$DYDX PRICE OUTLOOK | 3000%+ POTENTIAL FROM MACRO SUPPORT?DYDX/USDT PRICE OUTLOOK | Macro Support & High R:R Setup
DYDX is currently trading at a major higher-timeframe demand zone on the 2-week chart, following an extreme ~99.45% drawdown from its all-time high. Historically, such deep retracements often precede long-term re-accumulation phases, especially when aligned with structural support.
Market Structure Overview
Price remains within a multi-year descending channel active since 2022. The current price action is testing the lower boundary of this channel, which aligns with a clearly defined horizontal accumulation zone ($0.15–$0.20). This creates a strong confluence-based support region.
Technical Confluence
Descending channel support respected on HTF
Strong historical demand at $0.15–$0.20
~99% retracement from ATH completed
Compression near support suggests potential volatility expansion
Bias remains bullish as long as HTF structure holds
Upside Levels (If Breakout Confirms)
Resistance 1: $0.84
Resistance 2: $2.19
Resistance 3: $4.39
ATH Supply Zone: $27.85
A confirmed HTF close above descending trendline resistance would validate a structural trend reversal. The measured move from this base projects toward $3.85, representing a potential ~3200% upside from current levels.
Invalidation
Any 2-week candle close below $0.15 invalidates the accumulation thesis and requires reassessment.
Conclusion
This setup reflects a classic falling-wedge / descending-channel structure meeting historical demand. While risk remains elevated, the risk-to-reward profile is asymmetric at this level. Patience, confirmation, and position sizing are essential.
Analysis Type: Technical Analysis
Timeframe: Long-Term / Positional
Bias: Accumulation → Trend Reversal (Conditional)
TA only. Not financial advice. Always manage risk.
Harmonic Patterns
Earnings Season Trading: Opportunities, Risks, and StrategiesWhat Is Earnings Season and Why It Matters
Earnings season typically occurs four times a year, following the end of each financial quarter. In India, major earnings seasons usually unfold in April, July, October, and January. During this period, companies announce their financial performance, including earnings per share (EPS), revenue, margins, debt levels, and management commentary. Markets react not only to whether results are good or bad, but also to how they compare with expectations already priced into the stock.
Stock prices are forward-looking. This means a company can report strong earnings and still see its share price fall if results fail to meet market expectations. Conversely, a company with weak numbers may rally if the outcome is “less bad” than anticipated or if guidance improves. This expectation-versus-reality dynamic makes earnings season particularly powerful for short-term traders.
Volatility: The Core Feature of Earnings Trading
The defining characteristic of earnings season trading is volatility. Stocks often experience sharp price gaps on the day results are announced, especially if the earnings surprise is significant. These gaps can occur upward or downward and may range from a few percent to double-digit moves in extreme cases. For intraday traders, this volatility creates momentum-based opportunities, while swing traders look to capture post-earnings trends that may last days or weeks.
However, volatility cuts both ways. Sudden adverse moves can trigger stop-losses or cause significant losses if risk is not controlled. Therefore, earnings trading demands disciplined position sizing, predefined exit strategies, and an understanding that outcomes can be unpredictable.
Earnings Expectations and Market Psychology
A critical element of earnings season trading is market psychology. Analysts issue earnings estimates well in advance, and these numbers shape investor expectations. Traders closely monitor consensus EPS, revenue forecasts, and “whisper numbers” circulating in the market. The stock’s price movement before earnings often reflects these expectations, with rallies signaling optimism and declines indicating caution.
During earnings season, traders focus on three major aspects: actual results, comparison with estimates, and management guidance. Among these, guidance often has the strongest influence because it affects future valuations. A company beating estimates but lowering future guidance may still face selling pressure, while a modest miss combined with strong forward outlook can trigger buying interest.
Common Earnings Season Trading Strategies
Several strategies are commonly used during earnings season. One approach is pre-earnings momentum trading, where traders ride the price trend leading up to the results, exiting positions before the announcement to avoid uncertainty. This strategy benefits from speculation and anticipation but avoids overnight risk.
Another method is post-earnings reaction trading, where traders wait for results and then trade based on the market’s reaction. This reduces uncertainty and allows traders to align with confirmed momentum, though the initial move may already be partially priced in.
Derivative traders often use options-based strategies such as straddles, strangles, or spreads to benefit from volatility rather than direction. These strategies aim to profit from large price swings regardless of whether the stock moves up or down, but they require a solid understanding of implied volatility and option pricing.
Sector and Index-Level Impact
Earnings season does not affect all stocks equally. Heavyweight companies in sectors like banking, IT, FMCG, and metals can significantly influence broader indices such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex. Strong results from large banks or IT firms can lift the entire market, while disappointments can drag indices lower even if other stocks perform well.
Traders often analyze sector-wide earnings trends to identify leadership or weakness. For example, if multiple companies in a sector report margin expansion and strong demand, traders may adopt bullish positions across that sector. Conversely, widespread earnings downgrades may signal structural issues, prompting defensive or short-selling strategies.
