit concerns
Rate hike cycles
Why rebound is explosive
Operating leverage kicks in
Margins expand rapidly
Earnings surprise on the upside
📌 DIP logic: Buy when nobody believes capex will return—that’s usually the bottom.
5. FMCG & Consumer Staples
Why even defensive sectors dip
FMCG falls during:
Inflation spikes
Rural demand slowdown
Input cost pressure
Why it’s safe for DIP buying
Strong brands have pricing power
Demand never vanishes, only delays
Cash flows remain steady
Ideal DIP conditions
Margin compression due to raw material costs
Temporary volume slowdown
Sentiment-driven derating
📌 DIP logic: FMCG dips don’t last long. Institutions love buying these quietly during pessimism.
6. Energy, Oil & Gas
Why energy is deeply cyclical
Energy stocks swing due to:
Crude oil volatility
Government policy changes
Global demand fears
Why dips matter
Energy demand grows with GDP
Refining margins normalize over time
Transition to renewables creates optionality
Best DIP moments
Crude price crashes
Windfall tax fears
ESG-driven selling
📌 DIP logic: Energy is hated at bottoms and loved at peaks—DIP buying flips that psychology.
7. Metals & Mining
Why metals crash the hardest
Metal stocks are hit by:
China slowdown fears
Dollar strength
Global recession narratives
Why they rebound violently
Supply constraints kick in suddenly
Infrastructure demand revives
Commodity cycles turn faster than expected
DIP buying sweet spots
Panic around global growth
Inventory overhang fears
Peak pessimism headlines
📌 DIP logic: Metals are pure sentiment trades—best bought when macro fear dominates news flow.
8. Automobiles & Auto Ancillaries
Why autos dip frequently
Interest rate hikes
Fuel price volatility
Demand slowdown fears
Why they recover
Replacement demand never stops
EV transition creates new growth layers
Rural + urban demand cycles rotate
Best DIP phases
Sales slowdown narratives
Input cost pressure phases
Policy uncertainty
📌 DIP logic: Auto dips reward patience—cycles turn faster than expectations.
Key Rules for Sector DIP Buying
1. Buy fear, not hope
If headlines sound scary but balance sheets are intact—you’re close.
2. Time > Timing
Accumulate in tranches, not all at once.
3. Follow institutional footprints
Volume spikes at lows often signal smart money entry.
4. Avoid structurally broken sectors
DIP buying works for cyclical pain, not dying industries.
5. Align with macro cycles
Rate cuts, fiscal spending, and liquidity shifts fuel sector recoveries.
Final Takeaway
The best sectors for DIP buying are those that:
Are economically essential
Go through repeated cycles
Attract institutional capital
Have long-term relevance
Banking, IT, Pharma, Infrastructure, FMCG, Energy, Metals, and Autos consistently reward disciplined DIP buyers—not impulsive ones.
DIP buying isn’t about bravery.
It’s about preparation, patience, and psychology.
Option Chain – Terms and ConditionsIntroduction to the Option Chain
An option chain is a structured table that displays all available call (CE) and put (PE) options for a particular underlying asset (stock or index) across different strike prices and expiry dates. It is the most important tool for option traders because it reveals market expectations, positioning, liquidity, and risk at a glance.
The option chain is not just data—it reflects the collective psychology of traders, hedgers, institutions, and market makers.
1. Underlying Asset
The underlying is the asset on which the option contract is based.
Examples:
NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, FINNIFTY (Index options)
Reliance, HDFC Bank, Tata Motors (Stock options)
All option prices, risks, and payoffs are derived from the movement of the underlying.
2. Expiry Date
The expiry date is the last day on which an option contract is valid.
Types of Expiry
Weekly Expiry – High volatility, fast decay, mostly used by intraday traders
Monthly Expiry – Preferred by positional traders
Quarterly Expiry – Used by institutions and hedgers
After expiry, the option becomes worthless if it is Out of The Money (OTM).
3. Strike Price
The strike price is the price at which the underlying can be bought (Call) or sold (Put).
Types of Strike Prices
ITM (In The Money)
Call: Spot price > Strike
Put: Spot price < Strike
ATM (At The Money)
Strike ≈ Spot price
OTM (Out of The Money)
Call: Spot price < Strike
Put: Spot price > Strike
Strike selection defines risk, reward, and probability.
4. Call Option (CE)
A Call Option gives the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy the underlying at the strike price before expiry.
Conditions
Buyer pays premium
Maximum loss = Premium paid
Profit potential = Unlimited
Call options reflect bullish expectations.
