Weekly Timeframe Price Action MasteryObserve the red supply zone where price consistently faces resistance, halting upward moves with precision. The green demand zone, formed after a decisive breakout from prior resistance, now acts as robust support for subsequent bounces. The white counter trend line serves as the pattern's key action line, guiding price movements with remarkable adherence across multiple tests.
Zone Dynamics
Supply zones in red mark areas of overhead selling pressure on weekly charts, often leading to rejections. Demand zones in green emerge post-breakout when former resistance flips, attracting buyers on retracements. These zones filter noise effectively in trending markets.
Counter Trend Line Role
This white line defines the counter-trend structure, respected through pullbacks and rallies. Price follows it as a dynamic guide, confirming pattern integrity without implying direction. Such lines enhance zone analysis by highlighting momentum shifts.
Disclaimer
This post showcases historical price action only and constitutes neither financial advice nor trading signals. Trading involves substantial risk of loss; conduct your own analysis and consult professionals.
Wave Analysis
Part 4 Learn Institutional Trading What Are Options?
At its core, an option is a financial derivative contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). Unlike buying the asset outright, purchasing an option requires paying a premium, which is the cost of acquiring the right conveyed by the option.
Options are broadly classified into two types:
Call Option: Gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
Put Option: Gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
Unlock Market Rotation: Turn Shifting Trends into Powerful ProfiStay Ahead of Capital Flow & Capture the Next Big Opportunity
What Is Market Rotation?
Market rotation refers to the movement of capital from one sector, asset class, or investment theme to another as economic conditions, interest rates, inflation, and growth expectations change. Understanding this shift allows investors to align portfolios with where money is flowing next, not where it has already been.
Why Market Rotation Matters More Than Ever
In today’s fast-moving global markets, leadership changes quickly. Sectors that outperform in one phase of the cycle can underperform in the next. Investors who unlock market rotation gain a powerful edge by identifying early signals and positioning before the crowd reacts.
Economic Cycles Drive Rotation
Different sectors perform best at different stages of the economic cycle. Early recovery favors cyclicals, mid-cycle supports growth sectors, late-cycle shifts toward defensives, and slowdown phases reward capital preservation strategies. Market rotation is the bridge between macro trends and smart allocation.
Interest Rates as a Key Trigger
Rising interest rates often rotate money away from high-growth, high-valuation stocks toward value, financials, and commodities. Falling rates usually support technology, consumption, and growth-oriented sectors. Tracking rate expectations is critical to anticipating rotation.
Inflation and Sector Leadership
Inflation reshapes winners and losers. High inflation typically benefits energy, metals, and real assets, while compressing margins in rate-sensitive sectors. Unlocking rotation means understanding how inflation impacts pricing power across industries.
Institutional Money Leaves Clues
FIIs, DIIs, and large institutional players move capital systematically. Volume expansion, relative strength, and sectoral index breakouts often signal early institutional rotation. Smart investors learn to read these footprints rather than react to headlines.
Relative Strength Is the Core Tool
Market rotation is best identified through relative performance. Comparing sectors against benchmark indices reveals which areas are gaining strength and which are losing momentum. Sustained outperformance is a strong sign of rotation in progress.
From Sector to Stock-Level Rotation
Rotation doesn’t stop at sectors—it flows into sub-sectors and then into specific stocks. Leaders within a strong sector usually outperform peers. Unlocking market rotation means narrowing focus from macro to micro with precision.
Risk Management Through Rotation
Instead of exiting markets entirely, rotation allows investors to shift risk, not abandon opportunity. When one theme weakens, another strengthens. This approach smooths volatility and improves long-term consistency.
Psychology of Market Rotation
Most investors chase past performance. Market rotation rewards those who act before trends become obvious. Discipline, data-driven decisions, and patience are essential to avoid emotional investing.
Technical Indicators That Signal Rotation
Moving averages, sectoral relative strength lines, momentum oscillators, and trend confirmation tools help validate rotation. Technical confirmation ensures that allocation decisions are backed by price action, not assumptions.