Risk Management During Earnings Season
Risk management is especially important during earnings season trading. Price gaps can bypass stop-loss orders, leading to slippage. To manage this, traders often reduce position sizes, avoid holding leveraged positions overnight, or hedge exposure using options. Clear risk-reward ratios and strict discipline help protect capital during unpredictable market reactions.
Another important practice is avoiding overtrading. The abundance of opportunities during earnings season can tempt traders to take excessive positions. Successful traders focus on high-quality setups rather than chasing every earnings announcement.
Long-Term Perspective vs Short-Term Trading
While earnings season is popular among short-term traders, long-term investors also use this period to reassess portfolio holdings. Consistent earnings growth, improving margins, and strong guidance reinforce long-term investment theses. For traders, understanding this long-term context helps interpret short-term price movements more accurately.
A stock that corrects sharply after earnings may offer opportunities if the long-term fundamentals remain intact. Conversely, a sharp rally driven purely by short-term enthusiasm may fade if earnings quality is weak.
Conclusion
Earnings season trading is a powerful but demanding aspect of the stock market. It offers unique opportunities driven by volatility, expectations, and market psychology, but it also carries heightened risks. Successful earnings traders combine fundamental understanding with technical analysis, focus on expectations rather than headlines, and practice strict risk management. Whether trading stocks, indices, or derivatives, mastering earnings season dynamics can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to navigate markets with confidence and discipline.
Quantitative Trading The Science of Data-Driven Financial MarketCore Concept of Quantitative Trading
At its core, quantitative trading is built on the belief that market behavior follows identifiable patterns that can be measured, modeled, and exploited. Quant traders collect vast amounts of historical and real-time market data—such as price movements, volume, volatility, interest rates, and macroeconomic indicators—and apply mathematical techniques to uncover statistically significant relationships. These insights are then converted into precise trading rules that computers can execute automatically.
The goal is not to predict markets with certainty, but to gain a probabilistic edge. Even a small statistical advantage, when applied consistently across many trades, can lead to meaningful long-term profitability.
Key Components of Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading systems typically consist of several interlinked components. First is data acquisition, where clean, high-quality data is gathered from exchanges, economic reports, and alternative sources such as satellite data or social media sentiment. Second is model development, where traders use mathematics, statistics, and machine learning to design strategies. These models may focus on trends, mean reversion, arbitrage, or volatility patterns.
Next comes backtesting, a critical step in which strategies are tested against historical data to evaluate performance, risk, and robustness. Finally, execution and risk management ensure that trades are placed efficiently while controlling losses through position sizing, stop-loss rules, and portfolio diversification.
Common Quantitative Trading Strategies
Several well-known strategies form the foundation of quantitative trading. Trend-following strategies aim to capture sustained market movements by identifying upward or downward momentum. Mean reversion strategies assume that prices tend to return to their historical averages after extreme movements. Statistical arbitrage seeks to exploit temporary price discrepancies between related securities, often across stocks, futures, or ETFs.
Another important category is high-frequency trading (HFT), which uses ultra-fast algorithms to execute large numbers of trades within milliseconds, profiting from small price inefficiencies. Factor-based investing, commonly used by hedge funds and asset managers, ranks securities based on factors such as value, momentum, quality, and low volatility.
Role of Technology and Algorithms
Technology is the backbone of quantitative trading. Powerful computers process massive datasets, while programming languages such as Python, R, and C++ are used to build and deploy models. Machine learning and artificial intelligence have further expanded the scope of quant trading by enabling systems to adapt, learn from new data, and improve performance over time.
Algorithmic execution minimizes transaction costs by intelligently splitting large orders and timing trades to reduce market impact. As markets become more competitive, speed, efficiency, and technological sophistication often determine success.
Risk Management in Quantitative Trading
Risk management is just as important as strategy design. Quantitative traders focus on controlling downside risk through diversification, volatility targeting, and strict drawdown limits. Since quant strategies often rely on historical relationships, unexpected market events—such as financial crises or geopolitical shocks—can cause models to fail. Robust risk frameworks help mitigate these risks by limiting exposure and adapting to changing market conditions.
Stress testing and scenario analysis are widely used to evaluate how strategies might perform under extreme conditions. This disciplined approach helps protect capital and ensures long-term sustainability.
Advantages of Quantitative Trading
One of the biggest advantages of quantitative trading is objectivity. Decisions are based on data and rules rather than emotions like fear or greed. Quant strategies are also scalable, allowing traders to manage large portfolios across multiple markets simultaneously. Automation improves consistency, ensuring that strategies are executed exactly as designed without human error.
Additionally, quantitative trading can uncover opportunities that are invisible to the human eye, especially in complex, fast-moving markets where manual analysis is impractical.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its strengths, quantitative trading is not without challenges. Developing reliable models requires deep expertise in mathematics, programming, and financial theory. Data quality issues, overfitting, and changing market dynamics can reduce effectiveness. As more participants adopt similar strategies, competition increases and profit margins shrink.
Regulatory constraints, technological costs, and the risk of model breakdowns during extreme events also pose significant hurdles. Successful quant traders must continuously research, refine, and adapt their models.