5. Put Option (PE)
A Put Option gives the buyer the right but not the obligation to sell the underlying at the strike price before expiry.
Conditions
Buyer pays premium
Maximum loss = Premium paid
Profit potential = High (as market falls)
Put options reflect bearish expectations or are used for hedging.
6. Option Premium
The premium is the price of the option.
Premium Components
Intrinsic Value – Real value of the option
Time Value – Value of remaining time to expiry
Premium is influenced by:
Spot price
Volatility
Time to expiry
Interest rates
Demand and supply
7. Open Interest (OI)
Open Interest represents the total number of outstanding option contracts.
Interpretation
Rising OI + Rising price → Strong trend
Rising OI + Falling price → Short buildup
Falling OI → Position unwinding
OI shows where smart money is placed.
8. Change in Open Interest (ΔOI)
Change in OI indicates fresh positions added or old positions closed.
Market Signals
High ΔOI at a strike → Strong support/resistance
Call OI buildup → Resistance zone
Put OI buildup → Support zone
Institutions closely watch ΔOI, not just price.
9. Volume
Volume shows the number of contracts traded during the session.
High volume = liquidity and active interest
OI + Volume together confirm:
Genuine moves
Fake breakouts
Position rollovers
10. Implied Volatility (IV)
IV represents the market’s expectation of future volatility.
Key Points
High IV = Expensive options
Low IV = Cheap options
IV rises before events (results, RBI policy)
IV falls after events (IV crush)
IV is the backbone of option selling strategies.
11. Bid Price and Ask Price
Bid – Price buyers are willing to pay
Ask – Price sellers are willing to accept
A narrow spread means high liquidity. Wide spreads increase slippage and risk.
12. Greeks (Risk Parameters)
Delta
Measures price sensitivity to underlying
Call Delta: 0 to +1
Put Delta: 0 to -1
Gamma
Rate of change of Delta
High near ATM options close to expiry
Theta
Time decay of option value
Biggest enemy of option buyers
Vega
Sensitivity to volatility
Higher for long-dated options
Rho
Sensitivity to interest rates
Least impactful in Indian markets
13. Market Lot Size
Options are traded in fixed lot sizes.
Example:
NIFTY = 50 units per lot
BANKNIFTY = 15 units per lot (subject to exchange changes)
Lot size affects margin, risk, and capital allocation.
14. Margin Requirements
Option Buyers – Pay full premium upfront
Option Sellers – Must maintain margin (SPAN + Exposure)
Margins vary with:
Volatility
Strike distance
Market conditions
15. Settlement Conditions
In India:
Index options → Cash settled
Stock options → Mostly cash settled (physical settlement rules apply)
If ITM at expiry, settlement happens automatically.
16. Exercise Style
Indian options are European style:
Can be exercised only on expiry day
No early exercise allowed
17. Risk Disclosure and Conditions
Key conditions every trader must understand:
Options can expire worthless
High leverage increases losses
Time decay works continuously
Volatility can change abruptly
Gap openings can break strategies
SEBI mandates clear risk disclosures before trading options.
18. Institutional Perspective
Institutions use option chains for:
Hedging portfolios
Volatility trading
Range building
Market manipulation zones
Retail traders must trade with the option chain, not against it.
Conclusion
The option chain is not just a table of numbers—it is a live battlefield of money, probability, fear, and expectations. Every term in the option chain has a condition attached to it: time, volatility, liquidity, and risk. Understanding these terms deeply allows traders to move from guesswork to structured decision-making.
Mastery of option chain analysis is the foundation of professional options trading.
Mastering Technical Analysis: From Charts to Consistent Decision1. The Core Philosophy of Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is built on three foundational principles:
Price discounts everything
News, fundamentals, expectations, fear, and greed are all embedded in price. A chart is a real-time emotional record of market participants.
Prices move in trends
Markets rarely move randomly. Once a trend starts, it tends to persist until a clear reversal occurs.
History repeats itself
Human behavior does not change. Fear and greed create recurring patterns that appear again and again on charts.
Mastering technical analysis begins with accepting that certainty does not exist—only probability.
2. Understanding Market Structure
Before indicators, mastery begins with price structure.
a. Trends
Uptrend: Higher highs and higher lows
Downtrend: Lower highs and lower lows
Range: Sideways movement between support and resistance
Trading with the trend dramatically increases odds. Many traders fail not due to bad indicators, but because they fight the dominant trend.
b. Support and Resistance
Support is where demand overcomes supply. Resistance is where supply overwhelms demand. These levels form due to:
Institutional order placement
Psychological round numbers
Previous highs and lows
Advanced traders understand that support and resistance are zones, not exact lines.
