BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5% DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Resistance Breakout in LUMAXIND
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
Trend Analysis
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5% DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Trendline Breakout in MOTHERSON
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
How to Handle Loss in Trading?Handling loss in trading can be a difficult and emotional experience, but it’s an inevitable part of the process. Here are some strategies that you can use to manage losses:
1. Accept that losses are a normal part of trading:
One of the most important things to do is to accept that losses are an inevitable part of trading. No trader is immune to losses, and they are a necessary component of making profits in the long run.
2. Set a stop-loss:
A stop-loss is an order placed with your broker to automatically sell a security when it reaches a certain price. By setting a stop-loss, you can limit your losses and prevent them from escalating beyond your predetermined threshold.
3. Analyze your trades:
It’s important to analyze your trades to understand why you incurred a loss. Were there any errors in your analysis or execution? Did you follow your trading plan? Understanding why you lost money can help you avoid making the same mistakes in the future.
4. Adjust your risk management strategy:
Consider adjusting your risk management strategy. For example, you could reduce your position size or increase your stop-loss levels.
5. Take a break:
If you’re feeling overwhelmed or emotional after a loss, take a break. Step away from trading and focus on other activities that can help you clear your mind.
6. Learn from your losses:
Every loss is an opportunity to learn and improve your trading skills. Keep a trading journal and document your trades, including your thought process and the reasoning behind each trade. Reviewing your trades regularly can help you identify patterns and improve your decision-making skills.
7. Seek professional help:
If you’re struggling to handle losses or find yourself experiencing persistent losses, consider seeking professional help. A financial advisor or a trading coach can help you develop a better trading strategy and manage your emotions effectively.
8. Maintain a positive mindset:
It’s important to maintain a positive mindset and avoid getting discouraged by losses. Instead, focus on the long-term goals and keep a positive outlook. Remember that losses are a natural part of the trading process and can be valuable learning experiences.
9. Diversify your portfolio:
Diversifying your portfolio can help spread the risk and minimize the impact of losses on your overall investment. Consider investing in different asset classes, industries, or geographical regions to reduce your exposure to any single investment.
10. Avoid revenge trading:
Revenge trading is when you try to make up for your losses by immediately placing another trade. This can lead to emotional decision-making and further losses. Instead, take a break and analyse your trades before making any new decisions.
11. Follow a trading plan:
A trading plan is a set of rules that you follow when making trading decisions. Following a well-defined trading plan can help you make objective decisions and avoid impulsive actions that can lead to losses.
12. Practice risk management:
Practising good risk management is critical to managing losses. Always ensure that your trades have an acceptable risk-reward ratio, and never risk more than you can afford to lose.
13. Seek support from other traders:
Trading can be a lonely activity, and it’s important to connect with other traders who can provide support and guidance. Consider joining trading communities or forums where you can share your experiences and learn from others.
14. Avoid trading under emotional stress:
Emotional stress can cloud your judgment and lead to impulsive decisions that result in losses. If you’re under emotional stress, it’s best to take a break from trading until you’re in a better mental state.
15. Keep your losses in perspective:
It’s important to keep your losses in perspective and avoid dwelling on them. Remember that losses are a natural part of the trading process and that even the most successful traders experience them from time to time. Instead of focusing on your losses, focus on your overall trading strategy and long-term goals.
In summary,
handling losses in trading is about accepting them as a natural part of the process, learning from them, and taking steps to mitigate them in the future. By following these strategies, you can minimize the impact of losses on your trading portfolio and become a more successful trader over time.
Market Correlations & Intermarket Analysis1. Market Correlations: Definition and Importance
Market correlation refers to the statistical relationship between the price movements of two or more assets. Correlation is measured on a scale from -1 to +1:
+1 correlation: The assets move perfectly in the same direction. If one rises 1%, the other rises 1%.
-1 correlation: The assets move perfectly in opposite directions. If one rises 1%, the other falls 1%.
0 correlation: No discernible relationship exists; movements are independent.
Why correlations matter:
Risk Management: Portfolio diversification relies on understanding correlations. Assets with low or negative correlation can reduce overall portfolio volatility. For example, stocks and bonds often have low or negative correlations, helping stabilize returns during market turbulence.
Trading Strategies: Correlations help traders identify potential hedges or pairs trading opportunities. For example, if gold and silver are highly correlated, movements in one may predict the other.
Market Sentiment Insight: Correlations reveal the behavior of market participants. Strong correlations between equities and commodities may indicate risk-on or risk-off sentiment in the broader market.
2. Types of Market Correlations
Positive Correlation:
Examples include:
S&P 500 and Nasdaq: Broad stock indices often move together due to overall market trends.
Crude Oil and Energy Stocks: Rising oil prices generally boost energy sector equities.
Negative Correlation:
Examples include:
Stocks and Bonds: In periods of stock market decline, investors often seek safety in government bonds.
US Dollar and Gold: Gold often rises when the USD weakens, as it is priced in dollars globally.
Dynamic or Time-Varying Correlation:
Correlations are not static. They change over time due to macroeconomic events, policy shifts, or market cycles. For instance:
During financial crises, correlations between stocks tend to increase, a phenomenon known as “correlation breakdown” in diversification.
Cross-Asset Correlation:
Beyond traditional assets, correlations also exist across asset classes. For example:
The price of oil may influence the Canadian dollar because Canada is a major oil exporter.
Interest rate changes in the U.S. impact emerging market equities and currencies.
