PAYTM KARO ONE97 COMMUNICATIONS NSE:PAYTM
Paytm karo varna stock ko niche karo 😅😅
Paytm take strong resistance from his major resistance and also do classical pattern consolidation after breaking down that is double confirmation for trend direction.
now, 1000 is major support
this is not a any types of advice.
this is just chart analysis
do your own research
Community ideas
Eternal Zomato shows strong weakness NSE:ETERNAL
Zomato Near to end his up trend
major support is break near 300 and retested that level and gave another strong down move in daliy time frame. that retest also brakes another support with volume and big move.
chart picture explain all things.
next major support is gap is 230 and that whole zone till 200.
this is not any types of advice.
this is just chart analysis.
do your own research
$TVC:SILVER MOON MISSION:2025-29 is History Repeating Again? TP?🚀 Silver Feature Analysis 2026 – 2029: The Historical Repeat 🚀
TVC:SILVER has recently hit its All-Time High (ATH) three times in history with massive rallies. My analysis is based on the duration and percentage returns of these specific periods:
1️⃣ 1980: (1 Aug 1979 to 29 Jan 1980) – A 6-month rally with returns OVER 511% ($6.5 to $48). 📈
2️⃣ 2011: (1 Oct 2008 to 22 Apr 2011) – A 2y 6m 21 days rally with returns OVER 451% ($8.4 to $47.91). 📈
3️⃣ 2021: (2 Mar 2020 to 10 Feb 2021) – An 11m 8 days rally from $11.63 to $30.09. 📈
🔍 The Current Assumption 🔍
The ongoing rally started on 3 Feb 2025 and is continuing to the present day. Based on price action, silver has been manipulated many times (like in 1980, 2011, and 2021), and I expect this to happen again in the upcoming years of 2028-2029. ⚠️
🎯 Near-Term Goal: This rally is projected to go up to $119 – $129.88. 🔄 The Reversal: After hitting those levels, I anticipate a small reversal back to the $102 – $105 per ounce range. 📉 ⚡ The Final Leg: In Sep 2026 to Nov 2026, we could see a continuation, eventually reaching levels of $179 – $185 in the year 2028-2029 as silver repeats its historic data! 🚀🔥
📑 Key Support & Resistance Levels 📑
Based on the cycles, here are the critical levels to watch:
Year Support Resistance
1979-80 $6.5 $48
2008-11 $8 $47.91
2020-21 $11.63 $30.09
2025-28 $30.97 🟢 $129 - $169 🔴
2025-29 $79 - $86 🟢 $110 - $119 🔴
📊 Technical Snapshot (Current Stats) 📊
🟢 Trend: BULLISH (MTF Trend) 💪 ADX: 44.3 (Strong Trend Energy) 🔥 RSI: 94.5 (Extreme Momentum - Use Caution) ✅ Trade Mode: 🟢 LONG ONLY TILL RESISTANCE 🟢 🎯 Target Projection: Rally expected till the $129.44 level.
💡 Conclusion 💡
History is repeating! 🔁 After the accumulation that started on 03 Feb 2025, silver is on a path to mirror its 1980 and 2011 performance. Watch the $129 level closely for the first major milestone. 🏁💎
⚠️ RISK WARNING & DISCLAIMER ⚠️
This analysis is for educational and informational purposes only. Trading precious metals involves high risk. The projections mentioned (such as the $129 and $185 targets) are based on historical fractal data and current technical indicators, but market conditions can change due to global economic factors. Always do your own research (DYOR) and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results. 🛑
USDCHF trading above Decisive zoneThe USDCHF is currently at a critical "decision zone" after a period of significant volatility. Following a sharp decline earlier this week, price action is now signaling a potential shift in momentum.
1. Key Support Validation
The pair successfully tested a major support zone near 0.7870 – 0.7880. This area is historically significant (acting as a base for major rallies in late 2025) and has once again triggered a strong "buy the dip" response. The rejection at these lows suggests that the bears are losing steam at these psychological levels.
2. Rising Channel Formation
On the lower timeframes (15m), we are observing a Junior Ascending Channel.
The Structure: Price is carving out higher highs and higher lows, respecting the lower trendline of this corrective channel.
The Sentiment: This indicates a steady accumulation by bulls, though it remains a "corrective" move within a larger bearish trend.
