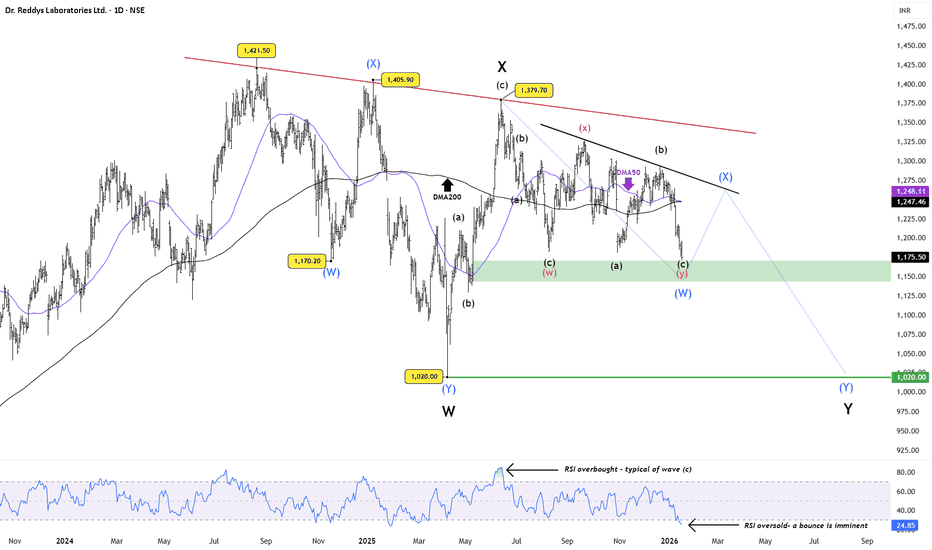
Dr Reddy’s Labs:Oversold Bounce Likely, But Structure Still WeakPrice has now reached a key demand / support zone , while RSI has slipped into oversold territory , a setup that often precedes a technical bounce . From a pure momentum perspective, a short-term relief rally looks likely .
However, the broader structure remains corrective . The stock continues to trade below two declining trendline resistances , and the 50-DMA is hovering near a bearish crossover with the 200-DMA , keeping the higher-timeframe bias under pressure.
The recent price action shows overlapping, choppy swings , best interpreted as multiple minor and higher-degree double corrections . Any bounce from current levels is therefore expected to be counter-trend and corrective in nature , not the start of a new uptrend.
Unless price can reclaim the falling resistance and sustain above key moving averages , the risk of a larger Wave Y decline toward the ~1,020 zone remains open. Rallies, if any, are likely to face supply and should be treated with caution.
In summary:
Oversold bounce likely from support
Bounce expected to be corrective
Trend still weak below resistances
Wave Y risk remains toward ~1,020
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please do your own research (DYOR) before making any trading decisions.
Wave Analysis
Part 12 Trading Master Class With Experts Types of Options
Options are mainly divided into two categories:
Call Options
A call option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) before or on the expiration date.
Example: Suppose a stock trades at ₹1,000, and you buy a call option with a strike price of ₹1,050, expiring in one month. If the stock rises to ₹1,100, you can buy it at ₹1,050 and profit from the difference, minus the premium paid.
Put Options
A put option gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price before or on the expiration date.
Example: Suppose a stock trades at ₹1,000, and you buy a put option with a strike price of ₹950. If the stock drops to ₹900, you can sell it at ₹950 and profit, minus the premium paid.
L&T: Wave 5 Exhaustion Signals a Corrective PhaseA clear 5-wave impulse has played out, with Wave 3 showing classic overbought RSI behavior while still respecting Elliott Wave rules.
Wave 5 ended with RSI divergence , signaling exhaustion near the highs.
Price has now slipped below the 100-DMA , reinforcing the view that the advance has likely stalled and a corrective phase is underway. The decline should unfold in at least a 3-wave structure . Importantly, Wave (a) may not be complete yet . Despite RSI reaching oversold levels, there is no decisive reversal signal so far. Any near-term bounce could turn out to be a dead-cat bounce , potentially forming Wave (b) rather than a trend reversal.
The previous accumulation zone , which also aligns with the 50% Fibonacci retracement , remains a key area to monitor. Until the corrective structure is fully resolved, bounces are best treated as counter-trend moves , not fresh longs.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please do your own research (DYOR) before making any trading decisions
Mistakes Traders Must Avoid to Succeed in Financial Markets1. Trading Without a Plan
One of the most common and dangerous mistakes traders make is entering the market without a clear trading plan. A trading plan defines entry points, exit targets, stop-loss levels, position size, and risk tolerance. Without a plan, decisions are driven by emotions rather than logic. Traders who operate impulsively often overtrade, exit too early, or hold losing positions for too long. A well-defined plan provides structure, reduces confusion, and helps traders stay disciplined even during volatile market conditions.
