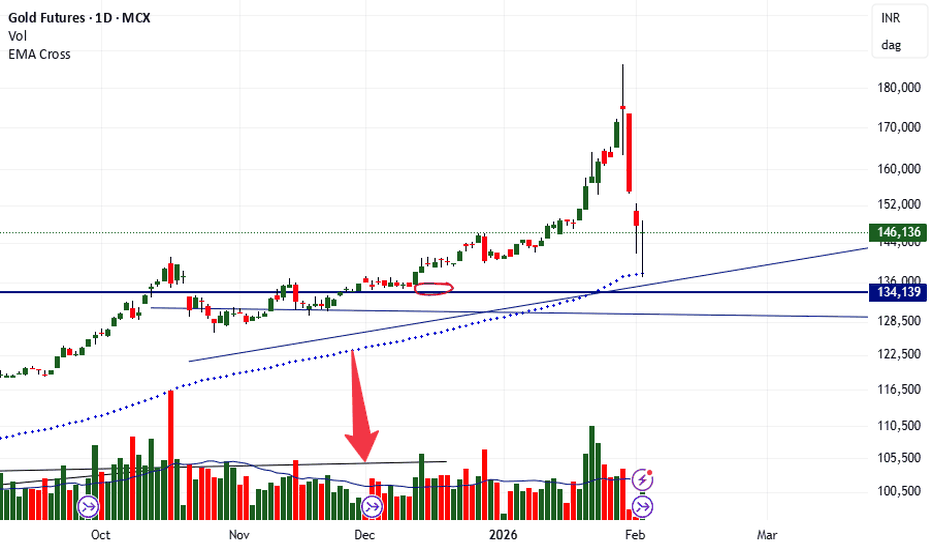
Possibility of some cooldown on GOLD for few months.Possibility of some cooldown on GOLD for few months.
Gold after Rally to ATH of 165000+ looks reached on top end of the Channel ... Possibilities are it can consolidate near 170-175K Level for few weeks before providing new direction to the commodity.
LTP - 164K
Range 150K to 175K.
View - Cautious / Consolidation
Technicals:
Crude is seen moving in upward direction ... Crude / Equities & Gold / Silver are seen moving in opposite directions in past ... With Equities market looking to bottomed out we can see big money moving from Metals to Equity in near months.
Happy Investing.
Gold Futures
No trades
What traders are saying
GOLD FUTURERS :Shooting star Candle shows exhaustion Buy on DipsGOLD Futurers : It has formed a Shooting Star at resistance shows exhaustion at higher levels. Expect a pullback towards 158000-151000.
Trend for Gold MCX remains bullish, but a Shooting Star at resistance signals a short-term pullback
As per Fib retracement and EMA Levels i will be a buyer at the following levels 1. At Between 10 EMA: 157,735-20 EMA: 150,960 zone -part
2.At 50% Fib retracement levels of around 1,39,000-Aggressive buy
For educational purpose only)
How ₹2 Lakh Can Be Invested in Gold & Silver Using SIP + GTTLet’s take a simple example of an investor who wants to invest ₹2,00,000 in Gold and Silver, but does not want to invest everything at one price.
Instead of predicting the bottom, the investor follows a rule-based SIP + GTT (dip buying) strategy.
📉 Market Context (At the Time of Planning)
Gold has already corrected ~22% from its all-time high
Silver has already corrected ~40% from its all-time high
Prices have cooled down, but further correction is still possible.
So the strategy is designed to work even if prices fall further.
📊 Current ETF Prices (Reference)
Gold ETF (GoldBeES): ₹115
Silver ETF (SilverBeES): ₹206
(Exact prices are not important — the strategy is percentage-based.)
💰 Total Capital in This Example
Total Investment Amount: ₹2,00,000
Investment Mode: ETFs (low cost, high liquidity)
Allocation
Gold ETF: ₹1,20,000
Silver ETF: ₹80,000
🪜 GTT “Dip Buying” Plan (Price-Based Buying)
In this example, the investor decides:
“I will invest more only when price falls, not based on news or emotions.”
So, GTT (Good Till Triggered) orders are placed at every 5% price fall.
🪙 Gold ETF – GTT Ladder (Example)
Current price: ₹115
Further possible correction assumed: 20%
Level Price (₹) Amount Invested
Current level 115 ₹30,000
5% fall 109 ₹25,000
10% fall 103 ₹25,000
15% fall 98 ₹20,000
20% fall 92 ₹20,000
Total Gold Investment — ₹1,20,000
👉 Result: Average price improves automatically if the market falls.
