News-Based Trading (Budget & RBI Policy)News-based trading is a market strategy where traders make decisions based on economic, political, and financial news events that can cause sudden changes in price, volume, and volatility. Unlike pure technical or long-term fundamental trading, news-based trading focuses on short-term price reactions driven by new information entering the market.
In India, two of the most powerful news events for traders are:
Union Budget
RBI Monetary Policy
Both events can move indices like NIFTY, BANK NIFTY, FINNIFTY, and individual stocks sharply within minutes.
1. Why News Moves Markets
Markets move because prices reflect expectations. When actual news differs from expectations, prices adjust rapidly.
Better than expected news → bullish reaction
Worse than expected news → bearish reaction
In-line with expectations → muted or volatile sideways move
News impacts markets through:
Liquidity changes
Interest rate expectations
Corporate earnings outlook
Investor confidence
For traders, news creates opportunity + risk.
2. Budget-Based Trading
What is the Union Budget?
The Union Budget is the annual financial statement of the Indian government, usually presented in February. It outlines:
Government spending
Taxation changes
Fiscal deficit targets
Sector-specific incentives
Why Budget Day is Important for Traders
High volatility across equity, currency, bond, and commodity markets
Sudden directional moves in indices
Sector-specific rallies or sell-offs
Key Budget Elements Traders Track
Fiscal Deficit – Higher deficit can pressure markets
Capital Expenditure (Capex) – Boosts infra, PSU, cement, steel
Tax Changes – Impacts FMCG, auto, real estate
Sector Allocations – Defence, railways, renewable energy, banking
Disinvestment Plans – Affects PSU stocks
Budget Trading Phases
1. Pre-Budget Phase
Markets often move on expectations and rumors
Certain sectors start outperforming early
Volatility gradually increases
Common trader approach:
Light positional trades
Avoid heavy leverage
Focus on sector rotation
2. Budget Day Trading
This is the most volatile phase.
Characteristics:
Sharp spikes in the first 30–60 minutes
Fake breakouts common
Option premiums expand rapidly
Index Behavior:
NIFTY & BANK NIFTY can move 2–4% intraday
Sudden trend reversals possible
Popular Budget Trading Strategies:
Option Straddle / Strangle (for volatility)
Post-speech breakout trading
Wait-and-trade strategy (after first hour)
⚠️ Many professional traders avoid trading during the speech and trade only after clarity emerges.
3. Post-Budget Phase
Real trend often emerges 1–3 days later
Markets digest data and reprice expectations
Best phase for positional trades
3. RBI Monetary Policy-Based Trading
What is RBI Monetary Policy?
RBI announces monetary policy every two months, focusing on:
Repo rate
Reverse repo
Liquidity measures
Inflation outlook
GDP growth projections
Why RBI Policy Impacts Markets
Interest rates influence:
Bank profitability
Loan demand
Corporate earnings
Currency valuation
Bond yields
Even a single word change in RBI commentary can move markets.
Key RBI Policy Components Traders Watch
Interest Rate Decision
Rate hike → bearish for equities, bullish for banks short term
Rate cut → bullish for equities
Policy Stance
Accommodative → growth-friendly
Neutral / Withdrawal → cautious sentiment
Inflation Outlook
Higher inflation → rate hike fears
Lower inflation → easing expectations
Liquidity Measures
Tight liquidity → market pressure
Easy liquidity → risk-on mood
RBI Policy Trading Phases
1. Pre-Policy
Markets move on expectations
Bond yields and banking stocks react early
Option IV rises
2. Policy Announcement (2:00 PM)
Immediate spike in volatility
Algo-driven moves dominate
Sharp whipsaws common
Common mistakes:
Market orders during announcement
Over-leveraged option buying
3. Governor’s Speech
Trend clarity often comes during speech
Commentary matters more than rate decision sometimes
4. Instruments Used in News-Based Trading
Cash Market
Suitable for experienced traders
Slippage risk high
Better post-event
Futures
High risk due to gap moves
Strict stop-loss required
Options (Most Popular)
Limited risk strategies
Best suited for volatility events
Common Option Strategies:
Long Straddle / Strangle (high volatility)
Iron Condor (if volatility expected to drop)
Directional option buying after confirmation
5. Risk Management in News Trading
News-based trading is high-risk, high-reward. Risk control is non-negotiable.
Key Rules:
Reduce position size
Avoid trading without a plan
Do not chase first move
Use defined-risk option strategies
Accept slippage as part of the game
Many traders lose money not because of wrong direction, but because of overconfidence and overtrading.
6. Psychology of News Trading
News trading tests emotional discipline.
Common psychological traps:
FOMO during fast moves
Panic exits
Revenge trading after loss
Successful news traders:
Stay calm during volatility
Trade reactions, not headlines
Accept that missing a trade is better than forcing one
7. Advantages of News-Based Trading
Large moves in short time
High liquidity
Clear catalysts
Opportunity across asset classes
8. Disadvantages
Extreme volatility
Algo dominance
Slippage and spread issues
Emotional pressure
Conclusion
News-based trading around the Union Budget and RBI Monetary Policy is one of the most exciting yet challenging styles of trading in the Indian market. These events can create massive opportunities, but only for traders who understand expectations, volatility, and risk management.
For beginners, it is better to observe first, trade later. For experienced traders, combining news understanding with technical levels and options strategies can be highly rewarding. Ultimately, success in news-based trading comes not from predicting the news, but from managing risk and trading market reactions intelligently.
Axis Bank Limited Sponsored GDR RegS
No trades
What traders are saying
Part 5 Advance Trading Strategies Why Do Options Have Time Decay? (Theta)
Options lose value as expiry approaches.
This is called Theta Decay.
Example:
Monday premium: ₹100
Thursday premium: ₹20
Expiry day: ₹0
This happens because time is part of the option’s value. If market doesn’t move, buyer loses money; seller gains.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 11 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 11 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Alignment)
This post shares a historical intraday observation showing how price interacted with a normal Square of 9 capacity level, leading to a temporary reaction when time and price aligned.
📊 Market Context & Reference Selection
Axis Bank displayed upward momentum after the completion of the first 15-minute candle.
