NIFTY KEY LEVELS FOR 04.02.2026NIFTY KEY LEVELS FOR 04.02.2026
Timeframe: 3 Minutes
If the candle stays above the pivot point, it is considered a bullish bias; if it remains below, it indicates a bearish bias. Price may reverse near Resistance 1 or Support 1. If it moves further, the next potential reversal zone is near Resistance 2 or Support 2. If these levels are also broken, we can expect the trend.
When a support or resistance level is broken, it often reverses its role; a broken resistance becomes the new support, and a broken support becomes the new resistance.
If the range(R2-S2) is narrow, the market may become volatile or trend strongly. If the range is wide, the market is more likely to remain sideways
please like and share my idea if you find it helpful
📢 Disclaimer
I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments.
Please consult with your SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any trading or investment decisions.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
Trend Analysis
BANKNIFTY Levels for Today
Here are the BANKNIFTY’s Levels for intraday (in the image below) today. Based on market movement, these levels can act as support, resistance or both
Please consider these levels only if there is movement in index and 15m candle sustains at the given levels. The SL (Stop loss) for each BUY trade should be the previous RED candle below the given level. Similarly, the SL (Stop loss) for each SELL trade should be the previous GREEN candle above the given level.
Note: This idea and these levels are only for learning and educational purpose.
Your likes and boosts gives us motivation for continued learning and support.
NIFTY Levels for Today
Here are the NIFTY's Levels for intraday (in the image below) today. Based on market movement, these levels can act as support, resistance or both.
Please consider these levels only if there is movement in index and 15m candle sustains at the given levels. The SL (Stop loss) for each BUY trade should be the previous RED candle below the given level. Similarly, the SL (Stop loss) for each SELL trade should be the previous GREEN candle above the given level.
Note: This idea and these levels are only for learning and educational purpose.
Your likes and boosts gives us motivation for continued learning and support.
Nifty50 analysis(4/2/2026).CPR: wide + ascending cpr: consolidtion
FII: 5,236.28 bought.
DII: 1,014.24 bought.
Highest OI:
CALL OI: 25800, 26000
PUT OI: 25700
Resistance: - 26000
Support : - 25500
conclusion:.
My pov:
1.today price consolidate towards 25250. because it is the place were huge support is seen.
2.in one hour candle the 200ma line is broken for first time , for 200ma line the price must break many time to get support ,so there is highly possible to go down to find support .
3.in 4hour candle has support of 200ma line at 25650 that itself give support or make market consolidate itself there 25650.
4.keep in mind that market is in bullish the price suddenly gapped up so most active player wait for the right place to entry long .
What IF:
market can go down to 25250 max.
if it 26000 is the high max.
psychology fact:
Trust the process, objectify the market, accept uncertainty.
note:
8moving average ling is blue colour.
20moving average line is green colour
50moving average line is red colour.
200moving average line is black colour.
cpr is for trend analysis.
MA line is for support and resistance.
Disclaimer:
Iam not Sebi registered so i started this as a hobby, please do your own analysis, any profit/loss you gained is not my concern. I can be wrong please do not take it seriously thank you.
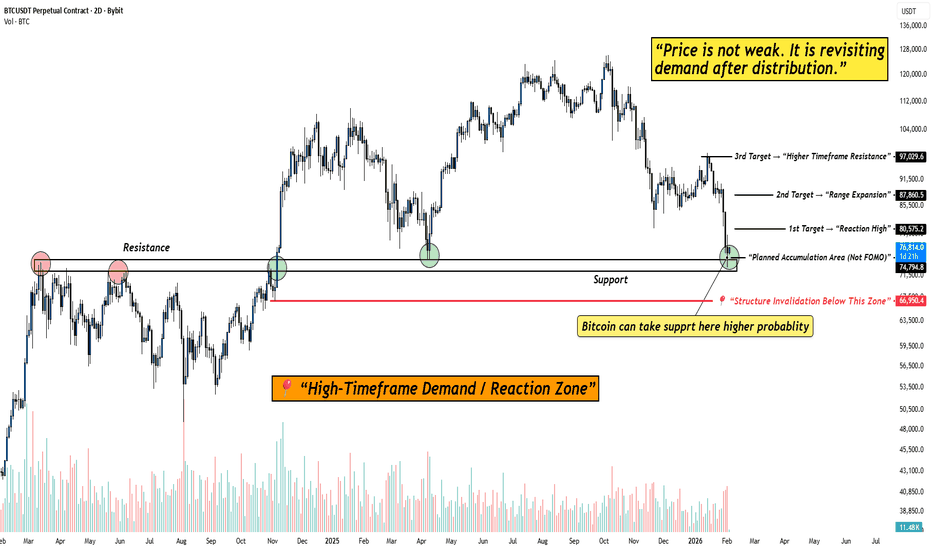
BITCOIN at High-Timeframe Demand: Reaction Zone in Play!When I look at this chart, I’m not seeing fear or structural damage.
