SWIGGY 1 Day View 📊 SWIGGY – 1-Day Time Frame Key Levels (Daily Technical View)
📍 Latest Price Context (Approx)
Current/Live price range (recent session): ~₹305–₹315 (trading range today)
🔑 Daily Support Levels
These are price zones where buying interest could emerge if the stock dips:
📌 S1 (Immediate Support): ~₹313–₹315
📌 S2: ~₹307–₹310
📌 S3 (Deeper support): ~₹295–₹300
(levels help define where the stock may stabilize on a pullback)
📈 Daily Resistance Levels
These are zones where price may face selling pressure:
🔹 R1: ~₹329–₹330
🔹 R2: ~₹335–₹336
🔹 R3: ~₹345–₹346
(above these, the stock needs strong momentum to continue higher)
📊 Daily Pivot Levels
Pivot levels often act as reference for thematic direction:
📍 Pivot (Central daily level): ~₹326–₹327
(Above this = mildly bullish bias for the day; below this = bearish bias)
📌 Based on Technical Indicators
Short-term indicators show mixed to bearish bias in daily trend, with several oscillators and moving average signals leaning sell/oversold — reflecting current selling pressure in the market.
Trend Analysis
Nifty 50 - 30.01.2026Nifty hovering in small zone as marked by the yellow line keeping buyers hanging suggesting indecisiveness or state of confusion. Any movements either upside or downside will fetch some good money. Else it’s looking like put writers day.
Stay focused and watch but do not take action till yellow line is passed.
ULTRACEMCO 1 Week View 📍 Current trading range (approx)
• Stock is trading near ~₹12,600-₹12,800 on NSE right now.
📊 Weekly Pivot Levels (1-Week Timeframe)
🔹 Resistance Levels
1. Major Resistance 3 (R3): ~₹13,190
2. Resistance 2 (R2): ~₹12,872
3. Resistance 1 (R1): ~₹12,621
➡️ If price closes above ₹12,620-12,630 on weekly close, momentum could pick up toward ₹12,870-₹13,190.
🔸 Support Levels
1. Support 1 (S1): ~₹12,051
2. Support 2 (S2): ~₹11,732
3. Support 3 (S3): ~₹11,481
➡️ Key weekly support is around ₹12,050-₹12,000 — break below this zone can accelerate downside toward ₹11,730-₹11,480.
🔁 Weekly Range Expectation
📍 Upside range: ₹12,620 → ₹12,870 → ₹13,190
📍 Downside range: ₹12,050 → ₹11,732 → ₹11,480
This gives an approximate weekly trading range of ~₹11,480 to ₹13,190 if volatility expands.
GIFTNIFTY IntraSwing Levels for 30th JAN 2026GIFTNIFTY IntraSwing Levels for 30th JAN 2026
🚀Follow & Compare NIFTY spot Post for Taking Trade
━━━━━━━━━₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹━━━━━━━━
💥Level Interpretation / description:
L#1: If the candle crossed & stays above the “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Bullish bias.
L#2: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLB#1 & UBTgt
L#3: If the candle stays above “Sell Gen” but below “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Sidewise. Aggressive Traders can take Long position near “Sell Gen” either retesting or crossed from Below & vice-versa i.e. can take Short position near “Buy Gen” either retesting or crossed downward from Above.
L#4: If the candle crossed & stays below the “Sell Gen”, it is treated / considered a Bearish bias.
L#5: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLS#1 & USTgt
HZB (Buy side) & HZS (Sell side) => Hurdle Zone,
*** Specialty of “HZB#1, HZB#2 HZS#1 & HZS#2” is Sidewise (behaviour in Nature)
Rest Plotted and Mentioned on Chart
Color code Used:
Green =. Positive bias.
Red =. Negative bias.
RED in Between Green means Trend Finder / Momentum Change
/ CYCLE Change and Vice Versa.
Notice One thing: HOW LEVELS are Working.
Use any Momentum Indicator / Oscillator or as you "USED to" to Take entry.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⚠️ DISCLAIMER:
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments. I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
"As HARD EARNED MONEY IS YOUR's, So DECISION SHOULD HAVE TO BE YOUR's".
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
❇️ Follow notification about periodical View
💥 Do Comment for Stock WEEKLY Level Analysis.🚀
📊 Do you agree with this view?
✈️ HIT THE PLANE ICON if this technical observation resonates with you. It will Motivate me.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💡 If You LOOKING any CHART & want for Level and ANALYZE?
