DAILY FOREX SCAN Session – 24 04 02 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
U.S. Dollar / Australian Dollar
No trades
What traders are saying
AUDUSD – Sell From Weak High RejectionPrice swept the weak high at 0.6772 and immediately rejected, confirming a liquidity grab. Structure shifted bearish, and price is now pulling back toward premium levels for a potential continuation down.
🔍 Bias: Bearish
Entry: 0.67722
Stop Loss: 0.67873 (above sweep)
Take Profit:
TP1: 0.67634
Reasoning: Liquidity sweep + bearish structure shift + clean inefficiencies below acting as magnets.
AUDUSD LONG SETUP — Bullish Reversal from DemandAUDUSD has tapped into a strong demand zone aligned perfectly with a long-term ascending trendline, showing signs of potential bullish reversal. Price swept the previous intraday liquidity and reacted strongly, indicating buyers are stepping in.
This confluence makes this area a high-probability long setup.
Description
Price dropped into a well-defined demand zone around 0.66720–0.66650, which overlaps with the ascending trendline support drawn from previous higher lows. The sweep of liquidity below the zone suggests a fakeout and accumulation, increasing the probability of a bullish move.
If price maintains above the zone and starts forming bullish structure, we can expect a continuation towards the previous swing highs.
📝 Trade Plan (Suggestive)
Entry: 0.66798 (within demand zone)
Stop Loss: Below zone at 0.662
Take Profit 1: 0.67100 (previous structure high)
Take Profit 2: 0.67320 (premium zone)
Risk–Reward: ~1:2
🔍 Reasons to Take This Trade
✔ Demand Zone Reaction
✔ Trendline Confluence
✔ Liquidity Sweep Below Zone
✔ Strong Wick Rejection Showing Buyers
✔ Price in Discount (Buy-side value area)
Disclaimer: for educational purpose
AUDUSD Buy Setup | Discount Zone Reaction + Trendline BreakBias: Bullish
Timeframe: 15M
Pair: AUDUSD
Market Structure & Context
AUDUSD has completed a corrective move within a descending channel after a strong impulsive rally. Price has now reached a higher-timeframe discount zone, aligning with a rising trendline support, where we see clear signs of seller exhaustion.
Downside liquidity has been swept below recent equal lows, followed by strong bullish displacement, indicating potential smart money re-entry from discount.
Technical Confluence
Price reacting from HTF discount zone
Liquidity sweep below equal lows
Descending channel break attempt
Bullish structure shift on lower timeframe
Mean reversion setup targeting equilibrium & premium
Trade Plan
Entry:
Buy on confirmation above 0.66936
Stop Loss:
Below demand & trendline at 0.66728
Targets:
TP1: 0.6725 (Equilibrium)
TP2: 0.6742 (Mid supply)
TP3: 0.6765 (Premium zone / HTF resistance)
Risk–Reward
Approx 1:3.5 – 1:5 RR
Invalidation
Strong close below 0.66728 invalidates bullish bias
Notes
Patience is key. Best entries occur after structure confirmation, not blind buying. This setup favors New York session expansion if DXY weakens.
MACRO FX COMPARISON: DXY vs AUDUSDMACRO FX COMPARISON: DXY vs AUDUSD – WHAT STRUCTURAL CHANGE REALLY MATTERS
This is a structure-first, educational view comparing DXY and AUDUSD to understand the broader macro environment — and why most “USD reversal” narratives are premature.
No forecasts.
No trade calls.
Only structure.
🔹 DXY – TIME CORRECTION, NOT TREND REVERSAL
DXY remains locked inside a large corrective / overlapping structure.
Price action shows range expansion in time, not impulsive price discovery.
Momentum (RSI) confirms compression, not trend acceleration.
Key point:
A sideways or corrective DXY does not automatically mean USD weakness — it means indecision in trend.
🔹 AUDUSD – MACRO CONFIRMATION FROM FX
On higher timeframes (Quarterly / Monthly), AUDUSD remains within a long-term corrective structure.
Multiple upside attempts have failed to transition into an impulsive trend.
Momentum remains muted — consistent with macro consolidation, not a new bull cycle.
Important insight:
If USD were entering a true bearish phase, AUDUSD would already be trending impulsively.
It is not.
🔹 WHY THIS COMPARISON MATTERS
Looking at DXY alone can be misleading.
