OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
6 Band Parametric EQ
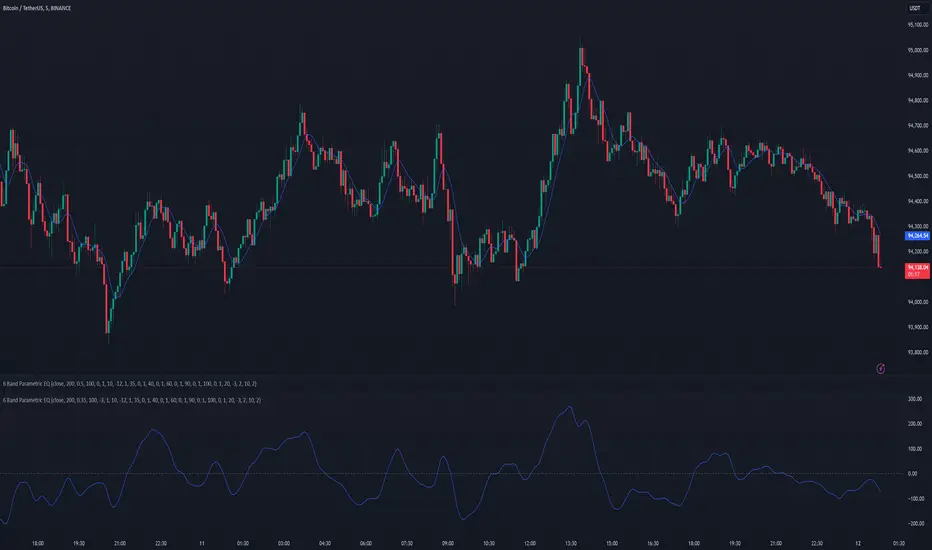
This indicator implements a complete parametric equalizer on any data source using high-pass and low-pass filters, high and low shelving filters, and six fully configurable bell filters. Each filter stage features standard audio DSP controls including frequency, Q factor, and gain where applicable. While parametric EQ is typically used for audio processing, this implementation raises questions about the nature of filtering in technical analysis. Why stop at simple moving averages when you can shape your signal's frequency response with surgical precision? The answer may reveal more about our assumptions than our indicators.
Filter Types and Parameters
High-Pass Filter:
A high-pass filter attenuates frequency components below its cutoff frequency while passing higher frequencies. The Q parameter controls resonance at the cutoff point, with higher values creating more pronounced peaks.
Low-Pass Filter:
The low-pass filter does the opposite - it attenuates frequencies above the cutoff while passing lower frequencies. Like the high-pass, its Q parameter affects the resonance at the cutoff frequency.
High/Low Shelf Filters:
Shelf filters boost or cut all frequencies above (high shelf) or below (low shelf) the target frequency. The slope parameter determines the steepness of the transition around the target frequency, with a value of 1.0 creating a gentle slope and lower values making the transition more abrupt. The gain parameter sets the amount of boost or cut in decibels.
Bell Filters:
Bell (or peaking) filters create a boost or cut centered around a specific frequency. A bell filter's frequency parameter determines the center point of the effect, while Q controls the width of the affected frequency range - higher Q values create a narrower bandwidth. The gain parameter defines the amount of boost or cut in decibels.
All filters run in series, processing the signal in this order: high-pass → low shelf → bell filters → high shelf → low-pass. Each stage can be independently enabled or bypassed.
The frequency parameter for all filters represents the period length of the targeted frequency component. Lower values target higher frequencies and vice versa. All gain values are in decibels, where positive values boost and negative values cut.
The 6-Band Parametric EQ combines these filters into a comprehensive frequency shaping tool. Just as audio engineers use parametric EQs to sculpt sound, this indicator lets you shape market data's frequency components with surgical precision. But beyond its technical implementation, this indicator serves as a thought experiment about the nature of filtering in technical analysis. While traditional indicators often rely on simple moving averages or single-frequency filters, the parametric EQ takes this concept to its logical extreme - offering complete control over the frequency domain of price action. Whether this level of filtering precision is useful for analysis is perhaps less important than what it reveals about our assumptions regarding market data and its frequency components.
Filter Types and Parameters
High-Pass Filter:
A high-pass filter attenuates frequency components below its cutoff frequency while passing higher frequencies. The Q parameter controls resonance at the cutoff point, with higher values creating more pronounced peaks.
Low-Pass Filter:
The low-pass filter does the opposite - it attenuates frequencies above the cutoff while passing lower frequencies. Like the high-pass, its Q parameter affects the resonance at the cutoff frequency.
High/Low Shelf Filters:
Shelf filters boost or cut all frequencies above (high shelf) or below (low shelf) the target frequency. The slope parameter determines the steepness of the transition around the target frequency, with a value of 1.0 creating a gentle slope and lower values making the transition more abrupt. The gain parameter sets the amount of boost or cut in decibels.
Bell Filters:
Bell (or peaking) filters create a boost or cut centered around a specific frequency. A bell filter's frequency parameter determines the center point of the effect, while Q controls the width of the affected frequency range - higher Q values create a narrower bandwidth. The gain parameter defines the amount of boost or cut in decibels.
All filters run in series, processing the signal in this order: high-pass → low shelf → bell filters → high shelf → low-pass. Each stage can be independently enabled or bypassed.
The frequency parameter for all filters represents the period length of the targeted frequency component. Lower values target higher frequencies and vice versa. All gain values are in decibels, where positive values boost and negative values cut.
The 6-Band Parametric EQ combines these filters into a comprehensive frequency shaping tool. Just as audio engineers use parametric EQs to sculpt sound, this indicator lets you shape market data's frequency components with surgical precision. But beyond its technical implementation, this indicator serves as a thought experiment about the nature of filtering in technical analysis. While traditional indicators often rely on simple moving averages or single-frequency filters, the parametric EQ takes this concept to its logical extreme - offering complete control over the frequency domain of price action. Whether this level of filtering precision is useful for analysis is perhaps less important than what it reveals about our assumptions regarding market data and its frequency components.
Open-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.
Open-source script
In true TradingView spirit, the creator of this script has made it open-source, so that traders can review and verify its functionality. Kudos to the author! While you can use it for free, remember that republishing the code is subject to our House Rules.
Disclaimer
The information and publications are not meant to be, and do not constitute, financial, investment, trading, or other types of advice or recommendations supplied or endorsed by TradingView. Read more in the Terms of Use.