🥈 Silver ETF – GTT Ladder (Example)
Current price: ₹206
Further possible correction assumed: 30%
Level Price (₹) Amount Invested
Current level 206 ₹15,000
5% fall 196 ₹15,000
10% fall 185 ₹15,000
15% fall 175 ₹12,000
20% fall 165 ₹12,000
25% fall 155 ₹6,000
30% fall 144 ₹5,000
Total Silver Investment — ₹80,000
👉 Silver is more volatile, so the investment is spread across more levels.
📅 SIP + GTT Hybrid Plan (Example)
Along with dip buying, the investor also uses monthly SIPs for discipline.
🔁 Monthly SIP Setup
ETF Monthly SIP
Gold ETF ₹4,000
Silver ETF ₹2,000
👉 Total monthly SIP = ₹6,000
SIP runs every month (market up or down)
GTT orders activate only when price falls
This creates a balance of consistency + opportunity.
📈 Expected Outcome (Realistic Range)
Based on historical behaviour:
After 2 years: ~₹2.4 – ₹2.5 lakh
After 3 years: ~₹2.8 – ₹3.0 lakh
(Actual returns depend on global cycles and market conditions.)
🔄 Profit Booking Rules Used in This Example
Gold ETF:
At ~25–30% profit → sell 20–30% of units
Silver ETF:
At ~40–50% profit → sell 40–50% of units
Partial profit booking helps lock gains and reduce volatility risk.
🧾 Tax Treatment (India)
Holding less than 3 years:
Profit taxed as per income slab
Holding 3 years or more:
20% tax with indexation
Long-term holding improves tax efficiency.
🧠 Key Takeaway from This Example
This ₹2 lakh example shows that:
You don’t need to predict the bottom
Discipline matters more than timing
SIP builds consistency
GTT removes emotion
Averaging happens automatically
Plan the investment.
Let the market do the rest.
⚠️ Disclaimer
This content is shared strictly for educational and informational purposes only.
It is not investment advice or a recommendation to buy or sell any security.
Markets involve risk, and returns are not guaranteed.
Investors should do their own research or consult a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
GOLD PRICE$ forecastgold huge discount price central banks still buying gold.dollar index is still weak.japanese yen is more weaker one of the big player of U$ BOND holder incase japan sells U$ bond dollar more bearish. only safe heaven asset in the entire world. the geopolitical tension is more chaos. #epstinfiles
Role of FII and DII in the Indian Stock MarketIntroduction
The Indian stock market is one of the fastest-growing capital markets in the world and attracts investments from both domestic and global participants. Among the most influential players in this ecosystem are Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs). Their investment decisions significantly impact market direction, liquidity, volatility, and investor sentiment. Understanding the role of FIIs and DIIs is crucial for traders, long-term investors, policymakers, and anyone seeking to analyze market movements in India.
What are FIIs?
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) are investment entities registered outside India that invest in Indian financial assets. These include:
Mutual funds
Pension funds
Hedge funds
Insurance companies
Sovereign wealth funds
Foreign portfolio investors (FPIs)
FIIs invest in equities, bonds, government securities, derivatives, and ETFs after registering with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Key Characteristics of FIIs
Operate with large capital
Highly sensitive to global economic conditions
Often short- to medium-term focused
Move funds quickly across countries
Strong influence on benchmark indices like NIFTY 50 and Sensex
What are DIIs?
Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) are India-based institutions that invest in Indian financial markets. These include:
Mutual funds
Insurance companies (LIC, GIC)
Banks
Pension funds
Provident funds (EPFO, NPS)
DIIs represent domestic savings channeled into capital markets.
Key Characteristics of DIIs
Long-term investment horizon
More stable and less speculative
Influenced by domestic economic growth
Act as counter-balance to FIIs
Increasingly powerful due to SIP culture
Role of FIIs in the Indian Stock Market
1. Liquidity Provider
FIIs bring massive liquidity into Indian markets. Their large trade volumes:
Increase market depth
Reduce bid-ask spreads
Improve price discovery
High FII participation makes Indian markets more efficient and globally competitive.