FX pairs like AUDUSD act as structural confirmation tools.
Right now:
DXY = correcting in time
AUDUSD = trapped in macro correction
No FX pair shows a clean impulsive USD breakdown
This combination defines a non-trending USD environment, not a trend reversal.
🔹 WHAT WOULD ACTUALLY COUNT AS A STRUCTURAL CHANGE?
Only the following would matter structurally:
✅ DXY
Clean impulsive breakdown
Loss of key higher-timeframe support with follow-through
Momentum expansion, not divergence
✅ AUDUSD
Clear 5-wave impulsive advance
Sustained breakout from long-term corrective boundaries
RSI regime shift above prior ranges
Until then:
The macro remains in transition, not resolution.
🔹 BOTTOM LINE
Current FX behaviour reflects time-based correction, not trend exhaustion.
Structural patience is required.
Noise increases near transitions — structure filters it out.
This is a study of market structure, not a trading signal.
#AUDUSD
#DXY
#ForexAnalysis
#MarketStructure
#ElliottWave
#StructureOverPrediction
#PriceAction
#EducationalAnalysis
Bullish FVG Retracement With RSI & MACD📈 AUDUSD – Bullish FVG Retracement With RSI & MACD Momentum Confluence
This chart highlights a well-defined bullish structure on AUDUSD, characterized by a sequence of Higher Lows (HL) followed by a clean Higher High (HH). The latest impulsive leg upward created multiple Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), each formed by sharp displacement that left behind inefficiencies in price.
As price extends higher, the nearest unmitigated FVG becomes the primary area of interest. This imbalance represents the most logical level for a corrective retracement before bullish continuation resumes.
While a deeper FVG exists below, the nearest imbalance tends to offer stronger stability and higher probability in forex due to tighter liquidity behavior and more frequent shallow retracements.
In this setup, the combination of FVGs + RSI Behavior + MACD Histogram provides a high-confluence framework for identifying discount retracement zones and timing momentum re-acceleration.
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
📊 Key Observations
1️⃣ Recent Bullish FVG Creation
The most recent impulsive leg upward generated a clear bullish FVG.
AUDUSD responded strongly to displacement, confirming active buy-side order flow.
Price has not yet returned to rebalance this inefficiency, making it the most probable retracement magnet.
2️⃣ Primary FVG (High-Probability Zone)
The upper FVG has the strongest confluence:
Formed by strong bullish displacement
Closest imbalance to current price (forex tends to fill nearest inefficiency first)
Aligns with bullish structure (HL → HH progression)
RSI remains elevated, signaling temporary overextension before a healthy pullback
MACD histogram shows slowing momentum, suggesting a cooling phase before continuation
This makes the upper FVG the most structurally significant level for a bullish reaction.
3️⃣ Secondary FVG Below
A deeper FVG also exists, but:
Formed during a smaller displacement
Much lower probability in forex due to shallower retracements
Carries less relevance unless the primary FVG fails
Momentum and structure currently favor reacting to the nearest imbalance
The zone may still attract price in extreme volatility, but it is not the main expectation.
4️⃣ RSI Behavior (Pullback Confirmation)
RSI is currently near the overbought region, indicating:
Market is stretched after a strong rally
A retracement is healthy and expected
During FVG entry, RSI must stay above 40 to maintain bullish structure and prevent a reversal signal
This acts as a structural momentum filter.
5️⃣ MACD Histogram Confirmation
MACD histogram is showing:
Momentum deceleration
A potential shift to light-green bars as price cools
A bullish continuation signal expected once the histogram begins turning upward from the pullback
Together, this confirms the classical model:
impulse → slowdown → retracement → continuation.
6️⃣ Structural Context
AUDUSD maintains a clean bullish sequence:
HL → HH progression
Deep liquidity sweep in the previous leg
Strong displacement aligned with bullish flow
As long as price holds above the FVG and prior HL, pullbacks are more likely to act as rebalancing events, not reversals.
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
📊 Chart Explanation
Symbol → OANDA:AUDUSD
Timeframe → 1D
This chart illustrates how Smart Money Concepts blend with momentum indicators:
Clean HL → HH bullish structure
Fresh bullish FVG acting as primary discount zone
Secondary FVG present but lower probability in forex
RSI signaling temporary exhaustion before a pullback
MACD histogram confirming momentum slowdown into the FVG
Expected sequence:
displacement → inefficiency → retracement → mitigation → continuation
Price remains bullish unless structure breaks below the HL and the FVG fails to hold.
