Divergence Secrets Intrinsic Value and Time Value
An option premium has two parts:
Intrinsic Value
The actual profit you would make if option were exercised now.
Time Value
Extra value based on:
Time left to expiration
Volatility
Market expectations
As expiry gets closer, time value decays—this is why options depreciate faster near expiry.
Trendlineanalysis
Part 2 Candle Stick Patterns How Put Options Work
Put Buyer
A put buyer expects the price to fall.
If stock is at ₹100 and you buy a Put Option at ₹95 for a premium of ₹4:
If stock falls to ₹80 → Profit
If stock stays above ₹95 → Loss limited to ₹4 premium
Put Seller
Expects price to stay above the strike.
They earn the premium but face large losses if price falls significantly.
Part 1 Support and Resistance What Are Options?
Options are derivative contracts—their value is derived from an underlying asset such as a stock, index, commodity, or currency.
Each option gives the buyer a right, but not an obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price (called the strike price) on or before a specific date (called the expiry date).
There are two types of options:
Call Options – Gives the right to buy the asset.
Put Options – Gives the right to sell the asset.
You pay a fee to purchase this right. That fee is called the premium.
Candle Patterns ExplainedBasics of Candlesticks
A standard candlestick contains:
Body: Difference between open and close
Wicks/Shadows: High and low
Color: Bullish (often green/white) or bearish (red/black)
The structure itself provides signals:
Long bodies → strong momentum
Small bodies → indecision
Long wicks → rejection or strong counterforce
No wick → full control by one side
Understanding this foundation helps interpret every pattern that follows.
APLAPOLLO 1 Day Time Frame 🔹 Recent Price Context (Indicative)
The stock is trading around ~₹1,850‑₹1,880 levels (recent session range) with a 52‑week high near ₹1,936 and low near ₹1,273.
📊 Intraday / 1‑Day Key Levels (Support & Resistance)
📈 Resistance Levels
These can act as intraday ceilings where price may stall or reverse:
R1: ~₹1,871‑₹1,875 area
R2: ~₹1,885‑₹1,900
R3: ~₹1,895‑₹1,915
(based on pivot analysis around recent highs/multiple technical sources)
📉 Support Levels
These are levels where price might find buying interest on a dip:
S1: ~₹1,840‑₹1,848
S2: ~₹1,830‑₹1,837
S3: ~₹1,825‑₹1,830
(short‑term pivot supports from multiple intraday pivot estimates)
Notes on pivots (classic & Fibonacci):
Pivot mid‑point often lies near ~₹1,860–₹1,865 on the day.
📍 Intraday Trading Tips
✔ Above the pivot (~₹1,860) → bullish bias for the day
✔ Below the pivot → intraday sellers may dominate
✔ Watch volume spikes at support or resistance for breakout confirmation.
Pivot and MA signals show a positive short‑term trend.
Chart Patterns: Deep, Easy & Practical GuideWhy Chart Patterns Matter
Every candle represents a war:
Buyers want price higher, sellers want price lower.
When multiple candles form repeated structures — triangles, flags, W-shaped patterns — it signals:
Market exhaustion
Momentum imbalance
Consolidation before expansion
Liquidity grabs
Trend reversals
Institutions often place orders at predictable zones:
Break of structure (BOS)
Lower highs / higher lows
Double tops / bottoms
Range highs and lows
Chart patterns help us read these footprints.