In such market conditions, the low of the first 15-minute candle (~1104) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This reference point was used to study the session’s expected price expansion.
Correct identification of the reference level is critical for objective Square of 9 analysis.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1104
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1121
The 45-degree level often represents the normal intraday movement range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Observed Price–Time Behavior
Price approached the 45-degree level well before the later part of the trading session.
Early completion of normal price capacity has historically been associated with short-term trend fatigue.
After interacting with this zone, price showed temporary selling pressure and moved lower.
A minor variation around the calculated level was observed, which is common in live market conditions.
This aligns with a widely observed Gann concept:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Early capacity completion can indicate temporary exhaustion
Time plays a supporting role in validating price-degree levels
Small price deviations are normal and should be viewed structurally
The method promotes rule-based observation over prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Economy Future at Risk: A Comprehensive Analysis1. Mounting Global Debt and Fiscal Fragility
One of the most serious threats to the future economy is the explosion of global debt. Governments, corporations, and households have borrowed aggressively, especially after the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. Ultra-low interest rates encouraged debt-fuelled growth, but rising rates have now turned that debt into a burden.
Many governments are trapped in a cycle where higher interest payments consume public finances, limiting spending on infrastructure, healthcare, and education. Developing economies face even greater risk as currency depreciation and capital outflows increase the cost of servicing foreign debt. If debt sustainability weakens further, sovereign defaults or forced austerity could slow global growth for years.
2. Inflation, Monetary Tightening, and Growth Slowdown
The resurgence of inflation has altered the economic landscape. After years of price stability, supply chain disruptions, energy shocks, and expansive fiscal policies triggered sharp inflation across major economies. Central banks responded with aggressive interest rate hikes to restore credibility.
While necessary, tight monetary policy carries risks. High interest rates slow consumption, reduce corporate investment, and weaken housing and credit markets. If tightening continues too long, economies may slide into prolonged stagnation or recession. On the other hand, easing too early risks reigniting inflation. This delicate balance makes future economic stability uncertain.
3. Geopolitical Fragmentation and Trade Disruptions
Globalization once acted as a stabilizing force, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Today, geopolitical fragmentation threatens those gains. Trade wars, sanctions, regional conflicts, and strategic decoupling between major powers have disrupted global supply chains.
Economic blocs are increasingly prioritizing national security over economic efficiency. This shift raises costs, reduces productivity, and increases volatility. Energy markets, semiconductor supply chains, and critical minerals have become geopolitical tools, making economies more vulnerable to external shocks.
4. Climate Change and Environmental Stress
Climate change is no longer a future risk—it is an economic reality. Extreme weather events damage infrastructure, disrupt agriculture, and strain public finances. Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities and trade hubs, while water scarcity impacts food security and industrial production.
The transition to a low-carbon economy also presents challenges. While green investment creates opportunities, poorly managed transitions can destroy jobs, destabilize energy markets, and widen inequality. Economies that fail to adapt face declining competitiveness and rising long-term costs.
5. Technological Disruption and Labor Market Uncertainty
Technology is both a driver of growth and a source of risk. Artificial intelligence, automation, and digital platforms are reshaping industries at unprecedented speed. While productivity gains are possible, job displacement remains a serious concern.
Many economies lack the education systems and reskilling frameworks needed to absorb displaced workers. This mismatch could increase unemployment, wage inequality, and social unrest. If the benefits of technological progress remain concentrated among a small segment of society, economic stability may erode.
6. Rising Inequality and Social Instability
Economic inequality has widened across and within countries. Wealth concentration, stagnant wages, and limited upward mobility weaken consumer demand and social cohesion. When large segments of the population feel excluded from growth, political polarization increases.
Social unrest, populism, and policy unpredictability follow economic inequality. These dynamics discourage investment, weaken institutions, and reduce long-term growth potential. A future economy built on unstable social foundations is inherently fragile.
7. Financial Market Excesses and Systemic Risk
Financial markets have become increasingly complex and interconnected. The growth of derivatives, shadow banking, high-frequency trading, and leveraged products has amplified systemic risk. Asset bubbles fueled by liquidity and speculation pose a constant threat.
When markets disconnect from real economic fundamentals, corrections become more severe. Sudden liquidity shortages or institutional failures can spread rapidly across borders, as seen in past crises. Without strong regulation and transparency, financial instability remains a persistent risk to economic futures.
8. Demographic Shifts and Productivity Challenges
Many advanced economies face aging populations and declining birth rates. A shrinking workforce places pressure on pension systems, healthcare spending, and productivity growth. At the same time, younger populations in developing economies often lack sufficient employment opportunities.
Without policies that encourage productivity, innovation, and labor participation, demographic imbalances could drag down global growth for decades. Immigration, education reform, and workforce flexibility will be crucial in managing this transition.
9. Policy Coordination Failures
Global challenges require global solutions, yet international coordination is weakening. Divergent monetary policies, inconsistent climate strategies, and fragmented trade rules reduce effectiveness. When countries act in isolation, spillover effects amplify instability.
Lack of trust between nations limits crisis response capacity. The future economy depends heavily on cooperation in finance, trade, health, and climate—areas where coordination is currently strained.
10. Is the Future Economy Doomed?
Despite these risks, the future is not predetermined. Economies have demonstrated resilience throughout history. Innovation, institutional reform, and adaptive policymaking can mitigate many of these threats.
Sustainable growth requires a shift from debt-driven expansion to productivity-led development. Investment in education, green technology, digital infrastructure, and inclusive growth models can restore long-term stability. Strong institutions, transparent governance, and prudent risk management remain key pillars.
Conclusion
The future of the economy is undeniably at risk—but not beyond repair. Structural weaknesses, global imbalances, and systemic shocks have exposed vulnerabilities that can no longer be ignored. Whether the coming decades bring stagnation or sustainable prosperity depends on choices made today.
Addressing debt, inequality, climate risk, and technological disruption with coordinated, forward-looking policies can transform current challenges into opportunities. The real danger lies not in the risks themselves, but in complacency and delayed action. The future economy will be shaped by how effectively the world responds to this defining moment.