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
📘How RSI & MACD Strengthen FVG Setups (Bullish & Bearish)
🔹 1. RSI + FVG
Bullish Setup:
RSI holding above 40 during the retracement confirms bullish structure.
Rising RSI from oversold strengthens the likelihood of continuation.
Bearish Setup:
RSI staying below 60 during the pullback confirms bearish structure.
Falling RSI from overbought increases the probability of downside continuation.
RSI shows whether the retracement is a healthy correction or a potential reversal.
🔹 2. MACD Histogram + FVG
Bullish Setup:
Decreasing histogram during the retracement = healthy cooldown.
Histogram turning upward inside or after the FVG = bullish continuation signal.
Bearish Setup:
Increasing histogram during the pullback = losing bearish momentum temporarily.
Histogram turning downward again at the FVG = bearish continuation confirmation.
MACD provides momentum timing for the reaction out of the FVG.
🔹 3. Combined Logic (Works Both Ways)
Displacement creates an FVG
Price retraces into the imbalance
RSI respects structural boundaries (bullish >40, bearish <60)
MACD momentum aligns with the trend direction
Price rejects the FVG and continues the trend
This combined approach filters low-quality FVG zones and identifies the highest-probability continuation setups in both bullish and bearish markets.
⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻⸻
⚠️ Disclaimer
📘 For educational purposes only
🙅 Not SEBI registered
❌ Not financial or investment advice
🧠 Smart-Money-Concepts explanation only
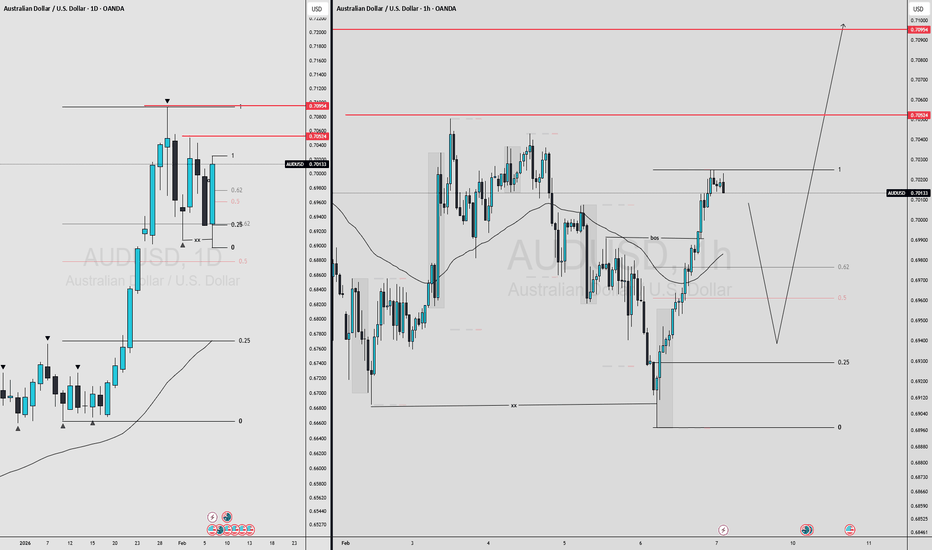
AUDUSD MULTI TIMEFRAME ANALYSIS AUDUSD remains bullish, even though we’re testing a premium area on the daily. Upside toward the weekly high of 10 Nov 2025 is still possible(PMH). Two scenarios for today:
(A) A setup inside the Asian range (B-grade idea).
(B) A deeper pullback toward ~0.65320, which is the higher-quality, A-plus discounted entry.
If price reaches either zone and I see a strong rejection + LTF structure shift, I’ll look for longs targeting the previous day’s high and the prior monthly high. A deeper correction is more likely, so Scenario A is my preferred setup.
setup quality B :⭐⭐⭐
setup quality A : ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
AUDUSD MULTI TIMEFRAME ANALYSIS Hello traders , here is the full multi time frame analysis for this pair, let me know in the comment section below if you have any questions , the entry will be taken only if all rules of the strategies will be satisfied. wait for more price action to develop before taking any position. I suggest you keep this pair on your watchlist and see if the rules of your strategy are satisfied.