2. Market Direction and Trend Formation
FII flows often decide market trends:
Net buying by FIIs → bullish markets
Net selling by FIIs → bearish or corrective markets
Sharp rallies and crashes are frequently linked to sudden FII inflows or outflows.
3. Impact on Blue-Chip Stocks
FIIs prefer:
Large-cap stocks
Index heavyweights
High-liquidity stocks
As a result, stocks like Reliance, HDFC Bank, Infosys, TCS, ICICI Bank are heavily influenced by FII activity.
4. Sensitivity to Global Factors
FIIs react strongly to:
US Federal Reserve interest rate decisions
Dollar strength or weakness
Global inflation data
Geopolitical tensions
Recession fears
This makes Indian markets sensitive to global news even if domestic fundamentals are strong.
5. Currency Impact
When FIIs invest:
They bring foreign currency → Rupee strengthens
When they exit:
Capital outflows → Rupee weakens
Thus, FII behavior directly impacts INR–USD exchange rates.
Role of DIIs in the Indian Stock Market
1. Market Stabilizers
DIIs act as a shock absorber during market downturns. When FIIs sell aggressively, DIIs often step in to buy, preventing deep crashes.
Example:
During global sell-offs, strong DII buying has helped Indian markets outperform peers.
2. Long-Term Wealth Creation
DIIs invest with a long-term vision aligned with:
India’s GDP growth
Corporate earnings
Demographic advantage
Their investments support sustainable wealth creation rather than short-term speculation.
3. Support from Retail Investors
The rise of:
SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans)
Mutual fund awareness
Digital investing platforms
has strengthened DIIs tremendously. Monthly SIP inflows provide consistent buying power even during volatile markets.
4. Reduced Dependence on Foreign Capital
As DII participation grows:
India becomes less vulnerable to sudden FII exits
Market volatility reduces
Financial independence increases
This shift is critical for long-term market stability.
5. Sectoral Impact
DIIs invest heavily in:
Banking and financial services
Infrastructure
FMCG
Manufacturing
PSU stocks
Their investments often align with national development priorities.
FII vs DII: Key Differences
Aspect FII DII
Origin Foreign Indian
Investment Horizon Short to medium Long term
Risk Appetite High Moderate
Sensitivity Global factors Domestic factors
Market Role Trend creator Trend stabilizer
Volatility Impact Increases volatility Reduces volatility
Interaction Between FIIs and DIIs
The Indian stock market often behaves like a tug-of-war between FIIs and DIIs.
When both buy → Strong bull market
When FIIs sell and DIIs buy → Sideways or controlled correction
When both sell → Sharp market crash
Understanding daily FII–DII data helps traders anticipate short-term market moves.
Impact on Retail Investors
Retail investors are indirectly influenced by FII and DII actions:
Rising FII inflows attract retail participation
DII buying builds confidence during corrections
Sharp FII selling can cause panic if not absorbed by DIIs
Smart investors track institutional flow data before making major decisions.
Regulatory Framework
SEBI closely monitors FII and DII activity to:
Prevent market manipulation
Ensure transparency
Maintain financial stability
Limits are placed on foreign ownership in certain sectors to protect national interests.
Importance for Traders and Investors
For Traders:
FII flow data helps in index trading
Short-term momentum often follows FII behavior
For Long-Term Investors:
DII accumulation signals confidence in fundamentals
Corrections caused by FII selling can offer buying opportunities
Conclusion
FIIs and DIIs are the backbone of the Indian stock market. FIIs bring global capital, liquidity, and momentum, while DIIs provide stability, long-term vision, and domestic strength. The growing influence of DIIs has made Indian markets more resilient and less dependent on foreign money.
For anyone serious about the Indian stock market, understanding the roles, behavior, and interaction of FIIs and DIIs is essential. Their combined actions shape market trends, influence valuations, and determine how India positions itself in the global financial landscape.
Part 1 Ride The Big Moves What Are Options?
Options are financial derivatives—meaning their value is derived from an underlying asset such as stock, index, commodity, etc. They are contracts between two parties: the option buyer and the option seller (writer).
There are two types of options:
Call Option (CE) – Right to buy the asset at a fixed price.
Put Option (PE) – Right to sell the asset at a fixed price.
The key point:
The buyer has a right but no obligation. The seller has an obligation but no rights.