Macro Events Accelerate Rotation
Central bank decisions, geopolitical shifts, policy reforms, and global growth changes can rapidly accelerate capital movement. Prepared investors use these events as catalysts rather than shocks.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Rotation
Rotation can be tactical (weeks to months) or strategic (quarters to years). Traders benefit from short-term sector momentum, while investors focus on structural shifts like digitization, energy transition, or infrastructure growth.
Equity, Debt, and Alternative Rotation
Rotation is not limited to equities. Capital also moves between stocks, bonds, commodities, and alternative assets. A holistic approach captures opportunities across asset classes.
Market Rotation in Indian Markets
In India, rotation often reflects domestic growth cycles, government policies, earnings visibility, and global capital flows. Understanding local drivers adds a significant advantage to portfolio positioning.
Avoiding Overcrowded Trades
When a sector becomes over-owned, upside potential reduces. Unlocking market rotation helps investors exit crowded themes early and enter emerging ones before valuations expand.
Consistency Beats Prediction
Market rotation is not about predicting tops or bottoms. It is about consistently reallocating capital toward strength and away from weakness based on objective signals.
Portfolio Rebalancing with Purpose
Regular rebalancing aligned with rotation trends keeps portfolios dynamic. This reduces drawdowns and improves risk-adjusted returns over time.
Long-Term Wealth Creation Advantage
Investors who master market rotation compound gains by riding multiple leadership cycles instead of staying stuck in one theme. This adaptability is key to sustainable wealth creation.
Unlock the Edge
Market rotation is the silent force behind every major rally and correction. Those who understand it move ahead of trends, protect capital during uncertainty, and capture opportunity when it matters most.
Unlock Market Rotation is not just a strategy—it’s a mindset. By tracking capital flow, aligning with economic cycles, and acting decisively, investors can transform uncertainty into opportunity and stay one step ahead of the market.
Understanding Rapid Price Movements Through Technical AnalysisTechnical Market Explosion:
A technical market explosion refers to a sudden, powerful, and often unexpected surge in price movement—either upward or downward—driven primarily by technical factors rather than immediate fundamental news. These explosive moves are commonly observed across equities, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies and are closely followed by traders because they often create high-profit opportunities within short time frames. Understanding why and how these explosions occur is essential for traders and investors who rely on technical analysis to navigate volatile markets.
1. Meaning of a Technical Market Explosion
A technical market explosion occurs when price action breaks out decisively from a consolidation zone, key resistance, or support level with strong momentum and volume. This move is usually rapid and sharp, leaving little time for indecision. Such explosions reflect a sudden shift in market psychology where buyers or sellers overwhelm the opposing side.
These movements are not random; they are often the result of prolonged price compression, accumulation, or distribution phases that eventually release stored market energy.
2. Role of Support and Resistance Breakouts
Support and resistance levels are the backbone of technical analysis. A technical explosion typically begins when price decisively breaks above resistance or below support. Traders place buy stops above resistance and sell stops below support, and when these levels are breached, a cascade of orders is triggered.
This chain reaction increases liquidity and momentum, accelerating price movement. The stronger and more tested the level, the more explosive the breakout tends to be when it finally occurs.
3. Volume as the Fuel of Explosion
Volume plays a crucial role in validating a technical market explosion. A genuine breakout is almost always accompanied by a sharp rise in volume, signaling strong participation by institutional and retail traders.
Low-volume breakouts often fail, while high-volume explosions suggest conviction and sustainability. Volume confirms that the move is supported by real money, not just speculative noise.
4. Volatility Compression and Expansion
Before a market explodes, volatility usually contracts. This phase is marked by narrow price ranges, tight Bollinger Bands, or triangle and wedge formations. Such patterns indicate indecision and balance between buyers and sellers.
When volatility expands suddenly, it signals the start of a technical explosion. Traders who recognize volatility compression early can position themselves ahead of the breakout.