2. Ignoring Risk Management
Risk management is the backbone of successful trading, yet many traders overlook it. Risking too much capital on a single trade can wipe out weeks or even months of gains. Professional traders usually risk only a small percentage of their capital—often 1–2%—per trade. Ignoring stop-loss orders, increasing position size after losses, or using excessive leverage exposes traders to catastrophic losses. Protecting capital should always be the first priority.
3. Letting Emotions Control Decisions
Emotional trading is a silent account killer. Fear, greed, hope, and frustration influence traders to make irrational decisions. Fear may cause early exits from profitable trades, while greed can lead to holding positions longer than planned. Revenge trading—placing impulsive trades after a loss to recover money quickly—is another emotional trap. Successful traders learn to detach emotionally from trades and follow their strategy consistently, regardless of short-term outcomes.
4. Overtrading
Overtrading occurs when traders place too many trades, often without valid setups. This usually happens due to boredom, overconfidence, or the desire to recover losses quickly. Excessive trading increases transaction costs, reduces focus, and leads to poor-quality decisions. Markets do not offer opportunities all the time, and waiting patiently for high-probability setups is a key skill every trader must develop.
5. Lack of Proper Market Knowledge
Many traders enter the market without fully understanding how it works. Trading without knowledge of market structure, technical analysis, fundamental factors, or economic events increases the chances of failure. For example, ignoring earnings announcements, economic data releases, or central bank decisions can lead to unexpected volatility. Continuous learning and staying updated with market dynamics are essential for long-term success.
6. Not Using Stop-Loss Orders
Refusing to use stop-loss orders is a costly mistake. Some traders avoid stop-losses hoping the market will reverse in their favor. Unfortunately, losses can grow rapidly, damaging both capital and confidence. Stop-loss orders act as a safety net, limiting losses and allowing traders to live to trade another day. Accepting small losses is a part of trading and is far better than suffering large, uncontrollable drawdowns.
7. Chasing the Market
Chasing trades after a big price move often results in entering at the worst possible time. Traders see a stock or asset moving sharply and fear missing out (FOMO). As a result, they enter late, just before a reversal or correction. Successful traders wait for proper pullbacks, confirmations, and setups rather than reacting emotionally to sudden price movements.
8. Poor Position Sizing
Even a good strategy can fail if position sizing is incorrect. Taking positions that are too large increases emotional stress and amplifies losses. Conversely, positions that are too small may not justify the effort or risk taken. Proper position sizing ensures that each trade aligns with the trader’s risk tolerance and overall capital management strategy.
9. Lack of Patience and Discipline
Markets reward patience, but many traders want quick profits. Impatience leads to entering trades prematurely, ignoring confirmation signals, or exiting winning trades too early. Discipline is required to follow the trading plan consistently, even after a series of losses or wins. Traders who lack discipline often change strategies frequently, never giving one approach enough time to prove its effectiveness.
10. Failing to Keep a Trading Journal
A trading journal is a powerful learning tool, yet many traders neglect it. Without reviewing past trades, it is difficult to identify mistakes, strengths, and patterns in behavior. A journal helps traders understand what works, what doesn’t, and why. Over time, this self-analysis leads to improved strategies and better decision-making.
11. Unrealistic Expectations
Many traders enter the market expecting quick and easy money. This mindset leads to excessive risk-taking and disappointment. Trading is a skill that requires time, practice, and patience. Unrealistic expectations often cause traders to abandon good strategies prematurely or take unnecessary risks in pursuit of fast profits.
12. Not Adapting to Market Conditions
Markets change over time—trends, volatility, and liquidity are not constant. Traders who fail to adapt their strategies to changing conditions often struggle. A strategy that works in a trending market may fail in a sideways market. Successful traders regularly review and adjust their approach based on current market behavior.
Conclusion
Avoiding common trading mistakes is just as important as finding profitable opportunities. Trading success is not about perfection, but about consistency, discipline, and continuous improvement. By developing a solid trading plan, practicing effective risk management, controlling emotions, and committing to lifelong learning, traders can significantly improve their performance. Markets will always be uncertain, but traders who avoid these critical mistakes place themselves in a far stronger position to achieve long-term success.
Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Modern Financial MarketsAI Trading Secrets:
The Evolution from Human Trading to AI-Driven Trading
Traditional trading relied heavily on human judgment, technical indicators, and fundamental analysis. While effective to a degree, human traders are limited by emotions such as fear and greed, slower reaction times, and the inability to process vast datasets simultaneously. AI trading systems emerged to overcome these limitations. By using algorithms trained on historical and real-time data, AI systems can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that are often invisible to the human eye. This evolution has shifted trading from being experience-based to intelligence-based.