3. Intermarket Analysis: Concept
Intermarket analysis is the study of relationships between different financial markets to forecast trends and confirm signals. The approach was popularized by John J. Murphy, who emphasized that no market moves in isolation. Intermarket analysis identifies leading, lagging, and coincident relationships between asset classes.
Key principle: Asset classes often react to the same economic forces but in different ways. By analyzing these reactions, traders can anticipate movements and make informed decisions.
4. Key Intermarket Relationships
Stocks vs. Bonds
Bonds are traditionally considered safe-haven assets, while stocks represent growth.
Rising interest rates usually depress bond prices and may negatively impact stock valuations due to higher borrowing costs.
Conversely, falling rates can boost equities while raising bond prices.
Stocks vs. Commodities
Commodity prices, such as oil or metals, impact inflation and corporate profits.
Higher oil prices may benefit energy stocks but hurt sectors sensitive to input costs.
Precious metals like gold often act as hedges against equity market volatility.
Commodities vs. Currencies
Commodity-exporting nations’ currencies often move in sync with their key exports.
Example: Canadian dollar vs. crude oil, Australian dollar vs. iron ore and gold.
Traders monitor these relationships to anticipate currency fluctuations.
Stocks vs. Currencies
Strong domestic currency can negatively affect exports, impacting companies’ earnings.
Conversely, weak currency can boost exporters but may increase import costs.
Interest Rates vs. Stocks
Rising interest rates increase the cost of capital, generally slowing equity growth.
Declining rates often create a favorable environment for stocks.
Sentiment & Risk-On/Risk-Off Relationships
In risk-on environments, equities and commodities rise while safe-haven assets like bonds and gold may decline.
In risk-off periods, the opposite pattern occurs.
5. Using Correlations in Trading
Practical applications:
Hedging Portfolios
Traders hedge exposure by taking positions in negatively correlated assets. For instance, long equities may be hedged with long bonds or gold.
Pairs Trading
Traders exploit temporary divergences in highly correlated assets. For example, if crude oil and energy stocks usually move together but diverge, a trade may profit from the eventual reconvergence.
Leading and Lagging Indicators
Certain markets act as leading indicators. For instance:
Bond yields often lead stock market trends.
Crude oil price changes may precede moves in commodity currencies.
Confirmation and Divergence
Correlations can confirm trends. For example, a rising stock market accompanied by declining bond yields may confirm a strong growth environment.
Divergences often signal caution. For example, equities rise while bonds and gold also rise, possibly indicating market stress.
6. Measuring Correlations
Statistical Measures
Pearson correlation coefficient: Measures linear relationships.
Spearman’s rank correlation: Captures monotonic relationships.
Rolling correlations: Show how relationships change over time.
Visual Tools
Correlation matrices are widely used to quickly identify relationships between multiple assets.
Intermarket charts plot asset classes together for comparative analysis.
7. Limitations
Correlation is Not Causation
Just because two assets move together does not mean one causes the other to move.
Dynamic Nature
Correlations change during market stress, economic cycles, or geopolitical events, sometimes reversing.
Over-Reliance Risk
Traders relying solely on historical correlations may be blindsided by sudden structural changes in markets.
8. Modern Intermarket Trends
Globalization has increased cross-market linkages.
Algorithmic trading exploits subtle correlations in milliseconds.
ETFs and derivatives amplify correlations across markets.
Central bank policies now have a global ripple effect, linking currencies, equities, and commodities more closely than ever.
9. Conclusion
Market correlations and intermarket analysis are indispensable tools for understanding financial markets. They help investors manage risk, identify opportunities, and anticipate market movements by analyzing how assets influence each other. While correlations offer quantitative insights, intermarket analysis provides a broader perspective, considering macroeconomic forces, market sentiment, and asset class interactions. Successful traders and investors integrate both approaches to create resilient portfolios and informed strategies, recognizing that markets are interconnected webs rather than isolated instruments.
In essence, understanding intermarket relationships allows one to see the market’s hidden signals, predict trends, and manage risks more effectively, making it a cornerstone of professional trading and investment analysis.
Commodity Currencies (AUD, CAD, NZD)Commodity Currencies Overview
Commodity currencies are national currencies of countries that rely heavily on the export of natural resources or commodities. These currencies are sensitive to global commodity prices because their economies are closely tied to the demand and supply of commodities such as metals, energy products, and agricultural goods. Among the most prominent commodity currencies in the world are the Australian Dollar (AUD), Canadian Dollar (CAD), and New Zealand Dollar (NZD). Each of these currencies reflects the underlying economic health and export performance of their respective nations.
1. Australian Dollar (AUD)
Economic Background:
Australia is rich in natural resources, including iron ore, coal, natural gas, and gold. The Australian economy is heavily reliant on the export of these commodities, particularly to Asian markets like China, Japan, and South Korea. Roughly 60–70% of Australia’s total exports are commodities, making the AUD highly sensitive to global commodity prices.
Relationship with Commodity Prices:
Iron Ore: Australia is the world’s largest exporter of iron ore, and changes in iron ore prices strongly affect the AUD. Rising demand from industrial powerhouses like China often strengthens the AUD.
Coal and Natural Gas: Australia is a leading exporter of thermal and metallurgical coal, as well as liquefied natural gas (LNG). Increases in global energy prices often lead to appreciation of the AUD.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates:
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) plays a critical role in influencing AUD value. Historically, the AUD has been considered a “high-yielding” currency because Australia has often maintained interest rates above other developed nations. Traders often engage in carry trades using the AUD, borrowing in low-interest currencies like JPY to invest in AUD for higher returns.
