$AAVE -86% CRASH CREATED A ONCE-IN-A-CYCLE OPPORTUNITY CRYPTOCAP:AAVE -86% CRASH CREATED A ONCE-IN-A-CYCLE OPPORTUNITY | $1,000 TARGET STILL IN PLAY?
#AAVE Is Trading Around $124 Above Major Weekly Strong TL Support at $90 Which is HTF Accumulation Zone.
Structure Is Showing Clear Liquidity Sweep + Reaction From Multi-Year Ascending Trendline That Has Held Since 2021.
Already Experienced -86% Correction From It's ATH, Classic Re-Accumulation Setup Forming.
Price Compressing Between Descending Resistance & Ascending Support. Breakout Imminent.
CURRENT TECHNICAL STRUCTURE:
➤ Bullish OB & Support (Accumulation Zone): $110-$90
➤ Price Must Hold Above $74 For Bullish Continuation
➤ Multi-Year Ascending Trendline + 0.618 Fib Confluence = Strong Demand
➤ Descending TL Compression + Higher Low Formation In Progress
➤ Weekly Close Below $74 = Bullish Invalidation
Upside Targets: $190 ➔ $345 ➔ $579 ➔ $1,000+ (~10x From Accumulation Zone)
IMO: #AAVE Is Currently Trading Between 0.618-0.786 Fib Strong Support A Generational Accumulation Range Before Massive Expansion. DeFi Blue Chip At 86% Discount.
Purely TA Only | Not Financial Advice | Always DYOR
Your Aave Target This Cycle?
Like + RT + Bookmark
Cryptomarket
Bitcoin’s Corrective Wave in Action 🚀 Bitcoin’s Corrective Wave in Action 📈💡
After touching a low near 60K, Bitcoin has begun rising within its Corrective ABC formation.
🔹 Wave A:
• Rose in 3 sub-waves, signaling a flat correction 🔄
• Hit a high of 72,271 📊
• Duration: 21 bars — a Fibonacci number ✨
🔹 Wave B (ongoing):
• Currently unfolding, with potential downside toward 64,500 📉
• Expected completion: 19th Feb, between 9:30 AM – 1:30 PM IST ⏰
🔹 Wave C (next):
• Likely to be impulsive, driving momentum upward ⚡
• Target: 80K+ 🚀💰
📊 Takeaway: The corrective phase is still in play. Patience is key — wait and watch as the structure completes 👀
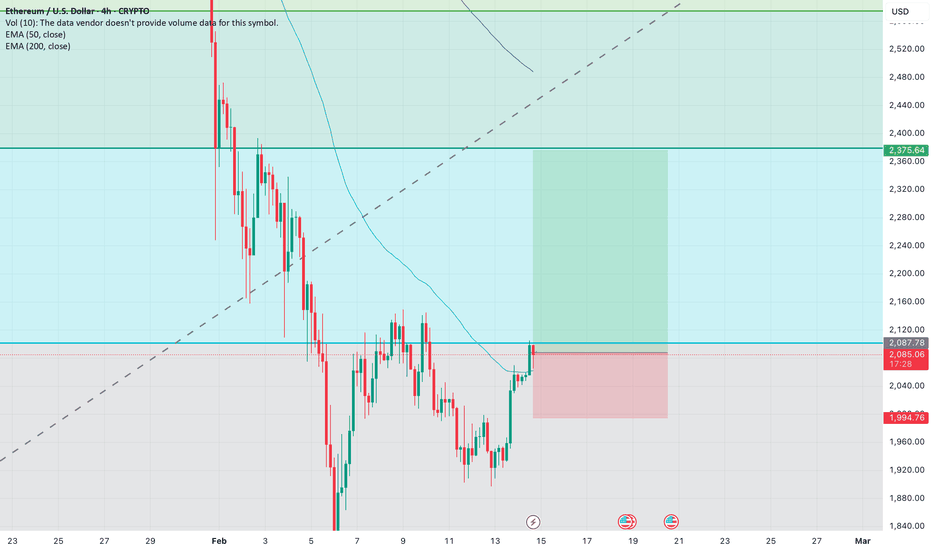
ETH on to the reversal.Hey folks,
I am seeing 4h TF of ETH. the coin is testing the price of 2100 from a quite time now.
