Open Interest & Option Chain Analysis Topic: Open Interest & Option Chain Analysis
1: What is Open Interest (OI)?
Simple Meaning:
Open Interest means the total number of active option or futures contracts in the market that haven’t been closed yet.
Easy Example:
If you and your friend enter into a new option trade, the open interest is 1. If someone else joins with a new trade, it becomes 2. But if you close your trade, it becomes 1 again.
What It Tells You:
If OI is increasing, more people are joining the market.
If OI is decreasing, traders are exiting their trades.
Combine OI with Price Movement:
Price going up + OI going up = New buying → Bullish
Price going down + OI going up = New selling → Bearish
Price going up + OI going down = Traders exiting shorts → Short covering
Price going down + OI going down = Traders exiting longs → Profit booking
2: What is an Option Chain?
Simple Meaning:
Option Chain is a table that shows all the call and put options for a stock at different strike prices.
What You’ll See in an Option Chain:
Strike Price: The price you agree to buy/sell.
Calls (CE): Right to buy.
Puts (PE): Right to sell.
Open Interest (OI): How many contracts are active.
Volume: How many were traded today.
LTP: Latest price of that option.
3: How to Read Option Chain Like a Pro
1. Spot the Support Levels:
Look for the highest OI on the put (PE) side → Big money sees this as support.
2. Spot the Resistance Levels:
Look for the highest OI on the call (CE) side → Traders think price won't go above this.
3. Track Market Mood:
If more puts are being written (PE OI going up) → Traders are bullish.
If more calls are being written (CE OI going up) → Traders are bearish.
4. PCR (Put Call Ratio):
PCR > 1 → More puts than calls = Bullish
PCR < 1 → More calls than puts = Bearish
Fundamental-analysis
Advance Institutions Option Trading - Lecture 5When it comes to low risk options strategies, selling a call spread and selling a put spread are techniques that traders often utilize. These strategies are characterized by a high probability of profit due to the low probability of loss, and they limit risk in case the trade doesn't go as planned.
While day traders look at minute-to-minute price changes, swing traders look at trends that play out over several days. This is considered one of the most profitable trading types that allows more flexibility, as you don't need to be glued to your computer screen all day.
Advance Institutions Option Trading - Lecture 3Options trading might feel like gambling on a single trade, but informed decisions make it fundamentally different. Reckless trading without a plan can resemble gambling but is not the proper way to trade. With discipline and skill, options trading stands apart from luck-based activities.
Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Certain requirements must be met to trade options. Before engaging in the purchase or sale of options, investors should understand the nature of and extent of their rights and obligations and be aware of the risks involved in investing with options.
Advance Institutions Option Trading - Lecture 4If you're looking for a simple options trading definition, it goes something like this: Options trading gives you the right or obligation to buy or sell a specific security on or by a specific date at a specific price. An option is a contract that's linked to an underlying asset, such as a stock or another security.
Options trading also involves two parties: the holder (buyer) and the writer (sometimes called the seller). Holders are investors who purchase contracts, while writers create them. The holder pays the writer a premium for the right to sell or buy a stock by a certain date.
Advance Institutions Option Trading - Lecture 1Institutional traders are professionals trading for large entities like mutual funds, hedge funds, etc. Oftentimes they will trade options to hedge their positions, but they may also trade options as pure speculation.
Equirus Securities is one of the leading domestic institutional equities brokerage firms in India with more than 180 companies under over coverage and empanelment with almost all domestic institutions and many leading FIIs.
NFP STORM BREWING: WILL GOLD BREAK HIGHER OR DIVE LOWER?XAUUSD – NFP STORM BREWING: WILL GOLD BREAK HIGHER OR DIVE LOWER?
Gold enters a highly sensitive phase ahead of tonight’s Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) release – one of the most influential data points for global financial markets. With US-China trade tensions rekindling and sovereign debt concerns mounting in the US, the yellow metal could experience a major breakout or a sharp reversal during the New York session.
🌍 MACRO & FUNDAMENTAL OUTLOOK
US-China trade talks have resurfaced, with concerns around tariffs and strategic metals dominating headlines. China's recent stance signals it may take stronger defensive actions.
The US national debt is projected to hit $55 trillion by 2034, prompting global central banks to ramp up gold purchases as a strategic hedge.
Fed Chair Powell reiterated a “no rush to cut” stance, yet political pressure is mounting – especially with Donald Trump urging immediate rate cuts following the weakest ADP job growth in two years.
Unemployment Claims released today came in slightly better than expected (236K vs. 240K), adding fuel to speculations around a softer NFP print – potentially bullish for gold.
🔍 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (H1 – EMA 13/34/89/200)
The chart shows a clean impulsive wave structure. After hitting the resistance zone at 3408–3410, gold entered a consolidation range.
Price is currently hovering around EMA 89–200, suggesting trend divergence and uncertainty ahead of NFP.
A breakdown below the 3344–3332 support zone could push price down to the FVG (Fair Value Gap) at 3320, which may act as a strong liquidity pool for buyers.