3. The "Decision Zone" Strategy
The pair is currently approaching a confluence of resistance. For a sustained reversal, traders should watch the following:
Bullish Breakout: A clean break and hold above the 0.7920 resistance zone would confirm the recovery and target 0.7960.
Bearish Continuation: If the price fails at the upper boundary of the rising channel, we could see a "Bear Flag" play out, leading to a retest of the recent 0.7878 lows.
NASDAQ bullish bias on HTF and ITFThe price is currently reacting to THE DAILY FAIR VALUE GAP , which is a good confluence for bullish and long clarity, as the dollar continues to freefall , we can consider the relative strength between the index and the currency to support our long idea.
The closest target would be the recents 4 hour highs.
Wait until 9:30 openin for any manipulation to frame our trade.
Invalidation :- closing below the (dfvg)
Intraday Institutiona TradingWhat Is an Option?
An option is a derivative contract whose value is derived from an underlying asset such as a stock, index, commodity, or currency.
Each option contract gives:
The buyer the right (not obligation)
The seller (writer) the obligation
to transact the underlying asset at a fixed price (strike price) on or before a specified date (expiry).
Key Types of Options
Call Option
Put Option
USDINR at Key Resistance – Break or Rejection?USDINR is currently trading near the upper boundary of a well-defined rising channel — a zone where price has historically faced strong rejection and profit booking.
This rally has been structural, not random. Price has respected the channel multiple times, creating higher highs and higher lows, showing steady demand for dollars over the rupee. However, every strong trend eventually meets a decision zone — and this upper band is one of them.
What makes this level more important is the timing.
The Union Budget is approaching — an event that directly impacts fiscal deficit, foreign flows, inflation expectations, and overall confidence in the Indian economy. Historically, such macro events act as catalysts, increasing volatility in USDINR and often triggering major reactions from key technical levels.
At this stage, USDINR is not about prediction — it’s about reaction.
• A sustained move and acceptance above this resistance zone could signal continuation of the bullish structure with momentum.
• A sharp rejection from here would indicate profit booking and a possible pullback toward the channel support.
In trending markets, price usually respects structure first — news simply accelerates the move.
Right now, structure is stretched, and sentiment is waiting for a trigger.
This zone will decide whether USDINR expands higher or breathes before the next leg.
Patience and price behavior near resistance will reveal the real story.
Intraday Institutiona Trading Introduction to Option Trading
Option trading is a sophisticated financial strategy that allows investors and traders to buy or sell the right—but not the obligation—to trade an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time period. Unlike traditional stock trading, where profits depend primarily on price movement direction, option trading enables participants to profit from price movement, volatility, time decay, and even stagnation.
Options are widely used across global financial markets, including equities, indices, commodities, currencies, and cryptocurrencies. They serve multiple purposes: hedging risk, generating income, speculation, and portfolio optimization.
While option trading can offer high reward potential, it also carries complexity and risk. A deep understanding of its mechanics is essential before participating actively.
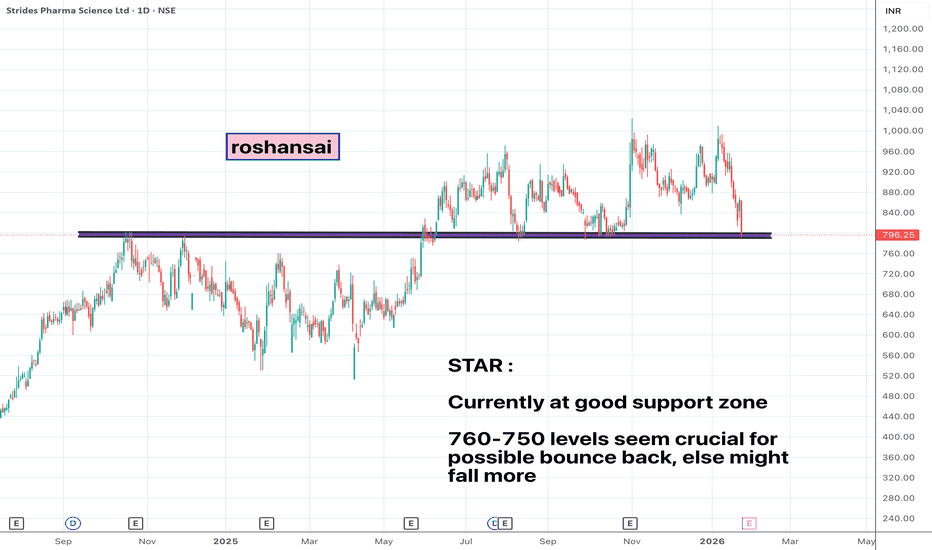
HDFC Bank Price Action Analysis for Feb-Mar 2026Analysis date: 26-Jan-26
HDFC Bank seems to have struggled at 990 levels before finally giving in Jan 2026 closing below 950 supportwhich it was holding since June 2025
Next support is likely to be near 875 levels as shown on the chart. Sell on rise strategy till it reaches 875-850 levels.
