DLF 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Latest Price Snapshot
Current price: ~₹690‑₹705 range on NSE (as of early Jan 2026) — recent close ~₹691 – ₹703.80.
1‑month performance: Slightly down (~‑1% to ‑3%) over last month.
🧱 Important Support Levels
Level Price Notes
Support 1 (Immediate) ~₹690 Near current trading zone; key short‑term support.
Support 2 ~₹685‑₹688 Break below 690 could test here next.
Support 3 (Lower) ~₹678‑₹680 Lower short‑term support if sellers strengthen.
Lower 1‑Month Floor (historical) ~₹672 1‑month low seen.
🚧 Resistance Levels
Level Price Notes
Resistance 1 (near pivot) ~₹697‑₹702 First upside hurdle.
Resistance 2 ~₹708‑₹710 Next supply zone if price breaks above short resistance.
Higher resistance ~₹720+ Mid‑term barrier near 50‑day MA range.
📌 Short‑Term Pivot Points (Daily/Weekly Reference)
Pivot Zone: ~₹697‑₹698 — acts as a neutral technical pivot.
📉 Short‑Term Technical Momentum
RSI (14‑day): Neutral‑slightly bearish (~39‑42).
Moving Averages:
20‑day MA ~₹695‑701 (neutral).
50‑day MA ~₹722+ (resistance overhead).
Technical signals show a neutral to slightly bearish short‑term bias, with potential for range‑bound action between ₹680‑₹710 unless a breakout occurs.
📈 How to Interpret These Levels (1‑Month View)
Bullish Scenario
✔ Stay above ₹690‑₹695 → next move toward ₹702‑₹710
✔ Break above ₹710 → expands upside toward ~₹720+ resistance
Bearish Scenario
✘ Fails below ₹690 → could test ₹685‑₹680 zone
✘ Close below ₹678‑₹672 → stronger downside risk near recent lows
📊 Summary — 1‑Month Range (Practical Trading Levels)
👉 Bullish range breakout: above ₹702–₹710
👉 Bearish support breakdown: below ₹685–₹680
👉 In‑range trade: ₹680 ↔ ₹710
Trendcontinuation
ATGL 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Latest Price (approx): ~₹590–₹595 on NSE (price fluctuates within the day) — current levels seen near this range.
📈 Weekly Support & Resistance Levels (pivot‑based)
These are weekly pivot‑derived levels that traders often use to gauge likely support and resistance zones for the week ahead:
🔹 Weekly Resistance Levels
R1: ~₹622
R2: ~₹637
R3: ~₹657
🔸 Weekly Pivot (mid zone): ~₹602
🛡️ Weekly Support Levels
S1: ~₹587
S2: ~₹567
S3: ~₹552
These weekly pivots are from standard pivot point calculations and give you the broad weekly range to watch.
📍 Key Round Levels to Watch (Weekly)
Resistance zones:
~₹620–₹630: short‑term overhead supply/resistance.
~₹650+: higher resistance if the market turns bullish later in the week.
Support zones:
~₹580: immediate support around current price band (often reacts intraday).
~₹560–₹570: stronger weekly support — key level if price weakens.
~₹550: deeper support on weekly frame.
📌 Weekly Strategy Levels
👉 Bullish scenario: A sustained close above ₹620 for the week could open up moves toward ₹637–₹657.
👉 Bearish scenario: If the stock breaks below ₹587 on a weekly close, watch support ₹567, then ₹552.
FINCABLES 1 Day Time Frame 📈 Latest Price Snapshot (Daily)
Approx. Current Price: ~ ₹780 – ₹786 (recent trading close / live range)
Recent Day’s High/Low Range: ~ ₹748 – ₹789
52-Week Range: Low ~₹707 | High ~₹1,189
📊 Daily Technical Levels (Support / Resistance / Pivot)
Technical pivot zones for today’s 1-day timeframe:
Level Type Price Approx.
Resistance 3 (R3) ~ ₹805
Resistance 2 (R2) ~ ₹797
Resistance 1 (R1) ~ ₹785
Pivot Point (PP) ~ ₹777
Support 1 (S1) ~ ₹765
Support 2 (S2) ~ ₹758
Support 3 (S3) ~ ₹745
Derived from real-time pivot calculations & chart studies for daily timeframe.
📌 How to Use These Levels Today
🔹 Bullish Scenario
Break & hold above ₹785–₹790 → potential short-term continuation up to ₹797–₹805.
A strong daily close above ~₹805 signals further upside momentum for the next legs.
🔸 Bearish Scenario
Below Pivot ~₹777 → increased risk toward ₹765 and deeper to ₹758–₹745.
A daily close under ₹758 could expose sellers and widen the downside.
📍 Key Intraday Reference
Pivot ~₹777 — acts as the central reference for trend bias today.
Range watch: ₹765–₹785 is the immediate trade zone.
🧠 Summary (1-Day View)
✔ Immediate resistance: ₹785–₹805
✔ Immediate support: ₹765–₹745
✔ Pivot: ~₹777
✔ Price action bias: Neutral-to-bearish with potential for short-term retracement or bounce
INDUSTOWER 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Price (Approx)
Last traded ~₹422 – ₹423 on recent session close.
🔑 Daily Pivot Levels (1D Timeframe)
Pivot levels help estimate daily market bias (above pivot = bullish bias; below pivot = bearish).
Pivot Point (Daily): ~₹422
Resistance Levels:
• R1: ₹425
• R2: ₹431
• R3: ₹434
Support Levels:
• S1: ₹417
• S2: ₹414
• S3: ₹408
Interpretation
Staying above ₹422 pivot suggests intraday strength.
A break above ₹431–434 can open up further upside moves.
A drop below ₹417–₹414 may bring selling pressure toward ₹408.
🔥 Alternate Support/Resistance Reference (from Multiple Sources)
Supports: ₹416–₹413–₹408 zone.
Resistances: ₹425–₹430–₹433 zone.
VWAP (short-term reference) near ₹410–₹412 supports price action above it.
📈 Trading Interpretation (1-Day Bias)
Bullish intraday view (if price holds above pivot):
Above ₹422 pivot → watch ₹425–₹431–₹434 resistance targets.
Weakness/Range view:
If price trades between ₹414–₹422, expect choppy action with possible fade to support.
Bearish pressure (if break below support):
📊 Extra Notes
The stock’s 52-week range is roughly ₹312 – ₹430 — current near higher end.Below ₹414–₹408 → watch for further weakness to deeper support levels.
📊 Extra Notes
The stock’s 52-week range is roughly ₹312 – ₹430 — current near higher end.
Technical indicators (moving averages/oscillators) vary by platform, but many show neutral to buy bias on daily charts.
Earnings Season Trading: Strategies, Opportunities, and RisksUnderstanding Earnings Season
Earnings season typically occurs four times a year, shortly after the end of each fiscal quarter. Companies release their income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and forward guidance during this time. In markets like the US and India, earnings seasons often cluster, with many companies reporting within a few weeks. This concentration of information increases overall market volatility and sector-wide movements. Stocks may move not only due to their own results but also in reaction to peer performance, sector trends, and macroeconomic signals.