Data Is the Core Secret of AI Trading
One of the most critical secrets behind AI trading success is data. AI thrives on data—price movements, volume, order flow, news, earnings reports, macroeconomic indicators, social media sentiment, and even geopolitical developments. Unlike traditional analysis that may focus on limited indicators, AI integrates structured and unstructured data to build a holistic market view. The more high-quality data an AI system processes, the more accurate and adaptive its predictions become.
Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
At the heart of AI trading lies machine learning. These models learn from historical market behavior and continuously refine themselves as new data becomes available. Instead of using fixed rules like “buy when RSI is below 30,” AI systems detect complex, non-linear relationships between variables. For example, they may recognize that a specific price pattern combined with volume spikes and sentiment changes often precedes a breakout. This adaptive learning capability is a major edge that AI traders possess.
Algorithmic Speed and High-Frequency Trading
Another powerful AI trading secret is speed. AI-driven algorithms can execute trades in milliseconds or even microseconds. In high-frequency trading (HFT), profits are made from very small price differences repeated thousands of times a day. Humans cannot compete at this level. AI systems monitor multiple markets simultaneously, react instantly to price changes, and execute trades without hesitation. This speed advantage is especially crucial in volatile markets where delays can lead to missed opportunities or losses.
Emotion-Free Decision Making
One of the biggest weaknesses of human traders is emotional bias. Fear causes premature exits, greed leads to overtrading, and hope results in holding losing positions too long. AI eliminates these emotional errors entirely. It follows predefined logic and statistical probability, executing trades based purely on data and strategy. This discipline is a hidden but extremely powerful secret behind consistent AI trading performance.
Risk Management and Capital Protection
AI trading is not just about maximizing profits; it is equally focused on minimizing risk. Advanced AI systems dynamically adjust position sizes, stop-loss levels, and exposure based on market volatility and probability analysis. They can detect when market conditions change—such as during news events or sudden trend reversals—and reduce risk automatically. This intelligent risk management often protects traders from catastrophic losses that occur due to emotional or impulsive decisions.
Predictive Analytics and Market Forecasting
AI excels at predictive analytics. By analyzing historical cycles, correlations, and behavioral patterns, AI models can estimate the probability of future price movements. While no system can predict markets with 100% accuracy, AI improves the odds by identifying statistically favorable setups. These predictions are constantly updated, making AI strategies flexible rather than rigid. This adaptability is a key reason why AI systems remain effective even as market conditions evolve.
Sentiment Analysis and Alternative Data
Modern AI trading goes beyond charts and financial statements. Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows AI to analyze news articles, earnings call transcripts, social media posts, and even government announcements. By gauging market sentiment—whether investors are optimistic or fearful—AI systems can anticipate market reactions before prices fully reflect the information. This use of alternative data provides a significant informational edge.
Retail Traders and AI Accessibility
Previously, AI trading was limited to hedge funds and institutional investors due to high costs and technological barriers. Today, cloud computing, open-source libraries, and AI-powered trading platforms have made these tools accessible to retail traders. While retail traders may not match institutional-level infrastructure, they can still benefit from AI-driven indicators, automated strategies, and decision-support systems. This democratization of AI is reshaping market participation globally.
Limitations and the Importance of Human Oversight
Despite its power, AI trading is not foolproof. AI models depend on historical data, which may not fully account for rare “black swan” events. Over-optimization, poor data quality, or incorrect assumptions can lead to losses. Therefore, the real secret to successful AI trading lies in combining AI intelligence with human oversight. Traders must understand the strategy, monitor performance, and intervene when necessary.
The Future of AI Trading
The future of trading is undeniably intertwined with AI. As computing power increases and data sources expand, AI systems will become even more sophisticated. We can expect deeper integration of real-time global data, improved predictive accuracy, and more personalized trading strategies. However, markets will always remain competitive, and no AI system will guarantee profits. Continuous learning, discipline, and adaptation will remain essential.
Conclusion
AI trading secrets are rooted in data mastery, machine learning, speed, emotional neutrality, and intelligent risk management. Artificial Intelligence does not replace traders; it empowers them with tools that enhance decision-making and consistency. Those who understand and responsibly use AI in trading gain a significant edge in modern financial markets. In an era where information moves faster than ever, AI is not just an advantage—it is becoming a necessity for sustainable trading success.