Future of Quantitative Trading
The future of quantitative trading is closely tied to advancements in artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing. Alternative data sources, such as satellite imagery and real-time consumer behavior, are expanding the analytical toolkit of quant traders. As markets evolve, quantitative trading is expected to become even more sophisticated, integrating human insight with machine intelligence.
Conclusion
Quantitative trading represents the fusion of finance, mathematics, and technology. By transforming market data into systematic strategies, it offers a disciplined and scalable approach to trading. While it requires significant expertise and resources, quantitative trading continues to shape modern financial markets, redefining how trades are analyzed, executed, and managed in an increasingly data-driven world.
A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Trading ApproachWhich Trading Style Is Best?
Trading in financial markets is not a one-size-fits-all activity. Every trader has different goals, risk tolerance, time availability, capital size, and psychological makeup. Because of these differences, multiple trading styles have evolved over time. The most important question for any trader—especially beginners—is not which trading style is the most profitable, but which trading style suits me best. Choosing the right trading style can significantly improve consistency, discipline, and long-term success.
Understanding Trading Styles
A trading style refers to the method and timeframe a trader uses to enter and exit the market. It determines how long trades are held, how frequently trades are taken, and how much risk is assumed per trade. Trading styles range from ultra-short-term approaches that last seconds or minutes to long-term strategies that span months or even years.
The most common trading styles include scalping, day trading, swing trading, position trading, and long-term investing. Each style has its own advantages, disadvantages, and suitability depending on the trader’s personality and lifestyle.
Scalping: Fast-Paced and High Intensity
Scalping is the shortest-term trading style. Scalpers aim to profit from very small price movements, often holding trades for seconds or minutes. They execute multiple trades in a single session, relying heavily on technical indicators, order flow, and high liquidity.
This style requires intense focus, quick decision-making, and the ability to handle stress. Scalping suits traders who can monitor markets continuously, have access to low brokerage costs, fast execution platforms, and strict discipline. While individual profits per trade are small, consistency and volume can lead to meaningful returns. However, transaction costs, emotional fatigue, and overtrading are major risks.
Day Trading: Intraday Opportunities
Day trading involves opening and closing all positions within the same trading day. Traders aim to capitalize on intraday volatility while avoiding overnight risks such as global news or gaps.
Day traders typically use technical analysis, chart patterns, volume, and indicators like VWAP, RSI, and moving averages. This style suits individuals who can dedicate several hours daily to the market and prefer quick feedback on their performance. Day trading offers flexibility and frequent opportunities, but it also demands discipline, risk management, and emotional control. Without a structured plan, losses can accumulate rapidly.
Swing Trading: Balance Between Time and Opportunity
Swing trading is one of the most popular trading styles, especially among retail traders. Swing traders hold positions for a few days to a few weeks, aiming to capture medium-term price movements or “swings” within a trend.
This style requires less screen time compared to day trading and allows traders to combine technical analysis with basic fundamentals. Swing trading is suitable for individuals who have jobs or other commitments but can analyze charts during evenings or weekends. While overnight risk exists, it is often manageable with proper position sizing and stop-loss placement. Swing trading offers a good balance between opportunity, time commitment, and stress levels.
Position Trading: Long-Term Market Participation
Position trading is a longer-term trading style where positions are held for weeks, months, or even years. Traders focus on major trends driven by economic cycles, sector performance, and company fundamentals.
This approach requires patience and a strong understanding of macroeconomic factors, financial statements, and long-term technical structures. Position trading suits individuals who prefer fewer decisions, lower trading frequency, and a calm approach to markets. Short-term volatility is largely ignored, which reduces emotional stress. However, capital may remain tied up for extended periods, and trend reversals can impact returns if not monitored carefully.
Long-Term Investing: Wealth Creation Focus
Although technically different from trading, long-term investing is often considered a trading style by market participants. Investors buy assets with the intention of holding them for several years, benefiting from compounding, dividends, and economic growth.
This style suits individuals seeking steady wealth creation with minimal daily involvement. It relies more on fundamental analysis, business quality, and long-term economic outlook rather than short-term price movements. Long-term investing carries lower transaction costs and emotional pressure but requires patience and the ability to endure market cycles.
How to Choose the Right Trading Style
The best trading style depends on several personal factors. Time availability is critical—if you cannot monitor markets during trading hours, intraday styles may not suit you. Risk tolerance also matters; shorter-term styles often involve higher emotional and financial stress. Capital size, brokerage costs, and access to technology play a role as well.
Equally important is psychology. Some traders thrive in fast-paced environments, while others perform better with slower, more deliberate decision-making. A trading style aligned with your personality increases consistency and reduces impulsive behavior.
Conclusion
There is no universally “best” trading style. The best trading style is the one that aligns with your goals, lifestyle, risk tolerance, and mindset. Scalping and day trading offer speed and excitement but demand high discipline and focus. Swing and position trading provide flexibility and balance, while long-term investing emphasizes stability and wealth creation.
Successful traders are not defined by how often they trade, but by how well their trading style fits them. Understanding yourself is just as important as understanding the market. When your trading style matches your personality and resources, long-term success becomes far more achievable.