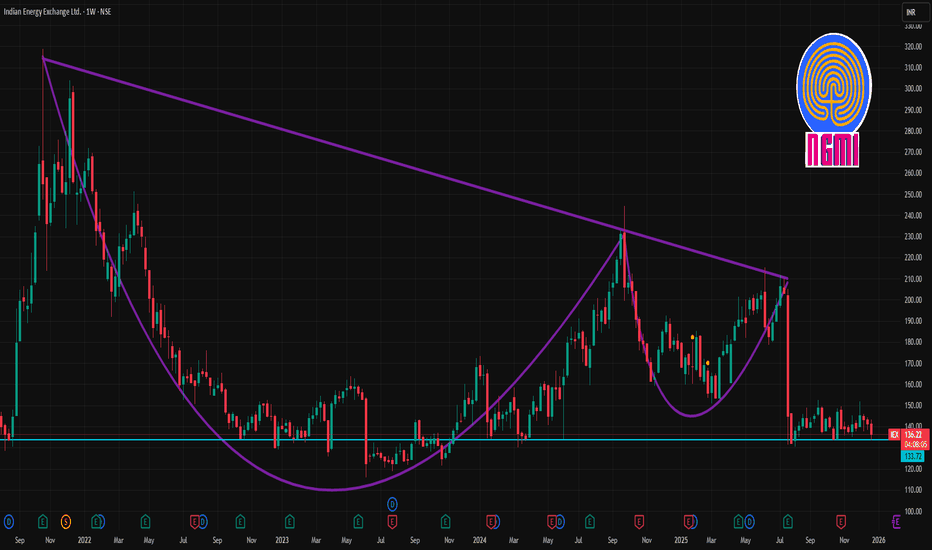
IEX 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Context
IEX is trading around ₹138–₹142 range recently.
Short‑term technical indicators show bearish bias but mixed signals overall.
📌 1‑Week Key Levels (Support & Resistance)
📈 Resistance Levels
1. ~₹142–₹143 — Immediate resistance / pivot cluster (key short term)
2. ~₹144–₹145 — Next resistance barrier, breakout level for bullish bias
3. ~₹147–₹150 — Major weekly resistance region (higher breakout zone)
📉 Support Levels
1. ~₹138–₹140 — Immediate support zone (near current value)
2. ~₹135–₹136 — Secondary support if breakdown below immediate zone
3. ~₹133–₹132 — Stronger lower support / swing lows for the week
📍 Short‑Term Technical Sentiment
Weekly ratings suggest a sell/neutral bias, indicating pressure below key resistances.
Oscillators (RSI/MACD) also point to bearish momentum on short timeframes.
📈 Actionable Levels to Watch
Bullish scenario
A clean daily close above ₹144–₹145 increases the likelihood of an upside toward ₹147–₹150.
Bearish scenario
Sustained trading below ₹138 could accelerate selling toward ₹135–₹132.
Neutral/Consolidation
Between ₹138–₹144 may remain a tight range unless triggered by a breakout move.
TITAN 1 Month Time Frame 📈 Current Price Context (as of latest market data)
• Titan is trading around ₹3,900‑₹3,925 and recently hit a 52‑week high of ~₹3,962.
• Over the past 1 month, the stock has shown a small positive return (~+0.9% according to Business Today data).
📊 1‑Month Time Frame Key Levels
🔥 Resistance Levels (Potential upside ceilings)
• R1: ~₹3,929–₹3,930
• R2: ~₹3,949–₹3,950
• R3/52W High: ~₹3,962–₹3,964 → a key breakout zone above which the next leg up may begin.
🔻 Support Levels (Potential downside floors)
• S1: ~₹3,894–₹3,895
• S2: ~₹3,879–₹3,880
• S3: ~₹3,859–₹3,860
These are short‑term pivot supports that have shown recent interest on price pullbacks.
Trend Indicators
• Short‑term moving averages (20/50/100/200‑day) are below the current price, suggesting the short/medium trend remains bullish.
• RSI is neutral (~57) — neither overbought nor oversold, giving room for momentum continuation.
⚠️ Notes
📌 These levels are drawn from commonly used technical pivot calculations and recent price action.
📌 Market behavior can shift on macro news, earnings, gold price moves (important for jewellery stocks), or broader index trends.
📌 Always combine with risk management (stop‑loss, position sizing) — technical levels are not guarantees.
HEROMOTOCO 1 Month Time Frame 📊 Key Levels for 1‑Month Time Frame
Pivot & Resistance Levels (near current price)
✔ Pivot: ~₹5,767–₹5,775
✔ R1: ₹5,810–₹5,815
✔ R2: ₹5,840–₹5,843
✔ R3: ₹5,880–₹5,885
(Source: Pivot/S3‑R3 data)
Support Levels
✔ S1: ~₹5,738–₹5,740
✔ S2: ~₹5,695–₹5,700
✔ S3: ~₹5,665–₹5,670
(Source: Pivot/S3‑R3 data)
🔍 Interpretation (1‑Month)
Resistance zones:
📈 ₹5,810–₹5,840 — first meaningful upside hurdle; break above this may open path toward ₹5,880+.