5. Indicator Alignment and Momentum
Technical indicators often align before a market explosion. Momentum indicators like RSI, MACD, and Stochastic Oscillators show strength or divergence prior to the move. For example:
RSI holding above 50 indicates bullish strength
MACD bullish crossover near zero line signals momentum buildup
Moving averages start flattening or converging before expansion
When these indicators turn simultaneously, the probability of an explosive move increases.
6. Chart Patterns Triggering Explosions
Certain chart patterns are well known for leading to technical market explosions, including:
Ascending and descending triangles
Cup and handle patterns
Flags and pennants
Head and shoulders (especially breakdowns)
These patterns represent structured market behavior, and once their boundaries are violated, price often moves swiftly toward projected targets.
7. Institutional Activity and Smart Money
Institutional players often accumulate positions quietly during consolidation phases. This accumulation is not obvious to most traders but can be detected through price structure and volume behavior.
Once institutions complete accumulation or distribution, they allow price to move aggressively. This is when retail traders observe a technical market explosion, often entering late but still benefiting from momentum.
8. Role of Algorithmic and High-Frequency Trading
In modern markets, algorithmic trading plays a major role in accelerating technical explosions. Algorithms are programmed to react instantly to technical signals such as breakouts, moving average crossovers, and volatility spikes.
When a key level breaks, thousands of automated orders execute simultaneously, intensifying the speed and magnitude of the move.
9. False Breakouts vs True Explosions
Not every breakout leads to a true explosion. False breakouts occur when price briefly moves beyond a key level but lacks volume or follow-through. Recognizing the difference is critical.
True technical explosions show:
Strong closing prices beyond the breakout level
Increasing volume
Momentum continuation across multiple candles
False moves often retrace quickly and trap impatient traders.
10. Risk Management During Explosive Moves
While technical market explosions offer high reward, they also carry high risk. Rapid price movement can lead to slippage and emotional decision-making.
Effective risk management includes:
Predefined stop-loss levels
Position sizing based on volatility
Avoiding over-leverage
Waiting for candle confirmation instead of chasing price
Discipline is essential to survive and profit consistently from explosive markets.
11. Psychological Impact on Traders
Explosive moves create fear and greed simultaneously. Traders who miss the initial move feel fear of missing out (FOMO), while those in profit may panic and exit early.
Professional traders remain calm, follow their strategy, and understand that technical explosions are part of a broader market cycle, not isolated events.
12. Timeframe Perspective
Technical market explosions occur across all timeframes. On lower timeframes, they may last minutes or hours, while on higher timeframes, they can develop into long-term trends lasting months or years.
Swing traders, day traders, and investors interpret explosions differently, but the underlying technical principles remain the same.
13. Post-Explosion Behavior
After an explosive move, markets often pause, consolidate, or retrace partially. This phase is healthy and allows new participants to enter.
Strong markets use post-explosion consolidation as a base for the next leg, while weak markets fail to hold gains and reverse.
Conclusion
A technical market explosion is the result of accumulated market energy released through key technical triggers such as breakouts, volume surges, indicator alignment, and volatility expansion. These moves reflect shifts in market psychology and institutional participation rather than pure randomness.
For traders who master technical analysis, recognizing early signs of an impending explosion can provide significant opportunities. However, success depends not only on identifying the move but also on managing risk, controlling emotions, and respecting market structure. In fast-moving markets, preparation—not prediction—is the true edge.