Share your desired stock names in the comments below! I will try to analyze the chart Levels, patterns and share my technical view (so far my Knowledge).
If Viewers think It can identify meaningful setups. Looking forward to hearing from all of you — let's keep this discussion going and help each other make better trading decisions.
Nifty50 analysis(30/1/2026).CPR: wide + overlapping cpr: range day.
FII: -393.97 sold
DII: 2,638.76 bought.
Highest OI: 25500 put oi. and 25300 and 25200 call oi.
P.C.R: 1 bearish.
Resistance:25500.
Support : 25200
Event: Budget on Feb. 1
conclusion: bullish but retest is highly possible.
My pov:
1.market opens with gap down almost 100 points.
2.until 25200 is crossed below down only bullish pov.
3.IN one hour candle if it takes support at 50ma (red line ) from there the bullish trend continues.
4. budget is highly a anticipated event so uncertanity highly present trade accodingly. anything can happen on monday. wait until event is closed.
What IF:
1.if price breaks 25200 and 25450 closed in day candle then overall trend bearish
psychology fact:
Fight like you deserve to win, but don’t focus on the outcome.
note:
8moving average ling is blue colour.
20moving average line is green colour
50moving average line is red colour.
200moving average line is black colour.
cpr is for trend analysis.
MA line is for support and resistance.
Disclaimer:
Iam not Sebi registered so i started this as a hobby, please do your own analysis, any profit/loss you gained is not my concern. I can be wrong please do not take it seriously thank you.
NIFTY 50 30/01/2026 IDEA INTRADAYKey Observations:
PCR: 0.98 → Neutral to slightly bullish, no extreme positioning
ATM IV: 15.43 → Low volatility, favoring range or breakout trades
Max Pain: 25,350 → Index likely to stay above this zone
Expiry: 4 days → Expect time decay and range compression
Support & Resistance Levels:
Immediate Resistance: 25,414 → 25,485 (R1–R2 zone)
Major Resistance: 25,598 (R3 – supply zone)
Immediate Support: 25,300 (Pivot)
Strong Support: 25,229 → 25,116
Trade Plan (Index View):
Bullish above 25,420: Targets 25,485 / 25,550
Rejection near 25,480–25,500: Expect pullback to 25,300
Break below 25,300: Weakness towards 25,230–25,120
Market Outlook & Trade Setup – Friday, 30th January 2025Major indices showed a sharp recovery yesterday and even crossed the opening day high. Silver and Gold has corrected by more than 6% overnight so some selling pressure could be seen.
We have the Budget on Sunday, 1st Feb, 2026, so heavy positions might not be build in the market today.
🔹 NIFTY
* Previous Close: 25,418
* Expected Range: 25,000 – 25,500
🔹 SENSEX
* Previous Close: 82,566
* Expected Range: 82,500 - 82,600
🌍 Global & Market Sentiment
* DJIA: +55 | S&P: -9
💰 Institutional Activity (Cash Market)
* FII: Net Sellers: - ₹ 394 Cr
* DII: Net Buyers: + ₹ 2639 Cr
🔥 Events this Week: US --- Trump Speech & FED Rate announcement
📌 Sectoral Focus
Metal, Energy
👉 Commodities in Focus: Gold, Silver, Copper, Crude, Natural Gas
💯 Important Quarterly Results: Cupid, GHCL, HUDCO, IEX, ITC,REC, Voltas
📈 Trade smart. Manage risk. Stay disciplined.
Perfect F&P on Bitcoins daily charts (21/01/26)Bitcoin forming good chart pattern on the daily charts.
The charts is a perfect example of a Flag and Pole pattern. If the pattern completes there are chance of seeing bitcoin dipping.
Identifying the last support around 85K. Be watchful if price dips below it.
#ETH ON THE EDGE DELTAIN:ETHUSD.P
ETH is on the edge of the cliff. If it breaks below this level, we can see a significant downward move to $2200 easily and worst case of $1500 & $1400.
Long term investors can accumulate on the supports. Follow me for more.
This indicator is provided for educational and informational purposes only.
It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or trade signals.
The creator and Systematic Traders Club are not responsible for any financial losses resulting from the use of this indicator.
