NIFTY 50 – Weekly Outlook (Key Levels & Structure)
NIFTY has decisively broken below the rising trendline that was supporting the index for the past few months. This trendline had multiple confirmations, and the breakdown signals a shift from bullish to corrective / sideways-to-bearish structure in the near term.
The index is currently testing a crucial horizontal support zone around 25,000–25,050. This level will be very important for next week’s price action.
⸻
Key Levels to Watch
Support Zones:
• 25,000 – 25,050 → Immediate and psychological support
• 24,600 – 24,650 → Major demand zone (next downside support)
• 24,350 – 24,400 → Strong long-term support if selling accelerates
Resistance Zones:
• 25,350 – 25,450 → Minor pullback resistance
• 25,750 – 25,850 → Breakdown retest zone
• 26,200 – 26,350 → Strong supply / rejection zone
⸻
Market Structure View
• As long as price remains below the broken trendline, rallies may face selling pressure.
• A sustained hold above 25,450 can lead to short-term relief bounce.
• Break and hold below 25,000 may open gates for 24,600 levels in coming sessions.
• Expect volatile moves, especially around weekly expiry and global cues.
⸻
Trading Approach
• Prefer wait & watch near support levels
• Avoid aggressive trades in the middle of the range
• Let price confirm direction before taking positional bias
⸻
Disclaimer
I am not a SEBI registered analyst/advisor.
This analysis is only for educational and informational purposes.
This is NOT a buy or sell recommendation.
Trading in the stock market involves risk. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trade.
I am not responsible for any profit or loss arising from this analysis.
Trend Analysis
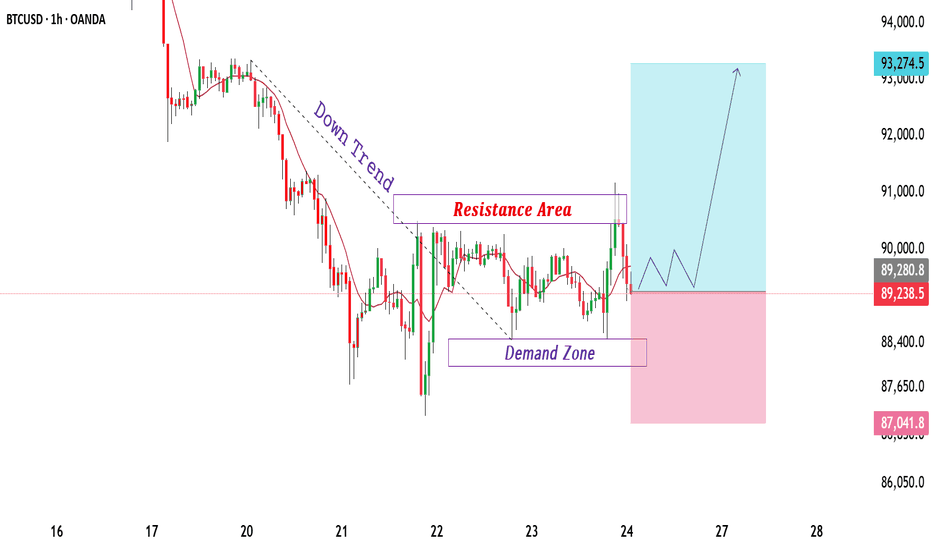
BTCUSD Trades Between Demand and Resistance Bearish Structure.BTCUSD is currently trading within a corrective structure after a strong bearish move, clearly respecting a descending trend. Price action shows lower highs and lower lows, confirming short-term bearish control. The marked resistance area near 90,800–91,200 has acted as a selling zone where price previously reacted and faced rejection, keeping upside pressure limited. This area remains a key resistance and may continue to attract selling interest on retests.
On the downside, a well-defined demand zone is visible around 88,000–88,600. This zone aligns with previous strong buyer reactions and short-term base formation, making it an important support area. Price has already shown multiple reactions from this demand, indicating active buying interest. As long as price holds above this zone, a temporary recovery or consolidation remains possible.
Current price action suggests range behaviour between demand and resistance, showing signs of accumulation near support. If demand continues to hold, price may attempt a gradual move back toward resistance. However, a sustained break below the demand zone would strengthen bearish momentum and open the path toward lower support areas. Overall structure remains cautious, with bearish bias dominant while price stays below resistance, and volatility expected around the marked zones.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Trading involves risk and uncertainty.