AUD/USD Long Setup – Buying the Pullback with Clear RiskPair: AUD/USD
Entry: 0.65335
Stop Loss: 0.65275
Take Profit: 0.65535
Risk–Reward Ratio: ≈ 1:3.3
This isn’t a signal — it’s a guide for structure-based entries with tight risk control.
Always wait for price action confirmation before jumping in 🚀
Market ThinkingThe market had been under pressure, but now it’s starting to show some bullish momentum building up — higher lows are forming, and each dip is getting bought up a little faster.
The entry around 0.6544 could be the start of a fresh upward impulse if price continues to hold above that zone. I’ll be looking for signs of confirmation: maybe a strong bullish candle, or a breakout above minor resistance.
If buyers stay active and momentum builds, there’s room for price to climb toward the 0.6712 target zone, which also matches a previous swing high — an area where profit-taking might start to happen
Risk is clearly defined — if price breaks below 0.64969, it means buyers failed.
Reward potential — aiming for a move toward 0.67123 gives a healthy risk-to-reward ratio (roughly 1:3).
The goal isn’t to predict perfectly, but to react to what the market confirms.
It’s a patient setup — waiting for the market to prove strength before committing fully
AUDUSD BREAKS CHANNEL RESISTANCE - TREND SHIFT AHEAD?Symbol - AUDUSD
AUDUSD is undergoing a corrective phase after breaking above the resistance of the descending channel. The market now requires consolidation or the formation of a trading range above 0.6525 to sustain bullish momentum.
The US dollar remains in a consolidation phase and shows limited potential for further appreciation. Mounting pressure ahead of the upcoming Federal Reserve meeting may act as a supportive factor for the Australian dollar.
The pair is transitioning into a distribution phase following a period of consolidation. The breakout above 0.6525 confirmed a breach of the descending channel’s resistance, signaling the early stages of a potential trend reversal. Sustained price action above this level could pave the way for continued upside movement.
Resistance levels: 0.6567, 0.6610
Support levels: 0.6525, 0.6493
Currently, the pair is attempting to establish a shift in trend direction. The ongoing consolidation and distribution above the previously broken trendline are constructive signs. However, the formation of a defined trading range will be essential to confirm the establishment of a new local uptrend.
AUD/USD (3H)...AUD/USD (3H) chart, here’s a breakdown of what I see and how the target can be projected:
---
🧠 Pattern Analysis
My identified a Cup and Handle pattern, which is a bullish continuation setup.
Cup low: around 0.6450
Cup rim (resistance / breakout level): around 0.6580 – 0.6590
Current price: ~0.6585 (right around the breakout level)
Handle: short pullback, touching near Ichimoku cloud support — healthy structure before potential breakout.
---
🎯 Target Projection (Cup & Handle Rule)
Cup and Handle target = Breakout level + Depth of the cup
Depth of cup:
0.6585 (rim) – 0.6450 (bottom) = 0.0135
Target = 0.6585 + 0.0135 = 0.6720
---
✅ Target Summary
Entry (breakout confirmation): above 0.6590
Target: 0.6720
Stop-loss: below 0.6535 – 0.6540 (below handle & cloud support)
Risk/Reward ratio: ~1:2.5
---
💡 Bonus Confirmation
Price is above the Ichimoku Cloud (bullish bias).
Handle retracement is shallow and respecting Tenkan/Kijun lines — typical of strong continuation setups.
Volume on breakout (watch for increase) would add confirmation.
---
Final Target: 0.6720 (main take-profit zone)
Growth in Emerging MarketsIntroduction
Emerging markets are nations that are transitioning from developing to developed status, characterized by rapid industrialization, growing financial markets, and increasing integration into the global economy. These economies — such as India, China, Brazil, Indonesia, South Africa, and Mexico — have become the engines of global growth over the past three decades. They represent not only significant opportunities for investment and trade but also a vital source of innovation, labor, and consumption.
In the 21st century, emerging markets have been at the forefront of global economic transformation. Their collective share of global GDP has risen dramatically, fueled by urbanization, technology adoption, infrastructure development, and a growing middle class. Yet, these markets also face substantial challenges — including income inequality, political volatility, inflationary pressures, and vulnerability to external shocks. Understanding their growth dynamics is crucial for policymakers, investors, and global businesses seeking to capitalize on the shifting balance of economic power.