I’m seeing price doing exactly what it should do after a distribution phase , revisiting demand and slowing down.
Bitcoin has come back into a clearly marked high-timeframe demand / reaction zone . This is not a random level. This is an area where price has previously flipped structure and attracted strong participation.
What stands out to me on the chart:
Price is holding above a major high-timeframe support , not slicing through it. That tells me sellers are no longer aggressive at these levels.
The current zone is labeled as a planned accumulation area (not FOMO) . Price is reacting here instead of accelerating lower, that’s important.
Downside risk is clearly defined with a structure invalidation level below demand. As long as that level holds, structure remains intact.
Upside targets are logical and sequential , starting from a reaction high, followed by range expansion, and then higher-timeframe resistance.
The psychology behind this phase:
This is the part of the market where most people feel uncomfortable.
Price isn’t exciting. It’s not trending fast. It’s just… sitting.
But that’s usually how strong moves begin.
If Bitcoin were truly weak, it wouldn’t pause here, it would break cleanly below demand.
So far, it hasn’t.
That tells me the market is evaluating value , not panicking.
My approach here is simple:
I don’t chase price away from demand.
I don’t panic inside support.
I observe how price behaves at this zone and let the market show its hand.
As long as price holds above the demand zone, reactions from here remain valid.
Only a clean acceptance below the invalidation level would change this view.
Until then, this is a patience zone .
And patience, more often than prediction, is what gets paid in this market.
Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. Not financial advice. Always manage risk and trade according to your own plan.
NIFTY- Intraday Levels - 4th Feb 2026not confident on the levels today. You can refer the levels marked on chart for your study.
However my guess would be, if market manages to close below 25727 to 25653 the n tomorrow will be sell on rise, if manages to close above this then Tommorow will be buy on dip
Consider some buffer points in levels marked on chart
Please do your due diligence before trading or investment.
**Disclaimer -
I am not a SEBI registered analyst or advisor. I does not represent or endorse the accuracy or reliability of any information, conversation, or content. Stock trading is inherently risky and the users agree to assume complete and full responsibility for the outcomes of all trading decisions that they make, including but not limited to loss of capital. None of these communications should be construed as an offer to buy or sell securities, nor advice to do so. The users understands and acknowledges that there is a very high risk involved in trading securities. By using this information, the user agrees that use of this information is entirely at their own risk.
Thank you.
Market Outlook & Trade Setup – Wednesday, 4th Feb 2026Nifty opened at a major gap up yesterday of 1200 points following the midnight announcement of the India US trade deal being secured leading to a huge upsurge in sectors across the board. However the momentum got lost in the initial 15 mins of the market opeing following which the index moved in a range throughout the day.
Gold & Silver futures in MCX bounced back to gain more than 6% and 15% yesterday.
🔹 NIFTY: Gift Nifty (25,769)
* Previous Close: 25,727
* Expected Range: 25,500 - 26,000
🔹 SENSEX
* Previous Close: 83,739
* Expected Range: 83,000 - 84,000
🌍 Global & Market Sentiment
* DJIA: -167 | S&P: - 58
💰 Institutional Activity (Cash Market)
* FII: Net Buyers: ₹ 5236 Cr
* DII: Net Buyers: ₹ 1014 Cr
🔥 Events this Week:
India - S&P Global Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
📌 Sectoral Focus (Positive)
Banks, Energy, Auto, Real Estate
👉 Commodities in Focus: Gold, Silver
✌️Important Quarterly Results: Bajaj Finserv, Century Ply, Tata Power
📈 Trade smart. Manage risk. Stay disciplined.
NIFTY : Trading levels and Plan for 04-Feb-2026📘 NIFTY Trading Plan – 4 Feb 2026
(Timeframe: 15-Min | Instrument: NIFTY 50 | Educational Purpose Only)
🔑 Key Intraday Levels (From Chart)
🟢 25,985 – 26,020 – Last Intraday Resistance Zone
🟠 25,569 – 25,696 – Opening Support / Resistance (Consolidation Zone)
🟢 25,472 – Last Intraday Support
🟢 25,221 – Lower Support / Breakdown Level
🟢 25,714 – 25,745 – Current Reference Price Area
🧠 Market Structure & Price Psychology
NIFTY witnessed a strong vertical recovery from lower levels, indicating aggressive short covering and panic exit of sellers.