⚠️ KEY LEVELS TO WATCH
Resistance: 3380 – 3392 – 3408 – 3436
Support: 3365 – 3350 – 3344 – 3332 – 3320
🧭 TRADE SETUPS
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3408 – 3410
Stop Loss: 3415
Take Profit: 3404 → 3400 → 3395 → 3390 → 3380 → 3370 → 3360 → 3350
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3318 – 3316
Stop Loss: 3310
Take Profit: 3322 → 3326 → 3330 → 3335 → 3340 → 3350 → 3360 → ???
✅ CONCLUSION
Gold is poised for a volatile breakout with NFP acting as the key catalyst. A soft jobs report may trigger a breakout above 3410, while stronger-than-expected numbers could fuel a bearish reversal. In this sensitive phase, traders should stick to defined zones and wait for confirmed liquidity reactions rather than chasing price impulsively.
Cummins India: Technical + Fundamental BreakdownIn this video, I dive into Cummins India, combining technical analysis with key fundamental insights. I cover chart patterns, volume action, support/resistance zones, and recent financial performance to help identify a potential investing & swing trade opportunity.
🔍 Perfect for traders who want both data and conviction behind their trades.
Watch, learn, and trade smarter.
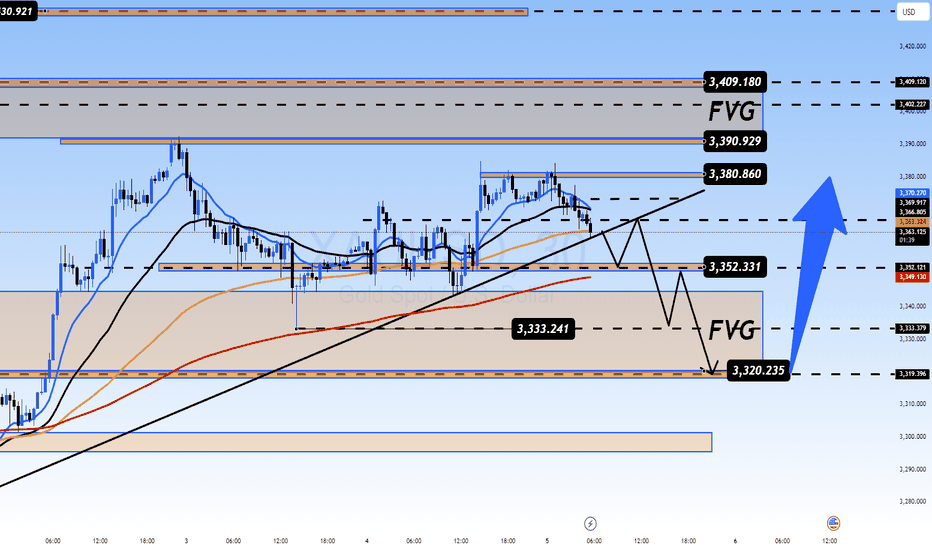
Gold Awaits NFP Data: Will It Explode or Break Down from Range?XAUUSD – Gold Awaits NFP Data: Will It Explode or Break Down from Range?
Gold remains in a consolidation phase, coiling tightly ahead of the highly anticipated Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report. With traders on edge, the market is poised for a breakout – but in which direction?
🌍 MACRO & FUNDAMENTAL INSIGHT
Donald Trump reignited pressure on the Federal Reserve, calling for an immediate rate cut, especially after the recent ADP Employment Report showed the weakest job growth in over two years.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell, however, maintains a cautious stance, emphasizing that “no rush” to cut rates unless inflation convincingly trends lower.
Meanwhile, U.S. national debt is projected to hit $55 trillion by 2034, with unchecked fiscal expansion. This is fueling a global central bank gold-buying spree, with many purchases not even officially reported.
💡 This confluence of macroeconomic stress, monetary uncertainty, and geopolitical tension is pushing gold into the spotlight as a safe haven.
🔍 MARKET POSITIONING & SHORT-TERM DRIVERS
Unemployment Claims released today: 236K vs previous 240K – slightly positive, but not strong enough to offset weak labor momentum.
Treasury yields remain high (10Y at 4.55%), suggesting that while inflation fears persist, risk appetite is fragile.
The NFP release will likely serve as the catalyst for gold's next directional move, especially as liquidity builds up in a narrowing technical structure.
📈 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (H1 – EMA 13/34/89/200)
Price is consolidating within a sideways range between 3333–3380, forming a classic liquidity trap just below key resistance.
The 3352–3333 zone is a critical structural support. A break below this level opens the door for a dip toward the FVG liquidity zone around 3320–3318.
On the upside, 3388–3400 remains a rejection zone. A clean breakout could target 3409 and even Fibonacci extension resistance at 3435–3445.