📈 Above ~₹5,880 could signal stronger bullish momentum toward recent highs.
Support zones:
📉 ₹5,738–₹5,740 — key short‑term support; breaking this could test ₹5,695.
📉 A drop below ₹5,695 may extend downward pressure toward ₹5,665/₹5,650 area.
📌 How Traders Use These Levels
➡ Bullish scenario:
Break and hold above R1 (~₹5,810) for targeting R2/R3 zones.
Volume confirmation adds strength.
➡ Bearish scenario:
Failure below support S1 (~₹5,738) can see price testing S2 (~₹5,695) & S3 (~₹5,665).
Momentum indicators trending down could increase selling pressure.
Weekly and Monthly Timeframes in TradingFramework for Consistent Market Analysis
In trading, timeframes define how a trader views the market, plans entries and exits, and manages risk. Among the most important higher timeframes are weekly and monthly charts, which are widely used by professional traders, investors, and institutions. While intraday and daily charts focus on short-term price fluctuations, weekly and monthly timeframes provide a broader market perspective, helping traders align their strategies with dominant trends, major support and resistance levels, and long-term market structure. Understanding how to use weekly and monthly timeframes effectively can significantly improve decision-making, reduce noise, and enhance consistency in trading performance.
Understanding the Weekly Timeframe in Trading
The weekly timeframe represents price movement over one full trading week, where each candlestick or bar reflects the open, high, low, and close of that week. This timeframe is particularly useful for swing traders and positional traders who aim to capture medium-term price movements lasting several weeks to a few months.
One of the primary advantages of the weekly timeframe is its ability to filter out daily volatility. Markets often experience sharp intraday or daily fluctuations driven by news, emotions, or short-term speculation. Weekly charts smooth these movements and highlight the true direction of the trend. When a stock consistently forms higher highs and higher lows on a weekly chart, it indicates strong bullish momentum, even if daily charts show temporary pullbacks.
Weekly charts are also highly effective for identifying key support and resistance levels. Levels formed on a weekly basis are generally stronger and more reliable than those on lower timeframes. A breakout above a weekly resistance or a breakdown below weekly support often signals a significant shift in market sentiment. Many institutional participants make decisions based on weekly levels, which is why price reactions around these zones tend to be powerful.
Another critical use of the weekly timeframe is trend confirmation. Traders often combine weekly charts with daily charts to ensure alignment. For example, if the weekly trend is bullish, traders may look for buying opportunities on daily pullbacks rather than taking counter-trend trades. This alignment improves probability and reduces the risk of trading against the dominant market force.
From a risk management perspective, weekly timeframes allow for wider stop-loss placements based on meaningful market structure rather than short-term noise. Although this may require smaller position sizes, it often results in more stable and disciplined trades with higher reward-to-risk potential.
Understanding the Monthly Timeframe in Trading
The monthly timeframe is the highest commonly used timeframe in technical analysis, where each candle represents one full month of price action. Monthly charts are primarily used by long-term investors, positional traders, and institutions to understand the overall market cycle and structural trend.
The biggest strength of the monthly timeframe lies in its ability to reveal the long-term trend and market phases. Whether a stock or index is in accumulation, markup, distribution, or decline becomes much clearer when viewed on a monthly chart. This helps traders avoid emotionally driven decisions and stay focused on the bigger picture.
Monthly charts are crucial for identifying major historical support and resistance zones. Levels formed over several months or years carry immense importance. When price approaches a long-standing monthly resistance, it often faces strong selling pressure. Conversely, monthly support zones tend to attract long-term buyers and institutions, making them ideal areas for strategic accumulation.
Another important application of the monthly timeframe is trend validation across market cycles. A bullish monthly structure indicates that the asset is suitable for long-term holding or buy-on-dips strategies. If the monthly trend turns bearish, traders may reduce exposure, shift to defensive strategies, or look for short-selling opportunities in relevant markets.