Trading Characteristics:
The AUD is highly liquid and traded against major currencies such as USD (AUD/USD), JPY (AUD/JPY), and EUR (AUD/EUR).
It is often considered a risk-on currency, meaning it appreciates when global risk sentiment is positive and depreciates in risk-off scenarios.
Market Influences:
Global Growth: Strong global economic activity increases demand for Australian exports, supporting AUD.
China’s Economy: Since China is Australia’s largest trading partner, Chinese GDP growth, industrial production, and infrastructure spending heavily influence AUD movements.
Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in iron ore, coal, and gold prices can trigger significant AUD volatility.
2. Canadian Dollar (CAD)
Economic Background:
Canada’s economy is resource-rich, with significant production of crude oil, natural gas, lumber, and metals. Oil exports, in particular, dominate Canada’s trade, making the CAD closely correlated with crude oil prices. Canada is one of the top global producers of crude oil, mainly from Alberta’s oil sands.
Relationship with Commodity Prices:
Oil: Approximately 40% of Canada’s total exports are energy products. The CAD is often referred to as a “petro-currency” because oil price movements have a direct effect on its value. Rising oil prices strengthen the CAD, while falling prices weaken it.
Natural Resources: Lumber, natural gas, and metals also contribute to CAD volatility, though oil remains the dominant factor.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates:
The Bank of Canada (BoC) manages the nation’s monetary policy, influencing CAD through interest rate decisions. Similar to the AUD, the CAD has historically offered relatively higher interest rates compared to some developed economies, making it attractive for carry trades.
Trading Characteristics:
The CAD is highly liquid and traded against the USD (USD/CAD), EUR, and JPY.
USD/CAD is particularly sensitive to both oil price fluctuations and U.S. economic performance, as the U.S. is Canada’s largest trading partner.
CAD also responds to global risk sentiment but less strongly than the AUD, given its more defensive economic ties to energy markets.
Market Influences:
Oil Prices: A surge in crude oil prices tends to boost the CAD, as higher energy revenues improve Canada’s trade balance.
Global Risk Appetite: Risk-on environments moderately strengthen CAD, while risk-off events may weaken it.
U.S. Economy: Given the close trade relationship, strong U.S. growth can positively affect CAD.
3. New Zealand Dollar (NZD)
Economic Background:
New Zealand’s economy is smaller than Australia’s and Canada’s but highly dependent on commodity exports. Agricultural products—such as dairy, meat, wool, and fruit—form the backbone of its export sector. Approximately 50–60% of New Zealand’s exports are commodities, making the NZD sensitive to global agricultural demand.
Relationship with Commodity Prices:
Dairy Prices: Dairy products are the largest export category, especially to Asian markets. Global milk and dairy prices influence NZD significantly.
Meat and Forestry Products: Meat and wood product exports also impact the currency, though to a lesser degree than dairy.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rates:
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) regulates interest rates, which historically have been relatively high compared to other developed nations. This has made the NZD a preferred currency for carry trades.
Trading Characteristics:
The NZD is traded primarily against the USD (NZD/USD), AUD (NZD/AUD), and JPY (NZD/JPY).
It behaves as a risk-on currency, often moving in tandem with global investor sentiment.
The NZD has high volatility relative to other major currencies, reflecting its dependence on agricultural commodity markets.
Market Influences:
Global Dairy Demand: Changes in Chinese and Asian demand for dairy exports strongly influence the NZD.
Commodity Prices: Milk, meat, and forestry prices can drive short-term NZD fluctuations.
Risk Sentiment: Like the AUD, NZD tends to appreciate during periods of global economic optimism.
Shared Characteristics of Commodity Currencies
Commodity Correlation:
All three currencies are closely linked to global commodity markets. AUD is linked to metals and energy, CAD to crude oil, and NZD to agricultural products.
Risk Sensitivity:
They are considered risk-on currencies, appreciating when global markets are bullish and depreciating during risk-off periods.
Interest Rate Differentials:
These currencies often offer higher interest rates relative to low-yielding currencies such as JPY or CHF, making them attractive in carry trades.
Export Dependency:
Their economies are export-driven, and changes in demand from major trading partners directly affect currency value.
Volatility:
Commodity currencies exhibit higher volatility than non-commodity currencies because commodity prices themselves are highly volatile, influenced by global supply-demand shifts, geopolitical events, and economic cycles.
Trading Strategies for Commodity Currencies
Commodity-Based Trading:
Traders often correlate currency movements with relevant commodity prices. For instance, rising oil prices could signal CAD strength.
Risk Sentiment Trading:
Since AUD and NZD are risk-on currencies, traders monitor global market risk appetite to anticipate currency moves.
Interest Rate and Carry Trades:
These currencies are favored in carry trades where investors borrow low-yielding currencies like JPY to invest in higher-yielding currencies such as AUD or NZD.
Fundamental Analysis:
Monitoring trade balances, GDP growth, and economic data releases from Australia, Canada, and New Zealand is essential for predicting currency strength.
Technical Analysis:
Due to their volatility, technical indicators like moving averages, support/resistance levels, and trend analysis are widely used in short- and medium-term trading.
Conclusion
The AUD, CAD, and NZD are quintessential examples of commodity currencies, with their values intrinsically tied to the performance of key export commodities and global economic trends. While the AUD and NZD are sensitive to metals, energy, and agricultural products and exhibit risk-on behavior, the CAD is strongly influenced by crude oil prices and trade relations with the U.S.