🔑 KEY TECHNICAL LEVELS
Resistance: 3388 – 3392 – 3400 – 3409
Support: 3355 – 3333 – 3320 – 3318
🧭 TRADING STRATEGY
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3320 – 3318
SL: 3314
TP: 3324 → 3328 → 3332 → 3336 → 3340 → 3350 → 3360 → ???
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3408 – 3410
SL: 3414
TP: 3404 → 3400 → 3396 → 3390 → 3386 → 3380 → 3370
✅ FINAL THOUGHTS
Gold is currently at the eye of the storm, with both fundamental and technical indicators aligned for volatility. The coming NFP release could tilt the balance sharply.
Stay disciplined: trade key zones only, wait for confirmation, and prioritize risk management. In markets like these, precision beats prediction.
Gold Stalls Ahead of Key Trade TalksGold Stalls Ahead of Key Trade Talks – Will Price Explode Out of the 3345–3370 Range?
After Monday’s explosive rally, gold is currently consolidating within a tight price range. The market is at a critical juncture, awaiting high-level trade talks between the U.S. and China — an event that could serve as a major catalyst for the next directional move.
🌍 MACRO OUTLOOK & MARKET SENTIMENT
A major trade call between Trump and President Xi Jinping is on the horizon. This conversation could reset global trade expectations and potentially trigger large moves in risk assets.
Last week’s strong U.S. jobs data (NFP) pushed back expectations of Fed rate cuts. Treasury yields remain elevated, which is temporarily capping gold’s upside.
Market sentiment is neutral-to-cautious, with traders waiting for confirmation of a breakout or breakdown before committing capital to new positions.
📈 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (H1 – EMA 13/34/89/200)
Gold appears to be in a wave 4 correction, consolidating after completing wave 3.
EMAs remain aligned to the upside (bullish), suggesting the broader trend still favors buyers.
Key range:
Above 3370 → breakout confirmation → momentum push toward 3400–3410
Below 3345 → breakdown → fast dip to 3310–3300 to complete wave 4 and initiate wave 5 upward
🧭 STRATEGIC ZONES
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3317 – 3315
Stop Loss: 3310
Take Profits:
3322 → 3326 → 3330 → 3334 → 3338 → 3345 → 3350 → 3360
This zone aligns with a strong FVG + EMA89 support. A bullish reaction here could provide a high-probability entry for the next impulsive leg upward (wave 5).
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3372 – 3374
Stop Loss: 3378
Take Profits:
3368 → 3364 → 3360 → 3356 → 3350 → 3345
3370 is a critical resistance zone. Any rejection at this level with weak momentum or divergence could open a short-term bearish correction back toward 331x levels.
✅ SUMMARY
Gold is trapped in a decision zone between 3345–3370. The market awaits clarity from macro headlines and technical breakout signals. Until then, traders should watch key levels closely, stay patient, and position accordingly based on price action confirmation at strategic zones.
Gold (XAU/USD) 1H Analysis – Potential Breakout Play🟡 Gold (XAU/USD) 1H Analysis – Potential Breakout Play 📈
🔎 Key Levels and Zones
Resistance Zone: Around $3,410 – $3,430.
Midpoint/Key Resistance-Turned-Support: Around $3,360 – $3,370.
Support Zone: Around $3,270 – $3,290.
🔀 Chart Structure & Momentum
The price is in a short-term bullish recovery after finding strong support at the $3,270 – $3,290 level.
The breakout above the midpoint around $3,360 is a significant bullish trigger, suggesting that bulls are taking charge.
📊 Scenario Analysis
Bullish Scenario (Primary Bias) 🟢: If the price holds above the midpoint ($3,360), we expect a push towards the resistance zone ($3,410 – $3,430). This aligns with the “resistance-flip-support” concept, where the previous resistance becomes a new support base.
Bearish Scenario (Alternate Bias) 🔴: If the price fails to hold above $3,360, a re-test of the support zone ($3,270 – $3,290) is likely. From there, bulls will likely try to defend the area and launch another attempt upwards.
📌 Conclusion
The path of least resistance currently favors the bulls while the $3,360 level holds.
Watch for consolidation near $3,360 – $3,370 as a healthy retest before potential continuation to the upside target zone ($3,410 – $3,430).
📅 Near-Term Bias
Remain cautiously bullish while above $3,360.
A confirmed breakout above $3,410 opens room for further bullish momentum, while a breakdown below $3,360 can re-test the key support at $3,270.
MARKET WAITS FOR TRUMP–XI TRADE CALL XAUUSD PLAN – JUNE 3XAUUSD PLAN – JUNE 3 | GOLD CORRECTS AFTER $100 SURGE | MARKET WAITS FOR TRUMP–XI TRADE CALL
After an explosive $100+ rally earlier this week, gold has entered a sharp correction phase, dropping $30 during the Asian session. This pullback comes as the market anticipates a high-level trade call between former President Trump and President Xi Jinping, which could reshape short-term expectations around US–China relations and global risk sentiment.