AXISBANK 1 Week Time Frame 📊 Current Context (As of 30 Jan 2026)
Last Close: ~₹1,370 – ₹1,378 range.
Recently traded near a 52-week high.
📈 Weekly Resistance Levels
These resistances act as potential upside barriers for the coming week:
R1: ~₹1,317 – ₹1,320 — first resistance zone.
R2: ~₹1,341 – ₹1,342 — next upside.
R3: ~₹1,370+ — major resistance breakout level.
➡️ Bullish scenario: A weekly close above ~₹1,317–₹1,320 increases chances of move toward ₹1,340+ / ₹1,370+.
📉 Weekly Support Levels
Support levels where price may find buying interest if it pulls back:
S1: ~₹1,262 – ₹1,265 — near-term support.
S2: ~₹1,230 — mid-range support.
S3: ~₹1,206 — broader downside buffer.
➡️ Bearish scenario: If the stock closes below ~₹1,262–₹1,265, further downside toward ₹1,230 → ₹1,206 could be possible.
📅 Likely Weekly Trading Range
Neutral / range-bound view:
₹1,262 – ₹1,320 — price may oscillate here unless a strong breakout/breakdown occurs.
📌 Quick Summary
Bullish break levels: above ₹1,317–₹1,320
Immediate upside resistances: ₹1,341 / ₹1,370+
Downside supports: ₹1,262 → ₹1,230 → ₹1,206
AXISBANK 40% upside possibility in 1-1.5 YearsAXISBANK 40% upside possibility in 1-1.5 Years
Fundamentals - Company has delivered good profit growth of 72.2% CAGR over last 5 years - Best among all Private banks.
Technical - Stock breaking from ATH backed with excellent Results.
LTP - 1325
Targets - 1850+
Timeframe - 1-1.5 Years.
Happy Investing.
Part 5 Advance Option Trading How Option Trading Works – Step-by-Step
You choose a strike price based on your directional view.
You decide whether to buy the option or sell it, depending on your risk appetite.
If you expect strong movement, you typically buy.
If you expect sideways movement, you typically sell.
When market moves in your direction, premium increases.
When market moves against you, premium decreases.
Premium also falls automatically due to theta decay, especially near expiry.
Option chain helps identify support and resistance based on OI built-up.
Volume profile shows where big institutions executed trades.
Market structure tells you whether to buy CE, PE, or sell options.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 12 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post presents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity and time alignment can highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Market Structure at the Open
Axis Bank displayed upward strength from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1166) was used as the 0-degree reference level, following Square of 9 methodology.
This level acts as the base point for mapping the day’s upward price vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree reference is essential for consistent Square of 9 studies.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1166
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1183
In intraday analysis, the 45-degree level often represents the stock’s normal price expansion range under typical market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior followed by short-term downside expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann concept:
Early completion of expected price capacity may increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than exceptional cases
Combining price structure with time context improves market clarity
Small deviations around calculated levels are part of normal market behavior
This approach supports rule-based observation, not prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 13 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post documents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity interacts with time to highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Initial Market Structure
Axis Bank showed upward momentum from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1148) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following standard Square of 9 practice.
This reference point acts as the base for mapping the day’s expected upward vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree is essential for meaningful Square of 9 observations.
🔢 Gann Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1148
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1165
In intraday studies, the 45-degree level often represents a stock’s normal price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior and short-term downside expansion.
This reflects a commonly observed Gann principle:
Early completion of expected price capacity can increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Key Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than rare cases
Combining price structure with time context improves clarity
The method supports rule-based observation, not prediction
Small variations around levels are part of normal market behavior
📌 Shared purely for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceTime
Exchange Rates: A Complete GuideWhat Is an Exchange Rate?
An exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. For example, if the USD/INR exchange rate is 83, it means one US dollar can be exchanged for 83 Indian rupees. Exchange rates act as a bridge between economies, allowing goods, services, and capital to move across borders.
Exchange rates can be quoted in two ways:
Direct quote: Domestic currency per unit of foreign currency (e.g., INR per USD).
Indirect quote: Foreign currency per unit of domestic currency.
These rates constantly fluctuate based on economic conditions, market sentiment, and policy decisions.
Types of Exchange Rate Systems
Countries adopt different exchange rate regimes depending on their economic priorities.
Floating Exchange Rate
In a floating system, currency values are determined by market forces of supply and demand. Major currencies like the US dollar, euro, and Japanese yen operate under this system. Central banks may intervene occasionally, but prices largely reflect market expectations.
Fixed or Pegged Exchange Rate
In this system, a country pegs its currency to another currency or a basket of currencies. For example, some Gulf countries peg their currencies to the US dollar. This provides stability but limits monetary policy flexibility.
Managed Float (Dirty Float)
This is a hybrid system where exchange rates mostly float, but central banks intervene to prevent excessive volatility. India follows a managed float regime.
Factors That Influence Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are influenced by a complex mix of economic, financial, and psychological factors.
Interest Rates: Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the currency and pushing it higher.
Inflation: Countries with lower inflation generally see their currencies appreciate over time.
Economic Growth: Strong GDP growth boosts investor confidence and currency demand.
Trade Balance: A trade surplus supports currency strength, while a deficit can weaken it.
Capital Flows: Foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio inflows increase currency demand.
Political Stability: Stable governments and policies attract investors and strengthen currencies.
Market Sentiment: Risk-on or risk-off behavior can rapidly move currencies regardless of fundamentals.
Major Exchange Rate Markets
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the largest financial market in the world, with daily turnover exceeding trillions of dollars. It operates 24 hours a day across global financial centers such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Singapore.
Key participants include:
Central banks
Commercial banks
Hedge funds
Corporations
Retail traders
Currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, or GBP/INR.
Spot, Forward, and Derivative Exchange Rates
Exchange rates exist in different market forms:
Spot Rate: The current exchange rate for immediate settlement.
Forward Rate: A rate agreed upon today for exchange at a future date.
Futures and Options: Derivatives that allow hedging or speculation on currency movements.
Swap Rates: Used by banks and institutions to manage liquidity and interest rate exposure.