Investors and traders closely monitor commodity price movements, global economic growth, and central bank policies when trading these currencies. Their higher interest rates and sensitivity to risk sentiment make them attractive in both fundamental and technical trading strategies, but also inherently more volatile than non-commodity currencies like the USD or EUR.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to trade, hedge, or invest in commodity currencies, as their fortunes rise and fall with the ebb and flow of global commodities and investor sentiment.
FOREX "PAIRS IN PLAY" Session 30 11 02 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
40% gains in 2-3 yrs - Eicher Motors - Long Term Compounder40% returns in next 2-3 years - Eicher Motors - Long Term Compounder
Fundamental Outlook
Almost debt free D/E ratio is 0.02, High ICR (110)
PE of 31.53, IND PE is 45.12, 0.7X of INdustry PE, expensive stock
PEG of 1.51, reasonable
ROE = 26.24%
ROCE = 32.43% , ROCE 5yrs = 25.16%
Sales growth = 14.12%, Sales Growth 5 yrs =15.57%
Profit growth = 18.3%, Profit Growth 5 yrs = 20.95%
Promoter holding at 49.08%, marginally reducing every quarter
Cumulative FII/DII holding making up for promoter dilution
Very less public holding, continually decresing, signalling strong hand holding
Technical Outlook
CMP : 5446
On Monthly charts ,
Stock has clearly followed a parallel channel since 2019
On Weekly charts ,
Stock is bullish, CMP is above all periodic EMAs
On daily charts
Relative strength and momentum on 20 day time period is lagging. Stock has not moved much in recent days
RS = 97, relatively weak strength compared to Nifty 500
Momentum = 99, relatively weak momentum compared to NIfty 500
RSI = 50 , neither oversold nor overbought , reasonable
Chart Patterns
On Monthly charts ,
Stock has clearly followed a parallel channel since 2019
Industry Outlook
Sector/Industry - Automobiles/2-3 Wheelers
Nifty auto is a leading index compared to other sectoral indices in the past 20 days.
Nifty Auto has formed a W pattern/double bottom in the recent past and is recovering appreciably.
Continuing momentum should take the Index past recovery to bullish phase
Latest Q4 Results
Mar 2025
NSE:EICHERMOT
QOQ
👉Revenue rose 5.39% to 5241
👉EBITDA rose 4.75% to 1258
👉EBITDA Margin drops -0.15% BPS to 24.00%
👉Net Profit rose 16.41% to 1362
👉EPS rose 16.35% to 49.68
YOY
👉Revenue rose 23.14% from 4256
👉EBITDA rose 11.52% from 1128
👉EBITDA Margin drops -2.50% BPS from 26.50%
👉Net Profit rose 27.29% from 1070
👉EPS rose 27.06% from 39.1
Fundamentals
👉Stock Price is 5446.5 as of 5/14/2025
👉Stock PE is 31.53
👉Stock EPS is 172.73
👉Dividend announced of Rs.70 per share
Growth
👉2 year Revenue CAGR is 14.31%
👉2 year Profit CAGR is 27.42%
👉2 year EPS CAGR is 27.32%
👉2 year Price CAGR is 35.90%
Disclosure 1 - Invested
Disclosure 2 - Not SEBI Registered
Disclosure 3 - This is Not investment advice. Treat it as educational
Growth vs. Value Investing Cycles1. Defining Growth and Value Investing
Growth investing focuses on companies that exhibit strong potential for future earnings growth. These companies often reinvest profits to fuel expansion rather than paying dividends. Investors in growth stocks pay a premium for anticipated high growth, accepting higher valuation ratios such as Price-to-Earnings (P/E) or Price-to-Book (P/B) multiples.
Key characteristics of growth investing:
High earnings growth rate.
Dominant or disruptive industry position.
Often innovative, technology-driven, or new market leaders.
Typically lower or no dividends, reinvesting profits into expansion.
Value investing, in contrast, targets companies whose stock prices are considered undervalued relative to fundamentals. These companies may have slower growth prospects but often trade at a discount due to market overreactions, temporary setbacks, or low investor sentiment. Value investors rely on metrics like P/E ratio, P/B ratio, and dividend yield to identify undervalued opportunities.
Key characteristics of value investing:
Stocks trading below intrinsic value.
Stable, mature companies with predictable earnings.
Often offers dividends.
Typically operates in traditional sectors such as industrials, energy, or consumer staples.
2. The Nature of Investing Cycles
Investment styles, including growth and value, tend to perform in cycles influenced by:
Economic Growth and Recessions:
During periods of strong economic expansion, growth stocks often outperform. Investors are willing to pay high premiums for companies expected to capitalize on increased consumer demand, technological advancement, or market expansion.
Conversely, during economic slowdowns or recessions, value stocks generally perform better. These companies are often financially stable, generate steady cash flow, and provide dividends, appealing to risk-averse investors.
Interest Rate Movements:
Low-interest-rate environments favor growth stocks, as cheaper borrowing costs allow companies to expand aggressively. Investors are more inclined to pay high valuations for future earnings.
High-interest-rate environments penalize growth stocks because future earnings are discounted more heavily. Value stocks, which often rely on tangible assets and stable cash flows, tend to be more resilient in such periods.
Market Sentiment and Risk Appetite:
Bull markets with high investor confidence favor growth investing, as optimism about future prospects drives higher valuations.