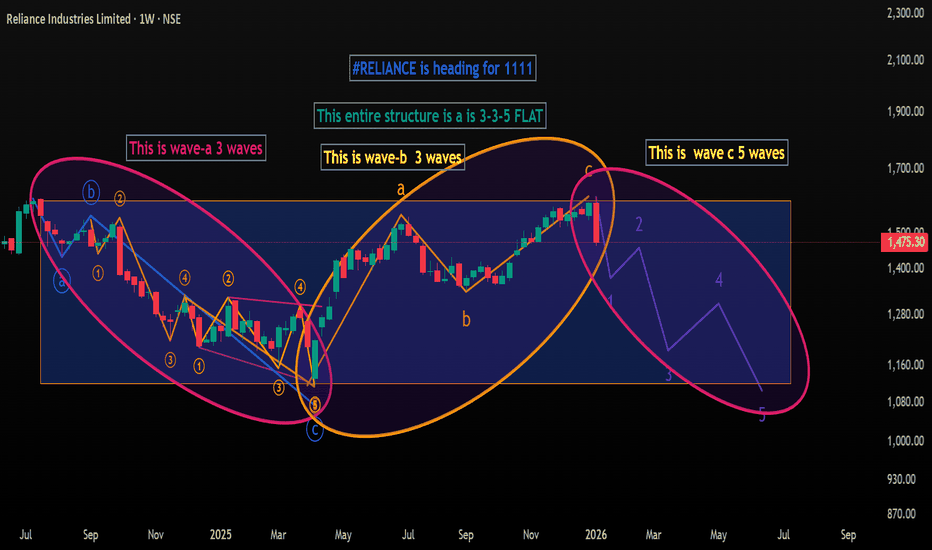
#RELIANCE at 1475 heading for 1111 in 3-3-5 Elliott Wave FLAT #RELIANCE at 1475 is forming a NEAT 3-3-5 FLAT and should head for 1111. Anybody in EW kindly study and share views. In simple terms if you see the two DTF and WTF charts , the stock is forming a 3-3-5 FLAT correction STARTING 12 July 2024 where sub wave -a has three sub waves culminating at 1114 on 07 Apr 2025 and sub sub -c of this wave is ending as a 5 wave Ending Diagonal. Then we have sub wave-b going up in three sub waves again culminating at 1611 high on 03 Jan 2026. Now I am looking for sub wave -c going deep down to 1111 in five sub waves 1-2-3-4-5 as I have shown in the DTF Chart. ANALYSIS INVALIDATION 1611 ( or even 1575 may be good enough for invalidation). Lets C
Catostrophic time aheadDear Humans,
I have a strange finding about the coming time which is going to be tougher than 2008, yes its 100years cycle and we are going to see repeat of 1929-1931, I have marked the fall in RED in WXYXZ style move, market always gives you one chance and we are still adamant on on upward direction and investing at top levels where smart money is selling quiet Easily....
Nifty doesn't have any charts or exchange was not there during this time while we can see in Dow john's chart.
the current scenario at ground levels is that even a Lower and medium class is suffering because of the money scarcity in the market..
I can see that we are going to fall around 78%(precisely 76.4%) from highs by may 2027 in just one and half years time as we are in era of social media where movements are very fast ,,1929-1931 was 2.5 years time great depression.. " what name the market will it be given to this Catastrophic fall" ..
those who were mongeringfall of 12500 levels pre covid high levels at 16000/18000/20000/23500, its time to see those levels again, yes by May/June 2026 . unfortunately they all became bulls now and talking of 28000-30000 levels. well the investor has to hold on for 6 years or more to see these levels again, as history suggest that once such brutal fall happens then time takes its own course to rise again.
even Astro is suggesting Jupiter in 6/8 axis and malific ketu during this 6 years so the journey will be tough to rise from 6000 levels .. so its a time and price fall this time, both together..
Great Depression / Recession/ stagflation/WW3 god knows what all we see ? but
chart is showing a horrific picture..
Its a bigger time frame fall ( weekly, monthly & Yearly) so post this destruction we will not see these brutal levels for next bigger cycle atleast.. may God gives energy & courage to face the tough time coming ahead..
Yes after this fall we will enter into big time bull ERA, Prosperity, growth and growth only..
This post will really help next to next generations to see this interesting finding, if this software pertains that time..
* disclaimer:
its my personal finding for education purpose only and don't take any trade on basis of this.
Short term Analysis of HDFC BankWrap up:-
HDFC Bank is making a wxy pattern in wave c and has completed its wave w at 1018 and wave x is completed at 933. Thereafter, HDFC Bank will head towards wave y.