Triangle Contraction Symphony: Hidden Supports, Inverted H&SWitness the mesmerizing dance of price action in this chart masterpiece. A pristine triangle contraction pattern emerges, bounded by a supportive yellow trendline below and a red counter-trendline above, perfectly channeling price within tightening bounds.
Layered hidden dotted support/resistance lines add depth, illustrating how price meticulously respects each level—time and again.
Culminating in a textbook inverted head and shoulders formation, this setup showcases contraction elegance at its finest.
Purely educational: Reliving how these levels held in the past. No directional bias here—just the raw beauty of price action precision.
Disclaimer: This post is for educational purposes only, demonstrating historical price action behavior and level interactions. No directional bias or trading recommendations are implied. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Trade at your own risk.
Sula Vineyards Ltd (SULA) - Analysis Bullish Levels -Above 208 then 246 to 258 above this bullish then around 292 will be the first target if sustains above this more bullish 439/509 and final target can be around 732 to 770
Bearish levels :- if sustain below 193/181 below this bearish 173/161 then last hope 148 to 137
**Consider some Points buffer in above levels
**Disclaimer -
I am not a SEBI registered analyst or advisor. I does not represent or endorse the accuracy or reliability of any information, conversation, or content. Stock trading is inherently risky and the users agree to assume complete and full responsibility for the outcomes of all trading decisions that they make, including but not limited to loss of capital. None of these communications should be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities, nor advice to do so. The users understands and acknowledges that there is a very high risk involved in trading securities. By using this information, the user agrees that use of this information is entirely at their own risk.
Thank you.
Part 1 Institutional vs. Technical Key Option Terminologies
1. Strike Price
The agreed price at which the asset can be bought or sold.
2. Expiry Date
The last date on which the option contract is valid.
3. Premium
The price paid by the option buyer to the seller.
4. Lot Size
The fixed quantity of underlying assets per option contract.
5. Open Interest (OI)
Total number of outstanding option contracts.
Kitex (W): Aggressive Bullish, Political Catalyst + Tech Rev(Timeframe: Weekly | Scale: Logarithmic)
The stock has staged a V-Shape Reversal from a fresh 52-week low, forming a textbook Bullish Hammer on the weekly chart. This technical move is powered by a major political development (joining NDA), which removes significant "Political Risk" from the stock valuation.
🚀 1. The Fundamental Catalyst (The "Why")
The technical bounce is driven by a sentiment shift:
> Political Alignment (NDA Entry): The market expects that joining the ruling alliance will fast-track the company’s massive expansion plans in Telangana and reduce friction in its home state of Kerala.
> Valuation Comfort: At ₹138 (the low), the stock was trading at attractive valuations, prompting value buying in the textile sector which is seeing a revival.
📈 2. The Chart Structure (The Bear Trap)
> The Support: ₹147 the support.
- Refinement: The price momentarily broke this support to hit ₹138.20 (on Jan 21), triggering stop-losses, before skyrocketing back up. This indicates a "Bear Trap" or "Spring" formation, where smart money buys the panic selling.
> The Pattern: The Weekly Hammer has a very long lower shadow, indicating that sellers pushed price down, but buyers overwhelmed them to close the week near the high.
📊 3. Volume & Indicators
> Volume Spike: The 12.43 Million volume is an "Ignition Bar." It is significantly higher than the 10-week average.
> RSI: RSI reversing from the "Oversold" zone (below 30 on daily, rising on weekly) is a classic momentum divergence signal.
🎯 4. Future Scenarios & Key Levels
The stock has cleared the "Panic Bottom."
🐂 Bullish Targets (The Recovery):
- Target 1: ₹200. .
- Target 2: ₹295 - ₹298.
- Blue Sky: If the political tailwinds persist, a breakout above ₹324 (ATH) is possible in the long term.
🛡️ Support (The "Line in the Sand"):
- Immediate Support: ₹147 – ₹150. The previous support level is now reclaimed.
- Stop Loss: A close below ₹135 (below the Hammer's wick) would invalidate the reversal.
Conclusion
This is a High-Conviction Turnaround.