Bear markets, uncertainty, or risk aversion shift preferences toward value stocks, as investors seek safer, undervalued assets with downside protection.
3. Historical Growth and Value Cycles
Historically, growth and value investing have alternated in dominance:
1990s – Growth Outperformance:
The late 1990s, marked by the dot-com boom, exemplify a prolonged growth cycle. Technology and internet stocks soared despite weak earnings, driven by investor optimism and disruptive innovation. Value investing lagged, as traditional sectors were less exciting to the market.
Early 2000s – Value Recovery:
Following the dot-com crash (2000–2002), growth stocks plummeted due to overvaluation and lack of profitability. Value stocks, characterized by tangible earnings and dividends, outperformed as markets rotated toward safety and fundamentals.
Mid-2000s – Growth Rebound:
Economic expansion fueled a brief resurgence in growth stocks, particularly in sectors like technology, consumer discretionary, and emerging markets.
2008 Financial Crisis – Value Resilience:
During the 2008 crisis, growth stocks suffered heavily due to uncertainty and high valuations. Value stocks with strong balance sheets and predictable cash flows outperformed as investors sought safety.
Post-2009 – Extended Growth Cycle:
After quantitative easing and low-interest rates post-2009, growth stocks enjoyed an unprecedented bull run, especially in technology and innovation-driven sectors. FAANG stocks (Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, Google) became emblematic of this era. Value lagged, particularly in traditional industries.
2022–2023 – Value Resurgence:
Rising inflation, higher interest rates, and global uncertainty shifted markets toward value stocks. Traditional sectors like energy, banking, and commodities outperformed high-growth technology stocks, demonstrating the cyclical nature of style investing.
4. Drivers of Growth vs. Value Cycles
The cycles are influenced by multiple interconnected factors:
Macroeconomic Conditions:
Growth thrives in low-rate, expanding economies.
Value prevails in high-rate, slowing, or uncertain economic environments.
Investor Psychology:
Herd mentality amplifies trends. In bullish periods, growth stocks may become overvalued, while in pessimistic periods, value stocks become oversold and attract attention.
Sector Dynamics:
Certain sectors naturally align with styles. Technology, biotech, and consumer discretionary often lead growth cycles. Industrials, utilities, energy, and financials frequently anchor value cycles.
Government Policies:
Fiscal stimulus, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks can favor growth or value sectors. For instance, tech-friendly policies boost growth stock performance, while energy subsidies or infrastructure spending favor value sectors.
5. Investing Strategy Implications
Understanding these cycles helps investors:
Portfolio Rotation:
Savvy investors may rotate allocations between growth and value depending on economic, interest rate, and sentiment signals. This requires timing insights but can enhance returns.
Diversification:
Maintaining a blend of growth and value investments reduces exposure to extreme swings. During prolonged growth cycles, value cushions downside risk; during value cycles, growth stocks provide upside potential.
Valuation Awareness:
Paying attention to valuation extremes helps anticipate style rotations. Historically, when growth valuations become stretched, value stocks often outperform subsequently.
Long-Term Perspective:
Cycles demonstrate that no style dominates permanently. Investors benefit from patience, understanding that both styles can thrive in different market phases.
6. Key Takeaways on Growth vs. Value Cycles
Growth and value investing alternate in performance due to economic conditions, interest rates, market sentiment, and investor psychology.
Growth stocks perform best during low-interest rates, economic expansion, and high risk appetite periods.
Value stocks shine during high-interest rates, economic slowdowns, or market uncertainty.
Historical cycles, from the 1990s dot-com boom to post-2009 tech dominance and the 2022 value resurgence, illustrate this alternating pattern.
Investors can leverage cycles by portfolio rotation, maintaining diversified allocations, and monitoring valuations.
Recognizing cycles reduces emotional decision-making, enabling disciplined long-term investing.
Both styles offer complementary advantages: growth for capital appreciation, value for downside protection and income.
Conclusion
Growth vs. value investing cycles are a natural and predictable part of market behavior. Neither style is universally superior; each excels under specific macroeconomic and market conditions. Successful investors understand these cycles, position their portfolios accordingly, and maintain a balance between chasing high growth and protecting capital through value investments. Ultimately, recognizing and responding to these cycles can enhance returns, reduce risk, and provide a strategic advantage in navigating the complex world of equity markets.
$ZRO Dropped 84% But What's Coming Next Could Shock Everyone CSE:ZRO Dropped 84% But What's Coming Next Could Shock Everyone 🚀
#ZRO Has Corrected ~84% Inside A Multi-Month Descending Channel Since 2024, Now Testing The HTF Breakout Level.
Price Is Compressing At Channel Resistance With Strong Accumulation Around $1.50–$1.20 👇
✅ Strong HTF Demand: $1.50–$1.20
✅ Breakout Trigger: HTF Close Above Channel $2.50
✅ Structure Turns Bullish On Acceptance Above $2.50
✅ Possible Retracement Before Next Expansion Leg
✅ $1.80 = Good Entry Level 1 If Price Pulls Back
✅ $1.50–$1.20 = Major Accumulation Zone (Best Long-Term Entry)
⚠️ Close Below $1.20 = HTF Structure Weakens
Upside Targets If Breakout Confirms: $6.83 ➔ $13.00 ➔ $25.00 (Full Measured Move ~1,500%+)
Why I’m Bullish Long Term On CSE:ZRO 👇
→ Tether Made A Strategic Investment In LayerZero Labs
→ USDT0 Has Processed $70B+ In Cross-Chain Volume
→ Backed By Citadel, Ark Invest, Google Cloud & DTCC
→ Infrastructure Layer For Cross-Chain Finance + AI Economy
→ Price Already Reacted +35% On Institutional News
HTF Compression + Real Adoption + Institutional Backing = Asymmetric Setup.
