EUR/USD | 1H | Smart Money OutlookPrice has swept the previous low and is reacting from a key liquidity pocket. Structure remains intact for a potential bullish delivery. With CPI expected to print on the stronger side, we could see a favorable USD reaction — but the market is already pricing in the move, setting up EUR/USD for a liquidity grab before a push higher.
I’m watching for:
Accumulation near 1.1680 zone
Break of internal structure for confirmation
Targeting the 1.1730 region as the next supply area
If CPI comes out as expected, we could get that impulsive leg upward aligning with this setup.
Gann
OIL 1 Day Time Frame 📊 Current Approx Price (as per today data): ₹488.90 – ₹514.4 range (varies by platform/time) — OIL has recently traded around this area near daily pivot/major levels.
📈 Daily Pivot & Key Levels (Classic method)
Level Price (₹) Role
R3 (3rd Resistance) 507.45 Strong upside hurdle
R2 499.40 Secondary resistance
R1 491.35 Near-term resistance
Daily Pivot 483.30 Trend bias line
S1 (1st Support) 475.25 Immediate support
S2 467.20 Next downside cushion
S3 459.15 Major support zone
👉 Interpretation (1-day frame):
Price above pivot (~483-484) = bullish bias on the daily.
Near-term resistance cluster: ₹491–₹499–₹507 — watch breakout closes above these for continuation.
Downside support cluster: ₹475 → ₹467 → ₹459 — breakdown below these suggests short-term correction.
📊 Short Summary (Daily Momentum & Indicators)
Technical bias:
• RSI near bullish/neutral zone — showing positive momentum without being extremely overbought.
• MACD / ADX generally leaning bullish indicating trend strength at the moment.
Overall daily structure favors bullish to sideways — supports holding and resistance being tested.
🧠 How to use these levels (Daily)
📍 Bullish setup:
• If price stays above pivot ~483 and holds above R1 (~491) → next target R2 ~499 → R3 ~507.
📍 Bearish setup:
• If price falls below pivot ~483 and breaks S1 (~475) → move down to S2 (467) & potentially S3 (459).
📍 Key breakouts:
• Clear daily close above 507 → strong bull confirmation.
• Close below 459 → negates short-term bull view.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 11 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 11 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Alignment)
This post shares a historical intraday observation showing how price interacted with a normal Square of 9 capacity level, leading to a temporary reaction when time and price aligned.
📊 Market Context & Reference Selection
Axis Bank displayed upward momentum after the completion of the first 15-minute candle.
In such market conditions, the low of the first 15-minute candle (~1104) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This reference point was used to study the session’s expected price expansion.
Correct identification of the reference level is critical for objective Square of 9 analysis.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1104
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1121
The 45-degree level often represents the normal intraday movement range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Observed Price–Time Behavior
Price approached the 45-degree level well before the later part of the trading session.
Early completion of normal price capacity has historically been associated with short-term trend fatigue.
After interacting with this zone, price showed temporary selling pressure and moved lower.
A minor variation around the calculated level was observed, which is common in live market conditions.
This aligns with a widely observed Gann concept:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Early capacity completion can indicate temporary exhaustion
Time plays a supporting role in validating price-degree levels
Small price deviations are normal and should be viewed structurally
The method promotes rule-based observation over prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 12 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 12 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday observation based on the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how early completion of price capacity can coincide with temporary market pressure.
📊 Market Structure & Reference Selection
Axis Bank opened with upward momentum during the first 15-minute candle.
In such conditions, the low of the opening candle (~1100) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This level served as the base point for measuring the session’s upward price capacity.
Accurate identification of the reference point is essential for reliable Square of 9 observations.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1100
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1117
The 45-degree level often reflects the normal intraday price expansion range under regular conditions.
⏱️ Price–Time Behavior (Observed)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around 9:30 AM).
Completion of normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically been associated with short-term exhaustion.
After reaching this zone, the market showed temporary selling pressure and downside expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann principle:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define intraday price limits in advance
Early completion of price capacity can signal temporary trend fatigue
Time alignment strengthens interpretation of price-degree levels
The method encourages structured observation over prediction
Focus remains on process, not precision
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Part 2 Ride The Big MovesLot Size
Options trade in lots, not single units.
Lot size varies by instrument.
Why Are Options Popular?
Low upfront premium.
Leverage.
Sophisticated hedging.
High liquidity.
European vs American Options
Indian index options are European — can only be exercised on expiry.
Stock options are American — can be exercised any time (but rarely done).
Financial Freedom Through Euro–Dollar DynamicsThe Euro–Dollar Relationship: A Global Financial Barometer
The EUR/USD pair represents the exchange rate between the euro (used by the Eurozone) and the U.S. dollar (the world’s primary reserve currency). Together, these two economies account for a significant share of global GDP, trade, and investment flows. As a result, EUR/USD reflects more than currency strength—it mirrors global economic confidence, monetary policy divergence, and geopolitical stability.
When the U.S. economy outperforms Europe, capital flows toward dollar-denominated assets, strengthening the USD and pushing EUR/USD lower. Conversely, when the Eurozone shows resilience or the Federal Reserve adopts a dovish stance, the euro strengthens. For individuals seeking financial freedom, understanding these shifts helps identify where money is moving—and how to position alongside it.
Interest Rates: The Core Driver of Currency Wealth
At the heart of Euro–Dollar dynamics lie interest rates, set by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed). Interest rate differentials determine where global investors park their money.
Higher U.S. rates attract capital into U.S. bonds and equities, strengthening the dollar.
Higher European rates improve euro demand and reduce dollar dominance.
For traders, this creates long-term trends that can last months or even years. Riding these trends—rather than chasing short-term noise—can generate consistent returns. For investors, understanding rate cycles helps in allocating capital between U.S. stocks, European equities, bonds, and currency-hedged instruments.
Financial freedom is rarely built through random trades; it is built by aligning with long-duration macro trends, and interest rate policy is one of the most reliable trend drivers.
Inflation, Purchasing Power, and Real Wealth
Inflation erodes purchasing power, silently damaging long-term financial security. The Euro–Dollar dynamic reflects how well each region controls inflation relative to growth.
If U.S. inflation is high and the Fed lags in response, the dollar may weaken.
If Europe faces energy-driven inflation shocks, the euro may depreciate.
For individuals, this matters because currency value affects real wealth. Income earned in a weakening currency loses global purchasing power, while assets held in a stronger currency preserve or enhance wealth.
Many financially independent individuals diversify income streams across currencies—earning in one currency while investing in another. Understanding EUR/USD trends helps protect savings from inflation and currency depreciation, a crucial but often overlooked step toward financial freedom.
Trading EUR/USD as a Tool for Income Independence
The Euro–Dollar pair is the most liquid currency pair in the world. High liquidity means tighter spreads, lower transaction costs, and smoother price action—ideal conditions for traders aiming to build consistent income streams.