50EMA support can be noticed now on the current 4hr candle. i.e after the downward rally ended first time 4h tf candle closed above 50ema.
there is a potential reversal to the true value of ETH soon.
My Trade Setup :
Early Entry : 2050 to 2100
confirmation Entry : above 2100
SL : 1990
TP : 2375
R:R = 1:3
:) Thanks. Happy Trading.
BTC/USD 45m Chart Analysis – Bearish Rejection at Supply1️⃣ Market Context
Timeframe: 45-minute
Price is trading around $69,768
Overall short-term structure shows recovery from ~65k into a key resistance zone near 70k–70.5k
2️⃣ Key Observations
🔴 Major Resistance (Supply Zone)
Strong rejection around $70,000–$70,500
Multiple prior reactions from this level
Long upper wick shows sellers defending aggressively
📈 Bullish Structure Before Rejection
Clean ascending channel from ~65k
Breakout above 67.7k level
Strong impulsive move into resistance
This looks like a liquidity sweep above previous highs, followed by rejection.
3️⃣ Trade Idea Shown on Chart
Entry: Near 69.8k–70k
Target: Around 67.7k
Bias: Short (counter-trend scalp)
The target aligns with:
Previous breakout level
Minor support / demand flip zone
Potential retest of structure
4️⃣ What Confirms the Short?
✅ Lower high on lower timeframe
✅ Breakdown below intraday support (~69.2k area)
✅ Increasing bearish momentum
Without breakdown confirmation, price could:
Consolidate under resistance
Attempt another push above 70.5k
5️⃣ Risk Factors
⚠️ Trend on this timeframe is still making higher lows
⚠️ A clean break and close above 70.5k invalidates short bias
⚠️ High volatility near psychological 70k level
6️⃣ Overall Outlook
Short-term: Bearish pullback likely toward 67.7k
Mid-structure: Still bullish unless 67k breaks decisively
Invalidation: Strong close above 70.5
BTC Reversal or still bearish (13/02/2026).BTC is trading in a parallel channel.
Major Trend :- Bearish
Minor Trend :- Range Bound.
A bearish scalp trade can be taken upto the support levels of the channel. With a SL being a candle closing above the channel.
If there are halt candle near the resistance levels and a BO occurs, a 1000 points trade in BTC can be taken and trailed upto the upper levels if the trend line resistance is also breached.
Actually, there are good targets on the upper side with good RR.
Bullish Plan
Entry :- Close above 67600
SL :- 66800
Target :- 68350, 71460.
R:R = 1:1 and 1:4.5 (considering Target 2).
As per the plan, BTC will give a double BO i.e. 20 EMA (4H) and Resistance Zone.
Wait for the price action. BTC is in a sideway to volatile zone.
Enter with a proper SL and trail target on the upper side.
On the Bearish side, there is limited targets or a scalp trade.
Happy Trading.
XAUUSD (Gold Spot) – 1H Chart Analysis & Trade Idea Gold has shifted into a short-term bullish structure after forming a higher low and reclaiming the key support zone. Price is consolidating above the former resistance, which is now acting as support—a typical continuation setup.
Key Levels
Support / Entry Zone: 5,000 – 5,030 (blue zone, prior resistance turned support)
Stop Loss: Below 4,950 (red zone, structure invalidation)
Target: 5,100 – 5,150 (green demand/supply objective)
Trade Idea
Bias: Bullish continuation
Entry: Buy on pullback into the support zone or on bullish confirmation above it
Stop Loss: Below the marked stop-loss zone to protect against a breakdown
Take Profit: Target the upper demand zone for continuation upside
Confluence
Break-and-retest of resistance as support
Higher low formation on H1
Momentum holding above the support line
Risk Management
Maintain disciplined position sizing. If price closes decisively below the support zone, the bullish setup is invalidated.
This idea is based on technical structure and zone analysis. Always manage risk according to your trading plan.