3. Candlestick Psychology
Candlesticks are the language of price.
Each candle tells a story:
Long bodies: Strong conviction
Long wicks: Rejection of price
Small bodies: Indecision
Key candlestick formations include:
Pin bars
Engulfing patterns
Inside bars
Doji structures
However, candlesticks must be read in context—at key levels, in trends, or during breakouts. Patterns alone are meaningless without location.
4. Indicators: Tools, Not Crutches
Indicators are derivatives of price. They confirm, not predict.
a. Trend Indicators
Moving Averages (EMA, SMA)
VWAP
Used to identify direction and dynamic support/resistance.
b. Momentum Indicators
RSI
MACD
Stochastic
Momentum reveals strength or weakness, divergence, and exhaustion points.
c. Volatility Indicators
Bollinger Bands
ATR
Volatility expands before big moves and contracts before breakouts.
A master trader uses 2–3 complementary indicators, not 10 conflicting ones.
5. Volume: The Institutional Footprint
Price moves, but volume explains why.
Rising price + rising volume = healthy trend
Rising price + falling volume = weak move
Volume spikes at support/resistance = institutional activity
Volume confirms breakouts, validates reversals, and exposes false moves. Without volume, price action is incomplete.
6. Chart Patterns and Market Behavior
Chart patterns represent crowd psychology unfolding over time.
Common patterns:
Head and shoulders
Double top/bottom
Flags and pennants
Triangles
Cup and handle
Patterns work not because of shape—but because they show accumulation, distribution, or continuation by large players.
7. Multi-Timeframe Analysis
Professionals analyze markets top-down:
Higher timeframe → trend and key levels
Lower timeframe → entries and exits
For example:
Weekly defines direction
Daily defines structure
Intraday defines execution
This alignment prevents trading against higher-timeframe forces.
8. Risk Management: The Real Edge
Technical analysis without risk control is gambling.
Key principles:
Risk only 1–2% per trade
Predefine stop-loss before entry
Maintain favorable risk-reward (minimum 1:2)
Accept losses as business expenses
Mastery is not about winning every trade—it’s about surviving long enough for probabilities to play out.
9. Trading Psychology and Discipline
Charts test emotions more than intelligence.
Common psychological traps:
Overtrading
Revenge trading
Fear of missing out (FOMO)
Moving stop-losses
Ignoring plans
Elite technical traders follow rules even when emotions disagree. Discipline turns strategy into consistency.
10. Developing a Personal Trading System
True mastery comes when you:
Trade specific setups only
Use clear entry, stop, and target rules
Journal every trade
Review mistakes objectively
A simple system executed perfectly will always outperform a complex system executed emotionally.
Conclusion: The Path to Mastery
Mastering technical analysis is not about finding a “holy grail” indicator. It is about:
Understanding price behavior
Aligning with trends
Managing risk
Controlling emotions
Repeating a proven process
Charts do not predict the future—they prepare you for it.
In the end, the best technical analysts are not those who forecast perfectly, but those who respond correctly when the market reveals its hand.
Part 4 Technical Analysis Vs. Institutional Option TradingPut Options (PE) Explained
Put = Right to sell
You buy a put when you expect the price to go down.
Loss is limited to premium paid.
Profit can rise significantly in sharp downtrends.
Example:
If Nifty is at 22,000 and you buy 21,900 PE, you are expecting Nifty to fall below 21,900.
RSI Indicator SecretsMastering Momentum Beyond Overbought & Oversold
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is one of the most popular technical indicators in trading—and also one of the most misunderstood. Created by J. Welles Wilder, RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements, oscillating between 0 and 100. While beginners treat RSI as a simple buy-low, sell-high tool, professionals use it as a market psychology meter, trend validator, and timing weapon.
Understanding RSI deeply can transform it from a basic indicator into a high-probability decision framework.
1. The True Purpose of RSI
Most traders think RSI measures overbought and oversold conditions. In reality, RSI’s primary job is to measure momentum strength.
Strong markets stay strong
Weak markets stay weak
Momentum often shifts before price does
RSI reveals whether buyers or sellers are gaining or losing control, not just whether price has gone “too far.”
That distinction alone separates amateurs from professionals.
2. The Biggest RSI Myth: Overbought ≠ Sell, Oversold ≠ Buy
One of the most dangerous mistakes traders make is:
Selling just because RSI is above 70
Buying just because RSI is below 30
In strong trends, RSI can remain overbought or oversold for extended periods.