Algorithmic AI Trading Strategies: Transforming Modern Markets1. Meaning of Algorithmic AI Trading
Algorithmic AI trading refers to the use of computer programs powered by AI to execute trades based on predefined rules and adaptive learning models.
Unlike traditional algorithmic trading, AI-based systems can learn from historical and real-time data, improving decisions over time.
These strategies reduce emotional bias and enable data-driven decision-making.
2. Core Components of AI Trading Strategies
Data Collection: Market prices, volume, order book data, news, social media sentiment, and macroeconomic indicators.
Data Processing: Cleaning, normalization, and feature extraction for accurate analysis.
AI Models: Machine learning, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and neural networks.
Execution Engine: Automatically places, modifies, and exits trades at optimal prices.
Risk Management Module: Controls exposure, position sizing, and drawdowns.
3. Types of Algorithmic AI Trading Strategies
Trend-Following Strategies:
AI identifies price momentum and trends using historical patterns.
Trades are placed in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Mean Reversion Strategies:
AI assumes prices revert to historical averages.
Trades are triggered when prices deviate significantly from the mean.
Arbitrage Strategies:
AI detects price inefficiencies across markets or instruments.
Executes simultaneous buy and sell orders to lock risk-free or low-risk profits.
Market-Making Strategies:
AI places buy and sell orders continuously to capture bid-ask spreads.
Requires ultra-low latency and precise risk control.
Sentiment-Based Strategies:
AI analyzes news, earnings reports, and social media sentiment.
Trades are aligned with positive or negative market sentiment signals.
4. Role of Machine Learning in Trading
Supervised Learning:
Uses labeled data to predict price direction or volatility.
Unsupervised Learning:
Identifies hidden patterns, clusters, and market regimes.
Reinforcement Learning:
AI learns by trial and error, optimizing strategies through rewards and penalties.
Deep Learning:
Neural networks analyze complex, non-linear relationships in market data.
5. Strategy Development Process
Idea Generation: Identifying inefficiencies or repeatable patterns.
Backtesting: Testing strategies on historical data to evaluate performance.
Optimization: Fine-tuning parameters to improve risk-adjusted returns.
Paper Trading: Simulating trades in real-time without real money.
Live Deployment: Executing strategies in real market conditions.
6. Risk Management in AI Trading
Position Sizing: Limits capital allocation per trade.
Stop-Loss Mechanisms: Automatically exit losing trades.
Diversification: Trading across multiple assets and strategies.
Drawdown Control: Prevents excessive losses during adverse market phases.
Model Risk Monitoring: Detects when AI models stop performing effectively.
7. Advantages of Algorithmic AI Trading
Speed and Efficiency: Executes trades in milliseconds.
Emotion-Free Trading: Eliminates fear, greed, and hesitation.
Scalability: Can trade multiple markets simultaneously.
Consistency: Follows rules strictly without deviation.
Data Utilization: Analyzes vast datasets beyond human capability.
8. Limitations and Challenges
Overfitting Risk: Models may perform well historically but fail in live markets.
Data Quality Issues: Poor data can lead to inaccurate signals.
Market Regime Changes: AI models may struggle during unexpected events.
High Infrastructure Costs: Requires powerful hardware and low-latency systems.
Regulatory Constraints: Compliance with market regulations is essential.
9. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Market Fairness: High-frequency AI trading can disadvantage retail traders.
Transparency: Black-box AI models are difficult to interpret.
Risk of Flash Crashes: Rapid automated trading can amplify volatility.
Regulatory Oversight: Authorities monitor algorithmic trading to prevent manipulation.
10. Role of AI Trading in Retail vs Institutional Markets
Institutional Traders:
Use advanced AI systems with large datasets and capital.
Focus on high-frequency and statistical arbitrage strategies.
Retail Traders:
Use simplified AI tools, bots, and platforms.
Emphasize swing trading, trend-following, and signal-based automation.
11. Integration with Other Technologies
Cloud Computing: Enables scalable data processing and storage.
Big Data Analytics: Enhances pattern recognition and forecasting.
Blockchain Integration: Improves transparency and settlement efficiency.
APIs and Trading Platforms: Allow seamless execution and monitoring.
12. Future of Algorithmic AI Trading
AI systems will become more adaptive and self-learning.
Greater use of alternative data such as satellite images and web traffic.
Improved explainable AI models for better transparency.
Increased regulatory frameworks to ensure market stability.
Wider adoption among retail traders through user-friendly platforms.
13. Conclusion
Algorithmic AI trading strategies represent a major evolution in financial markets.
They enhance efficiency, accuracy, and scalability of trading operations.
Despite challenges, proper risk management and ethical practices can make AI trading sustainable.
As technology advances, AI-driven strategies will continue to redefine how markets operate and how traders participate globally.
$XRP PRICE PREDICTION | MULTI-YEAR BREAKOUT TOWARD $10+?CRYPTOCAP:XRP is trading above a confirmed multi-year breakout zone on the higher timeframe after completing a long accumulation phase.
Price has already delivered a strong expansion move and is now building structure for the next leg higher.