However, price is now approaching important supply zones, where profit booking and fresh selling pressure can emerge.
👉 Tomorrow’s direction will depend on acceptance or rejection near the opening zones, not on emotional bias.
🚀 Scenario 1: GAP UP Opening (100+ Points)
(Opening near / above 25,850)
🧠 Psychology
Gap up after a sharp rally often reflects euphoria and short covering, but institutions usually sell into higher resistance zones.
🟢 Bullish Plan
🔵 If price sustains above 25,985 on a 15-min closing basis
🔵 Expect upside extension towards 26,020 and above
🔵 Momentum trades only after clean acceptance
🔴 Rejection Plan
🔴 Rejection near 25,985 – 26,020
🔴 Expect pullback towards 25,696 – 25,569
📌 Why this works
Breakout works only when buyers accept higher prices, not when price spikes emotionally.
➖ Scenario 2: FLAT Opening
(Opening between 25,650 – 25,780)
🧠 Psychology
Flat open after a sharp rally shows temporary balance. Market usually consolidates before next expansion.
🟢 Upside Plan
🔵 Sustaining above 25,696
🔵 Gradual move towards 25,985
🔴 Downside Plan
🔴 Failure to hold 25,569
🔴 Drift towards 25,472
📌 Important Note
🟠 25,569 – 25,696 is a consolidation zone
🟠 Expect whipsaws — trade only after confirmation
🔻 Scenario 3: GAP DOWN Opening (100+ Points)
(Opening near / below 25,472)
🧠 Psychology
Gap down after a sharp up-move signals profit booking or fresh short positions.
🟢 Bounce Setup
🔵 If 25,472 holds on 15-min basis
🔵 Expect technical bounce towards 25,569 – 25,696
🔴 Breakdown Setup
🔴 Clean break below 25,472
🔴 Downside opens till 25,221
📌 Why this works
Strong supports either create fast bounces or accelerated breakdowns — confirmation is critical.
🛡️ Risk Management Tips (Options Traders)
🟢 Trade only after first 15-min candle confirmation
🟢 Prefer option spreads near resistance zones
🟢 Avoid aggressive buying in gap-up opens ❌
🟢 Risk maximum 1–2% capital per trade
🟢 Book partial profits at next resistance/support
🟢 Discipline > Prediction 📌
🧾 Summary & Conclusion
📌 NIFTY is in post-short-covering consolidation
📌 25,696 & 25,472 are the most important intraday decision levels
📌 Break above 25,985 needed for bullish continuation
📌 Trade price reaction, not market excitement 📈
⚠️ Disclaimer
This analysis is strictly for educational purposes only.
I am not a SEBI registered analyst.
Please consult your financial advisor before taking any trades.
Market investments are subject to risk.
XAUUSD INTRADAY LEVELS Gold (XAUUSD) – Intraday Analysis (15M)
Gold is currently trading in a short-term bullish structure after forming a higher low and strong impulsive move upward. Price has broken above the recent consolidation zone and is now retesting the demand area, indicating potential continuation to the upside.
Trade Plan:
Bias: Bullish (Daily bias bullish)
Entry: Buy only after clear bullish confirmation from the marked demand zone
Invalidation: Sell positions below the marked support level
Targets:
Target 1: 5,101
Target 2: 5,239
Target 3: 5,312
A healthy pullback into the demand zone followed by bullish price action can provide a high-probability long opportunity. Risk management is crucial; avoid entries without confirmation.
BTCUSD Reacts From Demand Zone After Strong Bearish MoveBTCUSD has shown a sharp fall from the upper resistance area near 90,500–91,500, where sellers clearly dominated and price failed to hold higher levels. This rejection led to a strong bearish move, confirming a short-term downtrend with consistent lower highs and lower lows. The descending trendline reflects continued selling pressure and weak upside acceptance.
After the decline, price reached an important demand zone around 76,000–77,000. In this area, selling pressure reduced and buying interest appeared, leading to a short-term bounce. This zone is supported by previous price consolidation and acts as a key support in the current market structure. The reaction suggests temporary stability, not a confirmed trend change.
While price stays above 76,000, consolidation or a corrective move toward 82,000–85,000 is possible. This zone may act as near-term resistance, as it aligns with earlier breakdown levels. Acceptance above this range would reduce bearish strength and support further recovery.
If price fails to sustain above the demand zone, downside risk remains open toward the 73,000 support region. Overall bias stays cautious, with high volatility expected near marked levels.
ITC Level Analysis for 04th FEB 2026+Contd. to 03rd Feb Post.....