Pure TA + Narrative Confluence | Not Financial Advice | Always Do Your Own Research
What's Your Target For CSE:ZRO ? Let Me Know 👇
Like + Share if You Found This Useful!
Elliott Wave Analysis XAUUSD – February 11, 2026
Momentum
– D1 momentum is currently preparing for a bearish reversal. This suggests the current bullish move may be nearing completion. We need to wait for a confirmed D1 reversal signal before validating this scenario.
– H4 momentum is still rising. In the short term, H4 may continue to move higher or trade sideways in order to push momentum into the overbought zone.
– H1 momentum is compressing in the overbought region. This indicates the upward move can still extend, but it also carries the risk of an upcoming bearish reversal on H1.
Wave Structure
D1 Structure
On the daily timeframe, the current structure appears to be an ABC corrective pattern.
Wave B may be close to completion as D1 momentum is signaling a potential bearish reversal.
H4 Structure
Within the black Wave B, we observe a red ABC structure.
Price is currently trading sideways at the resistance level — the Wave A high around 5101 — which may represent absorption of early selling pressure.
However, since H4 momentum has turned bullish, there is a warning of a potential continuation to the upside. If that happens, H1 target zones must be monitored carefully.
H1 Structure
Price is compressing within the 4969 – 5095 range, reflecting strong conflict between buyers and sellers in this zone.
Therefore, we should remain patient and wait for a clear breakout beyond this range before looking for trade setups.
Confirmation Conditions
– As long as H4 momentum remains bullish, we will not look for sell positions until H4 reaches the overbought region.
– If price breaks below 4969, it would likely confirm that the red Wave C has completed.
– If price breaks above 5095, the red Wave C may still be extending upward. In that case, two upside targets are:
– 5136
– 5345
These will be our preferred areas to look for sell opportunities.
Trading Plan
Scenario 1: Break below 4969
– Execute a real-time sell breakout trade.
Scenario 2: Break above 5095
Sell Zone 1
– Entry: 5136 – 5138
– Stop Loss: 5176
– TP1: 4969
– TP2: 4827
– TP3: 4640
Sell Zone 2
– Entry: 5344 – 5346
– Stop Loss: 5384
– TP1: 5095
– TP2: 4969
– TP3: 4640
In summary, we are at a sensitive stage where D1 is preparing for a reversal while H4 remains bullish. Patience is essential. We wait for a decisive breakout of key levels to confirm direction and avoid entering prematurely before the structure is fully developed.
#TELSA 1hr wave analysis.🚀 What’s Next in Tesla?
After completing a powerful 5-wave impulsive structure on the 1-hour chart (from $222 on April 22, 2025 to $499 on December 22, 2025), Tesla wrapped up a remarkable 10-month bull cycle. 📈🔥
Now, the stock has entered its corrective phase:
• 🅰️ The A wave finished on Feb 5, 2026 at $388, retracing ~38.2% of the prior impulsive move.
• 🔄 Since the A wave unfolded in 3 waves, the correction is shaping into a flat pattern.
👉 This means the B wave is likely to retrace at least 61.8%, projecting Tesla’s price to rebound above $460 in the coming days. ⚡💹
Following this, the C wave will continue the corrective journey.
---
📊 Technical takeaway: Tesla’s chart is setting up for a short-term bounce before resuming its correction. Traders should stay alert for opportunities in this B wave rally. 🚀📉📈
After completing a powerful 5-wave impulsive structure on the 1-hour chart (from $222 on April 22, 2025 to $499 on December 22, 2025), Tesla wrapped up a remarkable 10-month bull cycle. 📈🔥
Now, the stock has entered its corrective phase:
• 🅰️ The A wave finished on Feb 5, 2026 at $388, retracing ~38.2% of the prior impulsive move.
• 🔄 Since the A wave unfolded in 3 waves, the correction is shaping into a flat pattern.
👉 This means the B wave is likely to retrace at least 61.8%, projecting Tesla’s price to rebound above $460 in the coming days. ⚡💹
Following this, the C wave will continue the corrective journey.
---
📊 Technical takeaway: Tesla’s chart is setting up for a short-term bounce before resuming its correction. Traders should stay alert for opportunities in this B wave rally. 🚀📉📈
GIFTNIFTY Intra-Swing Level Analysis for 11th FEB 2026GIFTNIFTY Intra-Swing Level Analysis for 11th FEB 2026
PCR Data Analysis as of Now:
Weekly Basis (17/02/2026) EXP=>
Put OI: 16,14,158, : all OI, 19,17,544: PCR: 0.84, Trend Strength: Neutral
Intraday Basis=>
Put OI Chg: 5,89,749, Call OI Chg: 9,21,771, COI PCR: 0.64. Trend Strength: BEARISH
Special NOTE: Now @ 25997, Nearing Reversal / Pullback @ 25960- 25975
━━━━━━━━━₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹━━━━━━━━
💥Level Interpretation / description:
L#1: If the candle crossed & stays above the “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Bullish bias.
L#2: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLB#1 & UBTgt
L#3: If the candle stays above “Sell Gen” but below “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Sidewise. Aggressive Traders can take Long position near “Sell Gen” either retesting or crossed from Below & vice-versa i.e. can take Short position near “Buy Gen” either retesting or crossed downward from Above.