Monthly charts also help in understanding macro influences, such as interest rate cycles, economic growth phases, and sectoral rotations. Since these factors evolve over long periods, their impact is best observed on monthly timeframes rather than short-term charts.
Weekly vs Monthly Timeframes: Key Differences
While both weekly and monthly timeframes belong to higher timeframe analysis, they serve different purposes. The weekly timeframe is more action-oriented, helping traders fine-tune entries, exits, and trade management within the broader trend. The monthly timeframe, on the other hand, is more strategic, guiding long-term bias and portfolio positioning.
Weekly charts react faster to changes in trend compared to monthly charts, making them suitable for swing and positional trades. Monthly charts move slowly but offer stronger signals with higher reliability. A change in monthly trend is rare, but when it happens, it often marks a major shift in market dynamics.
Combining Weekly and Monthly Timeframes Effectively
Professional traders often use a top-down approach, starting with the monthly timeframe, then moving to the weekly, and finally to the daily or intraday charts. The monthly chart defines the long-term bias—bullish, bearish, or sideways. The weekly chart refines this bias by identifying actionable levels and trend strength.
For example, if the monthly trend is bullish and price is above key monthly support, traders may look for weekly pullbacks or consolidations as buying opportunities. If both monthly and weekly trends align, the probability of success increases significantly.
This multi-timeframe alignment also helps traders avoid overtrading. Instead of reacting to every minor price movement, traders focus only on setups that align with higher timeframe structure, leading to more disciplined and selective trading behavior.
Risk Management and Psychology in Higher Timeframes
Trading based on weekly and monthly timeframes naturally improves trading psychology. Since these timeframes reduce market noise, traders experience fewer emotional swings caused by small price fluctuations. Decisions become more logical, patient, and rule-based.
Risk management also becomes more structured. Stops and targets are based on well-defined levels rather than arbitrary price points. Although trades may take longer to play out, they often offer better reward-to-risk ratios and lower stress.
Conclusion
Weekly and monthly timeframes are essential tools for traders seeking consistency, clarity, and long-term success. The weekly timeframe provides a balanced view between responsiveness and reliability, making it ideal for swing and positional trading. The monthly timeframe offers a macro-level perspective, helping traders understand market cycles, structural trends, and long-term opportunities.
When used together, weekly and monthly analysis forms a powerful framework that aligns trading decisions with dominant market forces. By focusing on higher timeframes, traders can reduce noise, improve discipline, and make more informed decisions—key ingredients for sustainable profitability in the trading markets.
Option Trading vs. Stock TradingUnderstanding Stock Trading
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of publicly listed companies. When an investor buys a stock, they gain partial ownership in the company along with associated rights such as voting and dividends (if declared). Stock trading can be done for short-term gains (intraday, swing trading) or long-term wealth creation (investing).
The primary driver of stock prices is the company’s fundamentals—earnings, growth prospects, management quality, and industry trends—along with broader market sentiment and macroeconomic factors. Profit in stock trading is typically generated by buying low and selling high, or through dividends in the case of long-term investments.
One of the major advantages of stock trading is its simplicity and transparency. The maximum loss is limited to the invested amount, and there is no expiry date on shares. This makes stock trading relatively easier to understand for beginners. However, returns may be slower compared to leveraged instruments, and capital requirements can be higher if one wants to build a diversified portfolio.
Understanding Option Trading
Option trading involves trading derivative contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset such as a stock or index. An option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before or on a specified expiry date.
Options are time-bound instruments and include additional factors like time decay (theta), volatility (vega), and price sensitivity (delta, gamma). Traders can profit not only from price movement but also from changes in volatility and time decay, making options far more versatile than stocks.
Option trading allows strategies that can generate profits in rising, falling, or even sideways markets. However, this flexibility comes at the cost of higher complexity and risk. While option buyers have limited risk (premium paid), option sellers can face substantial or even unlimited losses if risk management is poor.
Risk and Reward Comparison
Stock trading generally carries lower risk compared to option trading. Since stocks do not expire, investors can hold positions through market cycles and wait for recovery. Losses are unrealized until the stock is sold, giving investors psychological and strategic flexibility.