🌍 MACRO CONTEXT – POLITICS MEETS FINANCE:
The upcoming Trump–Xi call is expected to guide markets over the next few sessions and may impact trade risk positioning.
Investors have begun profit-taking following the aggressive rally, leading to temporary risk-off sentiment and cash-out flows.
From an Elliott Wave perspective, wave 3 (the strongest wave) may have completed, and price could now retrace into lower FVG zones to gather liquidity for the next upward move.
📈 TECHNICAL STRUCTURE (H1–H4 – EMA 13/34/89/200):
On higher timeframes (H4 and D1), gold maintains a strong bullish structure.
Price appears to have peaked near 3,402 – 3,409, and is now retracing toward the key FVG support zone between 3,320 – 3,310.
EMAs are beginning to compress after a strong expansion – suggesting the market may consolidate or correct further in the short term.
🧭 KEY PRICE LEVELS:
Support: 3,346 – 3,340 – 3,318 – 3,310 – 3,295
Resistance: 3,374 – 3,388 – 3,402 – 3,410
🔍 TRADE SETUPS:
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3,320 – 3,318
Stop Loss: 3,314
Take Profits:
3,324 – 3,328 – 3,332 – 3,336 – 3,340 – 3,344 – 3,350 – 3,360 – 3,374+
Buy on dips into the liquidity zone or after confirmation candles near EMA13–34 support. Ideal entry for positioning ahead of a potential wave 5 continuation.
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3,388 – 3,390
Stop Loss: 3,394
Take Profits:
3,384 – 3,380 – 3,376 – 3,370 – 3,366 – 3,360 – 3,350
Sell only if there is a strong rejection or bearish divergence near the recent highs – this zone marks the top of wave 3 and potential exhaustion.
📌 SUMMARY:
Gold’s macro structure remains bullish, but short-term corrections are expected. Price may dip into FVG zones to absorb liquidity before launching the next move. Avoid FOMO and follow technical zones with disciplined SL.
BULLISH GAP CONFIRMS BREAKOUT STRUCTUREXAUUSD PLAN – JUNE 2 | BULLISH GAP CONFIRMS BREAKOUT STRUCTURE | GOLD REGAINS SAFE-HAVEN DEMAND
The new trading week kicks off with a strong bullish gap in gold, signaling renewed investor confidence in safe-haven assets amid rising geopolitical tensions. With the US dollar showing early signs of weakness and no clear direction from the Fed, gold is quickly regaining strength as a defensive play.
🌍 MACRO CONTEXT:
US–China trade tensions and renewed Middle East geopolitical risks are pushing capital into gold as a risk hedge.
The US dollar is pulling back slightly, weighed by concerns over the upcoming labor data and persistent inflation.
Institutional portfolios are reportedly increasing exposure to gold as a hedge against macro instability.
➡️ In this context, gold has strong short-term upside potential, especially if price holds above the key breakout zone.
📈 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (H1 – EMA 13/34/89/200):
Price has broken out above the descending trendline and EMA200, confirming bullish momentum.
All EMAs (13–34–89–200) are aligned upward, supporting continuation of the uptrend.
As long as gold holds above 3,309, bulls will likely target previous highs near 3,348 and 3,361.
🔍 TRADE PLAN – JUNE 2:
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3,295 – 3,293
Stop Loss: 3,289
Take Profit Targets:
3,300 – 3,304 – 3,308 – 3,312 – 3,316 – 3,320
Ideal scenario: wait for a retest of the breakout zone or EMA support (13/34) for a low-risk long entry.
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3,347 – 3,349
Stop Loss: 3,353
Take Profit Targets:
3,343 – 3,340 – 3,336 – 3,332 – 3,328 – 3,324 – 3,320
Only consider SELL if there's a strong rejection or bearish divergence at the highs.
📌 SUMMARY:
The bullish gap at the start of the week is a strong signal of trend continuation. Priority should be given to long setups if the price structure stays above key EMAs. Watch for potential fakeouts during NY session or Fed-related headlines. Stick to tight risk management.
XAUUSD PLAN END-OF-MONTH CASHOUT OR TREND REVERSAL? XAUUSD PLAN – MAY 30 | GOLD DROPS SHARPLY IN ASIAN SESSION | END-OF-MONTH CASHOUT OR TREND REVERSAL?
Gold surprised the market this morning with a sharp drop of nearly $30/oz, despite closing yesterday with a strong bullish daily candle. Profit-taking pressure near month-end and uncertainty surrounding US–China trade negotiations have returned gold to a bearish technical structure in the short term.
🌍 MACRO OVERVIEW:
US–China trade talks show no clear progress, with both sides signaling a cautious and non-committal stance.
Hedge funds and large players may be exiting ahead of monthly/weekly candle closes, causing increased volatility.
Meanwhile, investors are waiting for key US PCE inflation data and more Fed speeches, keeping risk sentiment fragile.
➡️ The market remains technically weak and highly reactive. Price is vulnerable to quick liquidity sweeps and false breakouts — best to stay reactive and trade confirmed zones.