L#4: If the candle crossed & stays below the “Sell Gen”, it is treated / considered a Bearish bias.
L#5: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLS#1 & USTgt
HZB (Buy side) & HZS (Sell side) => Hurdle Zone,
*** Specialty of “HZB#1, HZB#2 HZS#1 & HZS#2” is Sidewise (behaviour in Nature)
Rest Plotted and Mentioned on Chart
Color code Used:
Green =. Positive bias.
Red =. Negative bias.
RED in Between Green means Trend Finder / Momentum Change
/ CYCLE Change and Vice Versa.
Notice One thing: HOW LEVELS are Working.
Use any Momentum Indicator / Oscillator or as you "USED to" to Take entry.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⚠️ DISCLAIMER:
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments. I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
"As HARD EARNED MONEY IS YOUR's, So DECISION SHOULD HAVE TO BE YOUR's".
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
❇️ Follow notification about periodical View
💥 Do Comment for Stock WEEKLY Level Analysis.🚀
📊 Do you agree with this view?
✈️ HIT THE PLANE ICON if this technical observation resonates with you. It will Motivate me.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💡 If You LOOKING any CHART & want for Level and ANALYZE?
Share your desired stock names in the comments below! I will try to analyze the chart Levels, patterns and share my technical view (so far my Knowledge).
If Viewers think It can identify meaningful setups. Looking forward to hearing from all of you — let's keep this discussion going and help each other make better trading decisions.
M&M is looking good for 21% upside in next 5-6 MonthsM&M is looking good for 21% upside in next 5-6 Months
LTP - 3528
SL - 3280
Targets - 4300+
timeframe - 5-6 Months
Fundamentals:
Mahindra & Mahindra operates diverse businesses including Auto, Farm, Financial Services. It holds market leadership in SUVs and LCVs, is the #1 tractor manufacturer, and #1 in EV Re.
Company has delivered good profit growth of 113% CAGR over last 5 years.
Happy investing.
INFOBEAN : Mid-Base VCP Breakout SetupTook an aggressive mid-base entry on INFOBEAN based on a clean VCP formation on the 1H timeframe.
Price showed three clear rejections from the supply zone, tightening volatility each time — classic contraction behaviour. Eventually, we got a decisive breakout above supply with strong volume expansion, confirming demand stepping in.
There’s a major supply zone overhead, so the plan is simple:
➡️ Expecting a run-up into that area
➡️ Move SL to breakeven once price approaches
➡️ Let the market decide the rest
Since I’m currently testing aggressive entries, risk is kept small at 0.1% of net capital.
Fundamentals add confidence:
• EPS and Sales trending up QoQ
• Minor EPS dip in Dec quarter, nothing structurally concerning
Low risk + technical strength + improving fundamentals = favorable asymmetric bet.
Let’s see if momentum follows through. 🚀
📢📢📢
If my perspective changes or if I gather additional fundamental data that influences my views, I will provide updates accordingly.
Thank you for following along with this journey, and I remain committed to sharing insights and updates as my trading strategy evolves. As always, please feel free to reach out with any questions or comments.
Other posts related to this particular position and scrip, if any, will be attached underneath. Do check those out too.
Disclaimer : The analysis shared here is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. Trading in all markets carries inherent risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. It’s essential to conduct your own research and assess your risk tolerance before making any investment decisions. The views expressed in this analysis are solely mine. It’s important to note that I am not a SEBI registered analyst, so the analysis provided does not constitute formal investment advice under SEBI regulations.
NIFTY KEY LEVELS FOR 11.02.2026NIFTY KEY LEVELS FOR 11.02.2026
Timeframe: 3 Minutes
Sorry for the delayed post..
If the candle stays above the pivot point, it is considered a bullish bias; if it remains below, it indicates a bearish bias. Price may reverse near Resistance 1 or Support 1. If it moves further, the next potential reversal zone is near Resistance 2 or Support 2. If these levels are also broken, we can expect the trend.
When a support or resistance level is broken, it often reverses its role; a broken resistance becomes the new support, and a broken support becomes the new resistance.
If the range(R2-S2) is narrow, the market may become volatile or trend strongly. If the range is wide, the market is more likely to remain sideways
please like and share my idea if you find it helpful
📢 Disclaimer
I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments.
Please consult with your SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any trading or investment decisions.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
Nifty50 analysis(11/2/2026).CPR: narrow + ascending cpr: trending
FII: 69.45 bought
DII: 1,174.21 bought
Highest OI: too soon to tell
CALL OI: 26000
PUT OI: 26000
Resistance: - 26000
Support : - 25950
conclusion:.
My pov
1.market is in buy on dip mode any fall or support can rise the market to 26000 to atm.
2. Yesterday forms a virgin cpr so today highly possible to touch cpr and rise . 25930 also today narrow cpr.
3. If it breaks 26000 then all time high is the target. Only if it close in day candle.
4. Fii and dii continusly buying this show the bullishness in market. Clearly market in trend and a trend rise from a sharp fall. Expect the anything can happen.
What IF:
1.market can fall upto 25900 there one hour candle 50ma support that gives a good support.
2. If market breaks 26000 then all time high is the resistance.
Psycology:
Make a trade with high possibilities. Dont hope one factor make multiple factor on your side.
note:
8moving average ling is blue colour.
20moving average line is green colour
50moving average line is red colour.
200moving average line is black colour.
cpr is for trend analysis.
MA line is for support and resistance.