TECHNICAL OVERVIEW (HTF):
✔ Descending Wedge Breakout (2020–2024)
✔ 600%+ Expansion From $0.60 Breakout
✔ Fair Value Gap / Accumulation Zone: $1.30 – $1.90
✔ Higher-Timeframe Bullish Structure Intact
✔ Bullish Bias While Price Holds Above $1.30
TARGETS (CryptoPatel): $3.50 / $5.00 / $8.70 / $10+
INVALIDATION:
❌ HTF Close Below $1.30
Technical analysis only. Not financial advice. DYOR.
XAUUSD Break in Structure Points to Continued Upward MomentumXAUUSD shows a clear bullish price structure supported by strong momentum and clean market behavior. After a sharp impulsive move, price shifted into an upward trend, forming consistent higher highs and higher lows. The breakout above the earlier resistance zone around 4,630–4,640 confirms a clear Break of Structure, indicating that buyers are in control and bullish strength remains active.
The earlier resistance area has now turned into a key support zone around 4,585–4,600. This zone is important because price reacted strongly from this level in the past, making it a potential buy-on-pullback area. As long as price holds above this support, the bullish structure stays valid. Small pullbacks into this zone may be part of a healthy continuation within the trend rather than a reversal.
On the upside, price is trading near recent highs, suggesting that liquidity may still be present above. If price continues to hold above the structure break level, further upside toward 4,670 and higher levels remains possible. A clear failure to hold above the support zone would indicate short-term weakness and may lead to a deeper correction.
Overall, the market bias remains bullish while price stays above support, with structure favouring continuation over reversal. This analysis is based purely on technical price action and is for educational purposes only.
BTCUSD Structure Break Defines Trend, Demand Zone, Risk AreaBTCUSD shows a well-defined bullish market structure supported by strong price action and a clear shift in momentum. After forming a solid base, price delivered an impulsive move higher, confirming a Break of Structure and aligning with the broader bullish trend. The ascending structure is marked by higher highs and higher lows, reflecting sustained buyer strength and healthy continuation behavior.
The highlighted demand zone near 90,000–91,000 represents a key support area where price previously consolidated before accelerating upward. This zone may act as a potential buy-on-pullback region if price revisits it with stable structure. As long as price holds above this area, the bullish bias remains intact and continuation scenarios stay valid.
On the upside, price is currently testing a newly formed resistance zone around 97,500–98,500. This area is critical, as selling pressure may appear and cause short-term consolidation or a corrective pullback. A clean acceptance above this resistance would signal strength and open the path toward higher psychological levels near 100,000.
If price fails to hold above the resistance and shows rejection, a controlled retracement toward demand would be considered healthy within the trend. A deeper move below demand would indicate a shift in short-term momentum and require reassessment.
Overall, BTCUSD remains structurally bullish while above demand, with price action favoring continuation over reversal.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Trading involves risk and uncertainty.
$PUMP PRICE OUTLOOK | 500%–1000% POTENTIAL? #PUMP Is Trading In A Bullish Expansion Zone After Breaking Long-Term Descending Resistance On The Daily Chart.
Price Has Completed A Prolonged Distribution → Correction Phase And Is Now Showing Early Reversal Signals.
Current Technical Structure:
✅ Long-Term Descending Trendline Break Confirmed
✅ Descending Wedge Breakout Structure
✅ Strong HTF Demand Zone Holding (0.0023–0.0021)
✅ Multiple Support Reclaims Indicate Accumulation
✅ Strength Signal: Bullish Above $0.0021
CryptoPatel Targets: $0.00449 / $0.00644 / $0.00872 / $0.015 / $0.026
As Long As PUMP/USDT Holds Above $0.0021, The Bullish Bias Remains Intact.
This Is A High-Risk, High-Reward Accumulation Setup With Asymmetric Upside Potential.
Invalidation: Daily Close Below $0.0021
TA Only. Not Financial Advice. DYOR.
$FET Price Prediction | 5000% Potential From Macro Support?Market Context
NYSE:FET is currently trading at a major Higher Timeframe (HTF) support zone after a deep corrective move from cycle highs.
Price has retraced ~97% from ATH, a level historically associated with long-term re-accumulation phases.
Technical Overview (HTF)
✔ Macro ascending channel support intact (since 2020)
✔ Strong HTF demand zone at $0.20 – $0.19
✔ 97%+ retracement from ATH completed
✔ Channel support + demand confluence holding
✔ Bullish structure as long as price holds above $0.19
This area represents a high-risk / high-reward macro support with asymmetric upside potential.
Upside Targets (CryptoPatel Levels) $0.60 / $1.00 / $2.80 / $5.00 / $10.00
➡️ This implies a potential ~50x (5000%) move if the macro structure plays out.
⚠️ Invalidation Level
❌ HTF close below $0.19
A breakdown below this level would invalidate the macro bullish thesis.
Conclusion
As long as FET/USDT holds above $0.19, the macro bullish bias remains valid.
This zone could act as a long-term accumulation base before the next expansion phase.
TA Only | Not Financial Advice
Always manage risk and DYOR.
breakout on the way📈 Tata Consumer Products | Breakout Loading? 👀
Tata Consumer Products is pressing against a long-term downward trendline resistance after a strong recovery from the 2024–25 lows.