Option trading, on the other hand, is a high-risk, high-reward activity. The leverage involved allows traders to control large positions with relatively small capital, amplifying both profits and losses. Time decay works against option buyers, meaning the value of options erodes as expiry approaches if the expected move does not happen quickly.
For disciplined and experienced traders, options can be used to hedge risk or generate consistent income. For inexperienced traders, however, options can lead to rapid capital erosion.
Capital Requirements
Stock trading typically requires higher capital to achieve meaningful returns, especially in high-priced stocks. However, margin trading in stocks is also available, though regulated and limited.
Option trading requires lower upfront capital due to leverage. A trader can participate in expensive stocks or indices with a small premium amount. This low entry barrier attracts many retail traders, but it also increases the likelihood of overtrading and excessive risk-taking.
Time Horizon and Flexibility
Stock trading suits both long-term investors and short-term traders. Investors can hold stocks for years, benefiting from compounding, dividends, and business growth. Swing and positional traders can also use stocks effectively without worrying about expiry.
Option trading is inherently short-term due to fixed expiries. Traders must be precise about timing, direction, and volatility. This makes options more suitable for active traders who can monitor markets closely and respond quickly to changing conditions.
Strategy and Skill Requirement
Stock trading strategies often revolve around fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or a combination of both. While skill is required, the learning curve is relatively gradual.
Option trading demands advanced knowledge of option Greeks, volatility analysis, probability, and risk management. Strategies such as spreads, straddles, strangles, and iron condors require careful planning and execution. Emotional discipline is also critical, as rapid profit and loss fluctuations are common.
Income Generation and Hedging
Stock trading primarily generates income through capital appreciation and dividends. It is less effective for regular income unless large capital is deployed.
Option trading excels in income generation, particularly through option selling strategies like covered calls and cash-secured puts. Options are also powerful hedging tools, allowing investors to protect stock portfolios against adverse market moves.
Psychological Impact
Stock trading is generally less stressful, especially for long-term investors. Market volatility affects portfolio value, but the absence of expiry reduces urgency.
Option trading is psychologically demanding. Rapid price changes, expiry pressure, and leveraged exposure can lead to emotional decision-making. Without discipline, traders may overtrade or chase losses.
Regulatory and Practical Considerations
In markets like India, option trading requires additional approvals and margin compliance. Regulatory frameworks are stricter due to higher risk. Transaction costs, taxes, and slippage can also significantly impact option trading profitability.
Stock trading regulations are comparatively straightforward, making it more accessible for retail participants.
Conclusion
Both stock trading and option trading have their own advantages and limitations. Stock trading is ideal for beginners, conservative traders, and long-term wealth creators who value stability and gradual growth. Option trading is better suited for experienced traders seeking leverage, income generation, and advanced risk management tools.
The choice between option trading and stock trading should depend on an individual’s risk appetite, capital availability, time commitment, and level of expertise. Importantly, these two approaches are not mutually exclusive. Many successful market participants use stocks for core investments and options for hedging or tactical opportunities. When used wisely and with discipline, both can play a valuable role in a well-rounded trading and investment strategy.
Institutional Option Writing StrategiesHow Smart Money Generates Consistent Income and Controls Risk
Institutional option writing strategies are advanced derivatives techniques used by large market participants such as hedge funds, investment banks, proprietary trading desks, insurance companies, and pension funds. Unlike retail traders, institutions approach option writing with deep capital, robust risk management systems, data-driven models, and a long-term perspective. Their primary objective is not speculation but consistent income generation, volatility monetization, and portfolio risk optimization.
Option writing (also known as selling options) involves collecting premiums by selling call or put options, benefiting from time decay (theta), volatility contraction, and probability-based outcomes. Institutions design these strategies carefully to maintain high win rates while controlling tail risks.
1. Core Philosophy Behind Institutional Option Writing
The foundation of institutional option writing lies in probability and statistics rather than directional prediction. Institutions understand that most options expire worthless due to time decay. By selling options with a high probability of expiring out-of-the-money, they position themselves as “insurance sellers” in financial markets.
Institutions also exploit the structural inefficiencies in option pricing, particularly the tendency of implied volatility to be higher than realized volatility. This volatility risk premium allows option writers to earn steady returns over time.