The Resurgence of India’s Public Sector Banking PowerHistorical Challenges Faced by PSU Banks
For a long time, PSU banks struggled under the weight of stressed assets, particularly after the corporate lending boom of the mid-2000s. Aggressive lending to infrastructure, power, steel, and telecom sectors, combined with economic slowdowns and policy bottlenecks, led to a sharp rise in NPAs. Weak credit appraisal systems, governance challenges, and limited autonomy further constrained performance. As a result, profitability declined, capital adequacy weakened, and market valuations remained subdued compared to private sector banks.
Government-Led Reforms and Recapitalization
A major catalyst behind the rise of PSU banks has been decisive government intervention. Large-scale recapitalization programs injected much-needed capital into banks, strengthening their balance sheets and enabling them to meet regulatory requirements. The government also initiated governance reforms, including improved board oversight, professional management practices, and performance-linked accountability. These steps restored stability and provided PSU banks with the confidence to resume lending activity.
Resolution of NPAs and Improved Asset Quality
One of the most significant contributors to the revival of PSU banks is the sharp improvement in asset quality. The introduction of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) created a structured mechanism for resolving stressed assets. Through recoveries, write-offs, and better provisioning practices, gross and net NPAs declined substantially across major PSU banks. Improved asset quality reduced credit costs, directly boosting profitability and strengthening investor sentiment.
Robust Credit Growth and Economic Recovery
India’s economic recovery and sustained growth momentum have provided a favorable backdrop for PSU banks. Rising demand for credit from infrastructure, manufacturing, MSMEs, agriculture, and retail segments has supported healthy loan growth. Government-led capital expenditure on roads, railways, defense, and renewable energy has especially benefited PSU banks, given their strong presence in project financing and public sector lending. This renewed credit cycle has translated into higher interest income and better utilization of capital.
Digital Transformation and Operational Efficiency
PSU banks have made significant strides in digital transformation, narrowing the gap with private sector peers. Investments in core banking systems, digital payment platforms, mobile banking apps, and fintech partnerships have improved customer experience and operational efficiency. Automation and data analytics have enhanced risk management and credit monitoring, reducing the likelihood of future asset quality stress. These technological upgrades have helped PSU banks remain competitive in an increasingly digital financial ecosystem.
Improved Profitability and Financial Metrics
As asset quality improved and credit growth picked up, PSU banks began reporting strong financial results. Many leading PSU banks have posted record profits, supported by lower provisioning requirements, stable net interest margins, and improved cost management. Capital adequacy ratios have strengthened, return on assets has improved, and balance sheets appear more resilient. This financial turnaround has been a key driver behind the rising stock market performance of PSU bank shares.
Investor Confidence and Market Re-Rating
The improved fundamentals of PSU banks have not gone unnoticed by investors. After years of underperformance, PSU bank stocks have seen significant re-rating in the equity markets. Domestic institutional investors and retail participants have shown renewed interest, attracted by improving earnings visibility, reasonable valuations, and strong dividend potential. The rising performance of PSU banks has also contributed positively to broader banking and financial sector indices.
Strategic Role in Financial Inclusion and Social Objectives
Beyond profitability, PSU banks continue to play a vital role in financial inclusion and social development. They are instrumental in implementing government schemes such as Jan Dhan Yojana, Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT), Mudra loans, and agricultural credit programs. Their extensive branch network in rural and semi-urban areas enables them to support inclusive growth while simultaneously expanding their customer base. This dual role of commercial performance and social responsibility strengthens their long-term relevance.
Challenges That Remain
Despite the impressive rise, PSU banks still face challenges. Competition from agile private banks and fintechs remains intense. Maintaining asset quality during rapid credit expansion requires disciplined risk management. Governance reforms must be sustained to ensure autonomy, transparency, and accountability. Additionally, global economic uncertainties, interest rate volatility, and sector-specific stress could test the resilience of PSU banks in the future.
Outlook: A Sustainable Revival
The rise of PSU banks marks a structural shift rather than a short-term recovery. With cleaner balance sheets, stronger capital positions, improved governance, and supportive macroeconomic conditions, PSU banks are well-positioned to sustain growth. Their role in financing India’s infrastructure push, supporting MSMEs, and expanding financial inclusion will remain crucial in the coming years. If reforms continue and risk management remains prudent, PSU banks are likely to emerge as stable, profitable, and trusted institutions in India’s financial landscape.
Conclusion
The resurgence of PSU banks represents one of the most significant success stories in India’s financial sector in recent times. From grappling with severe stress to delivering strong financial performance, PSU banks have demonstrated resilience and adaptability. Their rising trajectory reflects the combined impact of policy reforms, economic recovery, and internal transformation. As they continue to evolve, PSU banks are set to play a central role in shaping India’s growth story, reinforcing confidence in the public sector banking system, and contributing to long-term economic stability.