These instruments help manage currency risk and improve market efficiency.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a critical role in exchange rate dynamics. They influence currencies through:
Interest rate decisions
Open market operations
Foreign exchange interventions
Forward guidance and policy communication
For example, if a central bank raises interest rates to control inflation, its currency often strengthens due to higher yield attractiveness.
Exchange Rates and International Trade
Exchange rates directly affect export and import competitiveness:
A weaker currency makes exports cheaper and imports more expensive.
A stronger currency makes imports cheaper but can hurt export competitiveness.
For export-driven economies, maintaining a competitive exchange rate is crucial for growth and employment.
Exchange Rates and Inflation
Currency depreciation can lead to imported inflation, especially in countries dependent on foreign oil, food, or raw materials. Conversely, currency appreciation can help control inflation by reducing import costs. This relationship makes exchange rates a key variable in monetary policy decisions.
Exchange Rates and Investment
Foreign investors consider exchange rate risk when investing in equities, bonds, or real assets. Even if an investment performs well locally, adverse currency movements can reduce returns when converted back to the investor’s home currency.
As a result, many investors use currency hedging strategies to protect returns.
Exchange Rates in Emerging Markets
Emerging market currencies tend to be more volatile due to:
Higher inflation
Dependence on foreign capital
Commodity price sensitivity
External debt obligations
Currencies like INR, BRL, and ZAR are often influenced by global risk sentiment and US dollar strength.
Exchange Rate Forecasting
Forecasting exchange rates is challenging because markets quickly absorb information. Analysts use:
Fundamental analysis (economic indicators)
Technical analysis (charts and trends)
Sentiment analysis (positioning and risk appetite)
No method guarantees accuracy, but combining approaches improves decision-making.
Importance of Exchange Rates in Global Finance
Exchange rates influence:
Global capital allocation
Corporate profitability
Government debt servicing
Balance of payments stability
Financial market volatility
Sudden currency movements can trigger crises, as seen in past emerging market currency collapses.
Conclusion
Exchange rates are more than just numbers on a screen—they reflect the health, confidence, and competitiveness of economies. They connect nations through trade, investment, and finance while transmitting global shocks across borders. Understanding exchange rate systems, drivers, and impacts helps individuals and institutions manage risk, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions.
In a world of rising globalization and capital mobility, exchange rates remain one of the most powerful and sensitive indicators in the financial system. Mastering their dynamics is essential for anyone engaged in economics, finance, or global business.
Part 1 Support and Resistance Option Buyers
Limited risk (premium paid).
Require strong price movement.
Benefit from volatility.
Time works against them due to time decay.
Option Sellers (Writers)
Limited profit (premium received).
Potentially unlimited risk (especially naked positions).
Benefit from time decay.
Prefer range-bound markets.
Axis BankAXISBANK | 1D | Breakout Continuation Setup
After a strong up-move, price is consolidating near resistance.
📌 Buy above 1342 for continuation of trend.
🛑 Stop Loss below 1317 to manage risk.
🎯 Upside opens towards 1380 → 1420 if momentum sustains.
RSI holding above 50 and price above 20 SMA — bulls still in control.
Wait for confirmation. Follow price, not prediction.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 12 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 12 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday observation based on the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how early completion of price capacity can coincide with temporary market pressure.
📊 Market Structure & Reference Selection
Axis Bank opened with upward momentum during the first 15-minute candle.
In such conditions, the low of the opening candle (~1100) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This level served as the base point for measuring the session’s upward price capacity.
Accurate identification of the reference point is essential for reliable Square of 9 observations.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1100
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1117
The 45-degree level often reflects the normal intraday price expansion range under regular conditions.
⏱️ Price–Time Behavior (Observed)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around 9:30 AM).
Completion of normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically been associated with short-term exhaustion.
After reaching this zone, the market showed temporary selling pressure and downside expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann principle:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define intraday price limits in advance
Early completion of price capacity can signal temporary trend fatigue
Time alignment strengthens interpretation of price-degree levels
The method encourages structured observation over prediction
Focus remains on process, not precision
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
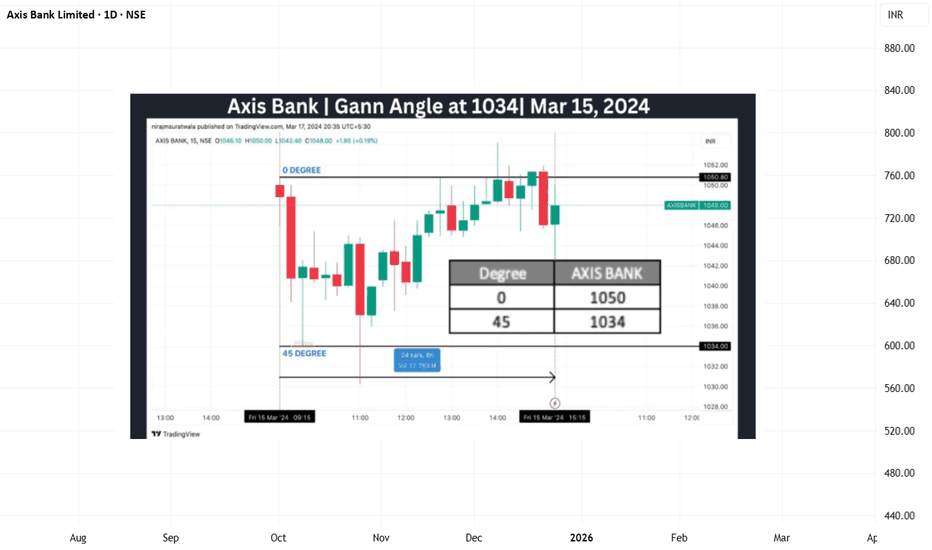
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 15 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 15 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method: Gann Square of 9 (Price Capacity & Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday market observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how price capacity, trend context, and time alignment can highlight potential intraday reaction zones.
📉 Market Context & Reference Point Selection
Axis Bank showed downside pressure from the opening 15-minute candle.
In such conditions, the high of the first 15-minute candle (~1050) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following Gann methodology.
This level acts as the starting point for measuring the intraday downward price cycle.
Correct trend identification and reference selection are essential before applying Square of 9 calculations.