Defining Emerging Markets
An “emerging market” is typically defined as an economy that exhibits some characteristics of a developed market but has not yet achieved that status. These economies are often marked by:
Rapid GDP growth and industrialization
Expanding middle-class populations
Developing but volatile financial markets
Institutional and infrastructural transformation
Increasing participation in global trade and investment
Organizations such as MSCI, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and World Bank classify countries as emerging markets based on factors like per capita income, market accessibility, and financial development. Major emerging markets are often referred to collectively as BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) or MINT (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey).
Historical Background
The term “emerging markets” was popularized in the early 1980s by the World Bank’s International Finance Corporation (IFC) to attract investors to rapidly developing countries. In the post-Cold War era, globalization and liberalization opened new opportunities for these nations to integrate into the global economy.
From 1990 to 2020, emerging markets experienced a profound transformation:
China’s economic reforms under Deng Xiaoping unleashed massive manufacturing growth.
India’s liberalization in 1991 opened its economy to foreign investment and competition.
Latin American economies, after periods of hyperinflation, adopted market-friendly reforms.
Eastern European countries transitioned from centrally planned to market economies after the fall of the Soviet Union.
During this period, emerging markets contributed more than two-thirds of global GDP growth, reshaping international trade, investment patterns, and geopolitical influence.
Key Drivers of Growth
1. Demographic Dividend
One of the strongest drivers of emerging market growth is their young and expanding population. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Nigeria possess large working-age populations, creating both a labor supply and a consumer base. This demographic advantage supports productivity, innovation, and domestic demand — essential elements for long-term growth.
2. Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Urbanization is a hallmark of emerging markets. Rapid migration from rural to urban areas has fueled demand for housing, transport, energy, and digital infrastructure. Cities have become centers of economic activity, contributing to higher productivity and consumption. Governments and private investors are heavily investing in infrastructure projects such as metro systems, smart cities, ports, and renewable energy.
3. Technological Leapfrogging
Emerging markets have harnessed technology to overcome traditional development barriers. The widespread adoption of mobile banking, e-commerce, and digital services has revolutionized sectors like finance, retail, and healthcare. For instance, India’s UPI digital payment system, Kenya’s M-Pesa, and China’s Alipay and WeChat Pay have made financial inclusion a reality for millions.
Additionally, emerging economies are becoming innovation hubs, contributing to global technology supply chains. Startups in fintech, edtech, and agritech are leveraging local needs and global technologies to create scalable solutions.
4. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Trade Integration
FDI has played a critical role in boosting industrialization, technology transfer, and job creation in emerging markets. Multinational corporations view these economies as growth frontiers due to their large markets and lower labor costs. The signing of regional trade agreements — such as RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) in Asia — has further deepened trade integration.
Emerging markets are also major players in global supply chains, especially in manufacturing, natural resources, and services. China became the “world’s factory,” while India emerged as a global IT and service hub.
5. Rising Middle Class and Consumption
The growth of the middle class has transformed emerging markets into major consumer economies. Rising incomes, better education, and urban lifestyles have driven demand for goods and services ranging from smartphones to automobiles. According to McKinsey, emerging markets will account for more than 50% of global consumption by 2030, making them pivotal for multinational corporations.
6. Policy Reforms and Economic Liberalization
Most emerging economies have undertaken structural reforms — privatization, deregulation, and financial liberalization — to attract investment and enhance competitiveness. Independent central banks, modern taxation systems, and digital governance have strengthened institutional frameworks and improved macroeconomic stability.
Challenges Facing Emerging Markets
While emerging markets have immense potential, their growth trajectories are not without obstacles.
1. Political and Institutional Instability
Weak governance, corruption, and policy inconsistency remain major barriers. Political instability can deter investors and slow reform implementation. For instance, frequent changes in government policies or bureaucratic inefficiencies can create uncertainty for long-term investments.
2. Income Inequality and Social Disparities
Economic growth has not always translated into inclusive prosperity. Many emerging economies face widening income gaps between urban and rural populations. Unequal access to education, healthcare, and digital resources hinders human capital development and social mobility.
3. Dependence on Commodities
Several emerging markets — particularly in Africa and Latin America — rely heavily on commodity exports such as oil, copper, and agricultural products. This makes them vulnerable to price volatility and global demand shifts. Diversification remains a persistent challenge.