Why Earnings Move Markets
Stock prices are forward-looking, meaning they reflect expectations about future performance rather than just past results. Earnings announcements act as a reality check against these expectations. If reported earnings exceed expectations (an earnings beat), the stock may rise. If earnings fall short (an earnings miss), the stock may decline. However, the reaction is not always straightforward. Sometimes a stock falls even after strong results if expectations were too high, or rises after weak earnings if the outlook improves. This dynamic makes earnings season trading both challenging and rewarding.
Pre-Earnings Trading Strategies
One common approach is pre-earnings positioning. Traders analyze estimates, historical earnings reactions, sector momentum, and technical setups before the announcement. Stocks often build up momentum leading into earnings, especially if there is optimism about results. Traders may enter positions days or weeks in advance, aiming to benefit from this “earnings run-up.” Technical indicators such as volume expansion, breakout patterns, and relative strength are often used to time entries. However, pre-earnings trades carry risk, as unexpected results can quickly reverse gains.
Post-Earnings Reaction Trading
Another popular strategy focuses on trading after earnings are released. Instead of speculating on the outcome, traders wait for the market’s reaction and then act. Post-earnings trading emphasizes confirmation—how price, volume, and trend behave once new information is fully absorbed. Strong earnings accompanied by high volume and a breakout above resistance may signal trend continuation. Conversely, a sharp drop below key support after disappointing results may indicate further downside. This approach reduces uncertainty but may miss the initial large move.
Gap Trading and Volatility Plays
Earnings often cause price gaps, where a stock opens significantly higher or lower than its previous close. Gap trading strategies aim to profit from either continuation or gap-filling behavior. Some stocks continue strongly in the direction of the gap due to sustained institutional interest, while others retrace as early traders take profits. Understanding the context—such as overall market sentiment, guidance quality, and historical behavior—is crucial when trading gaps.
Earnings season is also a period of elevated implied volatility, especially in options markets. Options traders use strategies like straddles, strangles, and spreads to benefit from large price moves or volatility changes. While these strategies can be powerful, they require a strong understanding of option Greeks, volatility crush, and risk-reward dynamics.
Role of Guidance and Management Commentary
Earnings numbers alone rarely tell the full story. Management guidance, conference calls, and future outlook often matter more than reported profits. Markets react strongly to changes in revenue growth expectations, margin outlook, capital expenditure plans, and commentary on demand conditions. A company may report solid earnings but issue cautious guidance, leading to a negative reaction. Successful earnings season traders pay close attention to these qualitative factors, not just headline numbers.
Sector and Index Effects
Earnings season trading is not limited to individual stocks. Strong or weak results from market leaders can influence entire sectors and indices. For example, earnings from major banks can impact the financial sector, while results from large IT or FMCG companies can move broader indices. Traders often monitor sector ETFs or index futures to capture these broader moves. Relative performance within a sector can also highlight leadership and laggards, offering pair trading or rotation opportunities.
Risk Management During Earnings Season
Risk management is critical during earnings season due to heightened volatility and unpredictable reactions. Position sizing should be adjusted to account for potential large price swings. Stop-loss orders, while useful, may not always protect against gaps, so traders must be prepared for slippage. Diversification across multiple trades and avoiding overexposure to a single earnings event can help reduce portfolio risk. Many experienced traders also avoid holding large positions overnight during earnings unless they have a strong edge or hedging strategy.
Behavioral Aspects and Market Psychology
Earnings season amplifies behavioral biases such as overconfidence, herd mentality, and loss aversion. Traders may chase stocks after strong earnings or panic-sell after disappointing results. Media headlines and social media commentary can further exaggerate emotional responses. Successful earnings traders remain disciplined, stick to predefined plans, and avoid impulsive decisions driven by short-term noise.
Long-Term Perspective vs Short-Term Trading
Not all earnings season activity is about short-term trading. Long-term investors use earnings to reassess company fundamentals, valuation, and growth trajectories. Consistent earnings growth, improving margins, and strong cash flows reinforce long-term confidence, while repeated disappointments may signal deeper issues. Understanding the difference between temporary earnings-related volatility and structural business changes is key to making informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Earnings season trading is a dynamic and complex aspect of financial markets that offers significant opportunities for traders and investors alike. It combines elements of fundamental analysis, technical trading, volatility management, and behavioral finance. While the potential rewards are high, so are the risks. Success during earnings season requires preparation, discipline, and a clear understanding of both market expectations and actual results. By focusing on strategy, risk control, and continuous learning, traders can navigate earnings season more effectively and turn market uncertainty into a structured trading advantage.
Managing Losses and Drawdowns: The Psychology Behind DrawdownsUnderstanding Drawdowns Beyond Numbers
A drawdown is not just a percentage decline in capital; it is an emotional experience. A 10% drawdown can feel manageable to one trader and devastating to another. This subjective experience arises because drawdowns threaten three deeply rooted psychological needs:
Ego and self-image (“I thought I was good at this”)
Sense of control (“The market is not behaving as expected”)
Fear of future loss (“What if this gets worse?”)
When capital declines, traders often interpret it as personal failure rather than statistical variance. This misinterpretation magnifies emotional pain and clouds judgment.
Loss Aversion and Emotional Asymmetry
One of the strongest behavioral finance principles at play during drawdowns is loss aversion. Psychologically, losses hurt roughly twice as much as equivalent gains feel good. This asymmetry explains why traders may:
Exit winning trades too early
Hold losing trades too long
Abandon a profitable system after a temporary drawdown
Loss aversion pushes traders to seek emotional relief instead of probabilistic advantage. The mind prioritizes stopping pain now over achieving long-term expectancy, which is why impulsive decisions increase during drawdowns.
Ego, Identity, and Overreaction
Many traders unconsciously tie their identity to trading performance. When equity curves fall, it feels like a judgment on intelligence, discipline, or competence. This ego involvement triggers:
Overtrading to “prove oneself”
Revenge trading after losses
Strategy hopping in search of instant recovery
The more ego-driven the trader, the more severe the psychological reaction to drawdowns. Professionals, in contrast, view drawdowns as operational events, not personal ones.
Fear, Stress, and Cognitive Narrowing
During drawdowns, stress hormones such as cortisol increase, leading to cognitive narrowing—a mental state where the brain focuses on threats and ignores nuance. In this state:
Risk perception becomes distorted
Probabilistic thinking declines
Rule-based discipline collapses
Traders begin to see the market as hostile rather than neutral. This “fight or flight” response is biologically outdated for modern financial markets but still governs behavior unless consciously managed.
The Illusion of Control and Panic Adjustments
Another psychological trap during drawdowns is the illusion of control. Traders may believe that frequent changes—adjusting stops, indicators, timeframes—will immediately stop losses. While adaptation is important, reactive tinkering driven by fear usually worsens outcomes.
Common panic behaviors include:
Reducing position size inconsistently
Removing stops after losses
Doubling down to recover faster
These actions are rarely strategic; they are emotional attempts to regain certainty in an uncertain environment.
Drawdowns as Statistical Reality, Not Failure
Every trading system has a maximum expected drawdown. Even highly profitable strategies experience losing streaks. The psychological error is assuming that a drawdown means:
The strategy is broken
Market conditions will never improve
Losses will continue indefinitely
In reality, drawdowns are the cost of participation. Accepting this intellectually is easy; accepting it emotionally requires experience, preparation, and mindset conditioning.