What I’m Watching for 🔍
Buy HDFC Bank @933 sl 927 for a target of 1027-1078.
Disclaimer: Sharing my personal view — only for educational purpose not financial advice.
"Don't predict the market. Decode them."
Real Knowledge of Candle patterns Candlestick patterns reflect the most important element in trading—market psychology and momentum. Each candle represents:
Open price
High
Low
Close
Candles show emotions like greed, fear, indecision, manipulation, and momentum.
Candlestick patterns can be categorized as:
1. Reversal Patterns
2. Continuation Patterns
3. Indecision Patterns
1. Reversal Candlestick Patterns
-Bullish Reversal Patterns
Hammer
Morning Star
Bullish Engulfing
Piercing Line
Dragonfly Doji
-Bearish Reversal Patterns
Shooting Star
Evening Star
Bearish Engulfing
Dark Cloud Cover
Gravestone Doji
STEELCAS 1 Day Time Frame 📊 Current Price Snapshot (Latest Available)
Approx Live Price: ~₹210–₹213 per share (recent session)
Today’s Day Range (recent close): ~₹208–₹214
📈 Accurate Daily Support & Resistance Levels
🔹 Pivot Point (Day Reference)
Pivot: ~₹206.55–₹213.62 (central reference)
📉 Support Levels
S1: ~₹203.7–₹205.8 – first key support
S2: ~₹197.1–₹201.1 – stronger secondary support
S3: ~₹188.8–₹193.3 – deep support zone
📈 Resistance Levels
R1: ~₹218.5–₹218.3 – first resistance
R2: ~₹226.8–₹226.1 – next upside target
R3: ~₹233.4–₹230.7 – higher resistance
🧠 How to Use These Levels (Daily Time Frame)
Bullish scenario
Break and hold above R1 (~₹218–219) could signal continuation toward R2 (~₹226+).
Sustained break above R2 strengthens trend.
Bearish scenario
Failure under Pivot (~₹206–213) with close below S1 (~₹204–206) may open S2 (~₹197) and S3 (~₹188).
Look for volume confirmation on breakdowns.
📍 Quick Reference Summary (Daily Levels)
Level Price Approx
R3 ~₹230–₹233+
R2 ~₹226–₹227
R1 ~₹218–₹219
Pivot ~₹206–₹213
S1 ~₹203–₹206
S2 ~₹197–₹201
S3 ~₹188–₹193
Crypto Investing Guide: Roadmap to Digital Asset InvestingCryptocurrency investing has evolved from a niche technological experiment into a global financial phenomenon. With Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of alternative digital assets now traded worldwide, crypto has attracted retail investors, institutions, and even governments. However, crypto investing is fundamentally different from traditional investing due to its high volatility, emerging technology, regulatory uncertainty, and unique market dynamics. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of crypto investing, covering fundamentals, strategies, risks, and best practices to help investors make informed decisions.
Understanding Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
At its core, cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency secured by cryptography and typically built on blockchain technology. A blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional financial systems controlled by central authorities, blockchains operate on consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). This decentralization is a key value proposition, offering transparency, immutability, and resistance to censorship.
Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Ethereum expanded the concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing programs that run on the blockchain—paving the way for decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and Web3 applications. Understanding these technological foundations is essential before investing, as the value of crypto assets is often tied to their utility, network adoption, and security.
Types of Crypto Assets
Crypto assets can be broadly categorized into several groups. Payment coins like Bitcoin and Litecoin focus on value transfer and store of value. Platform tokens such as Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche support decentralized applications. Utility tokens grant access to specific services within an ecosystem. Stablecoins are pegged to fiat currencies and aim to reduce volatility. Governance tokens allow holders to vote on protocol decisions. Each category carries different risk and return profiles, making diversification across types an important consideration.