📈 TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (H1 – EMA 13/34/89/200):
Gold has broken below EMA89 and is now trading beneath all major EMAs, indicating a strong short-term downtrend.
The resistance zone at 3,322–3,324 aligns with the EMA200 and a descending trendline, making it a prime area for short entries on rejection.
Key support sits at 3,266–3,264. A break below could send price to test deeper levels at 3,235 or even 3,210, following the broader descending channel.
The 3,274–3,276 zone (EMA13 crossing below EMA34) may offer minor reactions for scalpers in the London session.
🔍 TRADE SETUPS FOR TODAY:
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3,266 – 3,264
Stop Loss: 3,260
Take Profits:
3,270 – 3,274 – 3,278 – 3,282 – 3,286 – 3,290 – 3,300
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3,322 – 3,324
Stop Loss: 3,328
Take Profits:
3,318 – 3,314 – 3,310 – 3,306 – 3,300 – 3,295 – 3,290 – 3,280
🎯 INTRADAY SCALPING IDEAS:
BUY SCALP: 3,274 – 3,276 | SL: 3,270 | TP: 1R (50 pips max)
SELL SCALP: 3,302 – 3,304 and 3,310 zone | SL: 50–60 pips | Flexible TP
📌 SUMMARY:
The current momentum is bearish. Focus on short setups unless price clearly reclaims key EMAs. Scalping opportunities exist around reaction zones. With month-end volatility at play, avoid FOMO and stick to strict SL discipline.
💬 Found this plan helpful? LIKE – COMMENT – FOLLOW for daily GOLD strategies from the MMF Team, crafted for serious traders in India and beyond!
GOLD RETESTING KEY ZONES AHEAD OF INFLATION DATA XAUUSD PLAN – MAY 29 | GOLD RETESTING KEY ZONES AHEAD OF INFLATION DATA | HOLDING OR BREAKING?
After yesterday’s sharp decline, GOLD is showing signs of stabilization around the 3,270 region. This appears to be a consolidation phase before the market reacts to key macro events — particularly the upcoming Core PCE inflation report and a string of Fed speeches this week.
🌍 MACRO LANDSCAPE:
US 10-year yields are holding steady near 4.5%, continuing to pressure gold in the short term.
Fed officials remain cautious about rate cuts, pushing back against dovish expectations.
However, concerns over structural fiscal pressure (including Fed losses and budget cuts) support the long-term bullish case for gold.
➡️ In the short term, the market remains range-bound, and tactical entries near key zones offer the best opportunities.
📈 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK (H1):
Gold is consolidating below a major resistance zone at 3,308–3,310, which aligns with the descending trendline and 200 EMA.
Fibonacci retracement zones (0.5–0.618) also highlight strong resistance around 3,297–3,309.
On the downside, support at 3,263 is key; a break below may expose the broader demand zone near 3,246.
🔍 TRADE SETUPS – MAY 29:
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3,247 – 3,245
Stop Loss: 3,241
Take Profit Targets:
3,251 – 3,255 – 3,260 – 3,264 – 3,270 – 3,275 – 3,280
🔵 BUY SCALP: 3,263 – 3,261
Stop Loss: 3,257
Take Profit Targets:
3,266 – 3,270 – 3,275 – 3,280 – 3,290 – 3,300
🔻 SELL SCALP: 3,294 – 3,296
Stop Loss: 3,300
Take Profit Targets:
3,290 – 3,286 – 3,282 – 3,278 – 3,274 – 3,270 – 3,260
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3,308 – 3,310
Stop Loss: 3,314
Take Profit Targets:
3,304 – 3,300 – 3,296 – 3,292 – 3,288 – 3,280
📌 STRATEGY TIP:
Price is range-bound ahead of key data. Avoid entering mid-range. Wait for price to reach the edges (BUY/SELL zones) and look for clear rejection or confirmation candles. Stick to strict risk management.
XAUUSD PLAN – MAY 28 |WATCHING FOMC + EU TRADE TENSIONS XAUUSD PLAN – MAY 28 | GOLD REBOUNDS SLIGHTLY BUT REMAINS UNDER PRESSURE | WATCHING FOMC + EU TRADE TENSIONS
Gold staged a mild technical recovery after last week’s heavy sell-off of nearly $100. While the bounce offers short-term opportunities, overall structure remains under bearish pressure unless bulls can reclaim the upper distribution zone.
🌍 MACRO CONTEXT – TRADE POLICY & MONETARY UNCERTAINTY:
Trump has delayed the 50% tariff on EU goods until July, calling recent trade talks “positive.”
In response, US 10-year yields spiked back above 4.55%, signaling market expectations for prolonged high interest rates.
Meanwhile, the Fed has announced a 10% workforce cut due to ongoing operational losses from interest payments — a rare move that underscores deeper fiscal constraints.
➡️ With mixed risk sentiment and no clear policy direction, Gold remains a safe-haven focus — but vulnerable in the short-term if yields and the dollar continue to rise.