Managing Losses Through Psychological Preparation
Effective drawdown management begins before losses occur. Traders who survive long term typically:
Define acceptable drawdowns in advance
Risk small enough to stay emotionally stable
Expect losing streaks as normal
When losses occur within expected boundaries, the mind remains calmer. Surprise—not loss itself—is what destabilizes psychology.
Detachment and Process-Oriented Thinking
One of the most powerful psychological shifts is moving from outcome focus to process focus. Instead of asking:
“How much money did I lose?”
Ask:
“Did I follow my rules correctly?”
This reframing reduces emotional volatility and restores a sense of control. Over time, consistency of process matters far more than short-term equity fluctuations.
Confidence vs. Overconfidence During Drawdowns
Healthy confidence allows traders to continue executing a proven system during drawdowns. Overconfidence, however, collapses quickly when losses appear. True confidence is built on:
Data-backed expectancy
Historical drawdown analysis
Emotional self-awareness
Traders with grounded confidence do not panic during losses; they become more disciplined.
Recovery Psychology and the Urge to ‘Make It Back’
One of the most dangerous mental states is the recovery mindset—the urge to quickly make back losses. This mindset shifts goals from execution to emotional repair. Consequences include:
Taking suboptimal trades
Increasing risk unjustifiably
Ignoring market conditions
Professionals understand that capital recovery is a byproduct of good decisions, not a direct objective.
Learning vs. Self-Blame
Constructive reflection during drawdowns focuses on behavior, not self-worth. Questions that promote growth include:
Were losses within expected parameters?
Did emotions influence execution?
Is this variance or a structural issue?
Self-blame, on the other hand, drains confidence and increases hesitation, leading to missed opportunities when conditions improve.
Resilience and Long-Term Survival
Psychological resilience is the ability to stay rational under prolonged uncertainty. This is developed through:
Experience with past drawdowns
Journaling emotional responses
Gradual exposure to risk
Traders who survive multiple drawdowns develop emotional immunity. Losses no longer shock them; they become routine data points.
Conclusion: Mastering the Inner Game
Managing losses and drawdowns is less about eliminating pain and more about responding intelligently to it. The market will always test patience, discipline, and emotional stability. Those who understand the psychology behind drawdowns stop fighting reality and start working with it.
In the long run, strategies make money—but psychology keeps you in the game. Traders who master drawdown psychology transform losses from threats into teachers, building the emotional durability required for sustained success in the financial markets.
Part 1 Master Candle Patterns Risks in Option Trading
While options offer high potential, they also carry risks—especially for beginners.
1. Time Decay (Theta Loss)
Options lose value as expiry approaches.
Even if the price moves slightly in your direction, you may lose money because of time decay.
2. Volatility Crashes
When volatility drops, even profitable positions may give lower returns.
3. High Risk for Sellers
Option sellers (writers) take unlimited risk but earn limited premiums.
Hence, selling must be done with proper margin and risk control.
4. Sudden Market Moves
Events like RBI policy, global news, elections, and results can cause unpredictable losses.
Part 2 Support and Resistance How Option Prices Move (Option Greeks)
Option prices do not move exactly like stock prices. They depend on multiple factors called "Greeks". These help traders understand risk and movement.
1. Delta
Shows how much the option price changes with a ₹1 move in the underlying asset.
2. Theta
Measures time decay.
As expiry nears, options lose value quickly, especially OTM options.
3. Vega
Shows how changes in volatility affect option prices.
High volatility → higher premiums.
4. Gamma
Measures the rate of change of Delta.
It becomes powerful near expiry.
Part 1 Support and Resistance 1. Leverage
Options allow you to control a larger position using a small premium.
Example: Buying 1 lot of Nifty via futures may require ₹1.2 lakh margin, but an option may cost only ₹4,000–10,000.
2. Limited Risk for Buyers
Option buyers cannot lose more than the premium paid.
This gives traders a defined risk structure.
3. Hedging
Investors use options to protect portfolios from crashes.
Example: Buying a put acts like insurance.
4. Strategic Flexibility
Options allow you to build many strategies:
Bullish
Bearish
Neutral
Volatility-based
This makes options suitable for all types of market conditions.
5. Income Generation
Selling options (covered calls or spreads) helps generate regular income when markets are stable.
Part 11 Trading Master ClassWhat Are Options?
An option is a financial contract between two parties: a buyer and a seller (writer). The contract is linked to an underlying asset like stocks, indices, commodities, or currencies. Options are mainly of two types:
1. Call Option
A call option gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price, called the strike price, before the contract expires.
Traders buy calls when they expect the price to rise.
2. Put Option
A put option gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific strike price before expiry.
Traders buy puts when they expect the price to fall.
Market Microstructure and Institutional Trading Strategiesexecuted. However, beneath this surface lies a complex system known as market microstructure, which governs how trades are actually formed, matched, and settled. For institutional participants such as mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, banks, and proprietary trading firms, understanding market microstructure is not optional—it is essential. Their trading strategies are deeply shaped by liquidity, order flow, transaction costs, and the behavior of other large participants. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of market microstructure and explains how institutional trading strategies are built around it.
What Is Market Microstructure?
Market microstructure refers to the study of how markets operate at the trade-by-trade level. It focuses on the mechanisms through which orders are submitted, matched, and executed, and how these processes influence price formation. Unlike macro-level analysis that looks at economic data or corporate fundamentals, microstructure zooms in on order books, bid-ask spreads, volume, liquidity, volatility, and execution speed.
Key questions addressed by market microstructure include:
How are prices discovered?
Why do bid-ask spreads exist?
How does liquidity change during different market conditions?
How do large trades impact prices?
Understanding these dynamics is critical, especially for institutional traders whose large orders can move the market.
Core Elements of Market Microstructure
One of the most important elements is the order-driven market, where buyers and sellers place limit and market orders into an electronic order book. The best bid and best ask define the bid-ask spread, which represents the immediate cost of trading. Narrow spreads typically indicate high liquidity, while wide spreads suggest uncertainty or low participation.
Liquidity itself is a central concept. It reflects how easily an asset can be bought or sold without causing a significant price change. Institutions are highly sensitive to liquidity because executing large orders in illiquid markets can lead to unfavorable price movements, known as market impact.
Another critical component is order flow, which captures the sequence of buy and sell orders entering the market. Order flow carries information. Persistent buying or selling pressure often signals institutional activity and can influence short-term price movements even before fundamental news becomes public.
Price Discovery and Information Asymmetry
Market microstructure plays a vital role in price discovery, the process by which markets incorporate information into prices. Not all participants have the same information or the same speed of execution, leading to information asymmetry. Institutional players often invest heavily in research, data analytics, and technology to reduce this disadvantage.
In many cases, prices move not because of new public information, but because of changes in order flow or liquidity conditions. For example, when a large institution begins accumulating shares quietly, prices may gradually rise due to sustained demand, even without any news announcement.
Transaction Costs and Their Importance
For retail traders, transaction costs may seem minor, but for institutions trading millions of shares, they are crucial. Transaction costs include:
Explicit costs: brokerage fees, exchange fees, and taxes.
Implicit costs: bid-ask spread, market impact, and opportunity cost.
Institutional trading strategies are often designed primarily to minimize transaction costs, sometimes even more than to predict market direction. A strategy that predicts price movement correctly but incurs high market impact can still result in poor overall performance.