> Refinement: The "Hammer" is valid, but the Fundamental News (NDA) is what makes this a sustainable trend rather than a dead-cat bounce.
> Strategy: The reversal is confirmed. Use dips to accumulate.
MY ANALYSIS ON HDFC LIFE IN THE UPCOMING TRADING SESSIONS.On the weekly time frame, ₹750 can be clearly identified as a key support level. The stock attempted to hold this level on two earlier occasions but failed. On the third attempt, it decisively broke below ₹750.
Following this breakdown, the stock retested the ₹750 level on the weekly chart and then exhibited trend continuation, moving upward toward the ₹800–₹820 zone. However, this ₹800–₹820 range has now emerged as a strong resistance area. In particular, ₹820 is a critical level where the stock has repeatedly failed to sustain a breakout.
Additionally, the weekly chart shows the formation of a falling wedge pattern, developing within a well-defined channel. This channel represents a tight zone of price compression, suggesting that a decisive move is likely in the near term.
Shifting focus to the daily time frame, the lower trend line had been acting as a strong support. Each time the price touched this trend line, a pullback was observed. However, in the previous trading session, this lower trend line was decisively broken. Along with this breakdown, the ₹750 level—an important technical support—was also breached.
The breakdown of the lower trend line has resulted in a continuation of the downward move in HDFC Life.
From a technical perspective, the ₹720–₹730 zone now becomes a crucial level. If the stock manages to sustain above this range, it may be considered a stop-loss zone. Failure to hold this level could lead to further downside, with the next target expected around ₹680 and ₹650.
Eternal (Zomato) price action analysis for Feb-Mar 2026Analysis data: 26-Jan-26
Zomato had a good runup from 240 levels to 360 levels from May 2025 to Oct 2025.
Stock is currently at 258. It is likely to take support as buyers are expected in the 240-250 region again. However this time the targets would be 280, 290 & 300 levels.
Keep SL at 230
Happy Trading!
Colgate cmp 2166.30 by Weekly Chart viewColgate cmp 2166.30 by Weekly Chart view
- Support Zone 1910 to 2050 Price Band
- Resistance Zone 2200 to 2350 Price Band
- Stock was making Lower High Lower Lows since last week of Sept 25
- Stock seems attempting uptrend from Support Zone over the last 2 weeks
- Volumes seemingly seen increasing over past few weeks by demand base buying
- Stock Price seems coming out of Bearish Falling Price Channel taking a Bullish momentum
Bitcoin Bybit chart analysis JENUARY 22Hello
It's a Bitcoin Guide.
If you "follow"
You can receive real-time movement paths and comment notifications on major sections.
If my analysis was helpful,
Please click the booster button at the bottom.
This is a 30-minute Bitcoin chart.
Nasdaq indicators will be released shortly at 10:30 AM and 12:00 PM.
*The blue finger path indicates a short-to-long switching or a long-position waiting strategy. (Two-Way Neutral Strategy)
1. Short position entry point at $90,870.1 above / Stop loss if the orange resistance line is broken.
2. Long position switch at $90,170.2 / Stop loss if the green support line is broken.
3. Long position switch at $92,456 / Stop loss if the red resistance line is broken.
4. Long position switch at $91,612.7 / Stop loss if the green support line is broken.
If the price falls directly without touching the blue finger at the top (90.8K),
Pink finger at the bottom (1st section), $89,335.7.
Long position waiting strategy / Stop loss is the same if the green support line is broken.
If the price falls below that point, it could fall up to two times, so be cautious of Nasdaq fluctuations.
Up to this point, I ask that you use my analysis for reference only.
I hope you operate safely, with a focus on principled trading and stop-loss orders.
Thank you.
BTC Confirms Bearish Structure After Neckline RejectionBTC Confirms Bearish Structure After Neckline Rejection
#Bitcoin has rejected the 94k–98k neckline resistance, confirming a bearish market structure.
➡️ Resistance: 94k–98k
➡️ Supports: 80k → 75k → 70k
Structure shows a confirmed Head & Shoulders Pattern Failed, Followed by a bear flag breakdown, trend remains decisively bearish.
Outlook:
Below 90k, downside continuation is favored.
Measured move points to 75k–70k (~22% downside).