4. External Shocks and Currency Volatility
Emerging markets are highly sensitive to global financial conditions. Fluctuations in U.S. interest rates, trade tensions, and geopolitical risks can trigger capital outflows, currency depreciation, and inflation. Episodes like the 2013 “taper tantrum” and the COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of their financial systems.
5. Debt and Fiscal Pressure
Rising public debt, especially after the pandemic, has strained government budgets. Many countries have borrowed heavily to finance infrastructure and welfare programs, increasing vulnerability to credit downgrades and default risks.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Issues
Rapid industrialization has come at an environmental cost. Pollution, deforestation, and climate change pose existential threats to long-term development. Transitioning to green energy and sustainable industries is now essential but financially challenging.
Case Studies: Leading Emerging Markets
1. China
China is the quintessential emerging market success story. Through export-led growth, massive infrastructure investment, and state-directed capitalism, it became the world’s second-largest economy. However, China now faces slowing growth, demographic decline, and geopolitical pressures. The government’s push for technological self-reliance and green transition marks the next phase of its development.
2. India
India’s growth has been fueled by services, technology, and digital innovation. With a young population and expanding middle class, it is projected to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2030. Initiatives like “Make in India,” “Digital India,” and “Startup India” aim to boost manufacturing, innovation, and entrepreneurship.
3. Brazil
Brazil’s economy is driven by natural resources and agriculture but often hampered by political volatility and inflation. Recent efforts to promote renewable energy, fintech, and agritech indicate potential for sustainable diversification.
4. Indonesia and Vietnam
Southeast Asian economies like Indonesia and Vietnam have benefited from global supply chain shifts. Their competitive labor markets, stable governance, and reform-oriented policies make them attractive destinations for manufacturing and FDI.
5. African Emerging Economies
Africa, with its abundant resources and youthful population, represents the next frontier. Countries like Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa are witnessing rapid digitalization and entrepreneurship. However, infrastructure gaps and governance challenges persist.
Future Outlook
1. Digital Transformation
The future of emerging markets will be shaped by digital infrastructure — 5G, AI, and fintech will drive innovation across industries. Governments and private sectors are investing in digital literacy, e-governance, and data economies to enhance competitiveness.
2. Green Growth and Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming central to policy agendas. The shift toward renewable energy, electric vehicles, and sustainable agriculture offers both challenges and new growth avenues. International financing for green projects will be key to achieving low-carbon transitions.
3. Regional Integration and South-South Cooperation
Emerging markets are increasingly trading and investing among themselves. Initiatives like BRICS cooperation, African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), and ASEAN integration are strengthening economic ties and reducing dependency on developed economies.
4. Innovation and Entrepreneurship
The entrepreneurial ecosystem in emerging markets is booming. Startups in fintech, healthtech, and edtech are solving local problems with global scalability. This innovation wave can help create high-value jobs and promote inclusive growth.
5. Balancing Growth with Inclusion
To sustain growth, emerging markets must prioritize education, healthcare, and social equity. Policies that enhance skills, reduce poverty, and support SMEs will be crucial for ensuring broad-based prosperity.
Conclusion
Emerging markets have transformed the global economic landscape. They have become the new centers of growth, innovation, and consumption. While challenges such as inequality, governance, and volatility persist, their potential remains enormous. With continued reforms, digital adoption, and sustainable policies, emerging markets are poised to lead the next wave of global progress.
As the balance of economic power shifts eastward and southward, the future of global growth will increasingly be written in the cities of Asia, Africa, and Latin America — where ambition, technology, and resilience are redefining what it means to “emerge.”
AUD/USD on a 30-minute timeframe (based on the visible labels)..AUD/USD on a 30-minute timeframe (based on the visible labels). Let’s break it down carefully:
The pair AUD/USD is currently trading around 0.6518.
The chart shows a bullish breakout above a descending trendline.
The green zone marked looks like a demand/support zone.
A target line is already drawn near the top of the chart, labeled “Target Point”.
🔍 Based on the chart:
The “Target Point” appears to be at approximately 0.6600 – 0.6605 level.
🧭 Summary:
Type Level
Entry Zone Around 0.6500–0.6520
Target (TP) 0.6600 – 0.6605
Stop Loss (SL) Likely below the green zone, around 0.6480
💡 Interpretation:
This setup seems to be a breakout + retest trade idea where the expectation is that AUD/USD will move upward about 80–100 pips toward the 0.6600 target area.