Institutional Trading Strategies and Microstructure Awareness
Institutional trading strategies are tightly linked to market microstructure. Unlike retail traders, institutions rarely place large market orders at once. Instead, they use sophisticated execution strategies to manage risk and reduce visibility.
One common approach is order slicing, where a large order is broken into smaller pieces and executed gradually. This reduces market impact and makes the trade less detectable. Algorithms such as VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) and TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) are widely used to achieve this.
Another strategy involves liquidity-seeking behavior. Institutions may choose to trade during periods of high volume—such as market open, close, or during major news events—when liquidity is abundant and their trades can be absorbed with less price disruption.
Role of Algorithmic and High-Frequency Trading
Modern institutional trading relies heavily on algorithmic trading systems. These systems analyze real-time order book data, spreads, and volume to decide when and how to execute trades. Algorithms adapt dynamically to changing liquidity conditions, accelerating execution in liquid markets and slowing down when liquidity dries up.
High-frequency trading (HFT), although controversial, is also part of market microstructure. HFT firms act as liquidity providers, continuously posting bids and offers. While they tighten spreads and improve liquidity under normal conditions, they may withdraw during periods of stress, which can amplify volatility—something institutions must carefully manage.
Dark Pools and Off-Exchange Trading
To further reduce market impact, institutions often use dark pools, which are private trading venues where orders are not publicly displayed. Trading in dark pools allows large participants to execute trades anonymously without signaling their intentions to the broader market.
However, dark pool trading comes with trade-offs. While it reduces information leakage, it may offer less price certainty and slower execution. Institutions therefore balance between lit exchanges and dark pools depending on market conditions and urgency.
Risk Management Through Microstructure
Market microstructure is also crucial for risk management. Liquidity risk—the risk that a position cannot be exited without significant loss—is a major concern for institutions. By analyzing depth of market, historical volume, and spread behavior, institutions assess whether a position can be scaled in or out safely.
During periods of market stress, microstructure dynamics can change rapidly. Spreads widen, liquidity evaporates, and correlations increase. Institutional strategies often include contingency rules to pause trading, adjust order sizes, or switch venues when microstructure signals deteriorate.
Implications for Retail Traders
While retail traders do not operate at institutional scale, understanding market microstructure can still be highly beneficial. It explains why prices behave erratically during low-volume periods, why breakouts often fail when liquidity is thin, and why sudden spikes occur near market open or close.
By aligning trades with liquidity, avoiding low-volume traps, and recognizing institutional footprints through volume and order flow, retail traders can significantly improve execution quality and timing.
Conclusion
Understanding market microstructure provides a deep insight into how financial markets truly function beyond charts and indicators. For institutional traders, microstructure is the foundation upon which execution, strategy design, and risk management are built. Institutional trading strategies are not just about predicting price direction; they are about navigating liquidity, minimizing costs, managing information, and executing efficiently.
As markets continue to evolve with technology, algorithmic execution, and alternative trading venues, the importance of market microstructure will only increase. Whether you are an institutional participant or an individual trader aiming to think like one, mastering market microstructure is a powerful step toward more informed and disciplined trading decisions.
Trading Rate-Sensitive AssetsStrategies, Risks, and Opportunities in Interest-Driven Markets
Rate-sensitive assets are financial instruments whose prices and performance are significantly influenced by changes in interest rates and monetary policy. For traders and investors, understanding how interest rates move—and how different assets respond to those movements—is critical for building profitable strategies and managing risk. In an environment where central banks actively use interest rates to control inflation, growth, and currency stability, trading rate-sensitive assets has become one of the most important themes in modern financial markets.
Understanding Rate Sensitivity
Interest rates act as the “price of money.” When rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, liquidity tightens, and risk appetite often declines. When rates fall, borrowing becomes cheaper, liquidity improves, and asset prices generally benefit. Rate-sensitive assets are those whose cash flows, valuations, or demand patterns are directly affected by these changes. The sensitivity can be direct—such as bond prices moving inversely to yields—or indirect—such as equities reacting to higher discount rates.
The degree of sensitivity depends on duration, leverage, growth expectations, and dependency on external financing. Assets with long-dated cash flows or high debt levels tend to be more sensitive to interest rate movements.
Key Rate-Sensitive Asset Classes
1. Bonds and Fixed Income Instruments
Bonds are the most directly rate-sensitive assets. When interest rates rise, existing bond prices fall because new bonds offer higher yields. Conversely, when rates fall, bond prices rise. Long-duration bonds are more sensitive than short-duration bonds. Traders often use government bonds, treasury futures, and interest rate swaps to express views on rate direction.
In India, instruments like Government Securities (G-Secs), T-Bills, and corporate bonds respond strongly to RBI policy decisions, inflation data, and liquidity conditions.
2. Banking and Financial Stocks
Banks and NBFCs are highly rate-sensitive because interest rates affect their net interest margins (NIMs). Moderate rate hikes can benefit banks by improving lending spreads, but aggressive hikes can reduce credit demand and increase non-performing assets. Rate cuts, on the other hand, stimulate loan growth but may compress margins.
Traders often position in banking stocks or indices like Bank Nifty based on expectations of RBI policy changes.
3. Real Estate and Infrastructure
Real estate companies are extremely sensitive to interest rates because property purchases are largely debt-financed. Lower interest rates reduce EMIs, increase affordability, and boost demand, leading to higher prices and volumes. Rising rates typically slow down sales and pressure valuations. Infrastructure stocks also react similarly due to high capital expenditure and long-term borrowing needs.
4. High-Growth and Technology Stocks
Growth stocks derive much of their value from future earnings. Higher interest rates increase the discount rate used in valuation models, reducing the present value of those future cash flows. As a result, technology and new-age stocks often underperform in rising rate environments and outperform when rates fall.
5. Currencies (Forex Market)
Interest rate differentials between countries are a major driver of currency movements. Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, strengthening the currency, while lower rates can weaken it. Traders use carry trades, where they borrow in low-yielding currencies and invest in high-yielding ones, to exploit rate differences.
For example, RBI rate decisions impact the INR through capital flows, bond yields, and inflation expectations.
6. Commodities and Gold
Gold is inversely related to real interest rates. When interest rates rise (especially real rates), gold becomes less attractive because it does not generate yield. When rates fall or inflation rises faster than rates, gold often performs well. Industrial commodities may also react indirectly, as rates influence economic growth and demand.
Trading Strategies for Rate-Sensitive Assets
Monetary Policy Anticipation
Successful traders focus on anticipating central bank actions rather than reacting after decisions are announced. Inflation data, GDP growth, employment numbers, and central bank commentary are closely monitored. Positioning ahead of RBI, Fed, or ECB meetings can offer strong risk-reward opportunities.
Yield Curve Strategies
Instead of betting only on rate direction, traders analyze the yield curve (the relationship between short-term and long-term rates). Curve steepening or flattening trades can be executed using bond futures or sector rotation strategies.
Sector Rotation in Equities
In rising rate environments, traders often rotate into value stocks, banks, and defensive sectors. In falling rate cycles, capital typically flows into growth stocks, real estate, and capital-intensive sectors. Understanding this rotation helps equity traders align with macro trends.
Hedging with Derivatives
Interest rate futures, swaps, and options allow traders to hedge exposure. For example, equity traders may hedge rate risk using bond futures, while bond traders may use options to protect against sudden yield spikes.