🔢 Square of 9 Price Mapping
Based on the selected reference:
0 Degree: ~1050
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1034
The 45-degree level often represents the normal intraday price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price–Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around the third 15-minute candle).
Completion of normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown signs of temporary downside exhaustion.
After reaching this zone, the market displayed short-term stabilization followed by upward expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann concept:
When expected price capacity is completed early in time, the probability of a directional reaction may increase.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define intraday price limits in advance
Trend context determines how reference points are selected
Time alignment adds confirmation to price-degree levels
Normal (45-degree) reactions are more frequent than rare cases
The approach encourages rule-based observation over emotional reaction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Observation | 18 March 202Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 18 March 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
Method Used: Gann Square of 9 (Price–Time Study)
This post documents a historical intraday market observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how price movement capacity and time alignment can highlight potential intraday reaction zones.
📊 Initial Market Structure
Axis Bank displayed upward momentum from the opening 15-minute candle.
The low of the first 15-minute candle (~1043) was treated as the 0-degree reference level.
This reference point marks the start of the intraday price cycle and is used for further Square of 9 calculations.
Correct identification of the 0-degree level is a key requirement for consistent Square of 9 analysis.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Using Square of 9 price-degree relationships, the following levels were observed:
0 Degree: ~1043
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1057
The 45-degree level often reflects the normal intraday price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price interacted with the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After reaching this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior followed by short-term downside expansion.
This observation aligns with a commonly studied Gann principle:
Early completion of expected price capacity may increase the probability of a market reaction.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than exceptional cases
Time context adds important confirmation to price levels
Minor price deviations around calculated levels are part of normal market behavior
The method supports rule-based observation, not prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #PriceTime #TechnicalAnalysis
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 12 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post presents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity and time alignment can highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Market Structure at the Open
Axis Bank displayed upward strength from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1166) was used as the 0-degree reference level, following Square of 9 methodology.
This level acts as the base point for mapping the day’s upward price vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree reference is essential for consistent Square of 9 studies.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1166
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1183
In intraday analysis, the 45-degree level often represents the stock’s normal price expansion range under typical market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior followed by short-term downside expansion.
This aligns with a commonly observed Gann concept:
Early completion of expected price capacity may increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Educational Takeaways
Gann Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than exceptional cases
Combining price structure with time context improves market clarity
Small deviations around calculated levels are part of normal market behavior
This approach supports rule-based observation, not prediction
📌 Shared strictly for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 13 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post documents a historical intraday observation using the Gann Square of 9, focusing on how normal price movement capacity interacts with time to highlight potential reaction zones.
📊 Initial Market Structure
Axis Bank showed upward momentum from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1148) was treated as the 0-degree reference level, following standard Square of 9 practice.
This reference point acts as the base for mapping the day’s expected upward vibration.
Correct identification of the 0-degree is essential for meaningful Square of 9 observations.
🔢 Gann Square of 9 Level Mapping
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1148
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1165
In intraday studies, the 45-degree level often represents a stock’s normal price expansion range under regular market conditions.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Observed Behavior)
Price reached the 45-degree level early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal price capacity well before the later part of the trading day has historically shown temporary price pressure.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior and short-term downside expansion.
This reflects a commonly observed Gann principle:
Early completion of expected price capacity can increase the probability of a reaction.
📘 Key Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 helps define logical intraday price limits
Normal (45-degree) reactions occur more frequently than rare cases
Combining price structure with time context improves clarity
The method supports rule-based observation, not prediction
Small variations around levels are part of normal market behavior
📌 Shared purely for educational and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceTime
Axis Bank | Gann Square of 9 Intraday Study (Normal Case)Disclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered advisor. This is not financial advice.
Symbol: AXISBANK (NSE)
Date Observed: 14 November 2024
Time Frame: 15-Minute Chart
This post is a historical intraday case study showing how the Gann Square of 9 can be used to identify potential reaction zones by combining price movement capacity with time.
📊 Opening Market Observation
Axis Bank showed bullish intent from the first 15-minute candle.
The low of the opening candle (~1131.60) was treated as the 0-degree reference, following standard Gann methodology.
This reference level acts as the base point for measuring upward price vibration for the session.
🔢 Square of 9 Level Structure
Based on Square of 9 calculations:
0 Degree: ~1131
45 Degree (Observed Normal Capacity): ~1148
In intraday studies, the 45-degree level often represents the stock’s normal directional movement range.
⏱️ Price & Time Interaction (Educational Observation)
Price reached the 45-degree level very early in the session (around the second 15-minute candle).
Completion of the normal movement range well before the latter part of the trading session has historically shown temporary price pressure or hesitation.
After interacting with this zone, the market displayed rejection behavior and short-term weakness.
This reflects a commonly observed Gann principle:
When price completes its expected movement capacity too early in time, the probability of a reaction increases.
📘 Key Educational Takeaways
Square of 9 levels can be projected in advance for structured observation
Correct identification of the 0-degree reference is critical
Alignment of price and time improves analytical context
Normal (45-degree) cases occur more frequently than rare (90-degree) cases
This approach supports disciplined chart reading rather than emotional decisions
📌 Shared purely for learning and historical chart-study purposes.
#AxisBank #GannSquareOf9 #WDGann #IntradayAnalysis #MarketEducation #TechnicalAnalysis #PriceTime
Axis Bank | Intraday Price Behaviour Using Square-Based GeometryDisclaimer:
This analysis is for educational purposes only. I am not a SEBI-registered adviser. This is not financial advice.
Educational Case Study | 7 February 2025
This idea presents an educational intraday case study on Axis Bank, focusing on how price movement capacity and time awareness can be observed using square-based geometric methods commonly referenced in classical market studies.
The purpose of this post is to study historical chart behavior, not to suggest trades or outcomes.
📊 Chart Context
Instrument: Axis Bank Ltd. (NSE)
Date: 7 February 2025
Timeframe: 15-minute (Intraday)
During the early part of the session, Axis Bank showed strong downward momentum. A structured framework was applied to observe how price behaved relative to predefined reference levels as the session progressed.
