OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Updated Sprenkle 1964 Option Pricing Model w/ Num. Greeks [Loxx]
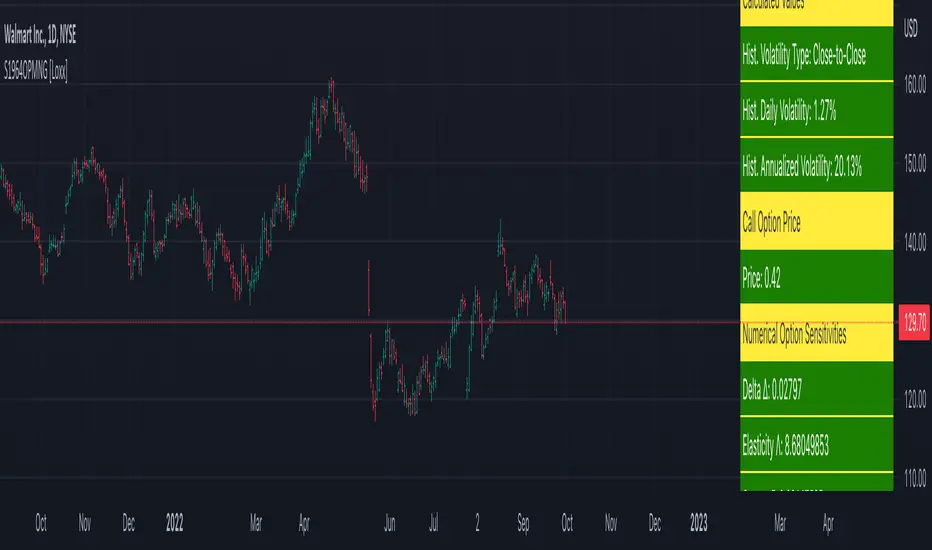
Sprenkle 1964 Option Pricing Model w/ Num. Greeks [Loxx] is an adaptation of the Sprenkle 1964 Option Pricing Model in Pine Script. The following information is an except from Espen Gaarder Haug's book "Option Pricing Formulas".
The Sprenkle Model
Sprenkle (1964) assumed the stock price was log-normally distributed and thus that the asset price followed a geometric Brownian motion, just as in the Black and Scholes (1973) analysis. In this way he ruled out the possibility of negative stock prices, consistent with limited liability. Sprenkle moreover allowed for a drift in the asset price, thus allowing positive interest rates and risk aversion (Smith, 1976). Sprenkle assumed today's value was equal to the expected value at maturity.
c = S * e^(rho*T) * N(d1) - (1 - k) * X * N(d2)
d1 = (log(S/X) + (rho + v^2 / 2) * T) / (v * T^0.5)
d2 = d1 - (v * T^0.5)
Inputs
S = Stock price.
X = Strike price of option.
T = Time to expiration in years.
r = Risk-free rate
v = Volatility of the underlying asset price
k = Market risk aversion adjustment
rho = Average growth rate share
cnd (x) = The cumulative normal distribution function
nd(x) = The standard normal density function
nd(x) = The standard normal density function
convertingToCCRate(r, cmp) = Rate compounder
Numerical Greeks or Greeks by Finite Difference
Analytical Greeks are the standard approach to estimating Delta, Gamma etc... That is what we typically use when we can derive from closed form solutions. Normally, these are well-defined and available in text books. Previously, we relied on closed form solutions for the call or put formulae differentiated with respect to the Black Scholes parameters. When Greeks formulae are difficult to develop or tease out, we can alternatively employ numerical Greeks - sometimes referred to finite difference approximations. A key advantage of numerical Greeks relates to their estimation independent of deriving mathematical Greeks. This could be important when we examine American options where there may not technically exist an exact closed form solution that is straightforward to work with. (via VinegarHill FinanceLabs)
Things to know
The Sprenkle Model
Sprenkle (1964) assumed the stock price was log-normally distributed and thus that the asset price followed a geometric Brownian motion, just as in the Black and Scholes (1973) analysis. In this way he ruled out the possibility of negative stock prices, consistent with limited liability. Sprenkle moreover allowed for a drift in the asset price, thus allowing positive interest rates and risk aversion (Smith, 1976). Sprenkle assumed today's value was equal to the expected value at maturity.
c = S * e^(rho*T) * N(d1) - (1 - k) * X * N(d2)
d1 = (log(S/X) + (rho + v^2 / 2) * T) / (v * T^0.5)
d2 = d1 - (v * T^0.5)
Inputs
S = Stock price.
X = Strike price of option.
T = Time to expiration in years.
r = Risk-free rate
v = Volatility of the underlying asset price
k = Market risk aversion adjustment
rho = Average growth rate share
cnd (x) = The cumulative normal distribution function
nd(x) = The standard normal density function
nd(x) = The standard normal density function
convertingToCCRate(r, cmp) = Rate compounder
Numerical Greeks or Greeks by Finite Difference
Analytical Greeks are the standard approach to estimating Delta, Gamma etc... That is what we typically use when we can derive from closed form solutions. Normally, these are well-defined and available in text books. Previously, we relied on closed form solutions for the call or put formulae differentiated with respect to the Black Scholes parameters. When Greeks formulae are difficult to develop or tease out, we can alternatively employ numerical Greeks - sometimes referred to finite difference approximations. A key advantage of numerical Greeks relates to their estimation independent of deriving mathematical Greeks. This could be important when we examine American options where there may not technically exist an exact closed form solution that is straightforward to work with. (via VinegarHill FinanceLabs)
Things to know
- Only works on the daily timeframe and for the current source price.
- You can adjust the text size to fit the screen
Release Notes
Revised compounding function"Period Rate" to adjust to T period calculation. Release Notes
Updated H. Vol display format to percentage.Release Notes
fixed errorOpen-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Public Telegram Group, t.me/algxtrading_public
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.
Open-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Public Telegram Group, t.me/algxtrading_public
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
VIP Membership Info: patreon.com/algxtrading/membership
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.