Disclaimer:
Iam not Sebi registered so i started this as a hobby, please do your own analysis, any profit/loss you gained is not my concern. I can be wrong please do not take it seriously thank you
NIFTY 50 INTRADAY LEVELS📊 Current Structure
Spot: 25,935
Pivot: 25,856
R1: 25,932 (already cross)
R2: 25,998
R3: 26,074
PCR 1.11 → Slight bullish bias
Max Pain 25,900 → Market magnet zone
🧠 Honest View
Abhi market weak nahi lag raha.
Structure mildly bullish hai jab tak 25,900 ke niche nahi jaata.
26000 CE = breakout trade
25,950–26,000 zone decide karega game.
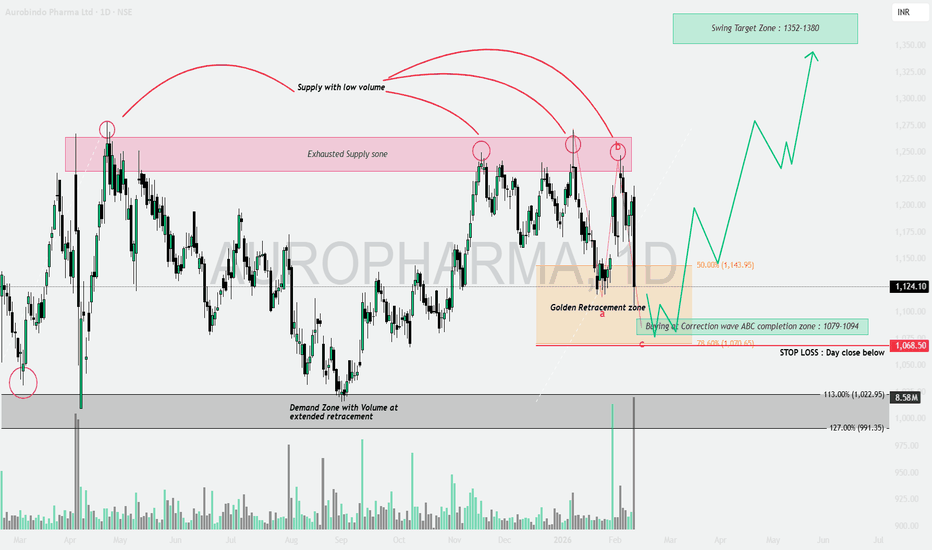
AUROPHARMA: Supply Exhaustion & The Golden Retracement📝 The Technical Breakdown (Educational Guide)
This chart is a masterclass in understanding Volume Price Analysis + Fibonacci Confluence. Let’s decode the setup through 4 key educational pillars:
1️⃣ Supply Exhaustion Zone 🔴
Observe the pink box marked as “Exhausted Supply Zone.”
Price has tested this resistance multiple times.
Notice the circled peaks — supply is appearing on declining volume.
➡️ When price hits resistance but volume keeps dropping, it signals that sellers are losing strength.
➡️ In simple terms, the supply “wall” becomes thinner after every test — increasing breakout probability over time.
2️⃣ ABC Correction Completion 📉
The structure shows a classic three-wave corrective pattern (A-B-C).
• Wave C is currently retracing into the ABC Completion Buying Zone (1,079 – 1,094).
• This phase is often called the final shakeout.
💡 Weak hands exit in panic while institutional Smart Money quietly accumulates positions at discounted prices.
3️⃣ Golden Retracement Confluence 🎯
Price is now entering the Golden Fibonacci Retracement Zone, positioned between:
• 50.0% level — 1,143.95
• 78.60% level — 1,070.65
📌 Historically, high-probability reversals occur when an ABC correction terminates inside this Fibonacci cluster — creating strong confluence support.
4️⃣ Volume-Backed Demand 🛡️
Now focus on the grey demand box below.
This marks a high-volume historical accumulation zone at extended retracement levels.
If the current support fails, the next major demand lies between:
➡️ 991 – 1,022 (113% – 127% Fibonacci extension)
This zone acts as a secondary safety net for positional and swing traders.
📊 Strategic Trade Setup
• Current Price: 1,124.10
• Accumulation Zone: 1,079 – 1,094
• Stop Loss: Daily candle close below 1,068.50 🛑
• Swing Target Zone: 1,352 – 1,380 🚀
📌 Summary
Price is approaching a high-confluence buying region backed by:
✔️ Supply exhaustion at resistance
✔️ ABC correction completion
✔️ Golden Fibonacci retracement
✔️ Historical volume demand support
Any bullish confirmation from this zone can trigger a strong swing reversal toward higher targets.
Market Outlook & Trade Setup – Wednesday, 11th Feb 2026🔹 NIFTY: Gift Nifty (26,077)
* Previous Close: 25,935
* Expected Range: 25,900 - 26,000
🔹 SENSEX
* Previous Close: 84,273
* Expected Range: 84,000 - 84,500
🌍 Global & Market Sentiment
* DJIA: +52 | S&P: -23
💰 Institutional Activity (Cash Market)
* FII: Net Buyers: + ₹ 69Cr
* DII: Net Buyers: + ₹ 1174 Cr
🔥 Events this Week:
India - US Crude & CPI data, UK GDP
📌 Sectoral Focus (Positive)
Media, Auto
👉 Commodities in Focus: Gold, Silver, Copper
✌️Important Quarterly Results: Capacite, Divis, Lenskart
📈 Trade smart. Manage risk. Stay disciplined.