Risks in Trading Rate-Sensitive Assets
Rate-sensitive trading carries unique risks. Central bank decisions can be unpredictable, especially during periods of high inflation or geopolitical stress. Sudden policy shifts can cause sharp market moves. Additionally, markets often price in expectations well in advance, leading to “buy the rumor, sell the news” reactions.
Another risk is misjudging the difference between nominal and real interest rates. Assets often respond more strongly to real rates (interest rates adjusted for inflation) than headline policy rates.
Conclusion
Trading rate-sensitive assets requires a strong understanding of macroeconomics, monetary policy, and market psychology. Interest rates influence nearly every asset class, making them a powerful driver of global markets. By identifying which assets are most sensitive, understanding the transmission mechanism of rate changes, and aligning strategies with the interest rate cycle, traders can uncover consistent opportunities.
In a world of dynamic central bank policies and evolving inflation trends, mastering rate-sensitive asset trading is not optional—it is essential for long-term success in modern financial markets.
Momentum Strategies: Riding the Strength of Market TrendsUnderstanding the Concept of Momentum
Momentum in financial markets refers to the rate of acceleration of an asset’s price movement. It does not focus on intrinsic value or fundamentals alone, but rather on price behavior and market psychology. When prices move persistently in one direction, it reflects collective market conviction. Momentum strategies aim to capture this conviction early and stay in the trade as long as the trend remains intact.
Momentum can be measured over different horizons. Short-term momentum may last from a few minutes to days and is commonly used by intraday and swing traders. Medium-term momentum typically spans weeks to months, while long-term momentum, often used by investors and funds, can extend over six months to a year or more.
The Behavioral Foundation of Momentum
One of the strongest explanations for momentum comes from behavioral finance. Investors do not always react instantly or rationally to new information. When positive news emerges, many participants initially underreact. As prices start rising, more investors notice the move and enter late, pushing prices even higher. Similarly, bad news can trigger gradual selling rather than an immediate price collapse.
Psychological biases such as herding, confirmation bias, fear of missing out (FOMO), and loss aversion all contribute to momentum. As trends become visible, market participants tend to follow them, reinforcing the price movement. Momentum strategies attempt to systematically exploit these recurring human behaviors.
Types of Momentum Strategies
Momentum strategies can be broadly classified into several categories based on timeframe and execution style.
Time-Series Momentum (Trend Following):
This approach focuses on an asset’s own past returns. If an asset has delivered positive returns over a given lookback period, the strategy takes a long position; if returns are negative, it may go short or exit. Moving averages, breakouts, and trend filters are commonly used in this form of momentum.
Cross-Sectional Momentum (Relative Strength):
Here, assets are ranked against each other. Traders buy the strongest-performing assets and sell or avoid the weakest ones. For example, in equities, a trader might rank stocks by their 6- or 12-month performance and invest in the top performers. This method is popular in portfolio construction and factor investing.
Short-Term Momentum:
Short-term momentum strategies attempt to capture rapid price movements driven by news, volume spikes, or intraday trends. These strategies require fast execution, tight risk controls, and often rely on technical indicators like RSI, MACD, and VWAP.
Tools and Indicators Used in Momentum Trading
Momentum strategies rely heavily on technical analysis. Common tools include moving averages, which help identify trend direction and strength. Crossovers of short-term and long-term moving averages are frequently used as entry and exit signals.
Indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Stochastic Oscillator measure the speed and magnitude of price changes. While these indicators are sometimes associated with overbought and oversold conditions, in momentum trading they are often used differently. Strong momentum can remain overbought for extended periods, and experienced momentum traders avoid fading such strength prematurely.
Price breakouts above resistance levels or below support levels are another key component. Breakouts often signal the start or continuation of momentum as new participants enter the market.
Risk Management in Momentum Strategies
Despite their effectiveness, momentum strategies carry unique risks. One of the most significant is the risk of sharp reversals. Momentum trades can unwind quickly when sentiment shifts, leading to sudden losses. Therefore, disciplined risk management is essential.
Stop-loss orders are a critical component of momentum trading. They help limit losses when trends fail unexpectedly. Position sizing is equally important; allocating too much capital to a single momentum trade can be devastating if the trend reverses.
Diversification across assets, sectors, or timeframes can reduce reliance on any single trend. Many professional momentum strategies operate as part of a diversified portfolio rather than as standalone bets.
Momentum Across Asset Classes
Momentum strategies are not limited to equities. They are widely used in commodities, currencies, bonds, and cryptocurrencies. In commodities, momentum often reflects supply-demand imbalances and macroeconomic cycles. In currencies, momentum can be driven by interest rate differentials and central bank policies. In crypto markets, momentum is especially pronounced due to high volatility and strong retail participation.
The adaptability of momentum strategies across asset classes is one reason they are favored by hedge funds, commodity trading advisors (CTAs), and quantitative funds.
Advantages and Limitations
One of the biggest advantages of momentum strategies is their simplicity and empirical support. Numerous academic studies have shown that momentum has delivered persistent excess returns over long periods. Momentum strategies are also adaptable and can be systematically implemented.
However, they are not without limitations. Momentum strategies often underperform during range-bound or choppy markets where prices lack clear direction. They can also suffer during sudden regime changes, such as market crashes or sharp policy shifts, when trends reverse violently.
Additionally, momentum requires patience and discipline. Traders must be willing to buy assets that already appear expensive and sell assets that feel cheap, which can be psychologically challenging.
Conclusion
Momentum strategies are a powerful way to participate in financial markets by aligning trades with prevailing trends rather than fighting them. Rooted in both market behavior and human psychology, momentum has proven to be a durable and versatile trading approach. When combined with robust risk management, clear rules, and emotional discipline, momentum strategies can serve as a reliable framework for traders and investors seeking consistent performance across different market environments.
Mastering Option TradingA Complete Guide to Building Skill, Discipline, and Consistency
Mastering option trading is a journey that blends market knowledge, mathematical understanding, strategic thinking, and emotional discipline. Unlike simple buying and selling of stocks, options are multi-dimensional instruments whose value changes with price, time, volatility, and market expectations. Because of this complexity, option trading offers powerful opportunities—but only to those who approach it with structure, patience, and continuous learning.
1. Understanding the Foundation of Options
At its core, an option is a derivative contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) before or on a certain date (expiry). There are two primary types:
Call options, which benefit from rising prices.
Put options, which benefit from falling prices.
To master option trading, one must fully understand intrinsic value, time value, expiration cycles, and the difference between in-the-money, at-the-money, and out-of-the-money options. Without a solid foundation, advanced strategies become risky guesses rather than calculated trades.
2. The Role of Option Greeks
Option Greeks are the backbone of professional option trading. They measure how an option’s price responds to different variables:
Delta shows price sensitivity to the underlying asset.
Gamma measures how Delta changes.
Theta reflects time decay.
Vega indicates sensitivity to volatility.
Rho captures interest rate impact.
Mastering options means thinking in Greeks rather than just price direction. Successful traders understand how Theta decay works in their favor as sellers, or how Vega expands premiums during high volatility. This knowledge transforms trading from speculation into probability-based decision-making.
3. Volatility: The Heartbeat of Options
Volatility is to options what fuel is to an engine. Implied volatility (IV) represents market expectations of future price movement, while historical volatility shows past behavior. Mastery involves recognizing when options are overpriced or underpriced relative to volatility.