BitCoin? a bit down or big downBitcoin is loosing it fizz now and rally may be about to end.
as per chart reading i can see that it is on the resistance levels
and as now world economies are also settling it should be possible that crypto frenzy get no hype and for that Bitcoin may see a down pludge
Possibly for next 2-2.5 Years Bitcoin won't cross the recent highs and may be retesting 72K level or more downside.
Up move will only continue after breaking and closing above this trendline.
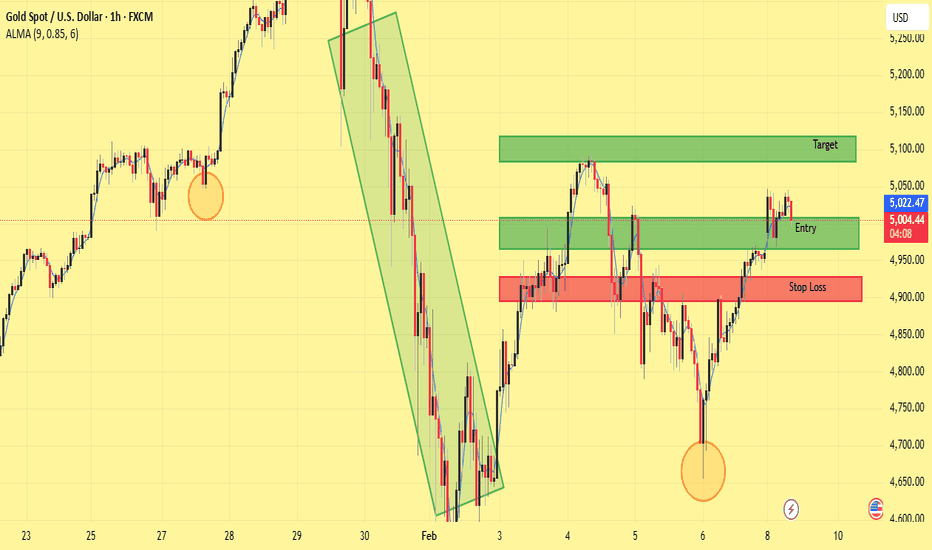
We’re looking at Gold vs USD on the 1-hour chartPrice recently completed a deep pullback after a strong bullish leg.
That pullback formed a rounded / cyclical bottom (purple curve), which often signals trend continuation, not reversal.
🧠 Structure & Price Action
What stands out:
Higher low formed after the sell-off → bullish market structure
Strong impulsive bullish candles off the lows → buyers in control
Price reclaimed and is holding above a key mid-range level (~4960)
This tells us:
The correction phase is likely complete, and price is transitioning back into an impulse phase upward.
🎯 Trade Idea (Based on Your Chart)
✅ Entry
Buy around 4,960 – 4,970
This is a pullback entry inside bullish continuation
🛑 Stop Loss
Below the recent structure low
Around 4,840 – 4,860
If price breaks here, the bullish idea is invalidated
🎯 Target
5,050 – 5,100 zone
This aligns with:
Prior resistance
Projected impulse leg (measured move)
Liquidity resting above highs
Risk–Reward:
Roughly 1:2.5 to 1:3, which is solid for an intraday/swing setup.
🔍 Why This Setup Makes Sense
Bullish continuation after correction
Structure shift confirmed (higher low)
Strong momentum candles
Clear invalidation level (clean risk)
The blue projected path you drew fits perfectly with a pullback → continuation → expansion model.
⚠️ Invalidation Clue
If price:
Breaks and closes below the stop zone
Or starts printing lower highs + strong bearish momentum
→ bullish bias is off, and we reassess.
XAUUSD (Gold) – 1H Chart Analysis & Trade Idea
Gold has completed a strong corrective phase after the sharp bearish impulse and is now showing signs of trend reversal and bullish continuation. Price respected the recent swing low (marked with the circle), forming a higher low, which confirms improving market structure.
After the rebound, price pushed above the short-term moving average and successfully retested a key demand zone, which now acts as support. This area aligns with previous consolidation, increasing the probability of bullish continuation.