Trading and investing involve risk. Always do your own analysis and use proper risk management.
xauusd recently i capture #XAUUSD xauusd recently i capture #XAUUSD
Agar ak strong poi hai daily time frame ka strong poi ( fvg + opposite color ka breaker block + orderblock ) bias ke opposite direction me volume gap , imbalance ho to volume imbalance , gap ka value nahi rahega tab wo poi ka first fvg+ob ko tap karne jarur jayega
Aur jab strong poi ko tap kar lega phir wo jayega gap ko respact dene
xauusd recently captured #XAUUSD
If there is a strong POI (FVG + breaker block of opposite color + order block) on the daily time frame, the volume gap is in the opposite direction of the bias. If there is a volume imbalance, the gap value will not be there, then the POI will first tap the FVG + OB.
And once the strong POI is tapped, it will then go to respect the gap.
sorry my english is weak padh lena bhai log
Why Good Setups Fail: The CAP NOTES That Block Bad Trades (ECI)ECI Panel (Execution Confidence Index)
Why this panel exists: execution governance, not prediction
Most traders don’t lose because they “didn’t know direction.”
They lose because they entered during low-quality execution conditions: mixed timeframes, thin liquidity, unstable volatility, or a setup that exists only on one chart layer.
The ECI Panel is built to solve that exact problem.
It is not a signal. It is a permission layer:
It compresses multiple execution risks into one readable state.
It stops “impulse entries” when the environment is structurally unstable.
It forces a trader to execute only when the market allows clean follow-through.
What ECI is measuring (in practical terms)
ECI is not “confidence” as emotion.
ECI is confidence as market permission.
It answers one question:
“If I execute right now, what is the probability that the market structure can carry the trade without forcing me into damage-control?”
The panel typically outputs:
ECI SCORE (Quality / Permission level)
RISK MOD (Risk modifier status)
CAP NOTES (Execution caps / constraints that limit trade validity)
CAP NOTES: the most important part of the panel
A trader can see a perfect entry candle and still be wrong — not because the setup is bad, but because the execution environment is capped.
CAP NOTES are non-negotiable constraints.
They don’t say “buy/sell.”
They say:
“Even if your setup is valid, the market is currently limiting execution performance.”
Think of it like this:
Setup = your idea
CAP NOTES = the market’s permission boundaries
ECI = the final execution gate
If CAP NOTES are active, ECI is telling you:
“Reduce size, delay entry, require stronger confirmation, or do not trade.”
Example from the panel shown
Your panel shows:
ECI SCORE: 38 (No-Trade)
RISK MOD: OFF
CAP NOTES: MTF CONFLICT | LOW LIQ
This is a textbook “execution-capped” environment.
Let’s break those CAP NOTES down.
1) MTF CONFLICT (Multi-Timeframe Conflict)
What it means
MTF Conflict is when higher timeframe intent is not aligned with the execution timeframe trigger.
Common real-market situations:
HTF is in distribution / reversal zone, while LTF shows a continuation entry.
HTF is bearish structure, LTF prints bullish breakout (often a trap / mitigation move).
HTF premium/discount context contradicts LTF entry direction.
HTF liquidity is targeted in the opposite direction of your LTF plan.
Why it kills execution quality
When timeframes conflict, price tends to behave like this:
sharp spikes
fake breakouts
stop hunts
whipsaw around levels
follow-through failure
Even if you “win,” the trade becomes messy:
large drawdown before moving
hard stop placement
emotional management load increases
How to execute when MTF CONFLICT is present
MTF conflict doesn’t always mean “never trade.”
It means you must upgrade requirements.
Execution rules (professional gating):
Trade only in the direction of HTF bias, unless you have an explicit reversal model.
If you take a counter-trend scalp:
smaller size
faster TP
tighter invalidation
no “hope holding”
Demand clear confirmation before entry:
displacement + structure break in your direction
clean retest / mitigation
liquidity sweep + reclaim
If HTF is near key zones (range extremes / major OB / major liquidity):
treat every LTF breakout as suspect until confirmed
In short:
MTF conflict converts “normal trading” into “advanced trading.”
If you don’t upgrade your confirmation, you’re just paying the market tuition.
2) LOW LIQ (Low Liquidity Condition)
What it means
Low Liquidity is not “market is quiet.”
It means the order book environment is not supporting clean execution.
This happens typically:
outside active sessions
between session transitions
during pre-news hesitation
after major impulses when market pauses
during thin participation windows
Why it damages execution
Low liquidity causes:
slippage and poor fills
random wicks
“one-candle stop-outs”
spreads widening
price jumping levels without trading through them
In low liquidity, levels don’t behave “technically.”