Key institutional principles include:
Selling options when implied volatility is elevated
Maintaining diversified option books
Avoiding naked directional exposure
Focusing on risk-adjusted returns instead of absolute returns
2. Covered Call Writing Strategy
Covered call writing is one of the most widely used institutional strategies, especially by asset managers and mutual funds. In this approach, institutions hold the underlying asset (stocks or indices) and sell call options against those holdings.
This strategy generates additional income through option premiums while slightly capping upside potential. Institutions prefer covered calls in sideways or moderately bullish markets where capital appreciation is expected to be limited.
Benefits include:
Enhanced yield on long equity positions
Partial downside protection through premium income
Lower portfolio volatility
Covered call strategies are commonly packaged into structured products and option income funds for conservative investors.
3. Cash-Secured Put Writing Strategy
Cash-secured put writing involves selling put options while holding enough cash to buy the underlying asset if assigned. Institutions use this strategy to acquire assets at discounted prices while earning premium income.
This strategy aligns well with long-term value investing. If the option expires worthless, institutions keep the premium. If assigned, they purchase the stock at an effective lower cost.
Institutional advantages include:
Disciplined asset entry points
Predictable income streams
Efficient use of idle cash
Large funds frequently deploy this strategy on index options and high-quality stocks.
4. Credit Spreads and Risk-Defined Structures
Institutions rarely sell naked options due to unlimited risk. Instead, they prefer credit spreads, which involve selling one option and buying another further out-of-the-money.
Popular spread strategies include:
Bear call spreads
Bull put spreads
Iron condors
Iron butterflies
These structures limit maximum losses while preserving a high probability of profit. Institutions use quantitative models to select strike prices that balance premium income with acceptable risk exposure.
Risk-defined strategies are essential for:
Regulatory compliance
Capital efficiency
Stress-test resilience
5. Iron Condors and Range-Bound Trading
Iron condors are a cornerstone of institutional volatility strategies. This approach involves selling both a call spread and a put spread, profiting when the underlying asset remains within a defined price range.
Institutions deploy iron condors in:
Low-volatility or mean-reverting markets
Index options such as NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, and S&P 500
Event-neutral environments
The strategy benefits from time decay on both sides and declining volatility after major events. Institutions manage these positions dynamically by adjusting strikes or reducing exposure as market conditions change.
6. Volatility Arbitrage and Vega Management
Institutional option writing is closely tied to volatility trading. Instead of betting on price direction, institutions trade volatility itself.
They analyze:
Implied volatility vs historical volatility
Volatility skew and term structure
Correlation breakdowns
When implied volatility is overpriced, institutions sell options to capture the volatility risk premium. Vega exposure is carefully managed to avoid large losses during volatility spikes.
Advanced desks hedge volatility exposure using:
Futures
Delta-neutral portfolios
Cross-asset hedges
7. Event-Based Option Writing Strategies
Institutions often write options around predictable events such as earnings announcements, economic data releases, and central bank meetings. These events inflate implied volatility, increasing option premiums.
After the event, volatility collapses, benefiting option writers. Institutions rely on historical volatility patterns and probabilistic models rather than directional forecasts.
Risk controls are strict, as unexpected outcomes can cause sharp market moves. Position sizing and defined-risk spreads are critical in these setups.
8. Portfolio-Level Option Writing
Rather than treating each option trade in isolation, institutions manage option writing at the portfolio level. They monitor:
Delta exposure
Gamma risk
Vega sensitivity
Correlation across positions
This holistic approach allows institutions to neutralize unwanted risks while maximizing theta income. Diversification across assets, expiries, and strategies reduces drawdowns and stabilizes returns.
9. Risk Management and Capital Allocation
Risk management is the most critical element of institutional option writing. Institutions impose strict limits on:
Maximum drawdowns
Margin utilization
Single-position exposure
Volatility regime shifts
Stress testing, scenario analysis, and real-time monitoring systems ensure that portfolios can withstand extreme market conditions. Institutions accept small, frequent profits while avoiding catastrophic losses.