From a financial freedom perspective:
Day traders benefit from predictable volatility during London–New York overlap.
Swing traders exploit macro themes like rate hikes, inflation data, and policy guidance.
Position traders ride multi-month trends driven by monetary cycles.
Unlike equities, forex markets operate nearly 24 hours a day, allowing flexibility for those balancing trading with jobs or businesses. While trading carries risk, disciplined EUR/USD trading—supported by macro understanding—can evolve into a scalable income source, supporting location-independent lifestyles.
Euro–Dollar Dynamics and Global Asset Allocation
Financial freedom is not only about earning more—it’s about allocating capital wisely. EUR/USD movements influence global asset performance:
A strong dollar often pressures emerging markets and commodities.
A weak dollar supports risk assets, global equities, and alternative investments.
Euro strength benefits European exporters and regional stock indices.
By tracking Euro–Dollar trends, investors can adjust portfolios proactively—reducing drawdowns and enhancing long-term returns. This macro-aware allocation reduces reliance on any single market or economy, making wealth more resilient.
Psychological Freedom Through Macro Understanding
One underrated aspect of financial freedom is psychological stability. Many retail investors panic during volatility because they lack context. Understanding Euro–Dollar dynamics provides that context.
When markets move sharply after central bank meetings, inflation reports, or geopolitical events, informed individuals recognize these moves as part of larger cycles—not random chaos. This clarity reduces emotional decision-making, improves discipline, and builds confidence—key traits of financially independent thinkers.
Business, Remittances, and Cross-Border Opportunities
For entrepreneurs, freelancers, and international workers, EUR/USD impacts:
Export and import costs
Overseas earnings
Profit margins on global contracts
Those who understand currency dynamics can time conversions, hedge exposure, or price services strategically. Over time, these small optimizations compound into significant financial advantages—another pathway to independence beyond traditional employment.
Risks and Responsible Use of Currency Dynamics
While Euro–Dollar dynamics offer opportunities, financial freedom requires risk awareness. Leverage misuse, overtrading, and ignoring macro shifts can quickly destroy capital. True freedom comes from risk-adjusted growth, not reckless speculation.
Successful participants treat EUR/USD as a strategic tool—not a gamble—combining technical analysis, macro data, and strict risk management.
Conclusion: Aligning With Global Money Flow
Financial freedom in the modern world is no longer confined to saving salaries or investing locally. It is about understanding how global money moves—and positioning oneself accordingly. The Euro–Dollar dynamic stands at the center of this global system, reflecting interest rates, inflation, economic confidence, and political stability.
By mastering EUR/USD dynamics, individuals gain more than trading profits or investment returns. They gain insight, flexibility, and control over their financial destiny. Whether through trading, investing, currency diversification, or global business, aligning with Euro–Dollar trends can transform money from a source of stress into a tool for long-term independence.
In essence, financial freedom is not about predicting every market move—it is about understanding the forces that shape them. And few forces are as powerful, persistent, and revealing as the Euro–Dollar relationship.
Inter-Market Edge: Mastering Cross-Asset TradesWhat Is Inter-Market Analysis?
Inter-market analysis studies the relationships between major asset classes, primarily:
Equities (stocks and indices)
Bonds (interest rates and yields)
Commodities (energy, metals, agriculture)
Currencies (forex pairs)
Volatility instruments (like VIX)
The core idea is simple: capital constantly rotates between asset classes based on economic conditions, monetary policy, inflation expectations, and risk sentiment. By tracking where money is flowing before it fully shows up in your trading instrument, you gain early insight.
Why Cross-Asset Trading Matters
Single-asset traders often react late. Cross-asset traders anticipate.
Key benefits include:
Early trend detection
Bond yields or currencies often move before equities.
Signal confirmation
A stock market breakout supported by falling bond yields and a weak currency is more reliable.
False signal filtering
If equities rise but bonds and commodities disagree, caution is warranted.
Superior risk management
Inter-market divergence frequently warns of trend exhaustion or reversals.
Broader opportunity set
When one market is range-bound, another may be trending strongly.
Core Inter-Market Relationships
To master cross-asset trades, traders must understand some foundational relationships.
1. Stocks and Bonds: The Risk Barometer
Rising bond prices (falling yields) usually indicate risk aversion.
Falling bond prices (rising yields) often signal economic optimism or inflation concerns.
Classic relationship
Stocks ↑ → Bonds ↓ (risk-on)
Stocks ↓ → Bonds ↑ (risk-off)
Trading edge
If bond yields start rising before equities rally, it often signals an upcoming stock market breakout. Conversely, falling yields during a stock rally can warn of weakness ahead.
2. Interest Rates and Equities
Central bank policy sits at the heart of inter-market analysis.
Low or falling rates support equity valuations and growth stocks.
Rising rates pressure high-valuation stocks, especially technology and small caps.
Cross-asset insight
Rate-sensitive sectors (banking, real estate, utilities) often move before broader indices. Watching rate futures can provide early sector rotation signals.
3. Currencies and Risk Sentiment
Currencies are not just exchange tools; they are risk indicators.
Safe-haven currencies: USD, JPY, CHF
Risk currencies: AUD, NZD, emerging market currencies
Key dynamics
Strong USD often pressures commodities and emerging market equities.
Weak domestic currency can boost exporters but increase inflation risk.
Trading edge
A strengthening USD alongside falling equities often confirms a risk-off environment. Conversely, a weakening USD with rising commodities supports a global risk-on trade.
4. Commodities and Inflation Expectations
Commodities reflect real-world demand and inflation trends.
Crude oil influences inflation, transport, and emerging markets.
Gold reflects real yields, inflation fears, and currency confidence.
Industrial metals signal economic growth.
Inter-market signal
Rising commodities with rising bond yields often indicate inflationary pressure, which can eventually hurt equity valuations.
5. Gold, Dollar, and Real Yields
Gold deserves special attention in cross-asset trading.
Gold rises when real yields fall.
Gold weakens when real yields rise, even if inflation is high.
Edge for traders
If gold rallies while equities rise and the dollar weakens, it often signals excess liquidity. If gold rises while equities fall, it reflects fear and capital preservation.
Volatility as a Cross-Asset Tool
Volatility indices, especially equity volatility, act as early warning systems.
Rising volatility during a price rally signals distribution.
Falling volatility during consolidation supports trend continuation.
Cross-asset traders watch volatility alongside bonds and currencies to judge whether risk appetite is genuine or fragile.
Practical Cross-Asset Trading Strategies
1. Confirmation Strategy
Before entering a trade, ask:
Do bonds agree?
Does the currency support the move?
Are commodities aligned with the macro narrative?
Example:
A stock index breakout supported by falling volatility and stable bond yields has higher probability.
2. Lead-Lag Strategy
Some markets move earlier than others:
Bonds often lead equities.
Currencies often lead commodities.
Commodities often lead inflation data.
Traders can position early in the lagging market once the leading market signals a shift.