They behave mechanically: gaps, thin prints, abrupt sweeps.
How to trade when LOW LIQ is present
You have two choices:
Option A: Don’t trade.
This is the professional choice for consistency.
Option B: Trade with liquidity-adjusted execution rules
Use confirmation entry (no blind limit entries)
Require stronger structure break
Reduce leverage / size
Use wider invalidation or smaller position — never both high-risk
Take partial profits faster
Avoid holding through “dead zones”
Simple truth:
Low liquidity turns good setups into low R:R outcomes because execution friction increases.
Why CAP NOTES matter more than indicators
Indicators are usually about “what price did.”
CAP NOTES are about “what price can realistically do next without breaking your execution.”
This is the real difference:
A setup can be valid on chart.
But CAP NOTES can still make it untradeable in live execution.
CAP NOTES protect you from:
trading inside chop disguised as signals
taking entries during unstable participation
forcing trades when market structure is not ready
How ECI + CAP NOTES should control your decision
Use a 3-state execution system:
State 1: NO-TRADE (ECI low + CAP NOTES active)
Observe only
Build context
Wait for caps to clear
Do not “revenge trade” the chop
State 2: CAUTION TRADE (ECI mid + 1 CAP NOTE active)
Reduce size
Require better confirmation
Tight rules on invalidation
Faster profit-taking
State 3: PERMISSION TRADE (ECI high + caps clear)
Standard sizing
Standard invalidation
Allow trade to breathe
Higher expectancy follow-through
In your screenshot, ECI 38 (No-Trade) with MTF Conflict + Low Liq is clearly State 1.
That is not weakness.
That is discipline automation.
The real value: ECI makes you consistent under pressure
Traders fail most during:
after a big move
after a loss
when they “feel they missed it”
when market becomes noisy
ECI + CAP NOTES solve that by removing emotional override.
They don’t “predict.”
They enforce execution quality.
That is how consistency is built.
CAP NOTES Dictionary (ECI Panel)
What “CAPS” mean in MARAL execution language
CAP NOTES = Execution Constraints
They are not opinions. They are environmental limitations that reduce trade expectancy even when a setup looks good.
Rule:
1 CAP active → reduce risk / require stronger confirmation
2+ CAPS active → no-trade unless you are executing a specialized model (advanced)
CAPS cleared → normal execution permission
CAP 01 — MTF CONFLICT
Meaning: Higher-timeframe bias is opposing the current execution direction (HTF flow disagrees with dir).
Risk: Follow-through becomes inconsistent; traps/stop-runs increase; LTF triggers fail more often.
Best action: Stand down until HTF context stops opposing (prefer MTF ALIGNED/MIXED).
Upgrade rule: If executing anyway, reduce size and require displacement + acceptance/retest before entry.
CAP 02 — VOL REGIME
Meaning: Volatility is outside your tradable operating band (ATR% not within your min/max bounds).
Risk: ATR-based SL/TP loses reliability; price either stalls (too low vol) or whipsaws (too high vol).
Best action: Avoid normal execution until volatility normalizes into the band.
Upgrade rule: If forced to trade, reduce leverage/size and use structure-based invalidation (confirmation-only entries).
CAP 03 — ADX WEAK
Meaning: Trend strength is insufficient (ADX below threshold); market is prone to rotation/chop.
Risk: Continuation expectancy drops; fake breaks increase; holding winners becomes difficult.
Best action: Wait for ADX to recover or trade only the cleanest confirmations.
Upgrade rule: Require displacement + structure follow-through (BOS + acceptance) and reduce risk.
CAP 04 — RSI CHOP
Meaning: Momentum is indecisive (RSI inside the chop band between your bear/bull levels).
Risk: Whipsaw environment; both long/short attempts get punished; signal quality collapses.
Best action: Stand down until RSI exits the chop band and direction is confirmed.
Upgrade rule: Only trade after RSI exits chop + price prints confirmation (displacement and/or structural break).
CAP 05 — STRUCT NEUTRAL
Meaning: No confirmed HH/HL or LL/LH sequence; structure bias is neutral (structBias == 0).
Risk: Invalidation and targets become unclear; entries become location-poor; rotation risk rises.
Best action: Wait for structure to resolve into Bull Struct or Bear Struct.