Trading Plan for SuccessUnderstanding the Purpose of a Trading Plan
The primary purpose of a trading plan is to bring structure and clarity to your trading activities. Markets are unpredictable, and no strategy works all the time. A trading plan does not eliminate losses, but it ensures that losses are controlled and gains are maximized when the market moves in your favor. It defines what you trade, when you trade, how much you trade, and why you trade. By following predefined rules, traders avoid emotional decisions such as overtrading, revenge trading, or holding losing positions for too long.
A trading plan also helps in maintaining consistency. Consistency is more important than occasional big profits. When you apply the same rules repeatedly, you can evaluate your performance objectively and make data-driven improvements.
Defining Clear Trading Goals
Every successful trading plan begins with clear and realistic goals. These goals should align with your financial situation, risk tolerance, and time commitment. Instead of focusing only on profits, goals should emphasize process-oriented objectives such as maintaining discipline, following risk management rules, and improving accuracy over time.
Short-term goals may include learning a specific strategy, reducing impulsive trades, or achieving consistent monthly returns. Long-term goals might involve building capital steadily, transitioning to full-time trading, or generating supplemental income. Clearly defined goals provide motivation and direction while keeping expectations realistic.
Choosing the Right Market and Time Frame
A good trading plan specifies the markets you will trade, such as stocks, indices, commodities, forex, or options. It is important to focus on a limited number of instruments rather than trading everything available. Specialization allows you to understand the behavior, volatility, and patterns of specific markets.
Time frame selection is equally important. Intraday traders focus on shorter time frames like 5-minute or 15-minute charts, while swing traders may use daily or weekly charts. Long-term investors rely on monthly or weekly time frames. Your choice should match your personality, lifestyle, and available time. A plan that does not fit your routine is difficult to follow consistently.
Developing a Trading Strategy
The trading strategy is the core of your trading plan. It defines the conditions under which you enter and exit trades. A strategy may be based on technical analysis, price action, indicators, volume analysis, or a combination of these. Regardless of the method, the strategy must have clear, objective rules.
Entry rules should specify the exact conditions that trigger a trade. Exit rules should define profit targets and stop-loss levels before entering the trade. A successful trading plan never leaves exits to guesswork. Risk-to-reward ratio plays a critical role here. Many professional traders aim for trades where potential reward is at least twice the potential risk, ensuring profitability even with a moderate win rate.
Risk Management: The Key to Survival
Risk management is the most critical component of a trading plan. Even the best strategy can fail without proper risk control. A trading plan must define how much capital you are willing to risk on each trade. Most successful traders risk only a small percentage of their trading capital, typically 1–2% per trade.
Position sizing is directly linked to risk management. It ensures that no single trade can cause significant damage to your account. Stop-loss placement must be logical and based on market structure rather than emotional comfort. Risk management protects traders from large drawdowns and helps them stay in the game during unfavorable market phases.
Emotional Discipline and Trading Psychology
Trading success is not just about strategy; it is also about mindset. Fear and greed are the biggest enemies of traders. A trading plan helps manage emotions by providing predefined rules, but discipline is required to follow those rules consistently.
Traders must accept that losses are part of the process. A loss does not mean failure; it means the plan is working as intended. Overconfidence after winning streaks and frustration after losses can lead to deviation from the plan. Maintaining emotional balance and trusting the process are essential for long-term success.
Maintaining a Trading Journal
A trading journal is an integral part of a successful trading plan. It records every trade, including entry, exit, reasoning, emotional state, and outcome. Over time, the journal becomes a powerful tool for self-analysis. It helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and recurring mistakes.
Reviewing the journal regularly allows traders to refine their strategies, eliminate bad habits, and reinforce good behavior. Continuous improvement is only possible when performance is measured and analyzed objectively.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Markets evolve, and a trading plan should be flexible enough to adapt to changing conditions. Continuous learning through market observation, backtesting, and performance review is necessary. However, frequent strategy changes should be avoided. Adjustments should be based on data and experience, not short-term results.
Successful traders treat trading as a business, not a gamble. They invest time in education, stay updated with market developments, and continuously work on improving their skills.
Conclusion
A trading plan for success is a combination of strategy, risk management, discipline, and self-awareness. It provides structure in an uncertain environment and transforms trading from an emotional activity into a systematic process. While profits are the ultimate goal, consistency, discipline, and risk control are the true pillars of long-term success. By creating, following, and refining a well-defined trading plan, traders significantly increase their chances of achieving sustainable success in the financial markets.