Keep 1000 as SL
Happy Trading!
the dip is an opportunityITC CMP 323
Elliott- this is the 4th wave correction and is still not over. Corrections tgt iv waves. I have marked that on the chart. The zone is 300/275. This is the likely place where this correction should end.
Fibs- the confluence zone at 317 is where it should halt temporarily. In my view the next confluence at 296 is a high prob reversal zone.
Conclusion - We will look at reversal signals once the stock comes down to support. In my view this dip will be a good buy for investors as the last impulse wave will be very strong. So people holding this counter u can look to average around 300 or simply sit tight.
Nifty weekly price action analysis for Feb-Mar 2026Analysis Date: 26-Jan-26
Happy Republic Day to all.
After making all time high at 26373 Nifty has nosedived and broken 2 trendlines within couple of weeks. 26000 and 25250 were major support trendlines. Nifty has given a close below the 25250 trendline which confirms downtrend has just begun.
It may go down to 23000 levels soon.
The best area to sell Nifty is 25500 levels for target 24500 and 23000. Keeping SL at 25700. Refer chart for price action analysis
Happy Trading!
Natural Gas : Bullish with the key level 2.600Earlier I posted but it this post I changed the count of motive waves instead of impulse wave!
i:e: taking this whole upside move as an expanding diagonal structure
which suggest wave 3 of higher degree can take the prices up to 6.500
key level for this scenario is 2.600
MPHASIS – Tight Structure Building Before the Next MoveMPHASIS is currently trading inside a well-defined triangle structure, where price is making lower highs and higher lows.
This clearly shows that the market is moving into a compression phase, with buyers and sellers gradually pushing price into a narrower range. Instead of trending strongly in one direction, the stock is taking time to build energy.
The upper trendline continues to act as resistance, while the rising base is providing consistent support. As price moves closer to the end of this structure, a strong directional move is usually expected.
At this stage, the focus is not on predicting the move, but on waiting for confirmation.
👉 A strong close above resistance may signal upside continuation.
👉 A clear break below support could invite further downside.
Until then, patience is key.
Let price decide the direction — structure only shows that a move is coming.
Unitdspr Short setup.Highlighting key zones and a potential short setup:
The stock is already on downtrend on the daily timeframe. With this the zone marked formed can act as a strong resistance as it is in confluence with 50 EMA on the daily and weekly.
The prices below the 21 Dema marks this significance too.
With the price breaking pivot levels with the move it can be opportunity for short trade.
Keep SL at or above the trap zone.
Hal short setupSpotted a high-probability short setup on Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd based on multi-timeframe confluence:
- 🔴 Supply Zone aligned with Daily EMA 50 and Weekly EMA 50 – strong resistance cluster.
- 🔄 Entry on retracement into the zone, post breakdown of prior pivot low.
- 🟠 Stop Loss placed at 15% DATR above the zone for volatility buffer.
- 🎯 Target set at 1:3 RR, respecting structure and momentum.
- 📉 EMA 21 < EMA 50 confirms short bias
The zone is placed with high probability.
The trade is valid till the time price retraces to to level and moves down.
The trade remains invalid if price moves down first to form lower high and lower low and then retraces back in sessions to come.