The Secret:
Overbought in an uptrend = strength
Oversold in a downtrend = weakness
Professional traders don’t fight RSI extremes—they trade with them.
3. RSI Trend Zones (A Game-Changer)
Instead of fixed 30–70 levels, experienced traders use RSI trend zones.
Bullish Market RSI Behavior
RSI support around 40–45
RSI resistance near 80–85
Pullbacks stop above 40
Bearish Market RSI Behavior
RSI resistance around 55–60
RSI support near 20–25
Rallies fail below 60
The Secret:
If RSI refuses to drop below 40, the trend is bullish—even if price pulls back sharply.
4. RSI Divergence: The Smart Money Signal
RSI divergence occurs when price and momentum disagree.
Types of Divergence
Regular Bullish Divergence
Price makes lower lows
RSI makes higher lows
Signals selling pressure is weakening
Regular Bearish Divergence
Price makes higher highs
RSI makes lower highs
Signals buying pressure is weakening
Hidden Divergence (Trend Continuation)
Bullish hidden divergence appears in uptrends
Bearish hidden divergence appears in downtrends
The Secret:
Divergence works best near support or resistance
Divergence alone is a warning, not a trigger
5. RSI Failure Swings: Pure Momentum Signals
Failure swings are one of RSI’s most powerful—but rarely used—patterns.
Bullish Failure Swing
RSI drops below 30
RSI rises above 30
RSI pulls back but stays above 30
RSI breaks its previous high → BUY signal
Bearish Failure Swing
RSI rises above 70
RSI falls below 70
RSI rallies but stays below 70
RSI breaks its previous low → SELL signal
The Secret:
Failure swings don’t need price confirmation—they reflect internal momentum shifts before price reacts.
6. RSI Support and Resistance (Yes, It Exists)
RSI forms its own support and resistance levels, just like price.
Horizontal RSI levels often repeat
Trendlines can be drawn directly on RSI
Breakouts on RSI often precede price breakouts
The Secret:
When RSI breaks a trendline before price, it’s often an early entry signal.
7. RSI and Market Structure
RSI becomes extremely powerful when combined with higher highs, higher lows, lower highs, and lower lows.
Higher highs in price + RSI holding above 50 = bullish continuation
Lower lows in price + RSI holding below 50 = bearish continuation
The 50-Level Rule
RSI above 50 → buyers dominate
RSI below 50 → sellers dominate
The Secret:
The 50 level is more important than 70 or 30 in trending markets.
8. Timeframe Secrets: RSI Is Not Universal
RSI behaves differently across timeframes.
Higher timeframes (daily, weekly) define trend bias
Lower timeframes (5m, 15m) define entries
Professional Approach:
Identify trend using daily RSI
Enter trades using intraday RSI pullbacks
The Secret:
Never trade RSI on a lower timeframe against higher timeframe RSI direction.
9. RSI Period Adjustment (Advanced Edge)
The default RSI period is 14—but that’s not sacred.
RSI 7 → faster, more signals (scalping)
RSI 14 → balanced (swing trading)
RSI 21 or 28 → smoother (position trading)
The Secret:
Shorter periods increase sensitivity but also noise. Match RSI length to your trading style, not convenience.
10. RSI with Volume & Price Action
RSI is strongest when it confirms price action and volume.
Bullish candle + RSI holding above 50 = high-probability setup
Volume spike + RSI divergence = strong reversal clue
Breakout + RSI expansion = momentum confirmation
The Secret:
RSI should confirm, not replace, price analysis.
11. RSI in Ranges vs Trends
Range-Bound Markets
Buy near RSI 30
Sell near RSI 70
RSI works extremely well
Trending Markets
Ignore extremes
Trade pullbacks to RSI 40–50 in uptrends
Trade rallies to RSI 55–60 in downtrends
The Secret:
Before using RSI, first ask: Is the market trending or ranging?
12. Common RSI Mistakes to Avoid
Using RSI alone without context
Blindly shorting overbought markets
Ignoring higher timeframe RSI
Over-optimizing RSI settings
Treating RSI as a prediction tool instead of a probability tool
Final Thoughts: The Real RSI Edge
RSI is not about predicting tops and bottoms—it’s about reading momentum, strength, and intent. When used correctly, RSI reveals:
Who controls the market
When momentum shifts
Whether trends are healthy or exhausted
The real secret isn’t the indicator—it’s how you think about it.
Part 1 Technical Analysis VS. Institutional Option Trading What Are Options?
Options are contracts that give you the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price before a certain date.
They are derivative instruments — their value comes from the underlying asset (index, stock, commodity, currency).
Options are mostly used for hedging, speculation, and income generation.