Upgrade rule: If trading neutral structure, require liquidity interaction + displacement (sweep/reclaim style confirmation).
CAP 06 — LOW LIQ
Meaning: Liquidity context is LOW (no sweep/event and not near PDH/PDL proximity).
Risk: Internal noise dominates; moves lack fuel; breakouts often fail or stall.
Best action: Wait for liquidity context to improve (NEUTRAL near PDH/PDL or HIGH via sweep/event).
Upgrade rule: If executing, reduce size and demand stronger confirmation (displacement + acceptance, no blind entries).
CAP 07 — DIV NEG
Meaning: Divergence is against your current direction (negative risk modifier when Divergence module is ON).
Risk: Continuation becomes fragile; deeper pullbacks; late entries get punished; expectancy compresses.
Best action: Avoid late entries and avoid adding risk into extension.
Upgrade rule: Prefer pullback/mitigation entries only; manage active trades tighter (protect/scale earlier).
Default — NO MAJOR CAPS
Meaning: None of the above caps are currently active (under enabled modules).
Risk: Not a guarantee—only indicates no ECI blockers detected by this build.
Best action: Execute normally while still following your setup/permission/risk rules.
Upgrade rule: Maintain standard confirmations; do not override risk discipline.
CAP NOTES are not “warnings to ignore.” They are execution limits. When a cap is active, the market is telling you: “Your setup may be visible, but your execution edge is capped.” The professional response is not to trade harder — it is to tighten permission.
How to use CAP NOTES correctly:
Treat ECI SCORE as the quality meter, and CAP NOTES as the gatekeeper.
If CAP NOTES increase, your job is to reduce exposure, not increase conviction.
If you feel urgency (“I might miss the move”), that’s usually the moment CAP NOTES are protecting you the most.
MARAL Rule
When conditions are capped, your best trade is often no trade. Consistency is built by the trades you refuse, not the trades you force.
Reminder:
ECI is a decision-support layer. It does not replace risk management, position sizing, or personal accountability. Always execute within your predefined risk limits.
Note : This article is educational and explains a decision-support framework. It is not financial advice, not a promise of performance, and not a buy/sell signal service. Trading involves risk; always apply your own risk management and confirm conditions independently.
#TradingPsychology #RiskManagement #TradingDiscipline #TradingEducation #PriceAction #MarketStructure #Liquidity #SmartMoneyConcepts #MultiTimeFrame #Volatility #ADX #RSI
BTCUSD Demand Zone in Focus After Strong Bearish MoveBTCUSD is currently trading after a strong bearish move, where price broke below the earlier sideways structure with high selling momentum. The market clearly respected a downward trend, forming lower highs and showing consistent selling pressure. The resistance area around 89,800–90,400 worked as a strong selling zone, where price faced rejection and sellers regained control, leading to a sharp fall.
After this decline, price has now reached a major demand zone near 83,500–84,000. This area is supported by earlier buying activity and base formation, making it an important support level. The present reaction from this zone indicates that sellers are slowing down and buyers are trying to hold price. As long as BTCUSD stays above this demand, short-term stability or a corrective move can be seen.
The risk area below demand shows where downside pressure may increase if support breaks. A clear move below this zone would strengthen the bearish trend further. For now, price is consolidating near support, and volatility is expected around these levels. Overall market bias remains cautious, with bearish control still active, but short-term recovery chances remain while demand holds.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Trading involves risk and uncertainty.
BTCUSD Consolidates Near Demand as Market Tests Key ResistanceBTCUSD is currently trading after a corrective phase that followed a strong bearish move. The earlier price action clearly respected a downward structure, with lower highs and consistent selling pressure. After reaching the recent lows, price started to stabilise and move sideways, indicating reduced selling momentum. This behaviour suggests the market is shifting into a consolidation phase rather than continuing aggressively lower.
A clear resistance area is visible around 89,800–90,200. This zone previously acted as a strong selling area where price faced rejection and failed to sustain higher levels. It remains an important upside barrier, and price reactions are expected if this area is retested. Acceptance above this resistance would weaken the bearish structure and improve recovery strength.
On the downside, a well-defined demand zone is located around 86,800–87,400. This area shows strong buying interest in the past, supported by sharp bullish reactions and base formation. It acts as a key support and potential buy interest zone as long as price holds above it. Below this, the marked risk area highlights where bearish momentum may increase if support fails.
