Chart Patterns
M&M: Unfazed by Global Entry, Primed for ₹4,000 MilestoneMahindra & Mahindra (M&M) remains a conviction bullish pick despite recent sectoral volatility. While the India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) has sparked concerns over cheaper European imports, the threat from luxury giants like BMW and Audi is largely overstated. These brands cater to the ₹50L+ luxury segment, whereas M&M’s "lifestyle" crown jewel—the Thar—and its premium SUV lineup (XUV700, Scorpio-N) dominate the high-growth ₹15L–₹30L bracket where brand loyalty is deeply entrenched.
Fundamentally, M&M’s Q3 FY26 performance underscores its resilience, supported by a massive order backlog and the successful rollout of the "Born Electric" (BE) series. The EU deal actually serves as a long-term catalyst for M&M’s global expansion rather than a domestic headwind.
Technically, the stock is consolidating near its 50-day EMA, forming a strong base. A decisive breakout above the recent resistance at 3,500 will signal a trend continuation. We maintain a strong buy with immediate technical targets of 3,750 and a long-term objective of 4,000.
XAUUSD (4H) – Buy Side ViewXAUUSD (4H) – Buy Side View
Overall Bias:
The higher-timeframe trend is still bullish. The current fall looks like a healthy correction, not a full trend reversal.
📍 Strong Buy Zones
5190–5110 → Primary demand / high-probability buy zone
4990–5050 → Deep buy zone (positional / swing)
✅ Buy Confirmation Needed
4H bullish engulfing or pin bar
Clear rejection wicks from the support zone
Optional: volume expansion on bullish candles
🎯 Buy Targets
TP1: 5355
TP2: 5465
TP3: 5600+
🛑 Invalidation
A 4H close below 4990 weakens the bullish outlook
XAUUSD Bullish Flag on 15-Min – Breakout Watch Above 5560✅ NEW TRADE (BEST RIGHT NOW)
🔵 BUY ONLY ON BREAKOUT (high-probability)
📌 Condition
👉 XAUUSD 15-min candle CLOSE above 5560
(No wick-only breakout. Close matters.)
🟢 Trade
Buy Gold
🎯 Targets
T1: 5600 → 5620
T2: 5660
🛑 Stop Loss
5535 (strict)
🧠 Why this works:
Range expansion after consolidation
Momentum resumes
Option premium expands fast
🟡 Alternate trade (only if rejection)
📌 Condition
Price fails at 5560
AND breaks below 5485
🔴 Trade
Buy Put / Sell Gold
Target: 5420 → 5380
SL: 5515
⚠️ This is secondary, not preferred.
❌ No trade zone (very important)
Between 5500 – 5555
This is chop → premium decay zone
🧭 Direction bias
Above 5560 → Strong bullish continuation
Below 5485 → Deeper pullback
$SVRS forming a multi year cup and handle breakoutTSXV:SVRS is a compelling setup, nearly 8 years of consolidation (cup phase) followed by an impulse movement in 2020, and again 5 year long time correction handle pattern. This is a solid setup which we don't find often. What i like is the volume buildup near the handle phase, which is a clear institutional smart money surge.
I am buying here, and clearly this is not a short term trade. My downside risk is capped at 30%.
GMDCLTD – Technical Update | Price Approaching Key ResistanceGMDCLTD has respected the previously identified support zone and is now trading near an important resistance area. The chart structure remains constructive, with price action showing controlled higher-high and higher-low formation.
🔍 Technical Overview:
• Major Support Zone: ₹480
Price formed a strong base near this level, which acted as a demand area and initiated the current upward move.
• Current Price: ₹618.35
• Trend Structure:
Price continues to move above an ascending trendline, indicating sustained buying interest on minor pullbacks.
• Volume Observation:
Volume expansion was visible during impulsive moves, suggesting active participation from buyers rather than weak speculative spikes.
⚠️ Key Levels to Monitor:
• Resistance Zone: ₹640
This level remains a near-term supply area.
• Continuation Scenario:
A daily close above ₹640 with strong volume would improve the probability of further upside and trend continuation.
• Consolidation Risk:
Failure to sustain above resistance may result in short-term sideways movement or a mild pullback toward the trendline.
🧭 Trade Structure:
• Support Levels:
– Rising trendline
– ₹480 (positional base)
• Bias:
Bullish above trendline, neutral to cautious near resistance until confirmation.