Two Types of Options
Call Option (CE): Right to buy at a chosen price.
Put Option (PE): Right to sell at a chosen price.
Part 3 Institutional Vs. Technical AnalysisMax Pain Theory
Price gravitates toward the strike where option writers lose the least.
Works well near expiry.
Building an Option Trading System
Identify trend with market structure.
Use volume profile for levels.
Use OI for confirmation.
Use Greeks for probability.
Execute with discipline.
Indicators & Oscillators (Technical Analysis) – Complete GuideIntroduction
In technical analysis, Indicators and Oscillators are mathematical tools derived from price, volume, or open interest data. Traders use them to analyze market behavior, identify trends, measure momentum, spot reversals, and improve trade timing.
While price action shows what the market is doing, indicators help explain how strong, how fast, and how sustainable that move is. They do not predict the future but increase probability when used correctly with price structure and risk management.
What Are Indicators?
Indicators are tools that follow price and help traders understand market direction, strength, and trend continuation.
Key Characteristics of Indicators
Usually trend-following
Work best in trending markets
Often lag price (because they are calculated from past data)
Help with trend identification and confirmation
What Are Oscillators?
Oscillators are indicators that move between fixed ranges (usually 0–100 or -100 to +100). They are mainly used to identify overbought and oversold conditions.
Key Characteristics of Oscillators
Work best in range-bound or sideways markets
Help identify potential reversals
Can give early signals but also produce false signals in strong trends
Difference Between Indicators and Oscillators
Aspect Indicators Oscillators
Market Type Trending Sideways / Range
Purpose Trend confirmation Reversal & momentum
Nature Lagging Leading or coincident
Examples Moving Average, ADX RSI, Stochastic
Commonly Used Trend Indicators
1. Moving Averages (MA)
Moving averages smooth price data to identify trend direction.
Types
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
Usage
Price above MA → Uptrend
Price below MA → Downtrend
MA crossover → Trend change signal
Popular Periods
20 EMA – short-term
50 EMA – medium-term
200 EMA – long-term trend
2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
MACD measures the relationship between two EMAs.
Components
MACD Line
Signal Line
Histogram
Signals
MACD crossover → Buy/Sell
Histogram expansion → Momentum strength
Divergence → Possible reversal
3. Average Directional Index (ADX)
ADX measures trend strength, not direction.
Interpretation
ADX below 20 → Weak or no trend
ADX above 25 → Strong trend
ADX above 40 → Very strong trend
Used with +DI and -DI to identify direction.
4. Parabolic SAR
Used to determine trend direction and trailing stop loss.
Usage
Dots below price → Uptrend
Dots above price → Downtrend
Dot flip → Trend reversal
Best in strong trends, weak in sideways markets.
Popular Oscillators
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures momentum and overbought/oversold conditions.
Range: 0–100
Key Levels
Above 70 → Overbought
Below 30 → Oversold
50 → Trend strength level
Advanced Usage
RSI above 60 = bullish trend
RSI below 40 = bearish trend
RSI divergence → Reversal signal
2. Stochastic Oscillator
Compares closing price with price range over a period.
Range: 0–100
Key Levels
Above 80 → Overbought
Below 20 → Oversold
Signals
%K and %D crossover
Divergence with price
Works best in range-bound markets.
3. Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
Measures price deviation from average price.
Range: No fixed limit
Levels
Above +100 → Strong bullish momentum
Below -100 → Strong bearish momentum
Used for early trend and reversal signals.
4. Williams %R
Similar to Stochastic but inverted.
Range: -100 to 0
Above -20 → Overbought
Below -80 → Oversold
Useful for short-term trading and scalping.
Volume-Based Indicators
1. On-Balance Volume (OBV)
Measures buying and selling pressure using volume.
Concept
Rising OBV → Accumulation
Falling OBV → Distribution
Volume leads price; OBV helps confirm breakouts.
2. Volume Oscillator
Shows difference between short-term and long-term volume averages.
Helps identify breakout strength and fake moves.
Momentum Indicators
1. Rate of Change (ROC)
Measures speed of price movement.
Positive ROC → Bullish momentum
Negative ROC → Bearish momentum
Used for momentum-based entries.
2. Momentum Indicator
Simple calculation of price change over time.
Good for spotting trend acceleration and exhaustion.
Divergence – A Powerful Concept
Divergence occurs when price and indicator move in opposite directions.
Types of Divergence
Bullish Divergence: Price makes lower low, indicator makes higher low
Bearish Divergence: Price makes higher high, indicator makes lower high
Divergence often signals trend exhaustion or reversal, especially near support/resistance zones.