3. Relative Strength Across Assets
Instead of predicting direction, compare strength between asset classes:
Equities vs bonds
Growth stocks vs value stocks
Commodities vs currencies
This helps identify capital rotation rather than guessing tops and bottoms.
4. Risk-On / Risk-Off Framework
Create a simple checklist:
Stocks ↑, yields ↑, volatility ↓ → Risk-on
Stocks ↓, yields ↓, volatility ↑ → Risk-off
Trading in alignment with the prevailing regime dramatically improves consistency.
Common Mistakes in Inter-Market Trading
Over-correlation bias: Relationships change over time.
Ignoring timeframes: Short-term trades may not follow long-term inter-market trends.
Confirmation paralysis: Waiting for every asset to align can lead to missed trades.
Macro blindness: News, policy, and global events matter in cross-asset trading.
Building the Inter-Market Mindset
Mastering cross-asset trades is less about predicting prices and more about understanding flows. Successful inter-market traders think like capital allocators, not just chart readers. They ask:
Where is money coming from?
Where is it going?
What fear or optimism is driving that movement?
By integrating equities, bonds, currencies, commodities, and volatility into one analytical framework, traders gain clarity in noisy markets.
Conclusion
The inter-market edge transforms trading from isolated decision-making into strategic positioning. In a world driven by global liquidity, central banks, inflation cycles, and geopolitical shifts, cross-asset awareness is no longer optional—it is essential.
Traders who master inter-market analysis don’t just react to price; they anticipate behavior, align with capital flows, and trade with context. That context is the real edge—quiet, powerful, and consistently profitable when applied with discipline.
If you want, I can also break this into headings for a blog, PDF notes, or turn it into a trading framework with examples from Indian markets 📈
PFC 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Market Price (Approx intraday)
• ~₹414–₹418 on NSE (trading range today: ₹413.10 – ₹420.40) as per real-time quotes.
📊 Key Daily Pivot & Levels (1-Day Timeframe)
🔹 Daily Pivot Reference (CPR / Pivot Zone)
• Central Pivot (CPR) / Pivot area: ~₹406.8 – ₹410.7 (bias reference)
📈 Resistance Levels (Upside)
R1: ~ ₹396–₹402 (initial resistance)
R2: ~ ₹402–₹406 (stronger sell zone)
R3: ~ ₹423–₹432 (higher resistance bands)
➡️ Above these, breakout zones could form if price closes strongly above ₹406–₹410.
📉 Support Levels (Downside)
S1: ~ ₹380–₹386 (first downside support)
S2: ~ ₹365–₹380 (secondary structural support)
S3: ~ ₹358–₹365 (deeper support zone)
➡️ Failure below ₹380–₹386 could tilt short-term bias more bearish.
📌 Daily Bias Interpretation
✔ Bullish bias if price holds above ~₹406–₹410 (CPR/pivot) — expect recovery toward ₹423+ zones.
✔ Neutral / slight bearish bias if price stays below ~₹406–₹410 — likely to test supports near ₹380–₹386.
📌 Context
The stock is trading well above its 20-day and 50-day moving averages, indicating short-term strength (based on recent MA data).
Over the past week/month, it’s shown positive momentum vs prior period.
Quarterly Results: High-Impact Trading Strategies1. Why Quarterly Results Matter So Much
Quarterly earnings influence markets because they:
Update real financial reality versus expectations
Reset valuation assumptions
Alter future growth outlooks
Trigger institutional rebalancing
Create liquidity surges and volatility expansion
Markets do not react to numbers alone. They react to the difference between expectations and reality, known as earnings surprise.
Key drivers of price reaction:
Revenue vs estimates
EPS vs estimates
Guidance upgrades/downgrades
Management commentary tone
Margin expansion or contraction
2. Pre-Earnings Trading Strategies
Pre-earnings trades aim to capture anticipation, positioning, and volatility buildup.
A. Earnings Run-Up Strategy
Many stocks trend upward before results due to:
Analyst upgrades
Institutional accumulation
Positive sector sentiment
Strategy logic
Buy strong stocks 2–4 weeks before earnings
Ride the momentum until just before results
Exit partially or fully before announcement
Best conditions
Strong relative strength vs index
Consistent higher highs and higher lows
Positive earnings history
Risk
Sudden negative leaks or macro shocks
B. Volatility Expansion Play
Implied volatility typically rises before earnings.
Approach
Trade breakout setups near key levels
Use tight stop losses
Target fast momentum moves
Technical focus
Compression patterns (triangle, flag, box range)
Rising volumes into earnings
Narrow daily ranges before expansion
C. Avoid Directional Bets Without Edge
Blindly buying or shorting before results is gambling. Pre-earnings trades should be momentum-based, not prediction-based.
3. Result-Day Trading Strategies (High Risk, High Reward)
Earnings day offers explosive opportunities—but also extreme risk.
A. Gap-Up Continuation Trade
When a stock gaps up strongly and holds above key levels:
Entry
After first 15–30 minutes
Above VWAP or opening range high
Confirmation
Strong volumes
Minimal selling pressure
Price acceptance above gap zone
Target
Measured move or intraday resistance
B. Gap-Up Failure (Fade Trade)
Not all positive results sustain.
Signs of failure
Price rejects opening highs
Heavy selling volume
Break below VWAP
Strategy
Short below VWAP with tight stop
Target gap fill or previous close
This works well when:
Valuations are stretched
Market sentiment is weak
Guidance disappoints despite good numbers
C. Gap-Down Reversal (Dead Cat Bounce or True Reversal)
Large gap-downs can lead to:
Panic selling
Forced institutional exits
Reversal signs
Long lower wicks
Volume climax
Stabilization near support
Only aggressive traders should attempt this strategy.
4. Post-Earnings Trading Strategies (Most Consistent)
Post-earnings trades are statistically safer because uncertainty is removed.
A. Earnings Momentum Continuation
Strong results often lead to multi-week trends.
Ideal setup
Breakout above long-term resistance
Rising volumes post earnings
Analyst upgrades after results
Holding period
Days to weeks
Tools
Moving averages
Trend channels
Trailing stop losses
B. Post-Earnings Drift Strategy
Markets underreact initially and adjust over time.
Characteristics
Gradual trend continuation
Pullbacks bought aggressively
Strong relative strength
This is one of the most reliable earnings-based strategies.
C. Earnings Breakdown Short Trade
Negative earnings surprises can cause:
Structural trend breakdowns
Long-term distribution
Entry
Breakdown below support after results
Failed pullback retests
Target
Next major support zones
Best for:
High-debt companies
Weak cash flows
Deteriorating guidance
5. Sector and Index Influence
Earnings reactions depend heavily on:
Sector sentiment
Index trend (NIFTY, SENSEX, NASDAQ, S&P 500)
Example
Strong results in a weak market may still fail
Moderate results in a bullish sector may outperform
Always align earnings trades with:
Sector momentum
Broader market structure
6. Position Sizing and Risk Management
Quarterly results can move stocks 5–25% overnight.