Focus on structure, volume, and confirmation rather than anticipation.
— Ayushi Shrivastava
NISM-Certified Research Analyst
Graphite- At a Critical Inflection Point – Breakout or Trap?Graphite India is currently trading near a multi-year decision zone, where both technical structure and long-term strategic shifts are converging. This makes the stock interesting — but also risky — at current levels.
By Ayushi Shrivastava | Market Analyst
🔹 Technical Outlook
Current Price: ~₹666
The stock is attempting to break a long-term descending trendline in place since 2018, which makes this zone structurally important.
A sustained breakout above ₹694–700, supported by strong volume expansion, could open the door for a meaningful upside move.
Recent sessions have shown above-average volume, hinting at increased participation from informed players.
⚠ False Breakout Risk:
A rejection near the ₹690–700 resistance zone or a breakout without follow-through volume could result in a bull trap and lead to range continuation or a pullback.
🔹 Fundamental Snapshot
Balance Sheet Strength: Virtually debt-free (D/E ~0.03), providing strong financial stability.
Earnings Pressure: Net profit has declined ~48% YoY due to weak global graphite electrode pricing and macro disruptions.
Valuation: Trading at a premium P/E compared to industry averages, implying that future growth is already partially priced in.
🔹 Strategic Optionality – EV Play
The company has announced a ₹4,330 crore investment into Synthetic Graphite Anode Materials (SGAM) for lithium-ion batteries.
This marks a strategic shift beyond cyclical steel demand into the EV value chain.
While the opportunity is large, execution and commercialization risks remain, and revenue visibility is medium-to-long term.
🔹 Smart Money Signals
FII holding has increased from ~4.27% to ~6.43%, even as retail participation softened.
This often reflects long-term positioning, not short-term momentum chasing.
🧠 Final View
Graphite India is in a transition phase — financially strong but earnings-challenged, with a promising yet execution-dependent EV strategy.
Long-term investors: Can track the EV project progress and accumulation patterns.
Short-term traders: Should wait for a clear breakout and sustained close above ₹694–700 with volume to avoid false signals.
📌 This is a stock to watch closely — patience and confirmation matter more than prediction.
Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Always manage risk and confirm setups with your own analysis.
Getting Creative on SilverThe RSI on Silver is now above 80/90 on all time frames, putting it in bubble territory. With the sixth consecutive day of gains going on, I am looking at the parallel channel and potential wedge formation for the next few days. Let us see if these trendlines can offer any resistance here. A reversal in the dollar could be one catalyst.
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Resistance Breakout in RAIN
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
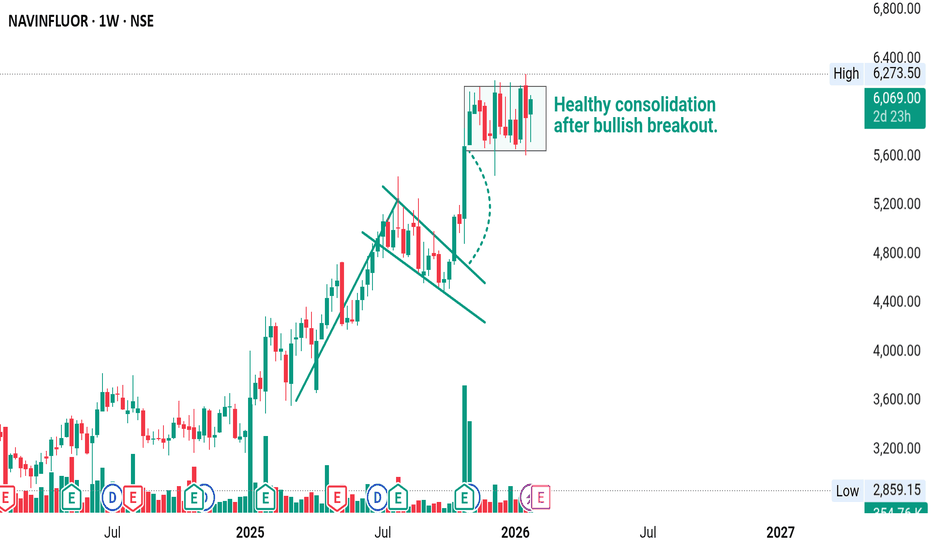
NAVINFLUOR – Breakout After Bullish Flag | Trend ResumesNAVINFLUOR was already in a strong uptrend, showing higher highs and higher lows.