NIFTY 50 Analysis: Bearish Flag Breakdown or Major Bounce? Nifty 50 is at a critical crossroads! 📉 After a sharp rejection from record highs, the index has formed a Bearish Flag pattern on the daily timeframe. In this video, we break down the crucial support at 25,600 and whether the IT-led recovery is enough to spark a reversal.
Key Discussion Points:
The Pattern: Analyzing the breakdown of the short-term uptrend and the current bearish flag formation.
Crucial Levels: Why 25,600 is the "Must-Hold" support and 25,800 is the immediate hurdle.
Indicators: RSI hovering near 40 and the impact of Nifty trading below its 20-day and 50-day EMAs.
Trading Strategy: Why "Sell on Rise" is the dominant theme until 25,950 is reclaimed.
ICICI Bank: Stable Results, Critical Technical TestICICI Bank Limited announced its Q3 FY26 results after market hours, delivering a quarter marked by stable core performance but profits below market expectations . While the balance sheet remains healthy, the earnings profile does not materially alter the broader technical structure visible on the chart.
This makes it important to assess earnings and price action independently , and then align them within a broader market structure.
Earnings Snapshot — Key Metrics Explained
Profit After Tax (PAT)
PAT: ₹11,318 crore
YoY comparison: Lower than ₹11,792 crore
Outcome: Below analyst expectations
What PAT means:
PAT represents the company’s net profit after all expenses and taxes . A miss here does not imply business weakness, but it does indicate that profits fell short of what the market had already priced in .
Net Interest Income (NII)
NII: ₹21,932 crore
Growth: +7.7% YoY
What NII means:
NII is the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits . It reflects the core earning power of a bank . ICICI Bank’s NII growth confirms steady loan growth and healthy lending activity .
Net Interest Margin (NIM)
NIM: 4.30% (stable)
What NIM means:
NIM measures how efficiently a bank converts lending into profit . Stability here suggests no margin pressure and continued pricing discipline.
Provisions — The Key Drag
Total provisions: ₹2,556 crore
Includes ₹1,283 crore additional standard asset provision following an RBI supervisory review
What provisions mean:
Provisions are buffers set aside to absorb potential future losses . In this quarter, the increase was regulatory in nature , not driven by deterioration in credit quality.
However, higher provisions directly reduce reported profits , which is why markets tend to react cautiously.
Asset Quality
Gross NPA: 1.53%
Net NPA: 0.37%
Provision Coverage Ratio: 75.4%
What NPAs mean:
Gross NPA shows total stressed loans
Net NPA reflects stress after provisioning
These numbers confirm that asset quality remains strong , with no visible stress on the balance sheet.
Technical Structure — Where Price Stands
From a technical perspective, price continues to trade within a larger corrective structure after forming an all-time high near 1500.
The recent rally appears counter-trend , pushing price into a well-defined supply zone
The 1445 region is acting as resistance
Momentum has improved, but RSI remains below bullish expansion territory , indicating the absence of impulsive strength
What RSI tells us:
The Relative Strength Index measures momentum. Sustained bullish trends usually hold RSI above 60–65 . Readings below this zone often accompany corrective or relief rallies .
Wave Context (High-Level View)
The broader price action still fits a corrective W–X–Y structure
The current advance aligns with a counter-trend X-wave
Unless price accepts decisively above 1500 , the structure continues to allow for a Y-leg decline toward lower support zones
This keeps the risk-reward skewed toward patience rather than aggressive positioning at current levels.
Key Levels to Watch
Major resistance / bearish invalidation: 1500
Immediate supply zone: 1445
Target support – 1: 1325
Target support – 2: 1265
Final View
Fundamentally, ICICI Bank remains a high-quality franchise with improving asset quality, stable margins, and healthy loan growth. However, the profit miss driven by higher regulatory provisions does not provide a strong catalyst for a fresh impulsive breakout.
Technically, price is reacting exactly where it should — into resistance within a corrective structure . Until there is clear acceptance above 1445/1500 , the broader setup remains range-to-corrective , not trend-expansive.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please do your own research (DYOR) before making any trading decisions.
Completion of 5 wavesPower India has completed 5 waves where wave 1 is the longest . It is in the form of a diagonal. The correction is still unfolding and should end i the vicinity of wave 2 , preferably near it low around 10000-11000. It is still making red candles . Correction will be over then we get a good green candle who top should be traded by another green candle or appearance of 3 white soldier in the vicinity of wave 2.