📈 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK (H1):
Gold is currently trading below the 3,335–3,346 resistance zone, which has repeatedly rejected bullish attempts.
If price fails to reclaim this zone, we could see renewed bearish momentum toward the lower FVG support.
The Fair Value Gap near 3,248 remains a major zone of interest if sellers regain control.
🔍 TRADE PLAN – UPDATED LEVELS:
🔻 SELL ZONE: 3,344 – 3,346
Stop Loss: 3,350
Take Profit: 3,340 – 3,336 – 3,332 – 3,328 – 3,324 – 3,320
🔻 SELL SCALP: 3,326 – 3,328
Stop Loss: 3,332
Take Profit: 3,322 – 3,318 – 3,314 – 3,310 – 3,305 – 3,300
🔵 BUY SCALP: 3,278 – 3,276
Stop Loss: 3,272
Take Profit: 3,282 – 3,286 – 3,290 – 3,294 – 3,298 – 3,302 – 3,310
🔵 BUY ZONE: 3,246 – 3,244
Stop Loss: 3,240
Take Profit: 3,250 – 3,254 – 3,258 – 3,262 – 3,266 – 3,270 – 3,280
📌 STRATEGY TIP:
Avoid mid-range entries. Let price come to your zones. Prioritize confirmed reactions, especially near structural levels like 3,335 and 3,248.
SWING/POSITIONAL PICKREMSONS INDUSTRIES LTD
TECHNICAL VIEW
Stock is shift the range and consoilidate near resistance or breakout zone. Buy 140-145 for 175-185 TGT, sl near 130 at closing basis..
FUNDAMENTAL VIEW
Quarterly/Yearly EBITDA & PAT Both Are Highest In History. ROE & ROCE Is Also Good.
I Am Not SEBI Registered Research Analyst. It Is Giving Only Educational Purpose. Trade In REMSONSIND After Discussing With Your Financial Advisor.
GOLD TRADING INSIDE COMPRESSION ZONE WAITING FOR A CLEAR BREAK XAUUSD PLAN – MAY 27 | GOLD TRADING INSIDE A COMPRESSION ZONE – WAITING FOR A CLEAR BREAKOUT
Gold continues to consolidate below the 3,364 resistance zone after a rejection late last week. The market is currently trading within a compression range, preparing for a breakout – but direction still depends heavily on macro triggers and technical structure.
🌍 MACRO CONTEXT:
U.S. 10-year yields remain above 4.5%, keeping the dollar stable and applying short-term pressure on precious metals.
The Fed’s cost-cutting moves and operational losses are raising deeper concerns about long-term monetary stability.
Risk sentiment is mixed, and institutional money continues to flow cautiously into gold as a long-term value hedge, especially with equities showing signs of exhaustion.
📈 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK (H1):
Price failed to break through the 3,345–3,364 resistance zone, triggering a pullback toward the mid-range.
Key support around 3,311 is now being tested – a decisive level that could determine whether bulls can regain momentum or bears take control.
If price breaks below 3,311, we could see a deeper dip toward the 3,298–3,288 demand zone, which may offer a better re-entry for buyers.
On the upside, a confirmed break above 3,364 could open the door for a move into the Fair Value Gap toward 3,407.
🔹 TRADE SETUPS:
🔵 BUY SCALP
Entry: 3,314 – 3,312
Stop Loss: 3,308
Take Profit Targets:
3,318 – 3,322 – 3,326 – 3,330 – 3,340 – 3,350
🔵 BUY ZONE
Entry: 3,298 – 3,296
Stop Loss: 3,292
Take Profit Targets:
3,302 – 3,306 – 3,310 – 3,314 – 3,320 – 3,330
🔻 SELL SCALP
Entry: 3,346 – 3,348
Stop Loss: 3,350
Take Profit Targets:
3,342 – 3,338 – 3,334 – 3,330 – 3,320 – 3,310
🔻 SELL ZONE
Entry: 3,364 – 3,366
Stop Loss: 3,370
Take Profit Targets:
3,360 – 3,356 – 3,352 – 3,348 – 3,344 – 3,340 – 3,330
📌 Note:
Price is trading in the mid-range of a larger structure. Best opportunities remain near the edges of support/resistance with confirmation. Avoid overtrading in the middle zone. Let the market come to your areas of value.
💬 If you found this plan helpful, Like + Comment + Follow for daily GOLD strategies from the MMF Team.
Arkade Developers IPO breakoutAfter ipo promoter promised in concall about 10000cr revenue till 2029 in next 5 years. so aprox considering 27% pat margin they will deliver 2700cr profit. which is current networth of company. very stong fundamental plus technical bet
in this market fall promoter bought very huge quantity of shares, which also shows that they bealive in their commitment and actions forward. track
EUR/CHF Technical Outlook – Potential Bullish Reversal Setup📈 Pair: EUR/CHF
📆 Date: May 27, 2025
📊 Timeframe: Daily (D1)
📌 Technical Highlights:
🔹 Current Price: 0.93456
🔹 Key Indicators:
50 EMA (Red): 0.93824
200 EMA (Blue): 0.94342
🧠 Chart Analysis:
🔻 Downtrend Resistance Line: A clear descending trendline is pressing price lower, reinforcing a bearish structure since March.