How to Use Indicators Effectively
Best Practices
Never use too many indicators
Combine one trend indicator + one oscillator
Confirm signals with price action
Always use stop loss
Understand market context (trend vs range)
Common Mistakes
Blindly following signals
Using oscillators in strong trends
Ignoring risk management
Over-optimization
Ideal Indicator Combinations
EMA + RSI
MACD + Support/Resistance
ADX + Moving Average
RSI + Divergence + Price Action
Conclusion
Indicators and Oscillators are decision-support tools, not decision-makers. They help traders understand trend direction, momentum strength, market conditions, and potential reversals. When combined with price action, volume, and risk management, they significantly improve trading accuracy.
Successful traders focus on simplicity, consistency, and discipline, not on finding the “perfect” indicator. Master a few tools, understand their behavior in different market conditions, and apply them with patience.
Derivatives Trading Strategies – A Complete GuideDerivatives are financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset such as stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, or interest rates. The most common derivatives used by traders are Futures and Options. Derivatives trading allows participants to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, and generate income with relatively lower capital compared to the cash market. However, derivatives are complex and require disciplined strategies and strong risk management.
Derivatives trading strategies can broadly be classified into futures-based strategies, options buying strategies, options selling strategies, hedging strategies, and advanced multi-leg strategies.
1. Futures Trading Strategies
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. They are linear instruments, meaning profit or loss moves directly with price.
a) Trend Following Strategy
This is one of the most popular futures strategies. Traders identify strong trends using indicators like Moving Averages, ADX, or trendlines.
Buy futures in an uptrend
Sell futures in a downtrend
This strategy works best in trending markets and requires strict stop-losses to manage risk.
b) Breakout Strategy
Traders enter trades when price breaks above resistance or below support with strong volume.
Buy on resistance breakout
Sell on support breakdown
This strategy captures sharp moves but may suffer from false breakouts in sideways markets.
c) Pullback Strategy
Instead of chasing price, traders enter during minor retracements within a trend.
Buy near support in an uptrend
Sell near resistance in a downtrend
This provides better risk-reward compared to chasing breakouts.
d) Calendar Spread (Futures)
This involves buying one expiry and selling another expiry of the same contract.
Profits from changes in spread rather than price direction
Lower risk compared to naked futures positions
2. Option Buying Strategies
Option buying involves purchasing Call or Put options with limited risk but high reward potential. Timing is crucial.
a) Long Call Strategy
Used when the trader is bullish.
Buy Call option
Limited risk (premium paid)
Unlimited profit potential
Works best when price moves fast and volatility increases.
b) Long Put Strategy
Used in bearish conditions.
Buy Put option
Limited risk
Profits from falling prices
Effective during strong downtrends or market crashes.
c) Directional Option Buying with Indicators
Traders combine options with indicators like RSI, MACD, or VWAP to time entries. This helps reduce time decay losses.
d) Event-Based Option Buying
Traders buy options before events such as results, budgets, or global news expecting big moves. High risk due to volatility crush after the event.
3. Option Selling Strategies (Income Strategies)
Option selling focuses on earning premium and benefits from time decay (Theta). These strategies require margin and strong risk control.
a) Covered Call
Hold stock + sell Call option
Generates regular income
Limited upside but safer than naked selling
b) Cash Secured Put
Sell Put option with sufficient cash
Suitable for acquiring stocks at lower prices
Generates income in sideways markets
c) Short Straddle
Sell Call and Put at same strike
Profits when market remains range-bound
High risk if market moves sharply
d) Short Strangle
Sell out-of-the-money Call and Put
Lower risk than straddle
Suitable for low-volatility markets
4. Non-Directional Option Strategies
These strategies do not require predicting market direction but depend on volatility.
a) Iron Condor
Combination of Call and Put spreads
Profits in sideways markets
Limited risk and limited reward
Very popular among professional traders.
b) Butterfly Spread
Buy one ITM option, sell two ATM options, buy one OTM option
Low cost strategy
Profits when price stays near middle strike
c) Calendar Spread (Options)
Sell near-term option, buy far-term option
Profits from time decay difference
Lower risk compared to naked selling
5. Volatility-Based Strategies
Volatility plays a major role in options pricing.
a) Long Straddle
Buy Call + Put at same strike
Profits from big moves in either direction
Requires strong volatility expansion
b) Long Strangle
Buy OTM Call and Put
Cheaper than straddle
Needs large price movement
c) Vega Trading
Professional traders buy options when volatility is low and sell when volatility is high.