Best Method to Trade Large Cap Stocks in 2026 ?Hello everyone, in this video I am explaining how to identify strategy locations - where exactly you need to look on the charts to create a better strategy in terms of Large cap stocks .
However the Mid and small ones do not follow these rules . I hope I was able to share my experience .
Charts used in the video explanation are older than 3 months
Part 10 Trade Like Institutions Open Interest (OI) – The Most Important Tool
OI reveals:
Where option writers (big money) are active
Market expectations
Support and resistance zones
CE OI Buildup
Resistance zone
Option sellers expect market to stay below these strikes.
PE OI Buildup
Support zone
Sellers expect market to stay above these strikes.
OI Shift
When PE writers exit and CE writers build → Trend reversal.
Part 9 Trading Master Class With Experts How Institutions Trade Options
Institutions focus on:
Selling premium (because they have capital)
Hedged positions
Large OI levels
Neutral strategies like condors and spreads
Market-making
Risk-neutral trades using delta-neutral strategies
Retail traders tend to chase:
Lottery OTM options
Low probability trades
News-based speculation
Institutions focus on consistency.
Angel One: Power Bounce or Wave 4 Noise?Since its inception low near ₹222 , Angel One Limited has delivered a strong multi-year advance. The initial rally into ₹1,689 is best viewed as Wave 1 , followed by a deep yet corrective decline toward ₹990.50, forming Wave 2 . This laid the foundation for an extended Wave 3 , which accelerated sharply and culminated near ₹3,896 .
Following the Wave 3 peak, price action transitioned into a sideways and overlapping phase , characteristic of a complex Wave 4 correction rather than the start of a fresh impulsive advance. The correction so far appears to be unfolding as a W–X–Y-type structure , with scope for further extension if price continues to face resistance. Crucially, Wave 1 remains intact , preserving the broader impulsive framework — though it remains unconfirmed at this stage.
The latest +17.94% weekly candle highlights strong reactionary demand . However, price continues to trade below the descending trendline resistance , and a clear impulsive breakout has yet to emerge. With the Union Budget (Feb 1) approaching, event-driven volatility remains a key near-term risk.
Bottom line:
Wave 3 stands extended.
Wave 4 is likely still in progress.
Wave 5 will only be considered on a clean impulsive breakout and a sustained close above descending trendline resistance.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please do your own research (DYOR) before making any trading decisions.
Gold weekly rotation between 4682 supply and 4420 demand🟡 XAUUSD – Weekly Smart Money Plan | by Ryan_TitanTrader (17/01)
📈 Market Context
Gold remains structurally bullish on the higher timeframe, but weekly price action has clearly transitioned into a controlled Smart Money rotation. After delivering buy-side liquidity into premium, continuation has stalled.
This week’s hot drivers — USD volatility, U.S. yield repricing, and renewed Fed rate-cut expectations amid sticky inflation data and geopolitical hedging flows — are creating ideal conditions for inducement and liquidity engineering rather than clean trend expansion.
With risk sentiment fragile and positioning crowded, Gold is behaving typically at extremes: sweeps, fake breaks, and mean reversion, not impulsive continuation.
🔎 Technical Framework – Smart Money Structure (H4–H1)
Current Phase:
HTF bullish bias remains valid, but internal structure shows distribution from premium after liquidity delivery.
Key Idea:
Sell reactions from premium supply, or wait patiently for a deeper pullback into HTF demand to reload longs.
Structural Notes:
• HTF BOS confirms bullish dominance
• Buy-side liquidity already taken above highs
• Clear rotation channel forming
• Liquidity shortage zone acting as magnet
• Discount demand aligns with prior OB + channel support
💧 Liquidity Zones & Key Levels
• 🔴 SELL GOLD 4680 – 4682 | SL 4690
• 🟢 OB BUY GOLD 4420 – 4418 | SL 4410
🧠 Institutional Flow Expectation
Liquidity sweep → MSS / CHoCH → BOS → displacement → OB / FVG retest → expansion or deeper rotation
🎯 Execution Rules
🔴 SELL GOLD 4680 – 4682 | SL 4690
Rules:
✔ Price taps premium channel supply
✔ Buy-side liquidity taken above recent highs
✔ Bearish MSS / CHoCH on H1–M15
✔ Downside BOS confirms distribution
✔ Entry via bearish FVG or supply OB
Targets:
• 4620 — internal reaction
• 4560 — liquidity shortage
• 4480 — deeper weekly rotation
• Trail aggressively (distribution play)
🟢 OB BUY GOLD 4420 – 4418 | SL 4410
Rules:
✔ Sweep into weekly discount zone
✔ Strong confluence: HTF OB + channel support
✔ Bullish MSS / CHoCH on M15–H1
✔ Impulsive BOS with displacement
✔ Entry via refined bullish OB
Targets:
• 4560 — first reaction
• 4620 — mid-range liquidity
• 4680+ — continuation if expansion resumes
⚠️ Risk Notes
• Premium zones = liquidity traps
• Expect false breaks during macro headlines
• No entry without MSS + BOS
• Reduce risk near HTF extremes
📍 Summary
Gold is bullish by structure, but this week is about precision execution, not prediction:
• Premium may deliver a Smart Money sell from 4680–4682, or
• Discount at 4420–4418 may reload longs for the next impulsive leg.