Price structure shows higher lows, indicating accumulation near resistance.
🔍 Technical View:
• Multiple tests of the same trendline
• Higher lows → buying pressure building
• Momentum positive, but confirmation pending
📊 Key Levels to Watch:
• Breakout confirmation: Daily close above ₹1,210–1,220
• Immediate support: ₹1,150–1,165
📌 Bias: Bullish only on confirmation
⚠️ Disclaimer: Educational purpose only. Not financial advice.
#TataConsumer #BreakoutWatch #AboutToBreak #StockMarketIndia #SwingTrading #TechnicalAnalysis #IndianStocks #PriceAction
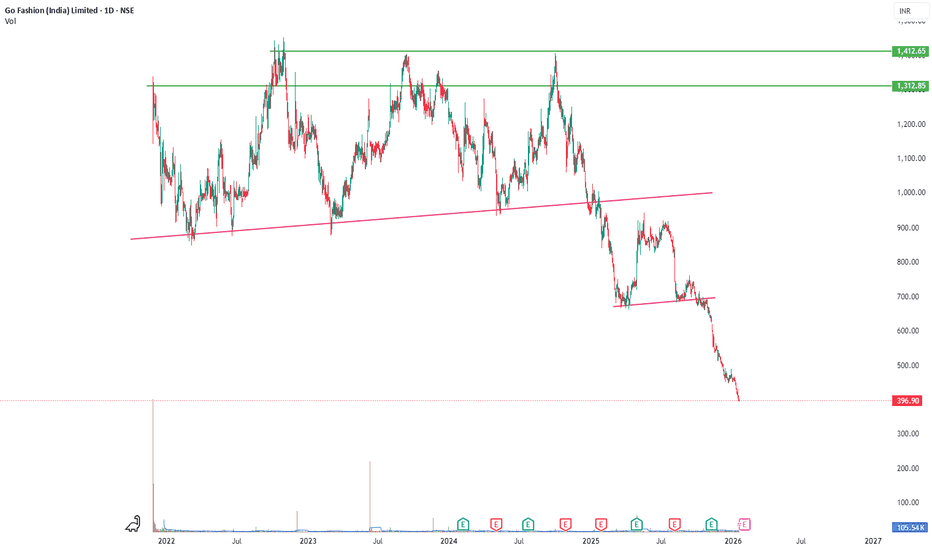
profit booked idea📉 Go Fashion (India) Ltd | Profit Booked ✅ | Trend Breakdown
Go Fashion has broken below key trendline supports after a prolonged distribution phase.
As highlighted earlier, profits were booked once price lost structure and downside momentum picked up.
🔍 What Changed Technically:
• Multiple lower highs → trend weakness
• Breakdown below rising support
• Sharp follow-through selling
• No immediate reversal signals yet
📊 Current View:
• Downtrend intact on daily timeframe
• Fresh entries only after base formation
• Avoid catching falling knife
📌 Status: ✅ Profit Booked | Capital Protected
⚠️ Disclaimer: Educational purpose only. Not financial advice.
#GoFashion #ProfitBooked #CapitalProtection #TrendBreakdown #StockMarketIndia #TechnicalAnalysis #RiskManagement #IndianStocks
about to break📈 Hindustan Copper | Strong Rally → Resistance Zone
Hindustan Copper has delivered a sharp multi-week rally and is now facing resistance near the ₹560–575 zone, which aligns with a major historical supply area.
🔍 Technical Summary:
* Massive breakout from long-term base (Weekly)
* Vertical up-move → momentum exhaustion signals
* Intraday & daily charts show selling pressure near resistance
* Healthy consolidation / pullback expected after sharp run
📊 Current View:
* Zone ₹560–575 = Major resistance
* Fresh breakout only on strong close above ₹580
* Support to watch on pullbacks: ₹520–500
📌 Status: Rally Extended | Caution Advised
⚠️ Disclaimer: Educational purpose only. Not financial advice.
#HindustanCopper #ProfitBookingZone #StockMarketIndia #RallyStock #TechnicalAnalysis #SwingTrading #PriceAction #IndianStocks
about to break idea📈 360 ONE WAM | Trendline Rejection → Consolidation
360 ONE WAM is trading below a declining trendline resistance after multiple rejection attempts.
Price is currently consolidating near ₹1,190–1,200, indicating a wait-and-watch zone.
🔍 Technical View:
• Downward trendline still intact
• Multiple rejections from the same zone
• Volatility contraction → breakout setup building
• No follow-through yet above resistance
📊 Key Levels:
• Breakout confirmation: Daily close above ₹1,220–1,240
• Support: ₹1,120–1,150
📌 Bias: Neutral (Bullish only on confirmation)
⚠️ Disclaimer: Educational purpose only. Not financial advice.
#360ONEWAM #StockMarketIndia #TrendlineResistance #BreakoutWatch #DailyChart #SwingTrading #TechnicalAnalysis #IndianStocks
Part 2 Technical VS. Institutional Common Options Trading Strategies
Options trading is not limited to buying calls and puts. Some widely used strategies include:
Covered Call: Holding a stock and selling a call option to earn premium income.