At present, price is moving between demand and resistance, showing range behaviour. Small higher lows suggest early accumulation, but confirmation is still required. Overall bias remains neutral to cautious, with volatility expected near key zones.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Trading involves risk and uncertainty.
MPWR: Break above a key zone, the retest decides if it’s realMPWR still shows an upward structure: pullbacks look more like pauses than a broken trend.
The area around ~1,111 is the visible decision zone. Above it, price recently accelerated.
Key detail: the breakout has already been retested. This is where the market proves acceptance.
As long as price stays above that zone, this reads like continuation after consolidation, not a random spike.
If price drops back below the zone and holds there, the logic shifts toward a failed breakout and a return into the prior range.
Chartnes Silent Flow is active here. I treat that as “continuation is favored,” not a promise.
This remains a probability setup: retests can hold, but they can also be the last test before a deeper pullback.
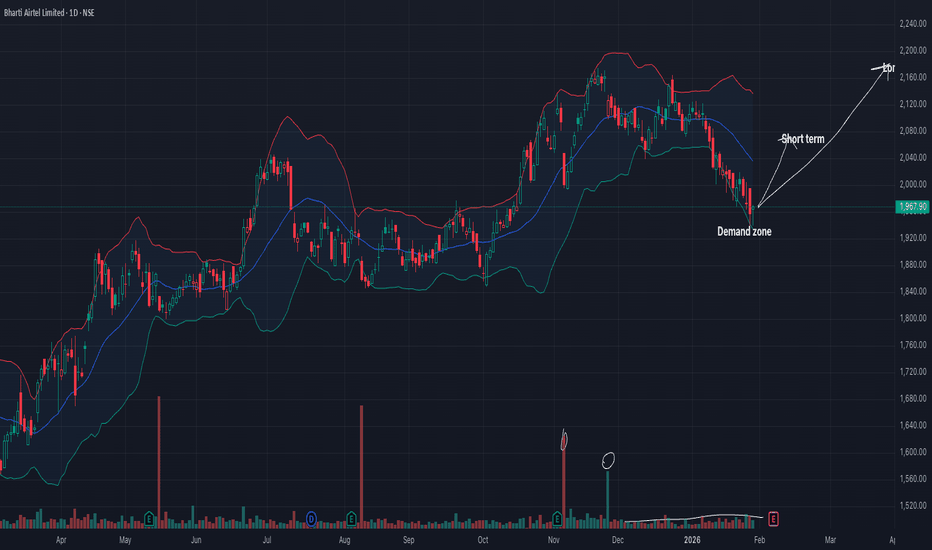
Bharti Airtel: Strategic Premiumization Signals Path to ₹2,100Bharti Airtel maintains a strong bullish outlook as it capitalizes on industry-leading growth metrics and a favorable technical setup. Fundamentally, the company’s focus on premiumization has pushed ARPU to a robust ₹256, supported by a rapid transition of users to its 167-million-strong 5G network. With the upcoming Board Meeting on February 5, 2026, to announce quarterly results, markets anticipate further earnings upgrades driven by steady 5G monetization and enterprise segment expansion.
Technically, the stock has demonstrated resilience, finding firm support at the ₹1,940–₹1,960 zone, coinciding with its long-term moving averages. A breakout above the immediate resistance at ₹2,050 is expected to trigger a fresh momentum wave.
Current Market Price ~1,985 Consolidating above key 200-DMA support.
Immediate Support 1,940 Recent swing low and crucial demand zone.
Interim Resistance 2,050 Pivot level; breach confirms the bullish breakout.
Technical Target 2,100 Primary objective based on structural recovery.
Upside Potential 2,174 Previous 52-week high and secondary target.
M&M: Unfazed by Global Entry, Primed for ₹4,000 MilestoneMahindra & Mahindra (M&M) remains a conviction bullish pick despite recent sectoral volatility. While the India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) has sparked concerns over cheaper European imports, the threat from luxury giants like BMW and Audi is largely overstated. These brands cater to the ₹50L+ luxury segment, whereas M&M’s "lifestyle" crown jewel—the Thar—and its premium SUV lineup (XUV700, Scorpio-N) dominate the high-growth ₹15L–₹30L bracket where brand loyalty is deeply entrenched.
Fundamentally, M&M’s Q3 FY26 performance underscores its resilience, supported by a massive order backlog and the successful rollout of the "Born Electric" (BE) series. The EU deal actually serves as a long-term catalyst for M&M’s global expansion rather than a domestic headwind.