Key risk rules:
Never risk more than 1–2% of capital per earnings trade
Reduce position size compared to normal trades
Avoid overexposure to multiple earnings trades at once
Respect gap risk—stop losses don’t work overnight
7. Common Mistakes Traders Make
Trading earnings without a plan
Ignoring guidance and commentary
Overtrading on result day
Holding losing trades hoping for reversal
Confusing good numbers with good price action
Remember: Price reaction > numbers
8. Professional Trader’s Earnings Checklist
Before every earnings trade:
Is the stock in a trend?
What is the market expecting?
How has the stock reacted to past earnings?
Where are key support/resistance levels?
What is my predefined risk?
If these answers aren’t clear, skip the trade.
9. Long-Term Perspective
Earnings trading is not about predicting results—it’s about reacting faster and smarter than the crowd. Professionals wait for confirmation, manage risk ruthlessly, and trade only high-quality setups.
The best traders treat earnings as:
Volatility opportunities
Trend accelerators
Risk events to be respected
Conclusion
Quarterly results are among the highest-impact events in financial markets, capable of reshaping trends in minutes and defining direction for months. High-impact earnings trading requires discipline, preparation, technical awareness, and emotional control.
Traders who focus on price behavior, volume confirmation, and post-earnings trends—rather than predictions—consistently outperform those who gamble on numbers alone.
Nifty & Bank Nifty Options: Smart Trading StrategiesIntroduction
Nifty 50 and Bank Nifty options are the most actively traded derivatives in India, offering high liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, and multiple weekly expiries. These characteristics make them attractive to traders—but also dangerous for those without a structured approach. Smart options trading is not about predicting the market every day; it’s about probability, risk control, and discipline.
This guide explains smart, repeatable strategies used by professional and experienced retail traders across different market conditions—ranging from intraday momentum to non-directional income setups.
Understanding Nifty vs Bank Nifty Behavior
Before strategies, it’s critical to understand how these indices behave.
Nifty 50
Broader market representation
Lower volatility compared to Bank Nifty
Better for positional options selling, spreads, and calm intraday trades
Moves smoothly and respects technical levels
Bank Nifty
Highly volatile and momentum-driven
Sensitive to RBI policy, bond yields, and banking stocks
Ideal for intraday option buying, scalping, and fast spreads
Requires strict risk management due to sharp swings
Smart traders choose the index based on market conditions, not habit.
Core Principles of Smart Options Trading
1. Trade Probability, Not Prediction
Most professional options traders focus on high-probability setups (60–80%) instead of directional certainty.
2. Risk Defined First
Every trade must have:
Fixed maximum loss
Pre-decided exit
Position size based on capital, not confidence
3. Time Decay Is a Weapon
Theta (time decay) works against buyers and for sellers, especially in weekly options.
Smart Intraday Strategies
1. Opening Range Breakout (ORB) – Option Buying
Best for: Bank Nifty & Nifty (high volatility days)
Setup
Mark high and low of first 15 minutes
Buy Call if price breaks above range
Buy Put if price breaks below range
Choose ATM or slightly ITM options
Why it works
Institutions establish direction early
Volatility expansion favors buyers
Risk management
Stop-loss: 30–40% premium
Partial profit booking recommended
2. VWAP Trend Following
Best for: Trending intraday markets
Rules
Price above VWAP → buy Calls on pullbacks
Price below VWAP → buy Puts on pullbacks
Avoid counter-trend trades
Smart tip
Trade only when VWAP is sloping clearly—flat VWAP = no trade.
Smart Positional Strategies
3. Bull Call Spread / Bear Put Spread
Best for: Directional view with limited risk
Example (Bull Call Spread)
Buy ATM Call
Sell OTM Call (same expiry)
Advantages
Lower cost than naked buying
Reduced time decay impact
Defined risk and reward
Ideal for
Breakouts
News-based positional trades
Budget day, RBI policy days
4. Calendar Spread
Best for: Low volatility → expected volatility expansion
Setup
Sell near-expiry option
Buy same strike next-expiry option
Why it’s smart
Takes advantage of faster decay in weekly options
Lower directional risk
Used by
Experienced traders before events like RBI policy or CPI data.
Smart Non-Directional Strategies (Option Selling)
5. Short Strangle
Best for: Sideways markets, low VIX
Setup
Sell OTM Call
Sell OTM Put
Same expiry
Profit source
Time decay
Range-bound price action
Risk control
Always hedge with far OTM options
Exit if spot breaches sold strike
Works best
In Nifty more than Bank Nifty
When India VIX < 14–15
6. Iron Condor (Hedged Income Strategy)
Best for: Consistent weekly income
Structure
Sell OTM Call + Buy higher Call
Sell OTM Put + Buy lower Put
Advantages
Defined maximum loss
Lower margin requirement
Stress-free compared to naked selling
Professional insight
Iron Condors outperform aggressive selling over long periods.
Expiry Day Smart Strategies
7. Intraday Short Straddle (Advanced)
Best for: Weekly expiry, post 1 PM
Logic
Volatility collapses rapidly on expiry
ATM options lose value quickly
Rules
Only when index is range-bound
Strict stop-loss on combined premium
Not for beginners
8. Directional Expiry Scalping
Best for: Bank Nifty expiry
Setup
Trade ATM options
Quick 5–15 point moves
High frequency, low holding time
Golden rule
One bad trade can wipe 5 good ones—size small.
Risk Management: The Real Edge
Capital Allocation
Risk max 1–2% of capital per trade
Never deploy full margin on one idea
Stop-Loss Discipline
Pre-defined SL beats mental SL
Exit without emotion
Avoid Overtrading
No trade is also a trade
Most losses happen due to boredom trades
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Buying weekly OTM options without momentum
Holding losing positions hoping for reversal
Trading during low-volume midday hours
Ignoring India VIX
Trading every expiry aggressively
Smart Trader’s Checklist (Before Every Trade)
Is the market trending or sideways?
What is India VIX doing?
Am I a buyer or seller today?
Is my risk predefined?
Is this trade worth taking?
If any answer is unclear—skip the trade.
Conclusion
Smart Nifty and Bank Nifty options trading is not about high returns every day, but about survival, consistency, and compounding. The market rewards patience, structure, and risk control far more than excitement.
Successful traders:
Adapt strategies to volatility
Prefer probability over prediction
Protect capital first, profits second
Mastering Advanced Option Trading StrategiesFoundation: What Makes a Strategy “Advanced”
Advanced option strategies differ from basic ones in three key ways:
Multi-leg structures – Using two or more option contracts simultaneously
Risk-defined frameworks – Maximum loss and profit are known in advance
Volatility-based logic – Trades are often placed based on implied volatility (IV), not just price direction
These strategies are designed to optimize probability of profit, time decay (Theta), and volatility shifts, rather than relying solely on price movement.