🔍 Observational Framework
The initial high of the session was treated as a reference point (around 1024.45)
From this reference, square-based projections were observed
A level near 1008 aligned with a 45-degree projection, often associated with normal intraday price reach in historical studies
This level was treated as a potential reaction zone, not a guaranteed support
All levels were used strictly as areas of observation.
📈 Observed Market Behavior
Price moved toward the projected zone during the morning session
Near this area, the market showed temporary pressure and a short-term response
The behavior aligned with previously observed historical interactions around similar geometric zones
Time context was noted as part of the observation, without implying causation
No trade execution, direction, or performance outcome is implied.
📘 Educational Insights from This Case
Square-based geometry can help outline normal intraday price movement capacity
Certain projected levels may act as areas where price behavior changes
Time awareness can provide additional context when studying intraday charts
This approach emphasizes structure and observation over indicators or predictions
All insights are based on historical chart study only.
📌 Important Note
This case study is shared strictly for learning and research purposes.
Geometric levels and time windows do not guarantee outcomes and should be treated as contextual analytical tools.
Market responses may include:
Temporary pauses
Short-term pressure
Continuation or expansion depending on broader structure
🚀 Summary
This intraday case study demonstrates how price geometry and time alignment can be used to observe market behavior in a structured and objective manner.
More educational chart studies will follow.
Cryptocurrency & Digital Asset MarketsIntroduction
The rise of cryptocurrencies and digital assets represents one of the most significant innovations in financial markets over the last decade. Originating with Bitcoin in 2009, cryptocurrencies have evolved from a niche technology experiment into a multi-trillion-dollar ecosystem encompassing thousands of digital assets, decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), stablecoins, and blockchain-based applications. These markets challenge traditional financial structures by providing decentralized, borderless, and programmable forms of money and value transfer. Understanding the structure, dynamics, and risks of cryptocurrency markets is crucial for investors, traders, and policymakers alike.
Cryptocurrency and Digital Asset Basics
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security, making them resistant to counterfeiting. Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, primarily using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger that records all transactions transparently and immutably.
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency, designed as a decentralized digital alternative to traditional currency.
Altcoins: Other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and Ripple (XRP) with specific use cases beyond payment, including smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and finance.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to traditional currencies like USD (e.g., USDT, USDC) to minimize volatility and serve as a medium of exchange in digital markets.
Tokens: Digital assets built on existing blockchains, representing assets, access rights, or utilities within ecosystems.
Digital assets encompass a broader category beyond cryptocurrencies. They include NFTs, tokenized securities, and digital representations of real-world assets. Digital assets are programmable, tradable, and often interoperable across blockchain networks.
Market Structure
Cryptocurrency markets differ from traditional financial markets in several key aspects:
Decentralization: Unlike stock or bond markets, many cryptocurrency markets operate without a central exchange or authority. Peer-to-peer trading, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and blockchain protocols allow transactions without intermediaries.
24/7 Trading: Cryptocurrency markets never close. Trading occurs continuously, globally, providing high liquidity opportunities but also exposing participants to constant market risk.
Market Participants: Participants include retail investors, institutional investors, miners, validators, and algorithmic trading bots. Institutional adoption has grown in recent years, introducing products like cryptocurrency ETFs, futures, and custody services.
Exchanges: Cryptocurrencies trade on centralized exchanges (CEXs) like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken, which provide liquidity, custody, and compliance. Decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Sushiswap operate without intermediaries, using smart contracts to facilitate trades.
Price Determinants
Cryptocurrency prices are influenced by multiple factors:
Supply and Demand: Fixed supply (e.g., Bitcoin’s 21 million cap) versus demand from investors, institutions, and retail users.
Market Sentiment: News, social media, and macroeconomic events can significantly impact crypto prices due to market psychology and herd behavior.
Regulation: Legal frameworks in different countries affect adoption and trading. Positive regulation encourages investment, while bans or restrictions can trigger sell-offs.
Technological Developments: Upgrades to blockchain protocols, new network features, or innovations in scalability and security can drive price appreciation.
Macro Factors: Inflation, interest rates, and currency depreciation indirectly influence crypto adoption as an alternative store of value.
Key Market Segments
Spot Market: The direct buying and selling of cryptocurrencies at current prices. Spot trading is the foundation of crypto markets.
Derivatives Market: Includes futures, options, and perpetual contracts allowing traders to hedge, speculate, or leverage positions. Derivatives markets add liquidity but increase systemic risk.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A rapidly growing sector offering lending, borrowing, yield farming, and automated market-making without traditional banks. DeFi uses smart contracts to automate financial services.
NFT Market: Non-fungible tokens represent unique digital assets such as art, collectibles, or virtual real estate. NFTs are changing the way ownership and creativity are monetized.
Tokenized Assets: Traditional assets like real estate, commodities, or stocks are increasingly tokenized to enable fractional ownership, faster settlements, and cross-border liquidity.
Trading and Investment Strategies
Cryptocurrency markets offer diverse opportunities, but they are highly volatile and risky. Common strategies include:
HODLing: Long-term holding of cryptocurrencies based on belief in their future adoption and value appreciation.
Day Trading: Short-term trading to exploit price volatility within intraday movements.
Swing Trading: Capturing medium-term price trends over days or weeks.
Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between exchanges or markets.
Staking and Yield Farming: Earning rewards by locking cryptocurrencies in networks or DeFi protocols.
Market Risks and Challenges
Cryptocurrency and digital asset markets are exposed to several unique risks:
Volatility: Price swings of 10–20% in a single day are common. Extreme volatility can lead to significant gains or catastrophic losses.
Security Risks: Hacks, scams, phishing, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts or exchanges have historically caused large financial losses.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still defining legal frameworks. Sudden regulations can restrict access or impact asset values.
Liquidity Risk: Smaller cryptocurrencies may have low trading volume, making it difficult to enter or exit positions at desired prices.
Technological Risk: Blockchain bugs, network forks, and software vulnerabilities can disrupt trading and asset functionality.
Market Manipulation: Low liquidity and lack of regulation in some areas make cryptocurrencies susceptible to pump-and-dump schemes and price manipulation.