Let liquidity move first.
Let structure confirm second.
Smart Money controls — patience pays. ⚡️
📌 Follow @Ryan_TitanTrader for weekly Smart Money gold breakdowns.
Gold fluctuates between 4672 resistance and 4560 support.🟡 XAUUSD – Intraday Smart Money Plan | by Ryan_TitanTrader (16/01)
📈 Market Context
Gold remains structurally bullish on the higher timeframe, but intraday price action has shifted into controlled rotation. With today’s hot drivers — USD volatility, U.S. yield fluctuations, and ongoing Fed rate-cut speculation — Smart Money is no longer pushing continuation. Instead, liquidity is being engineered around premium and discount zones.
Ahead of U.S. macro headlines and inflation-linked expectations, Gold is behaving typically at extremes: inducement, stop-hunts, and mean reversion rather than impulsive trend extension.
🔎 Technical Framework – Smart Money Structure (H1–M15)
Current Phase:
HTF bullish bias intact, while intraday structure shows corrective rotation after buy-side liquidity was taken.
Key Idea:
Look for distribution from premium supply or a deeper pullback into discount demand for buying/entry reloads.
Structural Notes:
• HTF BOS confirms bullish dominance
• Buy-side liquidity already delivered
• Price rotating, not expanding impulsively
• Internal FVG acting as downside magnet
• Discount demand aligns with prior OB support
💧 Liquidity Zones & Triggers
• 🔴 SELL GOLD 4670 – 4672 | SL 4680
• 🟢 BUY GOLD 4561 – 4559 | SL 4551
🧠 Institutional Flow Expectation
Liquidity sweep → MSS / CHoCH → BOS → displacement → OB/FVG retest → expansion
🎯 Execution Rules
🔴 SELL GOLD 4670 – 4672 | SL 4680
Rules:
✔ Price taps premium supply
✔ Buy-side liquidity taken above highs
✔ Bearish MSS / CHoCH on M5–M15
✔ Clear downside BOS
✔ Entry via bearish FVG or supply OB
Targets:
• 4620 — internal reaction
• 4585 — liquidity pool
• Trail aggressively (distribution play)
🟢 BUY GOLD 4561 – 4559 | SL 4551
Rules:
✔ Sweep into discount demand
✔ Confluence with OB + FVG
✔ Bullish MSS / CHoCH on M5–M15
✔ Strong upside BOS with displacement
✔ Entry via refined bullish OB
Targets:
• 4620 — first reaction
• 4670 — internal liquidity
• 4700+ — continuation if expansion resumes
⚠️ Risk Notes
• Premium zones = liquidity traps
• Expect fake breaks during news volatility
• No entry without MSS + BOS
• Reduce size near extremes
📍 Summary
Gold is bullish by structure, but today is about execution, not prediction:
• Premium may deliver a Smart Money sell from 4670–4672, or
• Discount at 4561–4559 may reload buying/entry for the next leg higher.
Let liquidity move first.
Let structure confirm second.
Smart Money controls — patience pays. ⚡️
📌 Follow @Ryan_TitanTrader for daily Smart Money gold breakdowns.
Candle Patterns How Candle Patterns Work with Market Structure
Candles do not work well in isolation. Their true power emerges when aligned with:
Support/Resistance Levels
Trend Direction
Breakouts and Pullbacks
Volume Profile Zones (HVN, LVN)
For example:
A Hammer at support = reliable reversal.
A Doji at resistance = caution for buyers.
Engulfing pattern after liquidity sweep = strong reversal.
Market structure helps validate candlestick signals and improve accuracy.
TECHM 1 Day Time Frame 📍 Latest Price Range (Today on NSE):
• Low ~ ₹1,600 and High ~ ₹1,681 (intraday range) from current data today.