Understanding the Greeks at an Advanced Level
Before executing advanced strategies, traders must internalize the option Greeks:
Delta – Measures directional exposure
Gamma – Rate of change of Delta (critical near expiry)
Theta – Time decay, a major income driver
Vega – Sensitivity to volatility changes
Rho – Interest rate sensitivity (minor but relevant in long-dated options)
Advanced traders do not avoid Greeks—they engineer trades around them.
Advanced Directional Strategies
1. Bull Call Spread and Bear Put Spread
These are risk-defined directional strategies.
Bull Call Spread: Buy a lower strike call, sell a higher strike call
Bear Put Spread: Buy a higher strike put, sell a lower strike put
Why advanced traders use them:
Lower cost than naked options
Reduced impact of volatility crush
Higher probability of controlled returns
These spreads are ideal when you expect moderate directional movement, not explosive breakouts.
2. Ratio Spreads
A ratio spread involves buying fewer options and selling more at another strike (e.g., buy 1 call, sell 2 calls).
Key characteristics:
Often initiated for low or zero cost
Profitable in a specific price range
Can become risky if price moves aggressively
Ratio spreads are best suited for traders who deeply understand Gamma risk and can actively manage positions.
Non-Directional and Income Strategies
3. Iron Condor
One of the most popular advanced strategies.
Structure:
Sell a call spread
Sell a put spread
Market outlook: Range-bound / low volatility
Advantages:
High probability of profit
Defined risk
Profits from time decay
Iron Condors are volatility trades. Advanced traders deploy them when implied volatility is high and expected to contract.
4. Butterfly Spreads
Butterflies are precision strategies.
Structure (Call Butterfly example):
Buy 1 lower strike call
Sell 2 middle strike calls
Buy 1 higher strike call
Best used when:
Expect price to expire near a specific level
Volatility is expected to fall
Butterflies offer high reward-to-risk ratios, but require accurate price targeting and timing.
Volatility-Based Strategies
5. Straddle and Strangle
These are pure volatility plays.
Straddle: Buy call and put at same strike
Strangle: Buy call and put at different strikes
Used when:
Expect a large move but unsure of direction
Ahead of earnings, events, or policy announcements
Advanced traders focus less on direction and more on whether realized volatility will exceed implied volatility.
6. Calendar Spreads
A calendar spread involves selling a near-term option and buying a longer-term option at the same strike.
Benefits:
Positive Theta
Positive Vega
Limited risk
Calendars work best when:
Short-term volatility is overestimated
Long-term volatility remains stable
They are commonly used by professionals to trade volatility structure, not price.
Advanced Hedging and Portfolio Strategies
7. Synthetic Positions
Options can replicate stock positions:
Synthetic Long Stock: Long call + short put
Synthetic Short Stock: Long put + short call
These are capital-efficient and useful for:
Regulatory constraints
Margin optimization
Tax or funding considerations
8. Delta-Neutral Strategies
Advanced traders often aim to remain direction-neutral while earning from Theta and Vega.
Examples:
Delta-neutral Iron Condors
Delta-hedged straddles
Delta neutrality requires active adjustments, especially as Gamma increases near expiry.
Risk Management: The Real Edge
Advanced option trading is less about finding the “best strategy” and more about risk control.
Key principles:
Never risk more than a small percentage of capital per trade
Predefine exit rules (profit targets and stop-losses)
Avoid overtrading during low-liquidity conditions
Adjust positions rather than panic-closing
Professional traders think in probabilities, not predictions.
Psychological Mastery
Options trading amplifies emotions due to leverage and time pressure.
Advanced traders develop:
Patience to let Theta work
Discipline to exit losing trades early
Emotional detachment from individual outcomes
Consistency comes from executing a well-tested process repeatedly—not chasing perfect trades.
Conclusion
Mastering advanced option trading strategies is a journey that blends mathematics, psychology, and market intuition. These strategies allow traders to profit in almost any market environment, but they demand respect for risk, deep understanding of volatility, and strict discipline. Success does not come from complexity alone—it comes from using the right strategy at the right time, for the right reason.
When advanced options trading is approached as a probability business rather than a prediction game, it becomes one of the most powerful tools in modern financial markets.
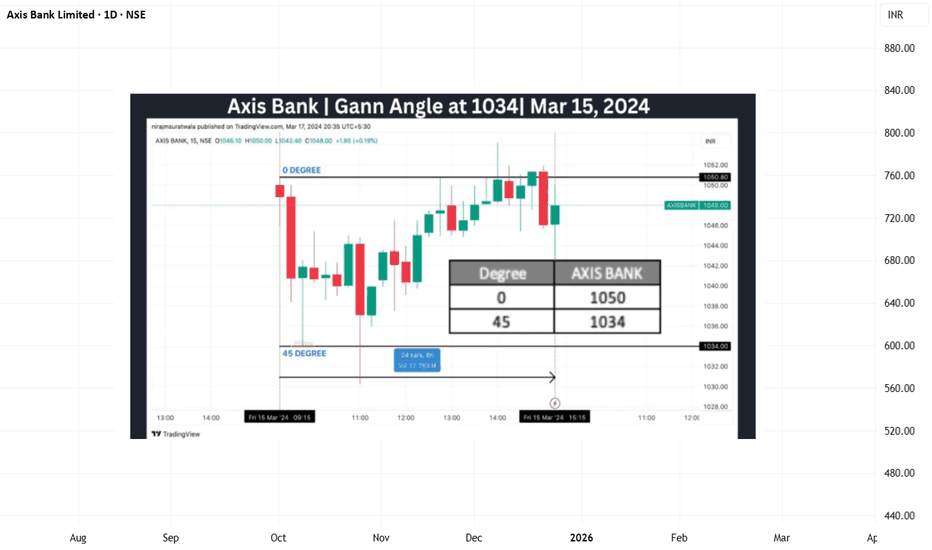
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 15 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 15 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday market observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how price capacity, trend context, and time alignment can highlight potential intraday reaction zones.
📉 Market Context & Reference Point Selection
Axis Bank showed downside pressure from the opening 15-minute candle.
In such conditions, the high of the first 15-minute candle (~1050) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This level acts as the starting point for measuring the intraday downward price cycle.
Correct trend identification and reference selection are essential before applying Square of 9 calculations.
🔢 Square of 9 Price Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1050
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1034
The 45-degree level often represents the normal intraday price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price–Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around the third 15-minute candle).
Completion of normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown signs of temporary downside exhaustion.
After reaching this zone, the market displayed short-term stabilization followed by upward expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann concept:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a directional reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define intraday price limits in advance
Trend context determines how reference points are selected
Time alignment adds confirmation to price-degree levels
Normal (45-degree) reactions are more frequent than rare cases
The approach encourages rule-based observation over emotional reaction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 18 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 18 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method Used: Gann Square of 9 (Price–Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday market observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how price movement capacity and time alignment can highlight potential intraday reaction zones.