10. Why Institutional Option Writing Consistently Outperforms Retail Approaches
The key difference between institutional and retail option writing lies in discipline, scale, and risk control. Institutions do not chase high returns or gamble on market direction. Instead, they focus on:
High-probability trades
Repeatable processes
Systematic execution
Long-term consistency
Their edge comes from data, infrastructure, and patience rather than prediction.
Conclusion
Institutional option writing strategies represent a sophisticated approach to derivatives trading, centered on probability, volatility, and risk management. By selling options strategically, institutions convert market uncertainty into steady income while maintaining controlled exposure to adverse outcomes. These strategies demonstrate that in professional trading, success is not about predicting markets, but about managing risk, exploiting statistical advantages, and maintaining consistency over time.
Part 12 Trading Master ClassHow Option Premium Is Calculated
Premium = Intrinsic Value + Time Value
Intrinsic Value (IV)
Value if the option were exercised today.
Example: Nifty at 22,000.
Call 21,800 intrinsic value = 22,000 – 21,800 = ₹200
Time Value
Extra cushion based on days left and expectations.
Near expiry, time value evaporates fastest.
Part 11 Trading Master Class Best Practices for Option Traders
To trade options effectively, follow these disciplined rules:
Focus on market structure and volume profile before entering trades.
Avoid buying options during low volatility periods.
Always hedge when selling options.
Trade liquid strikes—prefer ATM or near OTM.
Avoid holding OTM options on expiry day.
Use stop loss and position sizing.
Track Greeks, especially Theta and Delta.
Avoid revenge trades; options can wipe capital fast.
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%DON’T HAVE TIME TO MANAGE YOUR TRADES?
- Take BTST trades at 3:25 pm every day
- Try to exit by taking 4-7% profit of each trade
- SL can also be maintained as closing below the low of the breakout candle
Now, why do I prefer BTST over swing trades? The primary reason is that I have observed that 90% of the stocks give most of the movement in just 1-2 days and the rest of the time they either consolidate or fall
Trendline Breakout in ASHAPURMIN
BUY TODAY SELL TOMORROW for 5%
Part 10 Trade Like Institutions Risks in Option Trading
Options involve advanced risks:
a) Unlimited Loss for Sellers
If market moves violently, sellers face huge loss without protection.
b) High Volatility Risk
IV crush can destroy premiums instantly after news events.
c) Liquidity Risk
Low volumes lead to large bid-ask spreads.
d) Emotional Trading
Options move very fast, causing fear and overtrading.
Part 9 Trading Master Classa) Strike Price
The predetermined price at which you can buy (call) or sell (put) the asset.
b) Premium
The cost of the option. Determined by volatility, time left, and price difference from the strike.
c) Expiry Date
Options lose value over time. Closer to expiry = faster time decay.
d) Lot Size
Options are traded in fixed quantities. You cannot buy 1 unit like stocks.
e) In-the-Money (ITM), At-the-Money (ATM), Out-of-the-Money (OTM)
These terms describe how close the underlying price is to the strike.
Part 8 Trading Master ClassWhat Are Options?
Options are financial contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (like stocks, indices, commodities) at a specific price within a specific time period.
There are two basic types:
Call Option – Gives the right to buy an asset at a fixed price.
Put Option – Gives the right to sell an asset at a fixed price.
Options always involve a buyer and a seller (writer).
Buyers pay a premium to purchase the option.
Sellers receive the premium but carry the obligation to buy or sell the asset if the buyer exercises the contract.
CHART PATTERNSChart patterns reflect collective market behaviour over periods—from hours to days to months.
They help traders predict continuation or reversal of trends.
Two broad types:
A. Continuation Patterns (trend likely to continue)
B. Reversal Patterns (trend likely to reverse)
Support–Resistance and Breakouts
Most chart patterns rely on:
Breakout levels
Necklines
Trendlines
Horizontal supports/resistances
A breakout is more reliable with:
Above-average volume
Retest confirmation
Trend alignment
Strong candle close beyond levels
CANDLESTICK PATTERNS Candlestick charts originated in Japan in the 1700s. They capture four pieces of information for each time unit (1 min, 5 min, 1 hour, 1 day):
Open, High, Low, Close (OHLC).
Each candle tells a story of buying and selling pressure. Repeating stories form patterns.