Why People Invest in Crypto
Investors are drawn to crypto for multiple reasons. Some view it as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation, especially in economies with unstable monetary systems. Others are attracted by the potential for high returns, as early adopters of successful projects have historically seen significant gains. Additionally, crypto offers exposure to cutting-edge innovation in finance, technology, and digital ownership. However, these opportunities come with heightened risks that require careful evaluation.
Investment Strategies in Crypto
Crypto investing strategies range from conservative to highly speculative. Long-term investing (HODLing) involves buying fundamentally strong projects and holding them through market cycles, betting on long-term adoption. Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) reduces timing risk by investing fixed amounts at regular intervals. Active trading focuses on short-term price movements using technical analysis but requires experience, discipline, and risk management. Staking and yield farming allow investors to earn passive income by locking assets in networks or DeFi protocols, though they introduce smart contract and liquidity risks.
A disciplined strategy should align with the investor’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Overexposure to a single asset or strategy can significantly increase downside risk.
Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Successful crypto investing relies on analysis. Fundamental analysis examines factors such as the project’s use case, team, tokenomics, roadmap, community support, and real-world adoption. Metrics like active addresses, transaction volume, and total value locked (TVL) provide insights into network health. Technical analysis, on the other hand, studies price charts, trends, support and resistance levels, and indicators like RSI or moving averages to identify potential entry and exit points. Combining both approaches can lead to more balanced decisions.
Risk Management and Volatility
Crypto markets are notoriously volatile, with prices capable of swinging dramatically in short periods. Risk management is therefore critical. Investors should never invest money they cannot afford to lose, use position sizing to limit exposure, and avoid excessive leverage. Setting stop-loss levels, maintaining diversification, and periodically rebalancing portfolios can help manage downside risk. Emotional discipline is equally important, as fear and greed often drive poor decisions during extreme market moves.
Security and Storage
Security is a unique concern in crypto investing. Assets are controlled by private keys, and losing them can mean permanent loss of funds. Investors can store crypto on exchanges, software wallets, or hardware wallets. While exchanges offer convenience, they carry counterparty risk. Hardware wallets provide higher security for long-term holdings. Practicing good security hygiene—such as enabling two-factor authentication, avoiding phishing links, and backing up recovery phrases—is essential.
Regulation and Taxation
Crypto regulations vary widely across countries and are constantly evolving. Some jurisdictions embrace digital assets, while others impose restrictions or bans. Investors must stay informed about local regulations, compliance requirements, and tax obligations. Profits from crypto trading are often subject to capital gains tax, and improper reporting can lead to legal issues. Regulatory clarity can significantly impact market sentiment and asset prices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
New investors often fall into predictable traps: chasing hype, investing without research, overtrading, or relying solely on social media tips. Another common mistake is ignoring fees, liquidity, and security risks. Patience, education, and a long-term perspective can help avoid costly errors.
Conclusion
Crypto investing offers unique opportunities to participate in a rapidly evolving digital economy, but it is not a guaranteed path to wealth. Success requires a solid understanding of blockchain technology, thoughtful strategy selection, disciplined risk management, and continuous learning. By approaching crypto with a balanced mindset—embracing innovation while respecting risk—investors can navigate this dynamic market more effectively and build a resilient digital asset portfolio over time.
Updated Nifty Analysis for Jan 09, 2026Wrap up:-
As updated earlier, wave 1 was completed at 26057 but wave 2 counts have now been changed due to a sudden fall and is expected to be completed in the range of 25800-25850. Thereafter, nifty will head towards wave 3.
What I’m Watching for Jan 09, 2026 🔍
Buy Nifty only above @25971 sl 25858 (15 min. candle closing basis) for a target of 26447-26630.
Short Nifty in the range @25935-25921 sl 25971 (15 min. candle closing basis) for a target of 25818.
Disclaimer: Sharing my personal market view — only for educational purpose not financial advice.
"Don't predict the market. Decode them."
Tube Investments of India Ltd — Wave X Triangle in PlayAfter the sharp decline from ₹4,810, the recent advance initially looked like a potential leading diagonal of a new impulse. However, the internal overlaps and choppy rhythm point instead to a Wave X triangle, likely part of a larger corrective sequence (W–X–Y).