📊 Initial Market Structure
Axis Bank displayed upward momentum from the opening 15-minute candle.
The low of the first 15-minute candle (~1043) was treated as the 0-degree reference level.
This reference point marks the start of the intraday price cycle and is used for further Square of 9 calculations.
Correct identification of the 0-degree level is a key requirement for consistent Square of 9 analysis.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Using Square of 9 price-degree relationships, the following levels were observed:
0 Degree: ~1043
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1057
The 45-degree level often reflects the normal intraday price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After reaching this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior followed by short-term downside expansion.
This observation aligns with a commonly studied Gann principle:
Early completion of expected price capacity may increase the probability of a market reaction.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than exceptional cases
Time context adds important confirmation to price levels
Minor price deviations around calculated levels are part of normal market behavior
The method supports rule-based observation, not prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Stock Market Trading (Equities)Introduction
Stock market trading, often referred to as equity trading, is the buying and selling of shares of publicly listed companies through a regulated marketplace known as a stock exchange. Equities represent ownership in a company, and shareholders are entitled to a portion of the company's profits in the form of dividends and capital gains. Stock trading serves as a fundamental component of financial markets, providing liquidity, capital formation, and investment opportunities for individuals, institutions, and corporations alike.
The stock market is often perceived as a barometer of the economy, reflecting investor sentiment, corporate performance, and broader macroeconomic trends. Trading in equities is both an art and a science, combining analytical rigor, strategy, and psychological discipline.
Key Participants in Stock Market Trading
Retail Investors: Individual traders who buy and sell stocks for personal investment or short-term trading profits. Retail investors account for a significant portion of trading volume in major stock exchanges.
Institutional Investors: Entities such as mutual funds, hedge funds, insurance companies, and pension funds that invest large sums of money in equities. Their trades can significantly impact stock prices due to the size of their transactions.
Market Makers & Brokers: Market makers provide liquidity by quoting both buy and sell prices, facilitating smoother trading. Brokers act as intermediaries between investors and the exchange, executing orders on behalf of clients.
Regulators: Regulatory authorities like the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in India or the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) ensure fair practices, transparency, and protection for investors.
Types of Equity Trading
Equity trading can broadly be categorized into long-term investing and short-term trading, each with distinct objectives and strategies.
Long-Term Investing:
Investors hold stocks for an extended period, usually years, aiming to benefit from dividends and capital appreciation. This strategy is based on fundamental analysis, which evaluates a company's financial health, growth potential, and market position. Long-term investors are less concerned with short-term price fluctuations and focus on the company's intrinsic value.
Short-Term Trading:
Traders aim to profit from price volatility within short periods, ranging from seconds (high-frequency trading) to days or weeks. This category includes:
Day Trading: Buying and selling stocks within the same trading session.
Swing Trading: Holding stocks for several days or weeks to capture intermediate-term trends.
Scalping: Executing multiple trades in a day to profit from small price movements.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company's underlying financial health and growth potential to estimate its intrinsic value. Key aspects include:
Financial Statements:
Income Statement: Evaluates profitability through revenue, expenses, and net profit.
Balance Sheet: Assesses the company's assets, liabilities, and equity.
Cash Flow Statement: Analyzes liquidity and operational efficiency.
Ratios & Metrics:
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Measures stock valuation relative to earnings.
Return on Equity (ROE): Indicates profitability for shareholders.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Shows financial leverage and risk.
Macro & Industry Analysis:
Economic indicators like GDP growth, interest rates, and inflation impact stock performance.
Industry trends, competitive landscape, and regulatory policies influence individual company prospects.
Fundamental analysis is particularly favored by long-term investors seeking stable returns based on sound business fundamentals.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on stock price movements and trading volume to predict future price trends. Traders use historical data and chart patterns to identify entry and exit points. Key tools include:
Charts: Line charts, candlestick charts, and bar charts provide visual representations of price movements.
Indicators:
Moving Averages: Identify trends by smoothing out price fluctuations.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures overbought or oversold conditions.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Helps detect trend reversals.
Patterns: Head-and-shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and trendlines are common patterns used to anticipate price behavior.
Technical analysis is commonly applied by short-term traders and those seeking to exploit market psychology and price momentum.
Stock Market Orders
Traders and investors execute trades through different types of orders:
Market Order: Executes immediately at the current market price.
Limit Order: Executes only at a specified price or better.
Stop-Loss Order: Automatically sells a stock when it reaches a predetermined price to limit losses.
Stop-Limit Order: Combines stop-loss and limit orders for controlled execution.
Choosing the right type of order is crucial for managing risk and optimizing profits.
Risk Management in Equity Trading
Equity trading carries inherent risks, including market risk, company-specific risk, and liquidity risk. Effective risk management strategies include:
Diversification: Spreading investments across sectors, industries, and asset classes to reduce exposure to a single stock.
Position Sizing: Allocating a fixed portion of capital to each trade based on risk tolerance.
Stop-Loss Strategies: Limiting losses by setting predefined exit points.
Hedging: Using derivatives like options and futures to protect against adverse price movements.
Risk management is essential to survive in volatile markets and preserve capital.
Stock Market Strategies
Traders and investors employ various strategies depending on their objectives:
Value Investing: Buying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, aiming for long-term growth.
Growth Investing: Focusing on companies with high growth potential, even if currently overvalued.
Momentum Trading: Capitalizing on strong trends, buying rising stocks and selling before a reversal.
Dividend Investing: Targeting stocks that provide regular income through dividends.
Algorithmic Trading: Using automated systems and algorithms to execute trades at high speed and efficiency.
Behavioral Aspects of Trading
Psychology plays a crucial role in stock trading. Emotional biases such as fear, greed, overconfidence, and herd mentality can impact decision-making. Successful traders cultivate discipline, patience, and emotional control to make rational decisions.
Regulation and Compliance
Stock markets operate under strict regulations to ensure transparency and investor protection. Key regulatory practices include:
Listing Requirements: Companies must meet financial and disclosure standards to be listed on exchanges.
Insider Trading Regulations: Prevent individuals with non-public information from exploiting unfair advantages.
Market Surveillance: Exchanges monitor trading activity to detect manipulation and fraud.
Disclosure Norms: Companies must regularly disclose financial results, material events, and corporate governance practices.
In India, SEBI oversees the functioning of stock exchanges, brokers, and listed companies to maintain a fair and efficient market.
Technological Impact
Modern equity trading is heavily technology-driven. Online trading platforms, mobile apps, and algorithmic trading systems have democratized access, enabling retail investors to participate with ease. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics are increasingly used to identify patterns, forecast trends, and automate trading strategies.
Conclusion
Stock market trading in equities is a dynamic and multifaceted activity, offering opportunities for wealth creation and capital growth. Success in trading requires a blend of analytical skills, strategic planning, risk management, and psychological discipline. Understanding fundamental and technical factors, along with macroeconomic and behavioral elements, equips traders and investors to navigate market volatility effectively.