🟣 Reversal Zone (Support Area):
Price is currently hovering just above the marked Reversal Point, a demand zone between 0.93000–0.93400. Historically, this zone has acted as a launch pad for upward momentum.
🟪 Resistance Level:
Located around 0.94300–0.94600, this zone is reinforced by the 200 EMA, making it a critical breakout area. A strong bullish close above this region could invalidate the downtrend.
🔄 Two Scenarios to Watch:
✅ Bullish Breakout Scenario:
Price may bounce from the reversal zone.
A break and retest above the resistance level could lead to bullish continuation toward 0.9500–0.9550.
Confirmation above the 200 EMA will add confidence to the breakout.
📈 Potential Buy Entry: On breakout and retest of 0.9450
🎯 Target: 0.9550
🛡️ Stop Loss: Below 0.9320
❌ Bearish Continuation Scenario:
If price fails to hold above the reversal point, sellers may regain control.
A breakdown below 0.9300 could trigger further downside toward 0.9200 or lower.
📉 Sell Setup Invalid Until: Price closes below 0.9300 on strong volume.
🧭 Conclusion:
This chart suggests a critical decision point for EUR/CHF. A bounce from the reversal zone followed by a confirmed break above resistance could signal the start of a medium-term uptrend. Traders should monitor price action closely for confirmation signals near the trendline and EMA zones.
🚦 Bias: Neutral to Bullish, awaiting confirmation
🧠 Tip: Watch for candlestick patterns (like bullish engulfing or pin bars) near the support zone for early entries.
Will Gold Break Through 3366 or Pull Back Before NFP Week?XAUUSD PLAN – 26/05 | Will Gold Break Through 3366 or Pull Back Before NFP Week?
Gold is currently trading near a major resistance zone after a sharp rebound last week. With Fed policies still hawkish and trade tensions between the US and EU on hold, the market is entering a wait-and-see phase — ideal for structured trades.
🌍 MACRO CONTEXT:
Trump Delays 50% Tariffs on EU Until July 9: This cooled market tension temporarily but doesn’t eliminate the risk long term.
US 10-Year Yields Surge Back Above 4.55% right after, showing bond markets are still pricing in tighter conditions.
The Fed Faces Strategic Losses: As rate hikes increase reserve interest payments, the Fed is trimming 10% of its workforce — a rare signal of operational pressure.
➡️ Investors should brace for volatility ahead of NFP and watch closely for central bank reactions.
🔍 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK – H1/H4 View:
Gold is respecting a rising channel while consolidating near the 3360–3366 region — a key sell zone with potential for reversal.
The chart also shows clear Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) above and below current price, signaling pending liquidity sweeps.
🔑 KEY TECHNICAL LEVELS
🔺 Resistance Zones:
3364 – 3366 → Local top and key reversal zone
3406 – 3408 → FVG upper bound, potential blow-off target if breakout occurs
🔻 Support Zones:
3324 – 3326 → 20 EMA retest, potential bullish bounce
3310 – 3308 → Trendline + EMA89 confluence
3304 → Break below this area could invalidate short-term bull bias
🎯 TRADE SETUPS
🟢 BUY SCALP:
Entry: 3326 – 3324
Stop-Loss: 3320
Take-Profit: 3330 → 3334 → 3338 → 3342 → 3346 → 3350
🟢 BUY ZONE:
Entry: 3310 – 3308
Stop-Loss: 3304
Take-Profit: 3314 → 3318 → 3322 → 3326 → 3330 → 3340
🔴 SELL SCALP:
Entry: 3364 – 3366
Stop-Loss: 3370
Take-Profit: 3360 → 3356 → 3352 → 3348 → 3344 → 3340
🔴 SELL ZONE:
Entry: 3406 – 3408
Stop-Loss: 3412
Take-Profit: 3400 → 3396 → 3392 → 3388 → 3385 → 3380
⚠️ STRATEGY RECOMMENDATION:
If price breaks above 3366 with momentum, expect a run to 3408 and possibly 3450.
If price rejects 3366 or fails to hold above 3320, scalpers can look for quick shorts with tight stops.
📌 Avoid chasing price in the middle of the range. Wait for strong rejection or breakout confirmation to enter.
GOLD PLAN 23/05–YIELD CURVE FLIPS Will Gold Breakout or Sell Off🔥 GOLD PLAN 23/05 – YIELD CURVE FLIPS | Will Gold Breakout or Sell Off at 3360?
Global markets are heating up again as risk sentiment shifts. A major alert comes from the U.S. bond market:
For the first time since October 2021, the yield curve between the 5-year and 30-year treasuries inverted to +1.00%, signaling strong expectations for inflation and future growth concerns.