Protective Put: Buying a put option to protect a stock holding from downside risk.
Straddle: Buying both a call and a put at the same strike price to profit from high volatility.
Strangle: Similar to a straddle but with different strike prices.
Spread Strategies: Using multiple options to limit risk, such as bull spreads and bear spreads.
These strategies allow traders to tailor risk and reward according to their market outlook.
ETH Technical Outlook: Ethereum Attempts Base Formation Ethereum Attempts Base Formation Below Key Fibonacci Resistance
Ethereum’s price structure has been navigating a crucial juncture where key Fibonacci resistance levels are acting as decisive barriers to further upside. After months of corrective action and consolidation, ETH is showing early signs of stabilization and base building, but it remains capped below important Fibonacci retracement zones that historically define reversal and continuation points in a trend.
On the daily chart, price has been oscillating in a range roughly between major support near prior lows around the $2,600–$2,800 area and resistance clustered around the $3,300–$3,450 zone — where Fibonacci retracement levels from the recent high to low sit. Attempts to push above these zones have met selling pressure, keeping ETH from confirming a sustained breakout and forcing traders to watch for confirmation signals rather than chase upside impulsively.
Despite this resistance, buyers are showing resilience. Market structure reveals higher lows forming along a rising support trendline, suggesting that sellers have not fully regained control and that accumulation is occurring at these demand levels. This base formation beneath the key Fibonacci tiers represents a classic consolidation pattern that often precedes more decisive directional moves once a breakout occurs.
Traders looking for confirmation on the bullish side are targeting a clean daily close above the $3,350–$3,450 range, which would not only flip those Fibonacci retracement levels into support but also open the door toward extension targets higher up, where further Fibonacci extensions sit and where prior swing highs cluster. A break above these zones could signal a renewed trend shift and attract momentum flows back into the market.
On the downside, invalidation of this formative base — particularly if ETH loses demand zones below ~$3,000 — could invite deeper pullbacks toward structural supports near the lower Fibonacci retracement bands. For now, the incomplete breakout attempt combined with visible support accumulation paints a picture of cautious optimism, with bulls needing to prove strength at Fibonacci resistance before the next leg up can be confidently anticipated.
ACC (NSE) | Weekly | Harmonic Reversal This chart highlights a high-probability bullish reversal on ACC (Weekly timeframe) based on Harmonic structure + Smart Money Context.
🔹 Pattern Insight
A well-formed XABCD harmonic structure has completed near the 0.886–0.918 PRZ
Price has respected the D-point demand zone, indicating smart money absorption
Extended consolidation near lows suggests selling pressure exhaustion
🔹 Why This Setup Is Strong
✅ Confluence of harmonic PRZ + higher-timeframe demand
✅ Structural symmetry maintained throughout the pattern
✅ Risk clearly defined below the PRZ (ideal R:R setup)
✅ Weekly context favors trend resumption on the upside
🔹 Trade Plan (Positional View)
Entry Zone: Near D-point / demand area
Invalidation: Below structure low
Upside Projection: Towards 2800–2900 zone
Bias: Medium- to long-term bullish
📌 This setup is best suited for positional traders & investors who follow harmonics, market structure, and smart money concepts.
⚠️ This is not financial advice. Always manage risk and confirm with your own analysis.
Infosys Ltd (Infy) - Analysis Bullish Levels -Above 1728/36 above this bullish then around 2181 then first target can be around 2791 some profit booking may come around this level above this more bullish then around 3775 then last stop would be around 4511 above this wait
Bearish levels :- if sustain below 1357/49 below this bearish if it comes to this level will be a good apportunity for new entry with small stop loss as per your comfort.
**Consider some Points buffer in above levels
**Disclaimer -
I am not a SEBI registered analyst or advisor. I does not represent or endorse the accuracy or reliability of any information, conversation, or content. Stock trading is inherently risky and the users agree to assume complete and full responsibility for the outcomes of all trading decisions that they make, including but not limited to loss of capital. None of these communications should be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities, nor advice to do so. The users understands and acknowledges that there is a very high risk involved in trading securities. By using this information, the user agrees that use of this information is entirely at their own risk.
Thank you.
RADHIKAJWE 1 Day View 📊 Current Price
Around ₹73.5–₹75 on NSE/BSE.
📈 1-Day Technical Levels (Key Support & Resistance)
Pivot / Intraday Reference
Pivot Point (Daily): ~ ₹76.06
Resistance Levels
R1: ~ ₹77.6
R2: ~ ₹79.5
R3: ~ ₹81.1
(On a very short intraday basis from Kotak data)
First Resistance: ~ ₹75.9
Second: ~ ₹77.3
Third: ~ ₹78.2
Support Levels
S1: ~ ₹74.1
S2: ~ ₹72.6
S3: ~ ₹70.6
(Shorter intraday levels)
First Support: ~ ₹73.7
Second: ~ ₹72.7
Third: ~ ₹71.4
📉 Technical Bias Indicators (Daily)
Moving Averages (short & mid): price generally below short EMAs/SMA, currently bearish/slightly neutral in very short term.