While trading involves risks, disciplined approaches, continuous learning, and adherence to regulatory norms can significantly enhance the probability of long-term success. Whether one aims for long-term investment growth or short-term trading profits, equities remain a cornerstone of financial markets, providing avenues for participation in the wealth generated by companies and economies.
In essence, stock market trading is not merely about buying low and selling high; it is an intricate process of research, analysis, timing, and emotional control, offering immense learning opportunities and financial rewards for those who approach it with knowledge, patience, and strategy.
US100 (Nasdaq) – Structure & BiasPrice is currently trading inside a well-defined consolidation range, capped by a major resistance zone near 25,850–25,900 and supported around 25,230–25,250, which has acted as a strong demand flip multiple times.
The recent price action shows:
A liquidity sweep to the downside, followed by a sharp bullish reaction, indicating smart money absorption.
Price reclaiming the mid-range level, suggesting buyers are regaining short-term control.
Compression near support, often a precursor to expansion.
The projected path indicates a minor pullback or sideways consolidation, followed by a bullish continuation toward the upper resistance band. Structure favors upside as long as price holds above the marked support zone.
Key Levels
Support: 25,230 – 25,250
Mid-range equilibrium: ~25,300
Target / Resistance: 25,850 – 25,900
Bias
🟢 Bullish continuation, provided price maintains above the demand zone.
A clean breakout above consolidation could trigger momentum-driven expansion toward the highs.
Bitcoin Bybit chart analysis FEBURARY 3Hello
It's a Bitcoin Guide.
If you "follow"
You can receive real-time movement paths and comment notifications on major sections.
If my analysis was helpful,
Please click the booster button at the bottom.
This is Bitcoin's 30-minute chart.
There's a Nasdaq indicator release coming up shortly at 12:00 PM.
In the upper left corner, in purple, I've linked the strategy to yesterday's short position entry point, $78,592.3.
*The blue finger path indicates a two-way neutral strategy.
1. Short position entry point at $78,795.9 at the top / Stop loss if the pink resistance line is broken (same as yesterday's short stop loss of $78.9K).
2. Long position switch at $77,708.7 / Stop loss if the green support line is broken.
3. Long position 1st target at $80,967.2 -> Good -> Gap8. Target prices in that order.
If the rebound fails to break the orange resistance line at $80,196.8 at the top,
a stronger correction is likely.
If the price falls directly without touching the short position entry point at the top, the final long position entry point is the first section at $76,768.8.
Below that, the bottom -> section 2 is a dangerous area where the previous low is broken.
Please use my analysis to this point for reference only.
I hope you operate safely, with a strict adherence to principled trading and stop-loss orders.
Thank you.
Bitcoin Bybit chart analysis FEBURARY 2Hello
It's a Bitcoin Guide.
If you "follow"
You can receive real-time movement paths and comment notifications on major sections.
If my analysis was helpful,
Please click the booster button at the bottom.
This is Bitcoin's 30-minute chart.
The Nasdaq indicators will be released shortly at 12:00 PM.
We've proceeded as safely as possible, keeping in line with the current market conditions.
*When the light blue finger moves,
Two-way neutral strategy:
1. After touching the purple finger once at the top (autonomous shorting),
Switch to a long position at $77,247.9 at the light blue finger at the bottom.
/Stop-loss price if the light blue support line is broken.
If the price falls immediately without touching the first section,
Place the second section at the bottom as a long position waiting area. / Place the stop-loss price if the green support line is broken.
2. The top section is the target price -> If the price touches the good section repeatedly,
Maintain the long position. / If the price touches the top section and immediately falls,
Place the first section as a confirmation area for re-entry into the long position.
From the bottom, there's a possibility of further lows being broken.
The third section at the very bottom is a double bottom risk zone.
Currently, there's no clear support line, making long positions risky.
A rebound is needed, and I'll focus on this.
*Key criteria for this are a Nasdaq rise or sideways movement, and the XAUUSD gold price should continue to decline.
Please use my analysis to this point for reference only.
I hope you operate safely, with a focus on principled trading and stop-loss orders.
Thank you.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 12 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post presents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity and time alignment can highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Market Structure at the Open
Axis Bank displayed upward strength from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1166) was used as the 0-degree reference level, following Square of 9 methodology.
This level acts as the base point for mapping the day’s upward price vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree reference is essential for consistent Square of 9 studies.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1166
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1183
In intraday analysis, the 45-degree level often represents the stock’s normal price expansion range under typical market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior followed by short-term downside expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann concept:
Early completion of expected price capacity may increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than exceptional cases
Combining price structure with time context improves market clarity
Small deviations around calculated levels are part of normal market behavior
This approach supports rule-based observation, not prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 13 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post documents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity interacts with time to highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Initial Market Structure
Axis Bank showed upward momentum from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1148) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following standard Square of 9 practice.
This reference point acts as the base for mapping the day’s expected upward vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree is essential for meaningful Square of 9 observations.
🔢 Gann Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1148
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1165
In intraday studies, the 45-degree level often represents a stock’s normal price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior and short-term downside expansion.
This reflects a commonly observed Gann principle:
Early completion of expected price capacity can increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Key Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than rare cases
Combining price structure with time context improves clarity
The method supports rule-based observation, not prediction
Small variations around levels are part of normal market behavior
📌 Shared purely for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceTime
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 14 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post is a historical intraday case study showing how the Gann Square of 9 can be used to identify potential reaction zones by combining price movement capacity with time.
📊 Opening Market Observation
Axis Bank showed bullish intent from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1131.60) was treated as the 0-degree reference, following standard Gann methodology.
This reference level acts as the base point for measuring upward price vibration for the session.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Structure
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1131
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1148
In intraday studies, the 45-degree level often represents the stock’s normal directional movement range.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Educational Observation)
Price reached the 45-degree level very early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal movement range well before the latter part of the trading session has historically shown temporary price pressure or hesitation.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior and short-term weakness.
This reflects a commonly observed Gann principle:
When price completes its expected movement capacity too early in time, the probability of a reaction increases.
📘 Key Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 levels can be projected in advance for structured observation
Correct identification of the 0-degree reference is critical
Alignment of price and time improves analytical context
Normal (45-degree) cases occur more frequently than rare (90-degree) cases
This approach supports disciplined chart reading rather than emotional decisions
📌 Shared purely for learning and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceTime
Axis Bank | Intraday Price Behaviour Using Square-Based GeometryDisclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered adviser. This is not financial advice.
Educational Case Study | 7 February 2025
This idea presents an educational intraday case study on Axis Bank, focusing on how price movement capacity and time awareness can be observed using square-based geometric methods commonly referenced in classical market studies.
The purpose of this post is to study historical chart behavior, not to suggest trades or outcomes.