🌍 MACRO CATALYSTS DRIVING GOLD:
Iran warns the U.S.: “Leash your mad dog!” – escalating rhetoric as Israel is rumored to be preparing a strike on Iran's nuclear sites. Tehran vows to retaliate and holds the U.S. accountable.
Goldman Sachs says: “Only one way – BUY GOLD!”
Following the failed 20-year bond auction, rising deficits, and fiscal stress, GS urges investors to move into gold and crypto.
The return of risk-off sentiment makes Gold the #1 safe haven asset, attracting global institutional flow.
📈 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK (H1 Chart):
Critical resistance at 3358–3360 is a key decision zone.
A breakout here may trigger a strong move toward previous highs (ATH zone: 3390–3400).
Major support lies around 3276–3274.
A breakdown here may expose gold to deeper pullbacks below the 3200 handle, revisiting the FVG zone.
📌 TRADE PLAN FOR TODAY:
🔵 BUY ZONE:
Entry: 3276 – 3274
SL: 3270
TP: 3280 – 3284 – 3288 – 3292 – 3296 – 3300
🔵 BUY SCALP:
Entry: 3304 – 3302
SL: 3298
TP: 3308 – 3312 – 3316 – 3320 – 3325 – 3330 – 3340
🔻 SELL ZONE:
Entry: 3376 – 3378
SL: 3382
TP: 3372 – 3368 – 3364 – 3360 – 3350
🔻 SELL SCALP:
Entry: 3344 – 3346
SL: 3350
TP: 3340 – 3336 – 3332 – 3328 – 3324 – 3320
⚠️ Caution:
With geopolitical risk and bond market stress rising, volatility is expected to spike. Be patient and trade only on confirmation from key zones.
🎯 Stick to the plan. Don't chase the price. Protect your capital.
Is Gold Set to Explode or Fake Out at 3400?GOLD PLAN 22/05 – TERROR ATTACK SHOCKS MARKETS | Is Gold Set to Explode or Fake Out at 3397?
Markets have just been hit by fresh geopolitical tension:
An Israeli diplomat was shot dead in Washington D.C. during a high-profile Jewish community event near the Holocaust Museum. The shooter allegedly shouted political slogans, and the FBI is now treating the case as a potential anti-Semitic terrorist act.
Former President Donald Trump called the event “disgusting” and urged the U.S. to stand strong against extremism.
🟡 This incident triggered a wave of risk aversion, pushing safe-haven assets like GOLD into the spotlight once again.
🌐 FUNDAMENTAL CONTEXT:
The USD remains under pressure due to weak U.S. economic data (housing, manufacturing, retail).
Despite the Fed’s “higher for longer” tone, markets are pricing in potential rate cuts by Q3.
Rising geopolitical tensions in the Middle East & U.S. soil may fuel further gold demand in the short term.
📈 TECHNICAL OUTLOOK (H1 Chart):
Price is nearing FVG resistance at 3395–3397, which could serve as a liquidity trap for breakout traders.
Key mid-zone resistance: 3344–3356, where price might stall or reverse if upward momentum weakens.
Strong support levels: 3303 – 3288 – 3277, aligned with previous structure and demand zones.
📌 TRADE PLAN:
Buy zone: 3296 - 3294
SL: 3290
TP: 3300 - 3304 - 3308 - 3315 - 3320 - 3330 - ???
Buy Scalp: 3316 - 3314
SL: 3310
TP: 3320 - 3324 - 3328 - 3332 - 3340 - 3350
Look for bullish reaction from the support zone and enter with proper risk management.
🔻 Sell zone: 3395 – 3397
SL: 3401
TP: 3390 - 3386 - 3380 - 3376 - 3370
🔻 Sell Scalp: 3358 - 3360
SL: 3364
TP: 3354 - 3350 - 3346 - 3342 - 3338 - 3330
If price spikes into FVG and shows exhaustion or bearish reversal, short setup is valid.
⚠️ Warning: Due to geopolitical headlines and gold trading near psychological resistance, expect high volatility and potential for traps.
🎯 Stick to your zones. Manage TP/SL properly. Do not chase price!
Technical Levels Respected – BTC Reaches $108K Target📍 BTC Target Hit with Precision!
✅ As predicted in the previous analysis, Bitcoin has successfully tapped the $108K resistance zone — clean and technical execution!
📊 My chart spoke in advance... and the market listened.
🎯 Why miss out on these accurate forecasts?
📉 My strategies are not just random lines — they’re built on solid market structure, EMAs, and key price action zones.
📢 Let’s stay connected!
🧠 I’m committed to sharing educational content and professional trading insights to help you grow as a trader.
💡 Whether you're a beginner or seasoned trader, there’s always something new to learn with me.
📚 Join the journey — learn, trade, and win!
📩 DM or follow to get consistent updates and chart breakdowns.
🚀 Let’s trade smart, not hard!