⚠️ Due to Impact of EX-Dividend of Rs 6.50/Share,
ITC May Open Near "RLS#1" level
Best level to enter between "RLS#2 & USTgt
Screen shot in 5 min TF
━━━━━━━━━₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹₹━━━━━━━━
💥Level Interpretation / description:
L#1: If the candle crossed & stays above the “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Bullish bias.
L#2: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLB#1 & UBTgt
L#3: If the candle stays above “Sell Gen” but below “Buy Gen”, it is treated / considered as Sidewise. Aggressive Traders can take Long position near “Sell Gen” either retesting or crossed from Below & vice-versa i.e. can take Short position near “Buy Gen” either retesting or crossed downward from Above.
L#4: If the candle crossed & stays below the “Sell Gen”, it is treated / considered a Bearish bias.
L#5: Possibility / Probability of REVERSAL near RLS#1 & USTgt
HZB (Buy side) & HZS (Sell side) => Hurdle Zone,
*** Specialty of “HZB#1, HZB#2 HZS#1 & HZS#2” is Sidewise (behaviour in Nature)
Rest Plotted and Mentioned on Chart
Color code Used:
Green =. Positive bias.
Red =. Negative bias.
RED in Between Green means Trend Finder / Momentum Change
/ CYCLE Change and Vice Versa.
Notice One thing: HOW LEVELS are Working.
Use any Momentum Indicator / Oscillator or as you "USED to" to Take entry.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⚠️ DISCLAIMER:
The information, views, and ideas shared here are purely for educational and informational purposes only. They are not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any financial instruments. I am not a SEBI-registered financial adviser.
Trading and investing in the stock market involves risk, and you should do your own research and analysis. You are solely responsible for any decisions made based on this research.
"As HARD EARNED MONEY IS YOUR's, So DECISION SHOULD HAVE TO BE YOUR's".
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
❇️ Follow notification about periodical View
💥 Do Comment for Stock WEEKLY Level Analysis.🚀
📊 Do you agree with this view?
✈️ HIT THE PLANE ICON if this technical observation resonates with you. It will Motivate me.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💡 If You LOOKING any CHART & want for Level and ANALYZE?
Share your desired stock names in the comments below! I will try to analyze the chart Levels, patterns and share my technical view (so far my Knowledge).
If Viewers think It can identify meaningful setups. Looking forward to hearing from all of you — let's keep this discussion going and help each other make better trading decisions.
Gold Rebounds from the Bottom — Is the Bull Market Restarting?✅ From the 4-hour timeframe, gold has staged a continuous rebound from the 4402 low. Price has moved back above MA10 and the Bollinger middle band, and is gradually approaching the MA20 resistance area. The previous one-sided bearish structure has been broken, and the market is now entering a structural rebuilding phase after trend recovery. The 4950 level stands as a key bullish–bearish transition zone on the 4-hour chart. If price can hold firmly above it, further upside potential may open.
✅ On the 1-hour timeframe, price is forming a step-like upward structure, with MA5 / MA10 / MA20 aligned bullishly and the Bollinger Bands opening upward, indicating strong short-term bullish momentum. However, price is now close to the upper Bollinger band and a previous high-volume trading area, suggesting a need for short-term consolidation and pullback.
✅ Combining both timeframes, the market has shifted from a prior bearish trend into a bullish-led, oscillating upward rhythm. As long as price remains above 4900, pullbacks are more likely to be buying opportunities rather than signals for a renewed decline.
🔴 Resistance: 4980–5050
🟢 Support: 4900–4850
✅ Trading Strategy Reference:
The current approach focuses primarily on buying on pullbacks, with light short positions considered near resistance zones.
🔰 Long Strategy (Buy on Pullback)
👉 Entry Zone: 4850–4920, scale into long positions
🎯 Target 1: 4980
🎯 Target 2: 5050
🎯 Extended Target: 5130
📍 Logic:
This area is a confluence of 1-hour moving average support and the 4-hour middle band support, suitable for trend-following entries.
🔰 Short Strategy (Light Shorts at Resistance)
👉 Entry Zone: 4980–5050, light short positions
🎯 Target 1: 4920
🎯 Target 2: 4850
📍 Logic:
This area aligns with the 4-hour MA20 and previous structural resistance, where short-term technical pullbacks may occur.
✅ Risk Control Reminders
👉 The primary bias is bullish; shorts are for consolidation only
👉 If price holds firmly above 5000, the short bias becomes invalid
👉 As long as pullbacks do not break below 4850, the bullish rhythm remains intact
👉 In a ranging market, focus on scaling positions and strict stop-loss discipline.