Adoption and Institutional Participation
Institutional adoption has accelerated the growth of cryptocurrency markets:
Major financial institutions now offer crypto custody, trading, and investment products.
Hedge funds, pension funds, and insurance companies are allocating portions of their portfolios to digital assets.
Payment companies like PayPal and Mastercard facilitate crypto transactions.
Central banks are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), potentially integrating digital assets with traditional monetary systems.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulation remains a defining factor in the future of crypto markets:
Countries like the United States and the European Union are working on clear regulatory frameworks covering taxation, anti-money laundering (AML), and investor protection.
Some nations, such as El Salvador, have adopted cryptocurrencies as legal tender.
Others, like China, have banned crypto trading and mining, illustrating the wide divergence in global policies.
Regulatory clarity is expected to increase market legitimacy, attract institutional capital, and reduce systemic risks.
Future Trends
DeFi Expansion: Decentralized finance is expected to grow, providing more sophisticated financial services without intermediaries.
Web3 Integration: Blockchain technology will underpin digital identity, social networks, and decentralized applications, creating new ecosystems for value exchange.
Layer-2 Scaling: Solutions like Ethereum’s layer-2 protocols aim to reduce transaction costs and increase network speed.
Interoperability: Cross-chain solutions will enable seamless asset transfers between blockchain networks.
Sustainable Practices: Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) will gain traction over energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) models.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency and digital asset markets represent a paradigm shift in how value is created, transferred, and stored. They combine technological innovation with financial markets, providing opportunities for speculation, investment, and new financial services. However, these markets remain highly volatile, technologically complex, and subject to regulatory uncertainty. Successful participation requires a strong understanding of blockchain fundamentals, market dynamics, risk management, and strategic foresight. As adoption grows and regulation matures, digital assets are likely to become a mainstream component of global finance, reshaping economies, investment strategies, and the financial system itself.
Risk Management & Position Sizing in Trading1. Introduction
Risk management and position sizing are the foundation of long-term trading success. Many traders focus heavily on entry strategies—chart patterns, indicators, or news—but ignore risk. In reality, you can be profitable even with an average strategy if your risk management is strong, and you can lose everything with a great strategy if risk is uncontrolled.
Risk management answers one key question:
“How much am I willing to lose if this trade fails?”
Position sizing answers another:
“How many shares/lots should I trade based on that risk?”
Together, they protect your capital, control emotional stress, and allow you to survive long enough to benefit from market opportunities.
2. Understanding Risk in Trading
In trading, risk is the potential loss on a trade, not uncertainty. Every trade has three known variables:
Entry Price
Stop Loss
Position Size
Risk exists because the market can move against you. Professional traders accept losses as business expenses, not failures. The goal is not to avoid losses, but to keep losses small and controlled.
3. The Golden Rule: Capital Preservation
The first objective of trading is not to make money—it is to protect capital. Without capital, you cannot trade.
Key principles:
Never risk a large portion of capital on one trade
Avoid revenge trading after losses
Focus on consistency, not jackpots
A trader who protects capital gains a powerful advantage: the ability to stay in the game.
4. Fixed Percentage Risk Model
One of the most widely used risk management methods is the Fixed Percentage Risk Model.
How it Works:
You risk a fixed percentage of your total capital on each trade—usually 0.5% to 2%.
Example:
Trading Capital: ₹5,00,000
Risk per Trade: 1%
Maximum Loss Allowed per Trade: ₹5,000
No matter how confident you are, you never exceed this limit.
This method:
Prevents large drawdowns
Automatically reduces risk after losses
Allows compounding after profits
5. Position Sizing: The Core of Risk Control
Position sizing converts your risk limit into trade quantity.
Position Size Formula:
Position Size = (Capital × Risk %) ÷ (Entry Price – Stop Loss)
Example:
Capital: ₹5,00,000
Risk per trade: 1% = ₹5,000
Entry Price: ₹500
Stop Loss: ₹490
Risk per share: ₹10
Position Size = 5,000 ÷ 10 = 500 shares
This ensures:
Loss stays within ₹5,000
Emotions remain controlled
Decisions stay objective
6. Stop Loss: The Backbone of Risk Management
A stop loss defines where you admit you are wrong.
Types of Stop Loss:
Technical Stop: Based on support, resistance, trendline, or indicator
Percentage Stop: Fixed % from entry
Volatility Stop: Based on ATR
Time-Based Stop: Exit if trade doesn’t move in expected time
A stop loss must be:
Logical, not emotional
Decided before entering the trade
Never widened to avoid loss
7. Risk–Reward Ratio (RRR)
Risk management is incomplete without understanding reward potential.
Risk–Reward Ratio:
Risk : Reward = Stop Loss : Target
Common professional standards:
Minimum 1:2
Ideal 1:3 or higher
Example:
Risk per trade: ₹5,000
Target: ₹10,000 to ₹15,000
Even with a 40% win rate, a good RRR keeps you profitable.
8. Maximum Drawdown Control
Drawdown is the decline from peak capital.
Rules professionals follow:
Stop trading if drawdown reaches 10–15%
Reduce position size after consecutive losses
Never try to “recover quickly”
Survival during drawdowns is what separates amateurs from professionals.
9. Position Sizing in Different Markets
Intraday Trading:
Lower risk per trade (0.25%–0.5%)
Tight stop losses
Smaller targets
Positional Trading:
Risk per trade: 1%–2%
Wider stop losses
Fewer trades
F&O Trading:
Use defined-risk strategies
Avoid over-leveraging
Lot size must fit risk, not margin
10. Psychological Benefits of Proper Risk Management
Good risk management:
Reduces fear and greed
Prevents overtrading
Builds confidence
Makes results predictable
When you know the maximum possible loss, your mind stays calm and focused.
11. Common Risk Management Mistakes
Risking more after losses
Increasing position size emotionally
Trading without stop loss
Over-leveraging in options
Ignoring drawdown rules
One big loss can destroy months of discipline.
12. Professional Risk Management Rules
Risk small, trade consistently
Never risk more than you can afford to lose
Protect capital first, profits second
Think in series of trades, not single outcomes
Let probability work over time
13. Conclusion
Risk management and position sizing are not optional tools—they are the trading system itself. Entries and indicators only decide where you trade, but risk management decides whether you survive and grow.