Bullish bias only returns on a strong reclaim and acceptance above 92k.
Until then: sell the rallies, respect the trend.
Not financial advice. DYOR.
DABUR: Bearish Head & Shoulders Pattern in the Making?Market Insights by Ayushi Shrivastava | NISM-Certified Research Analyst
The daily chart of DABUR is flashing an important technical warning signal.
As of January 26, 2026, a classic Head and Shoulders pattern appears to be forming, with price now hovering around ₹519 — right near a critical support zone.
This is a zone where the market usually makes a decision:
hold and bounce… or break and accelerate lower.
🔍 Technical Structure Breakdown
The chart clearly shows a three-peak formation:
• Left Shoulder: Formed during mid-2025
• Head: A much higher peak near ₹570–₹580 in late 2025
• Right Shoulder: Currently consolidating in the ₹520–₹540 zone
This symmetry strengthens the probability of a classical Head & Shoulders setup.
📌 Key Observations
• Neckline / Trendline Support:
An ascending green trendline is acting as the neckline of this pattern.
• Price Action:
DABUR is down -0.41% today with volume around 12.33M,
hovering just above this neckline — a classic pressure zone.
• Volatility Clue:
A previous measured move on the chart shows a historical fall of
-28.24% (-189.95 points), highlighting how sharp moves can get
once structure breaks.
🎯 Potential Outlook
If DABUR breaks and sustains below the ascending neckline,
it could trigger a bearish continuation move.
📍 Immediate support to watch: ₹500–₹510
(This zone previously acted as a strong base near the Left Shoulder.)
A clean breakdown below this area could open the door for
a deeper corrective phase.
🤔 Final Thought
Right now, DABUR is sitting at a make-or-break zone.
• Hold above neckline → possible range continuation or bounce
• Break below neckline → pattern confirmation + downside momentum
Markets don’t move on opinions.
They move on structure, levels, and participation.
What’s your view?
Is DABUR headed for a breakdown…
or will this trendline once again act as strong support? 👇
— Ayushi Shrivastava
NISM-Certified Research Analyst
⚠️ Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice.
Stock market investments are subject to market risks. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trading or investment decisions.
ABSLAMC – Price at a Critical Support Inside a Falling ChannelThe stock has been moving within a clear falling channel, showing a controlled downtrend over time.
Every attempt to move higher has faced rejection near the upper trendline, keeping the overall structure weak.
Recently, price bounced from the lower channel and moved up, but once again got rejected near resistance and is now back near an important support zone.
This level is crucial because buyers have previously reacted from this area.
👉 If the support holds and price stabilizes, a short-term bounce toward the upper channel is possible.
👉 If this support breaks decisively, it could open the door for further downside continuation within the trend.
For now, this is a key decision zone — watching how price behaves here will give the next directional clue.
Part 1 Candle Stick Pattern Call Options Explained
A Call Option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified strike price before or at expiry.
Example:
Stock price: ₹100
Call strike price: ₹105
Expiry: 1 month
Premium paid: ₹3
If the stock rises to ₹115:
Intrinsic value = ₹10
Profit = ₹10 − ₹3 = ₹7
If the stock stays below ₹105:
Option expires worthless
Maximum loss = premium paid (₹3)
Use Cases:
Bullish market view
Leverage with limited downside
Substitute for stock ownership
DCM Shriram Approaches Long-Term Support – Reaction Zone AheadDCM Shriram continues to trade within a well-defined long-term rising channel, respecting higher highs and higher lows over time. Each major rally has been followed by a healthy pullback toward the lower trendline, where buyers have consistently stepped in to defend the trend.
The current move is another structural retracement, not a random sell-off. Price has now returned to the channel’s base — a zone that has previously acted as strong demand and launched multiple upside swings.
This area becomes a crucial reaction zone:
• If price holds and stabilizes here, it keeps the broader uptrend intact and opens room for another move toward the upper boundary of the channel.
• A decisive breakdown below the channel would signal weakening structure and potential trend shift.
Volume behavior also supports a corrective phase, with stronger participation during rallies and lighter activity during pullbacks — typical of healthy trending markets.
For now, patience is key. Let the market show its hand at this support instead of predicting the next move.
Structure will always speak louder than short-term noise.