Part 2 Ride The Big Moves Understanding Market Conditions for Options
A. Trending Market
Best for option buyers (long calls/puts).
B. Sideways Market
Best for option sellers (iron condor, short strangle).
C. High Volatility
Best for straddles/strangles.
D. Low Volatility
Best for spreads and premium selling.
How does today’s gold top compare to the 1980 and 2011 peaks?Gold is not just at a nominal high — it is trading at the highest real (inflation-adjusted) price in modern history.
How does today’s gold top compare to the 1980 and 2011 peaks?
1️⃣ GOLD MAJOR TOPS — NOMINAL vs REAL (TODAY’S MONEY)
🔴 1980 GOLD TOP (true panic peak)
Nominal price (1980): ~$850/oz
Inflation-adjusted to today: ~$3,200–3,400/oz
What the world looked like:
Double-digit inflation
Oil crisis
Cold War escalation
Dollar confidence collapse
Real rates deeply negative
Monetary panic
Meaning: This was a once-in-a-generation monetary crisis peak.
🟠 2011 GOLD TOP (QE / crisis fear)
Nominal price (2011) : ~$1,920/oz
Inflation-adjusted to today : ~$2,600–2,700/oz
What the world looked like:
Global Financial Crisis aftermath
QE everywhere
Eurozone debt crisis
Fear of currency debasement
Inflation still relatively controlled
Meaning: This was a financial-system fear peak, not a currency collapse.
🟡 TODAY (2025–26) GOLD ~ $4,584
Nominal price : ~$4,584/oz (new high)
Inflation-adjusted: $4,584 (today’s dollars by definition)
Compared to past real peaks:
~35–45% above the 1980 real peak (~$3,300 mid-range)
~70–75% above the 2011 real peak (~$2,650 mid-range)
This is extremely important : today’s gold price is already the highest real gold price in modern history.
2️⃣ TABLE SUMMARY
| Gold Peak | Nominal Then | Real Value Today |
| 1980 panic | ~$850 | ~$3,200–3,400 |
| 2011 QE | ~$1,920 | ~$2,600–2,700 |
| Today | ~$4,584 | $4,584 |
3️⃣ WHAT MAKES TODAY DIFFERENT FROM 1980 & 2011
Today:
Inflation already happened
Debt far higher than 1980 or 2011
Central banks trapped
Geopolitical fragmentation
De-dollarization pressure
Central banks buying gold aggressively
Takeaway: Today’s price reflects structural distrust , not just panic.
4️⃣ WHAT A REAL GOLD TOP USUALLY MEANS NEXT
Historically, after gold peaks in real terms:
Nominal price may still go higher briefly
Then:
Long consolidation
Sharp correction
Or years of underperformance vs inflation
Gold doesn’t crash like silver — it bleeds purchasing power over time . That’s how tops resolve.
Disclaimer:
This post is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or trading advice. Readers should conduct their own research or consult a professional before making any financial decisions.
Gold Futures | Bullish Reversal Setup from Demand ZoneThis chart shows a bullish setup on Gold Futures (GC1!) based on a pullback into a 2-Hour + 125-Minute Demand Zone confluence due to FII's pending orders.
I’m expecting the price to retrace back into the marked demand area before continuing higher toward the upside targets.
Plan
• Entry: Inside the 2H & 125m Demand Zone
• Stop Loss: Just below the zone
• Target 1: 4,401
• Target 2: 4,438
Gold : Preparing for Breakout for 84500-85000Gold is consolidating in Triangular Pattern to Breakout above 78800. Target will be 84500-8500.
Close below 76500 will make a breakdown.
Put Stoploss on closing basis.
(In Trading Time it may go above/below stoploss But closing price is most important).
These are levels are generated on the basis on Fibonacci Series
NOTE : I am not SEBI registered advisor in capital market.
Disclaimer:- Please always do your own analysis or consult with your financial advisor before taking any kind of trades. Please understand Risk in trading before taking any trade with your financial consult. I am only sharing my knowledge it may be right or sometimes wrong so I am not liable for any loss.
Dear traders, If you like my work then do not forget to hit like and follow me, and guy's let me know what do you think about this idea in comment box, i would be love to reply all of you guy's.
Thank you.