As long as price holds below ₹3,419.90, the bearish outlook remains intact, with the next leg — Wave Y — possibly aiming toward the 0.5–0.618 retracement zone (₹2,511–₹1,968). That region, close to the golden ratio, may act as a potential termination zone for the entire correction.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. Please do your own research (DYOR) before making any trading decisions.
Elliott Wave Analysis XAUUSD – January 9, 2025
1. Momentum
Daily (D1)
– Daily momentum has already turned bearish
– I expect the downside move to continue for the next few days until D1 momentum reaches the oversold zone
– This suggests that medium-term corrective pressure is still dominant
H4
– H4 momentum is preparing to turn bearish
– We need to wait for H4 candle close confirmation
– Once confirmed, price is likely to experience at least a few bearish H4 candles
H1
– H1 momentum is currently in the oversold zone
– In the short term, a technical rebound on H1 is likely
– This rebound will be critical for identifying a potential sell opportunity
2. Elliott Wave Structure
Daily Wave Structure (D1)
– With Daily momentum turning bearish, I expect price to continue developing the purple wave Y
– Based on last week’s analysis (which will be updated again this week), Weekly momentum still needs around two more weekly candles to reach the oversold zone
– This implies that wave Y may evolve as a time-consuming corrective structure, such as:
– A 5-wave structure
– A zigzag
– Or a triangle
– These scenarios align with the principle of alternation, where corrective structures tend to become more complex over time
– Therefore, we continue to let momentum and wave structure confirm each other
(This is a key difference in my Elliott Wave approach: I do not rely solely on wave patterns, but always integrate momentum — an approach I learned from Robert C. Minor.)
H4 Wave Structure
– H4 momentum is now turning bearish, as mentioned in yesterday’s plan
– The recent H4 momentum rally failed to break above 4500, which supports the view that wave 2 or wave B has already formed
– As H4 momentum moves toward the oversold zone:
– Price needs to break below 4402 to confirm the bearish trend
H1 Wave Structure
– On H1, a blue 1-2-3-4-5 structure has been tentatively assigned
– Price is currently developing blue wave 2
Invalidation scenarios
– If price reaches 4500:
– The current H1 wave count will be invalidated
– In this case, red wave C may continue toward 4521
– If price reaches 4550:
– The entire red ABC structure will be invalidated
– A full wave recount will be required
3. Outlook & Trading Bias
– With:
– Daily momentum already bearish
– H4 momentum turning bearish
→ I remain bearish on the development of wave Y
– The current H1 rebound is therefore crucial
– The ideal scenario:
– Price rallies below 4500
– H1 momentum reaches the overbought zone and turns down from there
→ This would provide a high-probability sell setup
4. Trading Plan (Unchanged)
– Sell Zone: 4481 – 4484
– Stop Loss: 4502
– TP1: 4440
– TP2: 4376
– TP3: 4348
NIFTY : Trading levels and Plan for 09-Jan-2026
(Timeframe: 15-min | Gap criteria considered: 100+ points)
🔑 Key Levels from Chart
Major Upside Resistance: 26,115
Last Intraday Resistance: 26,032
No-Trade / Supply Zone: 25,839 – 25,932
Opening Support / Pivot: 25,839
Last Intraday Support: 25,741
Lower Support Extension: 25,587
🧠 Market context: NIFTY is in a short-term corrective structure after a strong sell-off. Price is consolidating inside a well-defined no-trade zone, indicating balance before the next directional move.
🟢 1. GAP-UP OPENING (100+ Points)
If NIFTY opens above 25,932, it signals short-covering but into a supply zone.
🎓 Educational Insight
Gap-ups after a decline often face selling pressure near VWAP/supply zones. Sustainable upside requires acceptance above resistance, not just an opening spike.