The market rewards discipline, patience, and consistency—not aggression. Traders who master risk management stop chasing money and start building a professional trading business.
If you control risk, profits become a byproduct.
Axis Bank Ltd Daily Chart. Chart Pattern1. The chart pattern : Rounding Bottom Pattern:
Indicates a gradual reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
The white‑outlined area shows the consolidation phase forming the “bowl” shape.
A breakout above the resistance (upper rim of the bowl) would confirm the reversal and trigger a bullish move.
2. EMA Analysis:
EMA 21 (purple line) is crossing above EMA 55 (green line), showing short‑term momentum shift to bullish.
EMA 55 is above EMA 100 (blue line) and EMA 200 (orange line), indicating medium‑term bullish alignment.
Price is above all EMAs, suggesting strong support from the moving averages.
3. Volume:
Volume spikes during the decline into the bottom and increases near the breakout zone, confirming interest and potential strength in the reversal.
Watch for higher than average volume on the breakout to validate the move.
4.The View :
Measure the depth of the rounding bottom (from the lowest point to the rim) and project that distance upward from the breakout level.
Stop‑Loss: Place the SL below the recent swing low of the rounding bottom to protect against a false breakout.
Introduction to Cryptocurrency and Digital AssetsBlockchain Technology: The Backbone
At the heart of cryptocurrencies is blockchain technology, a distributed ledger system that records all transactions across a network of computers. A blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, each containing transaction data, timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This design ensures:
Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants.
Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect against fraud and unauthorized alterations.
Decentralization: No single entity controls the ledger, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be changed or deleted.
Beyond just financial transactions, blockchain enables smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded into the blockchain—which expand the utility of digital assets into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and digital identity verification.
Types of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
1. Cryptocurrencies:
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies designed to work as a medium of exchange. They include:
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, used as a store of value and medium of exchange.
Ethereum (ETH): A platform cryptocurrency that enables smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies like USD (e.g., USDT, USDC), designed to reduce volatility.
Altcoins: Alternative cryptocurrencies with varied purposes, such as Ripple (XRP) for cross-border payments or Cardano (ADA) for sustainable blockchain operations.
2. Digital Tokens:
These are blockchain-based units that can represent a variety of assets:
Utility Tokens: Provide access to a platform or service, like Binance Coin (BNB) for exchange fee reductions.
Security Tokens: Represent ownership of real-world assets such as shares, bonds, or real estate, regulated under securities laws.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique tokens representing ownership of digital or physical items like art, music, or collectibles.
3. Tokenized Assets:
Blockchain allows real-world assets—stocks, real estate, commodities—to be converted into digital form, making them easier to trade, fractionalize, and secure.
Use Cases of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Financial Transactions and Remittances:
Cryptocurrencies enable peer-to-peer payments without intermediaries, reducing fees and transaction times for international transfers.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DeFi platforms use smart contracts to offer banking services like lending, borrowing, and yield farming without traditional banks.
Digital Ownership and NFTs:
NFTs revolutionize digital ownership, allowing artists, gamers, and content creators to monetize their digital creations and maintain provable ownership.
Investment and Speculation:
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are increasingly seen as investment vehicles, attracting both retail and institutional investors seeking diversification and high returns.
Cross-Border Payments and Financial Inclusion:
Cryptocurrencies provide access to financial systems for unbanked populations, offering secure and cost-effective cross-border transactions.
Supply Chain and Identity Verification:
Blockchain’s transparency ensures traceability of goods, anti-counterfeiting measures, and secure digital identities.
Advantages of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Decentralization reduces reliance on central banks and financial institutions.
Transparency and security make financial operations more trustworthy.
Efficiency in cross-border transactions and settlements.
Innovation potential with smart contracts and tokenization.
Financial inclusion, particularly in regions with limited access to banking.
Challenges and Risks
Despite their promise, cryptocurrencies and digital assets face significant challenges:
Volatility: Prices can fluctuate wildly, making them risky for investors and unstable as currencies.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments vary in their approach to regulation, ranging from outright bans to active adoption.
Security Concerns: Hacks, scams, and loss of private keys pose risks to users.
Scalability Issues: Popular networks like Ethereum have faced congestion and high transaction fees.
Environmental Impact: Proof-of-work-based cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, consume enormous amounts of energy.
Adoption Barriers: Limited understanding, technological literacy, and infrastructure issues slow mainstream adoption.
Regulation and Legal Landscape
Governments worldwide are exploring how to regulate cryptocurrencies and digital assets to prevent fraud, money laundering, and market manipulation while enabling innovation. Regulatory approaches include:
Licensing cryptocurrency exchanges.
Taxation on transactions and holdings.
Oversight of stablecoins and digital banking platforms.
Creating central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as regulated alternatives.
Countries like Japan and Switzerland have embraced crypto-friendly regulations, whereas others like China have restricted trading and mining activities.
Future of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
The future of digital assets is promising but uncertain. Key trends include:
Integration with traditional finance: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly exploring crypto custody, trading, and payment systems.
Expansion of DeFi: More financial services may migrate to decentralized networks.
Tokenization of assets: Ownership of real-world assets will become more flexible, liquid, and transparent.
CBDCs and hybrid models: Central banks are exploring digital currencies that combine regulation with blockchain efficiency.
Greater mainstream adoption: Merchants, consumers, and enterprises may increasingly accept cryptocurrencies for payments and investments.
The evolution of cryptocurrency and digital assets could redefine how value is stored, transferred, and created globally, challenging traditional financial systems while opening new opportunities for innovation, inclusion, and efficiency.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets represent a revolutionary shift in the way people perceive and interact with money, ownership, and digital ecosystems. While they bring enormous opportunities for financial innovation, inclusion, and efficiency, they also carry inherent risks related to volatility, security, and regulation. The continued development of blockchain technology, smart contracts, tokenization, and decentralized finance is likely to shape the future of global finance, making it more transparent, accessible, and efficient. As adoption grows, understanding the fundamentals, potential, and pitfalls of cryptocurrencies and digital assets is essential for investors, policymakers, and the general public alike.