High IV environments favor option selling strategies like credit spreads, iron condors, and strangles. Low IV conditions often favor option buying strategies such as long calls, puts, or debit spreads. Understanding volatility cycles allows traders to align strategies with market conditions rather than forcing trades.
4. Strategy Selection and Market Context
One of the biggest mistakes beginners make is using the same strategy in every market. Mastering option trading requires adapting strategies to:
Trending markets
Range-bound markets
High-volatility events (results, news, macro data)
Low-volatility consolidation phases
For example, directional trades work best in strong trends, while non-directional strategies perform better in sideways markets. Professionals always ask: What is the market environment, and which strategy fits it best?
5. Risk Management: The True Edge
In option trading, risk management is more important than strategy selection. Even the best strategy can fail without proper position sizing and defined risk. Master traders:
Limit risk per trade (often 1–2% of capital).
Use defined-risk strategies.
Avoid overleveraging and revenge trading.
Plan exits before entering trades.
Options magnify both gains and losses, so discipline in risk management is what ensures survival during inevitable losing streaks.
6. Psychology and Emotional Control
Mastering option trading is as much a psychological challenge as it is a technical one. Fear, greed, impatience, and overconfidence are common emotional traps. Successful traders cultivate:
Patience to wait for high-probability setups.
Discipline to follow rules consistently.
Emotional neutrality toward wins and losses.
Acceptance that losses are part of the game.
Without emotional control, even deep knowledge of options can lead to inconsistent results.
7. Event-Based and Income Strategies
Advanced option traders often focus on event-based trading (earnings, economic data, policy decisions) and income generation. Strategies such as covered calls, cash-secured puts, and calendar spreads allow traders to generate consistent returns with controlled risk.
Mastery lies in understanding probabilities, adjusting positions, and managing trades dynamically rather than holding blindly until expiry.
8. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Markets evolve, volatility regimes change, and strategies that worked yesterday may underperform tomorrow. Master option traders maintain journals, review trades, track statistics, and refine their edge continuously.
They invest time in:
Backtesting strategies.
Studying market behavior.
Learning from mistakes.
Staying updated with macroeconomic trends.
9. Building a Professional Trading Mindset
True mastery comes when trading becomes systematic rather than emotional. This means having:
A written trading plan.
Clear entry, adjustment, and exit rules.
Realistic expectations.
Long-term focus over short-term excitement.
Option trading is not about hitting jackpots; it is about compounding small, consistent edges over time.
Conclusion
Mastering option trading is a gradual process that rewards discipline, knowledge, and patience. It requires understanding not just direction, but time, volatility, and probability. Those who treat option trading as a structured business—rather than a gamble—unlock its true potential. With the right mindset, risk management, and continuous learning, option trading can evolve from confusion to confidence, and from inconsistency to long-term success.
Option Greeks and Advanced Hedging Strategies1. Understanding Option Greeks
Option Greeks are mathematical derivatives that measure the sensitivity of an option’s price to different factors. Each Greek represents a specific dimension of risk.
2. Delta – Directional Risk Management
Delta measures how much an option’s price changes for a one-unit change in the underlying asset price.
Call options have positive delta (0 to +1)
Put options have negative delta (0 to -1)
At-the-money options typically have delta around ±0.5
Practical Use in Hedging:
Delta is used to hedge directional exposure
A delta-neutral portfolio is constructed by offsetting option delta with the underlying asset
Commonly used by market makers and professional traders
Example:
If a portfolio has +0.60 delta, selling 60 shares (or equivalent futures) neutralizes directional risk.
3. Gamma – Managing Delta Stability
Gamma measures the rate of change of delta with respect to the underlying price.
High gamma means delta changes rapidly
At-the-money options have the highest gamma
Gamma increases as expiry approaches
Importance in Advanced Hedging:
Gamma risk is critical for short option sellers
Large price movements can cause delta to shift sharply
Traders hedge gamma by adjusting delta frequently (dynamic hedging)
Institutional Insight:
Gamma-neutral hedging is essential for portfolios that must remain stable across volatile conditions.
4. Theta – Time Decay Control
Theta represents the rate at which an option loses value as time passes, assuming all else remains constant.
Always negative for option buyers
Positive for option sellers
Accelerates near expiry
Hedging Applications:
Theta-neutral portfolios balance time decay
Used in calendar spreads and diagonal spreads
Institutions combine theta-positive strategies with delta-neutral positioning
Strategic Perspective:
Theta is the silent force in options trading, rewarding patience for sellers and punishing indecision for buyers.
5. Vega – Volatility Risk Hedging
Vega measures sensitivity to changes in implied volatility.
Higher vega for longer-dated options
At-the-money options have maximum vega
Vega is not constant and changes with market conditions
Advanced Volatility Hedging:
Vega-neutral portfolios protect against volatility shocks
Used heavily during earnings, events, and macro announcements
Traders hedge vega using options with different expiries or strikes
Professional Use Case:
Funds hedge volatility exposure to avoid losses from IV crush or sudden volatility spikes.
6. Rho – Interest Rate Sensitivity
Rho measures sensitivity to changes in interest rates.
More relevant for long-dated options
Calls benefit from rising rates; puts lose value
Minor impact in short-term retail trading
Institutional Relevance:
Important in currency options and long-term index options
Used by banks and structured product desks
7. Advanced Hedging Strategies Using Greeks
A. Delta-Neutral Hedging
Eliminates directional risk
Portfolio profit depends on volatility and time decay
Requires frequent rebalancing
Used by:
Market makers, arbitrage desks, and volatility traders
B. Gamma Scalping
Traders remain delta-neutral
Buy low and sell high in the underlying asset
Profits from volatility rather than direction
Key Requirement:
Low transaction costs and high liquidity
C. Vega Hedging and Volatility Spreads
Combine long and short options to neutralize vega
Calendar spreads hedge near-term volatility risk
Used extensively during earnings seasons
D. Theta Harvesting Strategies
Iron condors, butterflies, and credit spreads
Designed to benefit from time decay
Require strict risk management against sudden price moves
8. Portfolio-Level Hedging Using Greeks
Instead of hedging individual trades, professionals hedge entire portfolios.
Net delta, gamma, vega, and theta are calculated
Hedges are applied at portfolio level
Reduces transaction costs and over-hedging
This approach is widely used by hedge funds and proprietary trading desks.
9. Dynamic Hedging vs Static Hedging
Static Hedging:
Hedge established once
Suitable for low volatility environments
Dynamic Hedging:
Continuous adjustment based on Greek changes
Essential during volatile markets
Requires discipline and automation
Advanced traders prefer dynamic hedging for accuracy and flexibility.
10. Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
Greeks are linear approximations. In real markets:
Large moves break assumptions
Stress testing evaluates portfolio under extreme conditions
Scenario analysis simulates volatility spikes, gap opens, and crashes
Institutions combine Greeks with Value at Risk (VaR) and stress models.
11. Common Mistakes in Greek-Based Hedging
Over-hedging small risks
Ignoring correlation between Greeks
Neglecting transaction costs
Focusing only on delta while ignoring gamma and vega
Assuming Greeks remain constant
Successful hedging requires continuous monitoring and adjustment.