Plan of Action
Avoid chasing longs in first 15 minutes ⏳
Sustain above 26,032 → upside toward 26,115
Rejection near 26,032 → pullback to 25,932 – 25,839
Fresh longs only on retest + higher low formation
Options idea: Bull Call Spread (ATM buy + OTM sell)
🟡 2. FLAT OPENING
If NIFTY opens inside 25,839 – 25,932, expect range-bound & whipsaw action.
🎓 Educational Insight
Flat opens within supply-demand overlap zones usually lead to false breakouts. Direction emerges only after range expansion with volume.
Plan of Action
Above 25,932 with hold → move toward 26,032
Failure above 25,932 → sideways to negative bias
Break below 25,839 → weakness toward 25,741
Avoid trades in mid-range 🚫
Options idea: Iron Fly / Hedged Short Strangle if volatility drops
🔴 3. GAP-DOWN OPENING (100+ Points)
If NIFTY opens below 25,839, bears remain in control.
🎓 Educational Insight
Gap-downs into prior supports can trigger panic selling, but sharp bounces are also common. Always wait for price confirmation.
Plan of Action
First demand zone: 25,741
Strong rejection from 25,741 → intraday bounce possible
Break & sustain below 25,741 → slide toward 25,587
Avoid fresh shorts exactly at support
Options idea: Bear Put Spread or Put Debit Spread
🛡️ Risk Management Tips (Options Trading)
Risk only 1–2% capital per trade 💰
Prefer spreads over naked buying in volatile zones
Book partial profits near resistance/support
No averaging against trend 🚫
Stop trading after 2 consecutive losses 🧠
🧾 Summary & Conclusion
Above 26,032: Short-term bullish toward 26,115
25,839 – 25,932: No-Trade / Chop Zone
Below 25,839: Weakness toward 25,741 → 25,587
Focus on price acceptance, not prediction 🎯
⚠️ Disclaimer
I am not a SEBI-registered analyst. This analysis is strictly for educational purposes only. Markets involve risk—please consult a certified financial advisor before trading.
BTCUSDT – Elliott Wave Completion → Short Sell SetupPrice action on BTCUSDT appears to be completing a 5-wave Elliott impulse structure inside a rising wedge / channel. Waves (1)–(5) are clearly respected, with Wave (5) now testing a major trendline resistance zone around 91,800–92,000.
Momentum indicators are showing loss of strength near the top, suggesting Wave (5) exhaustion. As per Elliott Wave theory, after a completed 5-wave move, a corrective ABC structure is expected.
Trade Idea:
Bias: Short / Sell
Sell Zone: 92000 – 92,200
Invalidation (SL): Above 92,600 (Wave 5 extension failure)
Targets:
TP1: 90,000
TP2: 88,700
TP3: 87,400 (major demand & channel support)
A breakdown from the upper trendline should accelerate downside pressure toward the lower channel support, aligning with a larger corrective move.
BEL – Setting Up for a 5% Move-Swing TradeBEL – Setting Up for a 5% Upside Move 🚀
BEL has taken strong support near ₹385–388 and is now reclaiming key moving averages with improving momentum. With the upcoming Union Budget expected to favor Defence spending, sentiment & flows remain supportive.
📌 Trade View
CMP: ~₹400
Targets: ₹420 (near-term), ₹431 (extendable)
Support: ₹388
Stoploss: ₹382 (strict)
💡 Why?
Strong bounce from key demand zone
Reclaiming trend levels + improving structure
Budget tailwinds + Defence sector strength
Trend intact. Dips buying. Ride the move! 🐊🔥
Nifty Analysis for Jan 09, 2026Wrap up:-
As updated earlier, wave 1 was completed at 26057 but wave 2 counts have now been changed due to a sudden fall and is expected to be completed at 25858 if nifty breaks and sustains above 25971. Thereafter, nifty will head towards wave 3.
What I’m Watching for Jan 09, 2026 🔍
Buy Nifty above @25971 sl 25858 (15 min. candle closing basis) for a target of 26447-26630.
Disclaimer: Sharing my personal market view — only for educational purpose not financial advice.
"Don't predict the market. Decode them."