RSI (14): ~ 42–47 — neutral to mildly bearish on daily.
MACD / Oscillators: mostly bearish to neutral in daily view.
Overall 1D technical summary: Mild bearish/neutral near current levels with possible rebounds at major support levels.
Choosing Banks Wisely for Success in the Trading MarketImportance of Banks in the Trading Market
Banking stocks attract traders because of their high liquidity, strong institutional participation, and regular price movements. Stocks like HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, SBI, Axis Bank, and Kotak Mahindra Bank often show clear trends and good volumes, making them suitable for intraday, swing, and positional trading. Since banks are directly influenced by interest rates, inflation, government policies, and economic growth, they tend to react quickly to news and macroeconomic data. This responsiveness creates frequent trading opportunities but also demands careful selection.
Understanding the Business Model of Banks
Before trading a bank stock, it is important to understand its business model. Some banks are retail-focused, others are corporate-lending heavy, while a few specialize in niche segments such as MSMEs or digital banking. Retail-focused banks generally have stable earnings and lower risk, which often results in smoother price trends. Corporate-heavy banks may offer higher returns during economic booms but can be volatile during slowdowns due to stressed assets. Traders who understand these differences can align their strategy with the risk profile of the bank they choose.
Asset Quality and Risk Management
Asset quality is one of the most critical factors when selecting banks for trading. Indicators such as Gross NPA (Non-Performing Assets), Net NPA, and provision coverage ratio reflect the bank’s ability to manage credit risk. Banks with improving or stable asset quality are preferred by institutional investors, leading to stronger price support and reliable trends. Sudden deterioration in asset quality often triggers sharp sell-offs, which can be risky for traders without proper stop-losses.
Capital Adequacy and Financial Strength
Capital adequacy ratio (CAR) shows how well a bank is capitalized to absorb potential losses. Well-capitalized banks inspire confidence among investors and traders, especially during uncertain market conditions. Banks with strong capital buffers tend to recover faster after market corrections, making them better candidates for positional and swing trading. Weakly capitalized banks may show erratic movements and are more vulnerable to negative news.
Impact of Interest Rates and RBI Policies
Interest rates and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) policies have a direct impact on banking stocks. Changes in repo rates, CRR, SLR, and liquidity measures influence banks’ margins and profitability. Traders should track RBI monetary policy announcements closely when trading bank stocks. Banks that manage interest rate cycles efficiently often outperform peers, offering better trading opportunities during both bullish and bearish phases.
Public Sector vs Private Sector Banks
Choosing between public sector banks (PSUs) and private sector banks is another important consideration. Private banks generally have better asset quality, advanced technology, and efficient management, leading to more consistent price movements. PSU banks, on the other hand, are more sensitive to government policies, recapitalization news, and reforms. While PSU banks can deliver sharp rallies, they also carry higher risk. Traders should select based on their risk appetite and market conditions.
Role of Technical Analysis in Bank Selection
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in choosing banks for trading. Banks with clear chart patterns, strong support and resistance levels, and high trading volumes are more suitable for traders. Indicators such as moving averages, RSI, MACD, and VWAP help identify trends and entry-exit points. A fundamentally strong bank showing technical confirmation provides a higher probability trade compared to a weak bank with random price movements.
Liquidity and Volatility Considerations
Liquidity is essential for trading, especially for intraday traders. Highly liquid bank stocks allow easy entry and exit without significant slippage. Volatility is also important, as it determines profit potential. The best bank stocks for trading offer a balance—enough volatility to generate profits but not so much that price movements become unpredictable. Overly volatile banks can lead to emotional decision-making and losses.
News, Results, and Event Sensitivity
Bank stocks are highly sensitive to quarterly results, credit growth data, mergers, regulatory actions, and management commentary. Traders should be aware of upcoming events and avoid taking large positions without a clear plan. Positive surprises in earnings or guidance can lead to strong breakouts, while negative news can break key support levels. Wise traders factor event risk into their bank selection process.
Long-Term Trends and Market Leadership
Banks that consistently outperform the market often become leaders during bull phases. Trading such leaders increases the probability of success, as they attract continuous institutional interest. Observing relative strength compared to the index helps traders identify which bank stocks are likely to sustain trends. Avoiding laggards and focusing on leaders is a key principle of wise bank selection.
Risk Management and Position Sizing
Even the best bank stock can move against expectations. Therefore, risk management is non-negotiable. Traders should define stop-loss levels, position size according to capital, and avoid overexposure to a single stock or event. Wise selection combined with disciplined risk management helps protect capital and ensures longevity in the trading market.
Conclusion
Choosing banks wisely for the trading market is a combination of understanding fundamentals, tracking macroeconomic factors, applying technical analysis, and managing risk effectively. Banks are powerful trading instruments, but they demand respect due to their sensitivity to economic and policy changes. Traders who focus on financially strong, well-managed, and technically sound banks increase their chances of consistent profits. In the long run, success in trading bank stocks does not come from frequent trades, but from informed selection, patience, and disciplined execution.