XAUUSD (H2) – Liam Weekly Risk StrategyXAUUSD (H2) – Liam Weekly Risk Plan
Late-stage rally into macro risk | Sell premium, buy liquidity only
Quick summary
Gold continues to push higher, driven by escalating geopolitical and macro risk:
🇺🇸🇮🇷 US–Iran tensions remain elevated
🏦 FOMC: ~99% Fed holds rates, with a high chance of hawkish guidance from Powell
🇺🇸 US government shutdown risk later this week
This is a classic environment for headline spikes and liquidity grabs. Price is now trading at premium levels, so the edge shifts to reaction trading, not chasing strength.
Macro context (supportive, but dangerous to chase)
Geopolitical stress keeps safe-haven demand alive.
A hawkish Fed message can trigger sharp USD/yield reactions, even if rates are unchanged.
Government shutdown headlines often produce fast whipsaws, not clean trends.
➡️ Conclusion: volatility will increase, but direction will be decided at liquidity levels — not by the news itself.
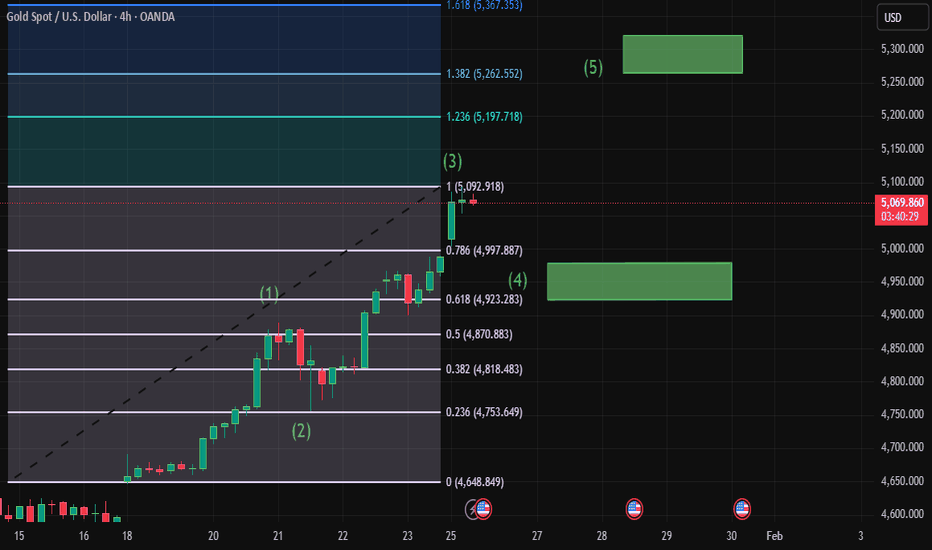
Technical view (H2 – based on the chart)
Gold is in a strong bullish structure, but price has entered a late-stage expansion after multiple impulsive legs.
Key levels from the chart:
✅ Major SELL zone (premium / exhaustion): 5155 – 5234
✅ Current impulsive high area: ~5060
✅ Buy-side liquidity (already built): 4700 – 4800
✅ Sell-side liquidity / value zone: 4550 – 4600
The structure suggests a high probability path: push higher to clear buy-side liquidity → rotate lower into sell-side liquidity.
Trading scenarios (Liam style: trade the level)
1️⃣ SELL scenarios (priority – distribution at premium)
A. SELL at premium extension (primary idea)
✅ Sell zone: 5155 – 5234
Condition: rejection / loss of momentum on M15–H1
SL: above the high
TP1: 5000
TP2: 4800
TP3: 4600 (sell-side liquidity)
Logic: This zone represents late buyers and FOMO entries. Ideal area for distribution and mean rotation, especially during macro headlines.
B. SELL failed continuation
✅ If price spikes above 5060 but fails to hold (fake breakout):
Sell on lower-TF breakdown
TP: 4800 → 4600
Logic: Headline-driven spikes often fail after liquidity is taken.
2️⃣ BUY scenario (secondary – value only)
BUY only at sell-side liquidity
✅ Buy zone: 4550 – 4600
Condition: liquidity sweep + strong bullish reaction
TP: 4800 → 5000+
Logic: This is the first area where long-term buyers regain R:R advantage. No interest in buying above value.
Key notes for the week
Expect false breaks around FOMC.
Reduce size during Powell’s speech.
Avoid mid-range entries between 4800–5000.
Patience pays more than prediction.
What’s your bias this week: selling the 5155–5234 premium zone, or waiting for a deeper pullback into 4600 liquidity before reassessing?
— Liam