We will cover:
1. Single-Candle Patterns
2. Double-Candle Patterns
3. Triple-Candle Patterns
How Candlestick Patterns Work with Market Psychology
Candlestick patterns reflect sentiment:
Long wicks → rejection
Full body → momentum
Small body → indecision
Gaps → aggressive imbalance
Patterns become stronger when:
They appear at key support/resistance
They align with trend
Volume confirms the move
They appear after an extended move (overbought/oversold conditions)
INDUSTOWER 1 Day Time Frame 📌 Current Price (NSE): ~₹423.9 – ₹424 area intraday.
📊 Today’s Price Range:
High: ~₹428.50
Low: ~₹412.00
📈 Key Daily Levels (Support & Resistance)
🔹 Intraday & Pivot Levels
Central Pivot (CPR): ~₹421.5 – ₹422.7 (important sentiment zone)
🟢 Resistance Levels
R1: ~₹430 – immediate resistance near recent high.
R2: ~₹437 – next supply zone on daily pivots.
R3: ~₹447 + (higher extension / breakout target).
🔴 Support Levels
S1: ~₹415 – first immediate support.
S2: ~₹411 – below recent intraday low.
S3: ~₹405 – stronger support zone.
S4: ~₹397 – deeper support if weakness continues.
📌 1‑Day Trading Notes
✅ Above CPR (~₹421–₹422): Positive intraday bias — buyers controlling near term.
❗ S1 (~₹415) breach: Could shift momentum lower intraday.
✨ Clear breakout above ₹430: Opens next resistance cluster toward ₹437+.
🧠 Technical Context (Daily Indicators)
Oscillators and moving averages on daily chart show bullish bias (buy and strong buy signals).
Price trading above VWAP (~₹410.5) indicates short‑term strength.
IOC 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Price (approx):
IOC trading around ₹161–₹163 on NSE/BSE recently.
📈 Weekly Resistance Levels
These are key upside levels where selling pressure may emerge this week:
1. Major Weekly Resistance Zones
R1: ~₹164–₹165
R2: ~₹167–₹168
R3: ~₹172–₹173
Why these matter:
• Above ₹164–₹165, bulls may gain control and momentum could push toward ₹168+.
• Levels above ₹170 would be significant weekly breakout territory.
📉 Weekly Support Levels
Key downside levels where buyers might step in:
1. Immediate Support
1: ~₹158–₹160
S2: ~₹155 (secondary support)
S3: ~₹151–₹150 (deeper support if breakdown)
👉 Holding above ~₹158–₹160 is important this week for near‑term bullish bias. A decisive break below opens room down toward ₹155 / ₹150.
📌 Pivot Reference (Weekly)
A commonly watched reference midpoint:
Central Pivot (~CPR): ~₹163–₹164 — acting as balance for the weekly.
Trading bias:
Above ₹164 → bullish bias.
Below ₹160 → bearish risk increases.
COALINDIA 1 Week Time Frame 📌 Current Price (approx)
Coal India is trading around ₹385 – ₹402 in live market data (varies with feed) — recent reports show it trading near ~₹400 after news‑driven moves.
📈 Weekly Time Frame — Key Levels
🔸 Immediate Resistance
1. ₹400 – ₹405 — Primary upside zone where supply historically shows selling pressure.
2. ₹405 – ₹410 — Secondary resistance if momentum continues.
3. ~₹416 – ₹420 — Broader upper range resistance (near yearly highs).
🔻 Immediate Support
1. ₹380 – ₹385 — Main weekly support zone. A weekly close above this strengthens bullish bias.
2. ₹375 – ₹378 — Next support if price dips below the main zone.
3. ~₹368 – ₹370 — Deeper demand area on stronger pullbacks.
📊 Weekly Pivot & Range
Weekly Pivot ~around ₹385–₹387 — central reference for bias (above = bullish, below = bearish for the week).
Range Expectation for the Week:
Bearish Scenario: down toward ₹370–₹375
Bullish Scenario: up toward ₹400–₹405+
🧠 How to Use These Levels
Bullish bias if weekly close > ₹400.
Neutral/Range trade between ₹380–₹400.
Bearish pressure increases only on sustained close < ₹375.