6. Hedging Strategies Using Derivatives
Derivatives are widely used for risk protection.
a) Portfolio Hedging
Buy Index Puts against stock portfolio
Protects against market crashes
b) Futures Hedging
Short index futures to hedge long equity holdings
Effective during uncertain market conditions
c) Protective Put
Buy Put option against stock holding
Acts like insurance
7. Risk Management in Derivatives Trading
Risk management is more important than strategy selection.
Always use stop-loss
Avoid over-leveraging
Risk only 1–2% of capital per trade
Understand Greeks (Delta, Theta, Vega, Gamma)
Avoid emotional trading
Conclusion
Derivatives trading strategies offer immense opportunities for profit, flexibility, and risk management. Futures strategies suit traders who prefer direct price movement, while options strategies provide multiple ways to trade direction, volatility, and time decay. However, derivatives amplify both profits and losses. Success in derivatives trading depends on discipline, risk control, strategy selection, and continuous learning.
For beginners, it is advisable to start with simple strategies like covered calls, cash-secured puts, or directional option buying before moving to advanced multi-leg strategies. With the right approach, derivatives can become a powerful tool in a trader’s arsenal.
Divergence Secrets Option Buyers vs Option Sellers
Option Buyers
Pay premium
Limited risk
Unlimited or high reward
Affected negatively by time decay
Option Sellers (Writers)
Receive premium
Limited reward
Potentially unlimited risk
Benefit from time decay
This buyer–seller dynamic is the backbone of option trading.
Trend Following SystemsCore Philosophy of Trend Following
At its heart, trend following is reactive, not predictive. A trend follower does not ask, “Where will the market go?” Instead, they ask, “What is the market doing right now?”
The system accepts three market truths:
Markets move in trends
Trends can last longer than logic suggests
No one can consistently predict reversals
Because of this, trend followers focus on price action rather than news, opinions, or forecasts. The market itself becomes the final authority.
What Is a Trend?
A trend is the general direction in which a market moves over time:
Uptrend: Higher highs and higher lows
Downtrend: Lower highs and lower lows
Sideways (Range-bound): No clear direction
Trend following systems are designed to profit from uptrends and downtrends, while accepting small losses during sideways markets.
Key Components of Trend Following Systems
A robust trend following system consists of four essential elements:
1. Trend Identification
This determines whether a trend exists and in which direction.
Common tools include:
Moving Averages (SMA, EMA)
Price structure (highs and lows)
Trendlines
Breakout levels
Channel indicators
The goal is not to catch the start of a trend perfectly, but to enter once the trend is confirmed.
2. Entry Rules
Entry rules define when to open a trade.
Typical entry methods:
Price crossing above/below a moving average
Moving average crossovers (e.g., 50 & 200)
Breakout above resistance or below support
Donchian channel breakouts
Entries are usually delayed by design. Trend followers willingly miss the early part of the move to reduce false signals.
3. Exit Rules
Exits are more important than entries in trend following.
There are two main exits:
Stop-loss exit: Limits downside risk
Trend exit: Signals the trend has ended
Common exit methods:
Trailing stop (ATR-based or percentage-based)
Moving average cross in the opposite direction
Break of trend structure
Volatility-based stop
Trend followers let profits run but cut losses quickly.
4. Position Sizing & Risk Management
Risk control is the backbone of trend following.
Key principles:
Risk a fixed percentage per trade (e.g., 0.5%–2%)
Use volatility-based position sizing
Never increase risk to “recover losses”
Expect multiple small losses before big winners
Trend following systems survive because losses are small and controlled, while winners are allowed to grow.
Characteristics of Trend Following Systems
1. Low Win Rate, High Reward
Trend followers often win only 30–45% of trades, but winning trades are much larger than losing ones.
This creates:
Many small losses
Few very large gains
Positive expectancy overall
2. Emotionally Challenging
Trend following tests discipline:
You enter late
You experience frequent losses
You often exit after giving back some profit
The system works only if rules are followed strictly.
3. Works Best in Trending Markets
Trend following performs exceptionally well during:
Strong bull markets
Bear markets
Crisis-driven volatility
It struggles in:
Sideways markets
Low-volatility environments
Popular Trend Following Techniques
Moving Average Systems
One of the simplest and most widely used methods.
Examples:
Price above 200 EMA → bullish
50 EMA crossing above 200 EMA → long signal
Opposite cross → exit
Simple, robust, and effective over long periods.
Breakout Systems
Based on the idea that new highs or lows indicate momentum.
Examples:
20-day high breakout → buy
20-day low breakout → sell
Exit on opposite breakout or trailing stop
Famous users include the Turtle Traders.