12. Strategic Importance of Greeks in Modern Markets
Option Greeks transform options trading from speculation into risk engineering. Advanced hedging strategies allow traders to:
Isolate specific risk factors
Monetize volatility and time decay
Protect portfolios during uncertainty
Improve consistency and survivability
In highly volatile and algorithm-driven markets, understanding Greeks is no longer optional—it is essential.
Conclusion
Option Greeks form the backbone of professional options trading and advanced hedging. Delta controls direction, gamma governs stability, theta defines time decay, vega manages volatility, and rho addresses interest rate exposure. When these Greeks are strategically combined, traders can design sophisticated hedging structures that perform across market cycles. Mastery of Greeks shifts the trader’s mindset from prediction to probability, from gambling to structured risk management—an indispensable evolution for long-term success in options markets.
Part 10 Trade Like Institutions Income Generation – Traders Use Options to Earn Regular Income
Option selling is extremely popular among professional traders because it provides regular, consistent income.
Why Option Selling Works
Most options expire worthless
Time decay (Theta) works in favor of sellers
They can design strategies with high win rates
Market stays sideways most of the time
Popular Income Strategies
Covered Calls
Cash-Secured Puts
Iron Condors
Credit Spreads
Short Strangles (experienced traders only)
This income-based approach makes options attractive not only for speculators but also for stable monthly earners.
Part 9 Trading Master Class Options Allow High Reward Compared to Risk
Options have an asymmetric payoff.
For buyers:
Maximum loss is limited
Maximum profit can be unlimited (for calls) or very large (for puts)
For sellers:
High probability of winning
Small and consistent profits
This ability to balance risk vs reward is what attracts different types of traders:
Aggressive traders → Buy options for big moves
Conservative traders → Sell options for steady income
Both types of traders find value in the options market.
Part 6 Institutional TradingLimited Risk for Buyers – You Know Maximum Loss in Advance
In normal stock trading or futures trading, losses can be unlimited. But with options, especially when you buy them, the maximum loss is the premium you pay.
This gives traders:
Peace of mind
Better risk control
More confidence in taking trades
Protection from sudden market crashes
Why traders love this?
Because they can take directional bets without worrying about:
Huge stop-losses
Gaps against their position
Sudden volatility spikes
News-based market crashes
For example:
You buy a Nifty 22,000 CE for ₹70.
Even if the market crashes 500–1000 points, your maximum loss is ₹70 per lot×lot size.
This predictability of risk makes options extremely attractive.
Part 4 Institutional TradingOptions Provide Leverage – Small Capital, Big Exposure
One of the strongest reasons traders use options is leverage. With a small amount of capital (called the premium), traders can control a much larger underlying position.
Example of Leverage
Buying 1 lot of Nifty futures may require ₹1.2 lakh margin.
But buying a Nifty option may cost just ₹1,500–₹5,000 depending on strike price and volatility.
This means:
Small capital controls big value
Potential profits can be large relative to cost
Options offer a low-risk way to speculate
Leverage is extremely attractive, especially for small and medium retail traders.
However, leverage cuts both ways.
Losses can also happen faster if the trade goes wrong.
But the real advantage is:
Option buyers have limited losses (only premium), unlimited gains.
This asymmetric payoff attracts many traders.
CANBK 1 Month Time Frame 📌 Current Price Context
Canara Bank is trading around ₹149–₹150 on NSE.
52‑week high ~₹154.21 and low ~₹78.60.
📊 1‑Month Timeframe – Key Levels
🔹 Immediate Resistance Levels
These are the levels where price may struggle to move higher:
Level Description
₹150–₹151 Immediate resistance zone seen from pivot bands & recent highs.
₹152–₹153 Stronger resistance, break above suggests continued upside.
₹155+ 52‑week high area — key breakout zone.
🔸 Support Levels
These are important on pullbacks:
Level Description
₹147–₹148 Immediate support zone (short‑term pivot).
₹145–₹146 Next strong support on 1‑month moves.
₹143–₹144 Broader support zone if deeper retracement happens.
📈 1‑Month Technical Outlook (Summary)
🔄 Trend Indicators (Monthly View)
Monthly pivot point ~ ₹146.88 — this is a key center price for the past month’s activity.
Price currently above pivot, favoring mildly bullish/neutral short‑term tone.
📉 Momentum Summary
Multiple technical sites show mixed signals for short vs. long momentum, but daily/weekly signals often lean buy/strong buy.
📍 Practical Levels for 1‑Month Trading
Bullish Scenario
If price breaks and holds above ₹152–₹153, next upside target ~ ₹155–₹157+.
Neutral Zone
Between ₹147–₹152 — range trading possible.
Bearish Scenario
A break below ₹145 may open pathway to lower supports around ₹143–₹140.
Bonds and Fixed Income Trading StrategiesNavigating Stability, Yield, and Risk
Bonds and fixed income instruments form the backbone of global financial markets, providing stability, predictable income, and diversification to investors and traders alike. Unlike equities, which are driven largely by growth expectations and corporate performance, bonds are influenced by interest rates, inflation, credit quality, and macroeconomic policy. Fixed income trading strategies aim to generate returns through interest income, price appreciation, or relative value opportunities while managing risks such as interest rate volatility, credit events, and liquidity constraints. Understanding these strategies is essential for traders, portfolio managers, and policymakers operating in an increasingly complex financial environment.
Understanding Bonds and Fixed Income Markets
Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, and institutions to raise capital. In exchange, issuers promise to pay periodic interest (coupon) and return the principal at maturity. Fixed income markets include government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, treasury bills, notes, debentures, and structured products. The “fixed income” label reflects the predictable cash flows, although bond prices themselves fluctuate based on market conditions.
The bond market is heavily influenced by interest rates set by central banks. When interest rates rise, bond prices generally fall, and when rates fall, bond prices rise. Inflation expectations, fiscal deficits, monetary policy signals, and global capital flows also play a major role. As a result, fixed income trading strategies often combine macroeconomic analysis with quantitative techniques and risk management frameworks.
Interest Rate Trading Strategies
One of the most common fixed income strategies is interest rate trading. Traders seek to profit from anticipated changes in interest rates or yield curves. Directional strategies involve taking long or short positions in bonds based on expectations of rate cuts or hikes. For example, if a trader expects rates to decline, they may buy long-duration bonds to benefit from price appreciation.
Yield curve strategies focus on the shape and movement of the yield curve rather than absolute rate levels. Strategies such as curve steepeners and flatteners involve positioning for changes in the spread between short-term and long-term interest rates. A steepener strategy benefits when long-term rates rise faster than short-term rates, while a flattener benefits when the spread narrows. These strategies are widely used by banks, hedge funds, and institutional investors.
Carry and Roll-Down Strategies
Carry and roll-down strategies are popular among fixed income traders seeking relatively stable returns. Carry refers to the income earned from holding a bond, typically the coupon minus funding costs. Roll-down refers to the price appreciation that occurs as a bond moves closer to maturity and “rolls down” the yield curve to a lower yield point.
Traders often select bonds with attractive carry and roll-down characteristics, especially in stable or moderately declining rate environments. While these strategies can generate steady income, they are vulnerable to sudden interest rate spikes or yield curve shifts, making risk management crucial.