A Complete Guide to Professional Trading MasteryTrade Like a Pro
Trading like a professional is not about making quick money or taking random bets in the market. It is a disciplined, structured, and highly skill-based approach that combines knowledge, psychology, risk management, and consistency. Professional traders treat trading as a business, not a gamble. They focus on long-term survival and steady growth rather than short-term excitement. This guide explains what it truly means to trade like a pro and how retail traders can develop a professional mindset and process.
Understanding the Professional Trader’s Mindset
The first and most important difference between amateur and professional traders is mindset. Professionals accept that losses are a normal part of trading. They do not aim to win every trade; instead, they focus on executing their strategy correctly. A pro trader thinks in probabilities, not certainties. Each trade is just one of many in a long series. Emotional reactions such as fear, greed, and revenge trading are controlled through discipline and experience. This calm and objective mindset allows professionals to make rational decisions even during high market volatility.
Trading as a Business, Not a Hobby
Professional traders operate like business owners. They have a well-defined trading plan, performance metrics, risk rules, and regular reviews. Every trade has a reason, an entry point, a stop-loss, and a target. Just like a business tracks profits and expenses, traders track wins, losses, drawdowns, and expectancy. Without a structured approach, trading becomes impulsive and unsustainable. Treating trading as a business ensures accountability and long-term focus.
Importance of a Solid Trading Plan
A trading plan is the backbone of professional trading. It outlines which markets to trade, which time frames to use, what setups are allowed, and how much capital to risk per trade. Professionals do not change their plan based on emotions or market noise. They follow predefined rules and only refine their plan after proper analysis. A clear plan removes confusion and prevents overtrading, which is one of the biggest mistakes among retail traders.
Risk Management: The Core of Professional Trading
Risk management is what separates professionals from beginners. Pro traders focus more on how much they can lose rather than how much they can gain. They typically risk only a small percentage of their capital on each trade, often 1–2%. This ensures that even a series of losses does not wipe out their account. Stop-loss orders are mandatory, not optional. By controlling risk, professionals stay in the game long enough to benefit from profitable opportunities.
Mastering Market Structure and Price Action
Professional traders understand how markets move. They study market structure, trends, support and resistance, supply and demand, and price behavior. Instead of relying on too many indicators, they focus on clean charts and price action. This helps them read market sentiment and identify high-probability setups. Understanding how institutions operate and where liquidity lies gives professionals an edge over random retail participation.
Choosing the Right Strategy and Sticking to It
There is no single best strategy in trading. Professionals choose a strategy that suits their personality, time availability, and risk tolerance. Some prefer intraday trading, while others focus on swing or positional trading. What matters is consistency. A professional trader does not jump from one strategy to another after a few losses. They trust their tested system and allow probabilities to play out over time.
The Role of Discipline and Consistency
Discipline is the foundation of professional success. Pro traders follow their rules even when emotions push them to act differently. They avoid overtrading, impulsive entries, and emotional exits. Consistency in execution leads to consistency in results. Even a profitable strategy will fail if applied inconsistently. Professionals understand that discipline is more important than intelligence in trading.
Psychology: Controlling Emotions Under Pressure
Trading psychology plays a critical role in professional performance. Fear can cause traders to exit too early, while greed can lead to holding losing trades. Professionals work continuously on emotional control. They develop routines, take breaks, and avoid trading when emotionally disturbed. Many professionals journal their emotions along with trade details to identify psychological patterns and improve decision-making.
Continuous Learning and Market Adaptation
Markets are dynamic and constantly evolving. Professional traders never stop learning. They analyze past trades, study market changes, and adapt strategies when needed. However, adaptation is based on data and experience, not impulse. Professionals stay updated with macroeconomic factors, global events, and sector trends that influence market behavior. Continuous improvement keeps them relevant and competitive.
Patience and Long-Term Vision
Patience is a rare but essential trait in professional trading. Pros wait for the right setup instead of forcing trades. They understand that opportunities come and go, and missing a trade is better than entering a bad one. Their focus is on long-term capital growth, not daily excitement. This long-term vision allows them to survive drawdowns and benefit from compounding returns over time.
Conclusion: Becoming a Professional Trader
Trading like a pro is a journey, not a destination. It requires dedication, discipline, emotional strength, and continuous self-improvement. Professional traders are not perfect, but they are consistent, prepared, and controlled. By treating trading as a business, managing risk effectively, mastering psychology, and following a structured plan, any serious trader can move closer to professional-level performance. Success in trading is not about predicting the market—it is about managing yourself within it.