📊 Chart Context
Instrument: Axis Bank Ltd. (NSE)
Date: 7 February 2025
Timeframe: 15-minute (Intraday)
During the early part of the session, Axis Bank showed strong downward momentum. A structured framework was applied to observe how price behaved relative to predefined reference levels as the session progressed.
🔍 Observational Framework
The initial high of the session was treated as a reference point (around 1024.45)
From this reference, square-based projections were observed
A level near 1008 aligned with a 45-degree projection, often associated with normal intraday price reach in historical studies
This level was treated as a potential reaction zone, not a guaranteed support
All levels were used strictly as areas of observation.
📈 Observed Market Behavior
Price moved toward the projected zone during the morning session
Near this area, the market showed temporary pressure and a short-term response
The behavior aligned with previously observed historical interactions around similar geometric zones
Time context was noted as part of the observation, without implying causation
No trade execution, direction, or performance outcome is implied.
📘 Educational Insights from This Case
Square-based geometry can help outline normal intraday price movement capacity
Certain projected levels may act as areas where price behavior changes
Time awareness can provide additional context when studying intraday charts
This approach emphasizes structure and observation over indicators or predictions
All insights are based on historical chart study only.
📌 Important Note
This case study is shared strictly for learning and research purposes.
Geometric levels and time windows do not guarantee outcomes and should be treated as contextual analytical tools.
Market responses may include:
Temporary pauses
Short-term pressure
Continuation or expansion depending on broader structure
🚀 Summary
This intraday case study demonstrates how price geometry and time alignment can be used to observe market behavior in a structured and objective manner.
More educational chart studies will follow.
Geopolitical Events & Global ConflictsUnderstanding Geopolitics
Geopolitics refers to how geographical factors such as location, natural resources, population, borders, and strategic routes influence political power and international behavior. Countries do not act in isolation; their decisions are shaped by neighboring states, access to oceans, energy resources, trade corridors, and military vulnerabilities.
For example, control over choke points like the Strait of Hormuz, the Suez Canal, or the South China Sea holds immense strategic value because a large share of global trade and energy supplies passes through these regions. Any disruption in such areas can ripple through the global economy, causing spikes in oil prices, supply chain disruptions, and market volatility.
Types of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can take many forms, not all of which involve direct warfare:
Military Conflicts and Wars
These include full-scale wars, regional conflicts, border skirmishes, and civil wars with international involvement. Examples include interstate wars, proxy wars, and internal conflicts that draw global attention due to humanitarian or strategic concerns.
Diplomatic Tensions and Alliances
Diplomatic standoffs, sanctions, treaty breakdowns, or the formation of new alliances (such as military or trade blocs) are major geopolitical events. Organizations like NATO, BRICS, ASEAN, and the United Nations play central roles in shaping these dynamics.
Economic and Trade Conflicts
Trade wars, sanctions, tariffs, and restrictions on technology or capital flows are increasingly common tools of geopolitical competition. Economic power has become as important as military strength in influencing global outcomes.
Energy and Resource Disputes
Conflicts over oil, gas, water, rare earth metals, and food security are becoming more prominent as global demand rises and resources become scarcer.
Political Instability and Regime Changes
Coups, revolutions, contested elections, and sudden policy shifts can alter regional balances of power and affect global markets.
Causes of Global Conflicts
Global conflicts rarely arise from a single cause. Instead, they are the result of overlapping and reinforcing factors:
Territorial Disputes: Disagreements over borders, islands, or strategic regions are among the most common triggers of conflict.
Economic Inequality and Competition: Competition for markets, resources, and technological dominance often fuels tensions between major powers.
Ideological Differences: Conflicts between political systems, governance models, or belief systems have historically driven major global confrontations.
Ethnic and Religious Divisions: Internal conflicts rooted in identity can escalate into regional or global crises when external powers intervene.
Power Transitions: When a rising power challenges an established global leader, instability often follows as both sides seek to protect their interests.
Role of Major Global Powers
Major powers such as the United States, China, Russia, and the European Union play outsized roles in global geopolitics. Their military capabilities, economic influence, technological leadership, and diplomatic reach shape global outcomes.
The United States has long acted as a global security provider, with military bases and alliances around the world.
China focuses on expanding economic and strategic influence through trade, infrastructure investment, and regional dominance.
Russia leverages energy resources, military power, and regional influence to maintain its geopolitical standing.
The European Union emphasizes diplomacy, economic integration, and regulatory power, though internal divisions sometimes limit unified action.
Smaller regional powers also play critical roles, especially in geopolitically sensitive regions such as the Middle East, South Asia, Eastern Europe, and East Asia.
Impact on the Global Economy
Geopolitical events and conflicts have immediate and long-term economic consequences:
Financial Markets: Stock markets often react sharply to geopolitical uncertainty, while safe-haven assets like gold, government bonds, and certain currencies gain demand.
Commodity Prices: Conflicts involving energy-producing regions can cause oil, gas, and food prices to surge, fueling inflation.
Supply Chains: Wars, sanctions, and political tensions disrupt global supply chains, forcing companies to rethink sourcing and production strategies.
Investment Flows: Political instability discourages foreign investment and increases risk premiums.
For investors and traders, geopolitical risk has become a key factor in decision-making, alongside traditional economic indicators.
Humanitarian and Social Consequences
Beyond economics and politics, global conflicts have profound human costs. Armed conflicts lead to loss of life, displacement of populations, refugee crises, and long-term social trauma. Infrastructure destruction, food shortages, and healthcare disruptions often persist long after fighting ends.
International organizations, humanitarian agencies, and NGOs play vital roles in conflict zones, but their efforts are frequently constrained by security risks and political barriers.
Technology and Modern Warfare
Modern geopolitical conflicts increasingly involve technology rather than traditional battlefield engagements. Cyber warfare, misinformation campaigns, satellite disruptions, and economic coercion are now standard tools of statecraft. A conflict may unfold in cyberspace, financial systems, or media narratives long before—or instead of—physical confrontation.
This shift has blurred the line between war and peace, making geopolitical risk more complex and harder to predict.
Geopolitics in a Multipolar World
The world is gradually moving from a unipolar or bipolar structure toward a multipolar one, where multiple centers of power coexist. This transition increases uncertainty, as rules and norms are contested and alliances become more fluid.
At the same time, global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and technological disruption require cooperation, even among rival states. This creates a paradox where competition and interdependence exist simultaneously.
Conclusion
Geopolitical events and global conflicts are central forces shaping the 21st century. They influence international relations, economic stability, technological progress, and human security. While conflicts often appear sudden, they are usually the result of long-term structural tensions rooted in geography, power, and interests.
Understanding geopolitics does not mean predicting every conflict, but it helps individuals and institutions make sense of global developments and manage risk more effectively. In an increasingly interconnected world, geopolitical awareness is no longer optional—it is essential for informed decision-making, whether in policy, business, investment, or everyday life.