Technically, the stock is consolidating near its 50-day EMA, forming a strong base. A decisive breakout above the recent resistance at 3,500 will signal a trend continuation. We maintain a strong buy with immediate technical targets of 3,750 and a long-term objective of 4,000.
BTC 4H UpdateToday’s market is throwing a massive curveball, and if you aren’t playing the levels, you’re playing with fire. 📉🔥
As of January 29, 2026, Bitcoin has taken a sharp dive, sliding from its recent highs above $90,000 to test critical support around $84,700. This move is being driven by a mix of macro caution following the Fed's decision to hold rates steady and a broader rotation of capital into traditional safe havens like gold.
🔍 The Technical Breakdown (BTC/USDT 4H & 1H)
The Breakdown: We’ve officially lost the $88,000 support. On the 1H chart, we saw a vertical drop that sliced right through our previous consolidation zones.
The "Blood in the Streets" Zone: I’m watching the $83,786 – $84,408 range very closely. If we lose this level, the next major "X" on the map is all the way down at $80,600.
The Recovery Path: To even talk about a bull case, we need to reclaim $86,355 and turn it back into support. Only a reclaim of $90,592 puts us back on the path to the $95k–$97k liquidity targets.
⚠️ My Game Plan
The Senate Agriculture Committee just advanced a major crypto market structure bill, which is a massive long-term win, but right now, the "risk-off" sentiment is king. Don't catch falling knives—wait for the 4H candle to show clear buyer absorption at these lower levels.
#Bitcoin #BTC #CryptoTrading #TechnicalAnalysis #TradingView #Web3 #FOMC #BTCUSD
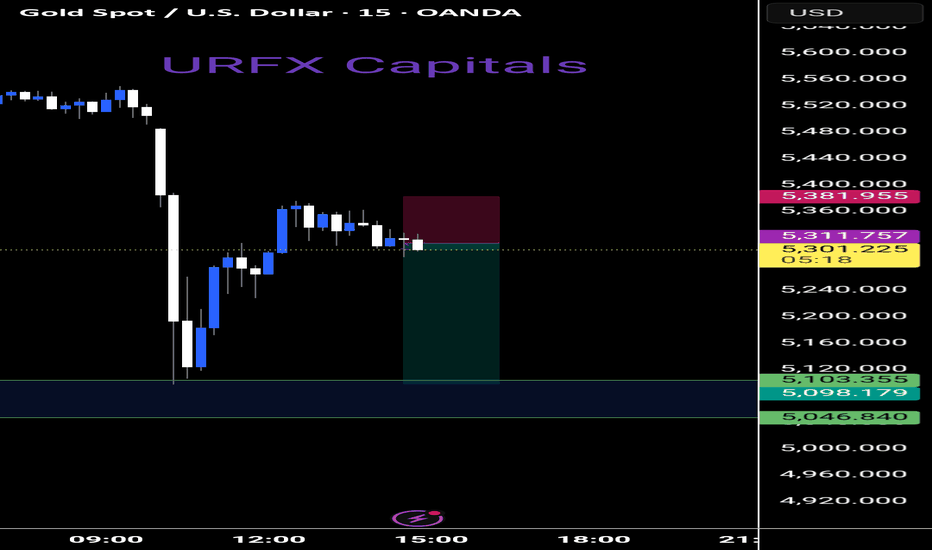
XAUUSD (4H) – Buy Side ViewXAUUSD (4H) – Buy Side View
Overall Bias:
The higher-timeframe trend is still bullish. The current fall looks like a healthy correction, not a full trend reversal.
📍 Strong Buy Zones
5190–5110 → Primary demand / high-probability buy zone
4990–5050 → Deep buy zone (positional / swing)
✅ Buy Confirmation Needed
4H bullish engulfing or pin bar
Clear rejection wicks from the support zone
Optional: volume expansion on bullish candles
🎯 Buy Targets
TP1: 5355
TP2: 5465
TP3: 5600+
🛑 Invalidation
A 4H close below 4990 weakens the bullish outlook
US Oil Has just broken out of Inverted H&S PatternTVC:USOIL has broken the neckline at $62 on a daily chart and, along with other commodities, is ready to climb to $70 levels in the coming weeks.
We keep $58 is the hard stop if the price recedes below the neckline.
Historically, rallies in Gold, Silver, and Crude Oil go hand in hand, though this time Oil started late.