Credit Trading Strategies
Credit strategies focus on the credit quality of bond issuers. Traders analyze credit spreads, which represent the yield difference between a corporate bond and a comparable government bond. When traders expect a company’s creditworthiness to improve, they may buy its bonds, anticipating a tightening of spreads and price gains. Conversely, if credit risk is expected to increase, traders may short bonds or buy credit protection.
High-yield and distressed debt strategies fall under credit trading. These involve investing in lower-rated bonds that offer higher yields but carry greater default risk. Successful credit strategies rely on deep fundamental analysis, including balance sheets, cash flows, industry trends, and macroeconomic conditions.
Relative Value and Arbitrage Strategies
Relative value strategies aim to exploit pricing inefficiencies between related fixed income securities. These strategies are generally market-neutral, meaning they seek to profit regardless of overall market direction. Examples include bond spread trades, swap spread trades, and treasury versus futures arbitrage.
In these strategies, traders simultaneously take long and short positions in similar instruments that are mispriced relative to historical or theoretical values. While returns may be modest, leverage is often used to enhance profitability. However, these strategies require sophisticated risk controls, as unexpected market dislocations can lead to significant losses.
Inflation-Linked and Real Return Strategies
Inflation-linked bonds, such as inflation-indexed government securities, provide protection against rising inflation. Trading strategies in this space focus on breakeven inflation rates, which represent the market’s inflation expectations. Traders may position themselves based on views about future inflation, central bank credibility, and supply-demand dynamics.
Real return strategies are especially important during periods of high inflation uncertainty. These strategies help preserve purchasing power while offering diversification benefits to traditional nominal bond portfolios.
Liquidity and Volatility-Based Strategies
Liquidity plays a critical role in fixed income markets, which can become fragmented and less transparent during periods of stress. Some traders focus on liquidity premiums, buying less liquid bonds at a discount and holding them until liquidity improves. Others trade volatility through options on bonds, interest rates, or bond futures.
Volatility-based strategies involve positioning for changes in interest rate volatility rather than rate direction. These strategies are often used by hedge funds and sophisticated institutional players, as they require advanced models and derivatives expertise.
Risk Management in Fixed Income Trading
Risk management is central to all bond trading strategies. Key risks include interest rate risk, credit risk, inflation risk, currency risk, and liquidity risk. Duration and convexity are widely used metrics to measure sensitivity to interest rate changes. Credit exposure is managed through diversification, position limits, and hedging instruments such as credit default swaps.
Stress testing and scenario analysis are also essential, especially in an era of rapid policy shifts and geopolitical uncertainty. Effective risk management ensures that fixed income strategies remain resilient across different market cycles.
Conclusion
Bonds and fixed income trading strategies offer a wide range of opportunities, from stable income generation to sophisticated relative value and macro-driven trades. While often perceived as conservative, fixed income markets are dynamic and deeply interconnected with global economic forces. Successful trading requires a strong understanding of interest rates, credit dynamics, yield curves, and risk management techniques. As financial markets evolve, bonds and fixed income strategies will continue to play a vital role in portfolio construction, capital preservation, and long-term financial stability.
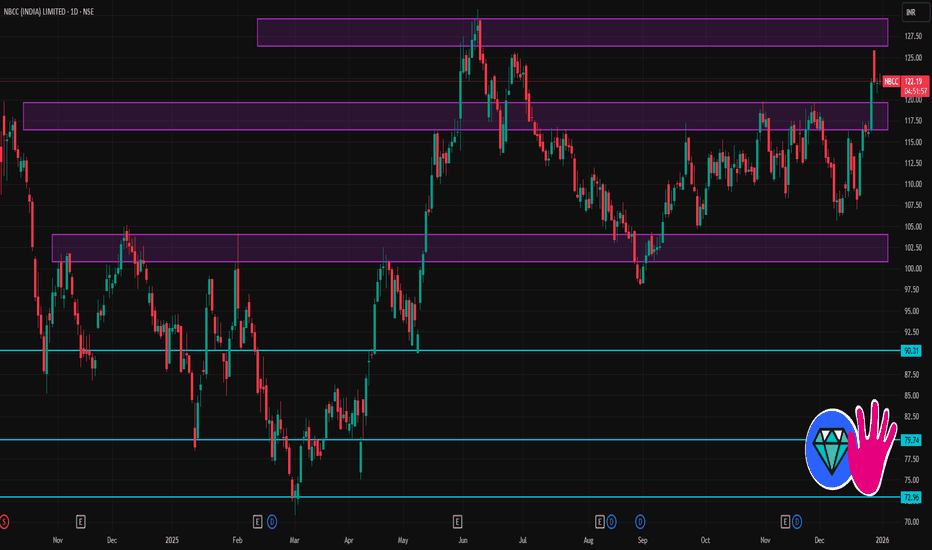
NBCC 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Live Price (Daily)
Current trading price: ~₹122.0 – ₹122.7 per share during the session.
Today’s range: ₹121.7 – ₹123.1.
52-Week range: ₹70.80 – ₹130.70.
📊 Daily Pivot & Key Levels
Daily Pivot Point (standard):
Pivot (P): ~₹122.7 – Acts as the central bias level.
Daily Support Levels:
S1: ~₹121.7
S2: ~₹120.9
S3: ~₹119.9
(Lower supports can act as short-term buy zones on pullbacks.)
Daily Resistance Levels:
R1: ~₹123.5
R2: ~₹124.5
R3: ~₹125.8
📊 Short-Term Technical Notes
✅ Above daily pivot (₹122–₹123) → bullish intraday bias.
❗ If price fails to hold above pivot → may test support levels.
⚠ Volume and momentum indicators should confirm breakouts.
📉 Trading Bias (Intraday)
Bullish conditions likely if:
✔ Maintains above ₹122.7 pivot
✔ Break above ₹124.5–₹125.0 resistance
Bearish conditions if:
✔ Breakdown below ₹121.7–₹120.9 support
✔ Then watch ₹119–₹118 support zone
VIPIND 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Price Action (Latest):
• Last traded around ₹379–₹380 in recent sessions. Daily price range seen near ₹374–₹384.
📊 Daily Pivot & Key Levels (Current)
Based on pivot-point calculations from live technical data:
📍 Pivot Zones (Daily):
• Central Pivot (Standard): ~₹403.27
📈 Resistance Levels:
• R1: ~₹420.13
• R2: ~₹430.37
(above current price – upside targets)
📉 Support Levels:
• S1: ~₹393.03
• S2: ~₹376.17
• S3: ~₹365.93
• S4: ~₹349.07
📌 Support/Resistance Summary (Daily):
Near-term resistance: ~393–420
Immediate support: ~376–365
Deeper support: ~350 and below
📌 Short-Term Intraday/1-Day Reaction Levels
Based on recent technical analysis:
Upside Resistance:
~₹386–₹393 (near current trading highs)
~₹400+ (psychological/local resistance)
Downside Support:
₹376–₹374 (short-term support)
₹371–₹369 (secondary support
₹365 / lower (deeper level)
📈 How to Use These Levels Today
Bullish scenario:
✔ If price holds above ₹376–₹380 range and breaks ₹393+, upside toward ₹400–₹420 becomes probable.
Bearish scenario:
✘ If price breaks below ₹374–₹370, the next support targets are ₹365 and then ₹350.
Neutral / Range:
📍 Between ₹374–₹393, expect sideways or consolidation movement in the 1-day chart.