After a sharp bullish move, the stock didn’t collapse — instead, it moved into a controlled pullback inside a downward sloping channel (bullish flag).
This is a sign of profit booking, not weakness.
Price then broke out of the flag with strength and is now consolidating near highs, which shows buyers are still in control.
This type of price action usually indicates: 👉 Strong demand
👉 Trend continuation
👉 Institutions accumulating on dips
As long as the consolidation holds above the breakout zone, the overall structure remains bullish and favors further upside over time.
No panic selling.
No distribution.
Just a healthy pause in a strong trend.
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5% DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Trendline Breakout in KARURVYSYA
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Resistance Breakout in OIL
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
KIRLOSENG Healthy Pullback After Strong RallyKIRLOSENG continues to trade inside a well-defined rising channel. After a strong impulsive move to the upside, the stock is now consolidating near channel support — a sign of healthy price action rather than weakness.
The structure remains bullish as long as price respects the lower trendline. A bounce from this zone could lead to another move toward the upper channel resistance around previous highs.
Trend remains intact unless the channel support breaks decisively.
MTARTECH Near Multi-Year Resistance After Strong RallyMTARTECH has made a sharp recovery from lower levels and is now moving back toward a major multi-year resistance zone that has capped price since 2021.
This resistance trendline has acted as a strong supply area in the past, leading to multiple rejections. The current move shows strength and momentum, but price is still below the long-term breakout level.
A decisive weekly close above this resistance with volume would confirm a structural breakout and open room for further upside.
Until then, this zone remains a critical area where profit booking or consolidation can occur.
GVT&D Strong Bounce From Trendline — Key Resistance AheadGVT&D has taken strong support from the falling trendline, which has acted as a key demand zone in the past.
From this support area, price has bounced sharply and is now approaching the major horizontal resistance zone where sellers have previously stepped in multiple times.
This resistance remains a crucial level to watch.
A strong breakout and close above this zone would open the door for further upside momentum.
However, if price faces rejection again from this area, consolidation or a pullback could follow.
For now, the trendline support has done its job — next move depends on how price reacts at resistance.
ANET | No Fireworks, Just Higher Prices to 178 target📡 Arista Networks, Inc. (ANET)
Calm Pullback, Serious Business | Bullish Continuation Setup
🧠 Let’s be honest…
Not every stock needs fireworks to make money.
Some just do the work quietly — and ANET is one of them.
After a healthy reset, Arista is back above key value and VWAP, telling us something simple but important: big money didn’t leave — it waited.
📊 What the Chart Is Saying (No Drama)
✔ Higher-timeframe uptrend still intact
✔ Pullback respected demand (no panic selling)
✔ VWAP reclaimed → acceptance, not rejection
✔ Overhead supply mostly chewed through
Translation: This is digestion, not distribution.
🎯 Trade Plan (Clean & Disciplined)
🟢 Buy Zone
$138 – $145
Where value lives, risk is defined, and emotions stay out.
🎯 Upside Targets
Target 1: $165
Target 2: $178
Stretch Target: $195 (if momentum keeps its foot on the gas)
🔴 Stop Loss
Below $128 (daily close)
If it breaks demand, we walk away — no hero trades.
⚖️ Risk–Reward Snapshot
Risk: ~8–9%
Upside potential: 20–28%
High-confidence upside: 10–14%
Not flashy. Just efficient.
🏢 Company Profile (Why Institutions Care)
Arista Networks builds high-performance networking gear that keeps modern data centers running at scale.
🧩 Core Products
Cloud networking switches
High-speed Ethernet platforms
EOS (software-driven network OS)
🤝 Customers
Hyperscale cloud providers
AI & data-center operators
Large enterprises moving serious data
If AI is the brain, ANET is part of the nervous system.
💼 Business Model in One Line
High-margin hardware + sticky software + exploding data demand
= repeat customers with deep pockets
No gimmicks. No hype cycles. Just infrastructure that has to work.
🧭 Final Take
ANET doesn’t need to scream to move higher.
As long as price holds above the $128–130 demand zone, the path of least resistance remains up. Pullbacks are opportunities, not warnings.