🔁 Key Levels for 1‑Day Timeframe
Immediate Resistance Levels
These are zones where price may face selling pressure if it rises:
R1: ~ ₹1,700 – ₹1,702
R2: ~ ₹1,731 – ₹1,732
R3: ~ ₹1,781 – ₹1,782
Pivot
Daily Pivot Point: ~ ₹1,659 – ₹1,660 (indicative mid‑point of the current range)
Support Levels
These are zones where price may find demand on declines:
S1: ~ ₹1,620 – ₹1,621
S2: ~ ₹1,569 – ₹1,570
S3: ~ ₹1,539 – ₹1,540
📊 Technical Indicators Snapshot
(Not direct price levels, but useful context on daily price behavior)
Moving averages (20/50/100/200) are in the ~₹1,530‑₹1,590 range, offering dynamic support/resistance clusters.
RSI & momentum oscillators on some indicators show mixed to neutral momentum on daily charts — suggesting a range‑bound bias unless there’s a breakout.
📌 How Traders Use These Levels
Bullish scenario: A sustained close above ₹1,700 could open upside to ₹1,730/₹1,780.
Bearish scenario: Breakdown below ₹1,620 and ₹1,570 may head toward ₹1,540 support.
Pivot area (~₹1,660) acts as a short‑term balance zone: above it favors buyers, below it favors sellers.
BTCUSD — Long-Term Structural Context (Monthly)Bitcoin continues to trade within a well-defined long-term rising structure on the monthly timeframe.
Price remains above the primary structural pivot, indicating that the broader uptrend is intact, despite intermediate volatility.
Key Observations:
• Long-term rising channel remains respected
• Recent price action reflects structural digestion, not trend reversal
• No higher-timeframe invalidation observed at present
Key Levels (Structural Reference):
• 69,000 — Major regime / structural pivot
• 15,479 — Cycle-degree base support
• 3,122 — Long-term historical support
• 152 — Extreme tail reference (legacy)
Structural Invalidation:
• A sustained break below 15,479 would question the long-term bullish structure
• Above this level, pullbacks remain corrective in nature
Context Note:
This chart reflects structural positioning , not short-term trading signals.
#Bitcoin #BTCUSD #CryptoMarket #MarketStructure #ElliottWave #LongTermTrend #TechnicalAnalysis #MarketOmorph
PIDILITIND 1 Week Time Frame 📌 Current Weekly Price Context (as of 16‑17 Jan 2026)
Last seen price: ~₹1,475 on NSE (latest technical snapshot)
Weekly momentum on short/medium averages is neutral (no strong trend bullish or bearish on EMA/SMA clusters)
RSI and other oscillators are also neutral to modestly positive — not extreme.
📈 Weekly Pivot & Key Levels (classic weekly pivot analysis)
Resistance Zones
1. R1: ~₹1,498–₹1,500
2. R2: ~₹1,507–₹1,520
3. R3: ~₹1,520+ (next cluster)
(Weekly pivot resistances based on recent price action)
Pivot Point
Weekly Pivot: ~₹1,484–₹1,486
Above this pivot → slightly bullish bias; below → slightly bearish
Support Zones
1. S1: ~₹1,476–₹1,478
2. S2: ~₹1,462–₹1,470
3. S3: ~₹1,453–₹1,456
(Weekly pivot support levels)
📅 Weekly Levels Summary (Rounded)
Level Price Zone (Approx)
R3 ₹1,520+
R2 ₹1,507–₹1,520
R1 ₹1,498–₹1,500
Pivot ₹1,484–₹1,486
S1 ₹1,476–₹1,478
S2 ₹1,462–₹1,470
S3 ₹1,453–₹1,456
RBLBANK 1 Day Time Frame 📊 Daily Support & Resistance Levels
Immediate resistances:
~₹315–₹318 area — observed short-term resistance zone and recent highs.
~₹325–₹330 — upper resistance band near recent 52-week highs.
Immediate supports:
~₹300–₹295 — important short-term support zone on daily charts.
~₹285–₹280 — next support cluster if breakdown below ₹295 occurs.
📉 Pivot & Intraday Levels (Indicative)
(These are based on typical pivot calculations from recent sessions — actual values will vary daily)
Pivot: around ₹290–₹295.
R1: ~₹295–₹300
R2: ~₹300–₹305
S1: ~₹285–₹280
S2: ~₹280–₹275
(Pivot-based levels give clues for intraday trading and are often recalculated each day.)
📈 Technical Indicator Context (Daily)
RSI (~50) — neutral momentum, neither overbought nor oversold.
Short MA structure shows mixed signals; some shorter SMAs/EMAs near current price.
MACD slightly bearish to neutral on some sources.
🧠 Notes for Daily Traders
Bullish break above ~₹318–₹320 with volume can open up short-term upside towards ₹325–₹330+.
A daily close below ~₹295 may signal short-term weakness and can expose deeper support around ₹285–₹280.