Channel-Based Systems
Uses price channels such as:
Donchian Channels
Keltner Channels
Bollinger Bands (trend context)
Breaks outside the channel suggest trend continuation.
Timeframes in Trend Following
Trend following works across all timeframes:
Intraday: Short trends, higher noise
Swing trading: Days to weeks
Position trading: Weeks to months
Long-term investing: Months to years
Higher timeframes tend to:
Have fewer trades
Produce stronger trends
Reduce emotional stress
Advantages of Trend Following Systems
Objective and rule-based
Works across markets and instruments
No need for prediction or fundamentals
Scales well with capital
Survives market crashes and booms
Many hedge funds and CTAs rely heavily on trend following due to its robustness.
Disadvantages and Limitations
Frequent small losses
Underperforms in sideways markets
Requires strong discipline
Psychologically uncomfortable
Late entries and exits
Trend following rewards patience, not excitement.
Psychology of Trend Following
Trend following demands a mindset opposite to most traders:
Accept being wrong often
Detach ego from predictions
Trust probabilities over outcomes
Follow rules even after drawdowns
The biggest enemy is not the market—it is rule-breaking due to emotions.
Who Should Use Trend Following?
Trend following suits traders who:
Prefer systematic trading
Can follow rules strictly
Are patient with drawdowns
Focus on long-term performance
Avoid overtrading
It is less suitable for traders who:
Need frequent wins
Trade based on intuition
Chase tops and bottoms
Conclusion
Trend Following Systems are not about forecasting the future or finding perfect entries. They are about aligning with market direction, controlling risk, and letting probabilities work over time. Though simple in concept, they are difficult in execution due to emotional challenges.
When applied with discipline, sound risk management, and consistency, trend following systems have proven their ability to survive market cycles, crises, and changing conditions—making them one of the most powerful approaches in trading history.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Who Should Trade Options?
People who:
- Understand options and risks.
- Have experience trading stocks/derivatives.
- Want to hedge existing positions.
- Are comfortable with potential losses.
Not suitable for:
- Beginners without knowledge.
- Risk-averse investors.
Part 2 Technical Vs. Institutional Option Trading Types of Option Trading: Calls and Puts- Call Option:
- Gives buyer the right to BUY the underlying asset.
- Buyer expects price to RISE.
- Example: Buy Nifty Call at 22,000 strike, profit if Nifty goes above 22,000 + premium paid.
- Put Option:
- Gives buyer the right to SELL the underlying asset.
- Buyer expects price to FALL.
- Example: Buy Nifty Put at 22,000 strike, profit if Nifty goes below 22,000 - premium paid
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingBest Practices for Retail Traders
1. Start with Buying Options
Risk is limited.
2. Prefer ATM or Slight ITM
Better stability, realistic probability.
3. Avoid Holding Overnight
Unless you understand IV, theta, and event risk.
4. Track Implied Volatility
Buy when IV is low, sell when IV is high.
5. Use a Trading Plan
Entry levels
Stop loss
Target
Position size
6. Don’t Chase Cheap OTM Options
They expire worthless most of the time.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Types of Option Traders Use
1. In-the-Money (ITM) Options
High intrinsic value, costlier, but more stable.
2. At-the-Money (ATM) Options
Strike price closest to spot price; very popular for intraday.
3. Out-of-the-Money (OTM) Options
Cheap but time-decay heavy. High risk, high reward.
ULTRACEMCO 1 Week View 📍 Current trading range (approx)
• Stock is trading near ~₹12,600-₹12,800 on NSE right now.
📊 Weekly Pivot Levels (1-Week Timeframe)
🔹 Resistance Levels
1. Major Resistance 3 (R3): ~₹13,190
2. Resistance 2 (R2): ~₹12,872
3. Resistance 1 (R1): ~₹12,621
➡️ If price closes above ₹12,620-12,630 on weekly close, momentum could pick up toward ₹12,870-₹13,190.
🔸 Support Levels
1. Support 1 (S1): ~₹12,051
2. Support 2 (S2): ~₹11,732
3. Support 3 (S3): ~₹11,481
➡️ Key weekly support is around ₹12,050-₹12,000 — break below this zone can accelerate downside toward ₹11,730-₹11,480.
🔁 Weekly Range Expectation
📍 Upside range: ₹12,620 → ₹12,870 → ₹13,190
📍 Downside range: ₹12,050 → ₹11,732 → ₹11,480
This gives an approximate weekly trading range of ~₹11,480 to ₹13,190 if volatility expands.