Trade Idea
Entry: Buy from the highlighted green support / entry zone
Stop Loss: Below the red support zone (below recent higher low)
Target: Upper green resistance zone (prior supply area)
Technical Confluence
Higher low formation (bullish structure shift)
Strong rejection from demand zone
Moving average support holding
Previous resistance turned support
Favorable risk-to-reward setup
Conclusion
As long as price holds above the stop-loss zone, the bullish bias remains valid. A sustained move toward the marked target zone is expected. A break below support would invalidate this setup.
This analysis is for educational purposes only. Always manage risk properly.
If you want, I can also:
Rewrite this in short TradingView post style
Translate it into German, French, Spanish, Italian, Turkish, or Polish
Create a title-only version for quick posting
How Regulations Shape the Crypto Market1. Why Governments Regulate Crypto
Regulators intervene primarily to address risk, stability, and control. Cryptocurrencies challenge the traditional financial system in several ways:
They bypass banks and intermediaries
They enable anonymous or pseudonymous transactions
They operate across borders instantly
They introduce volatile, speculative assets
From a government perspective, unchecked crypto adoption can threaten monetary policy, capital controls, tax collection, and consumer protection. High-profile failures—such as exchange collapses, fraud, hacks, and stablecoin de-pegging—strengthened the case for regulation.
Thus, regulation aims to:
Protect investors and consumers
Prevent money laundering and illicit finance
Maintain financial stability
Integrate crypto into existing legal frameworks
2. Regulation and Market Legitimacy
One of the most important effects of regulation is legitimization. When governments define legal frameworks for crypto, institutional investors gain confidence to participate.
Clear rules allow:
Banks to offer crypto services
Asset managers to launch crypto funds and ETFs
Corporations to hold crypto on balance sheets
Payment firms to integrate blockchain rails
For example, regulatory approval of Bitcoin ETFs in some jurisdictions significantly boosted market participation and liquidity. Regulation transforms crypto from a speculative fringe asset into a recognized financial instrument.
However, legitimacy comes at a cost—compliance.
3. Compliance Reshapes Crypto Businesses
Crypto regulation fundamentally changes how companies operate. Exchanges, wallets, and DeFi platforms must adapt to rules traditionally applied to banks and financial institutions.
Key compliance requirements include:
KYC (Know Your Customer)
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) checks
Transaction monitoring
Licensing and reporting obligations
This reshapes the market in several ways:
Smaller or undercapitalized projects exit
Well-funded players gain dominance
Decentralized ideals face practical limits
As a result, the industry becomes more institutionalized and consolidated. While this reduces fraud and instability, it also raises concerns that crypto is becoming “traditional finance with blockchain branding.”
4. Regulation and Innovation: Constraint or Catalyst?
A common argument is that regulation stifles innovation. Overly strict or unclear rules can push developers offshore or discourage experimentation. Startups struggle with compliance costs, and decentralized protocols face legal ambiguity.
However, smart regulation can accelerate innovation by:
Providing legal clarity
Attracting long-term capital
Encouraging responsible product design
Jurisdictions with balanced frameworks often become crypto hubs, attracting talent and investment. Innovation thrives when builders understand the rules of the game instead of operating in legal grey zones.
The key issue is not regulation itself—but how well it is designed.
5. Impact on Decentralization and DeFi
Decentralized finance (DeFi) presents the biggest regulatory challenge. DeFi protocols operate without central entities, making enforcement difficult.
Regulators struggle with questions like:
Who is responsible for a smart contract?
Can code be regulated like a company?
How do you apply KYC to decentralized protocols?
As a result:
Some DeFi platforms introduce front-end restrictions
Developers geo-block certain regions
Governance tokens come under scrutiny
Regulation may push DeFi toward hybrid models, blending decentralization with compliance. While purists argue this undermines crypto’s core philosophy, others see it as necessary for mass adoption.
6. Stablecoins and Monetary Control
Stablecoins sit at the intersection of crypto and traditional money, making them a top regulatory priority. Because stablecoins resemble private digital currencies, governments fear loss of monetary sovereignty.
Regulation of stablecoins focuses on:
Reserve transparency
Issuer accountability
Redemption guarantees
Systemic risk
Strict oversight transforms stablecoins into regulated financial products rather than experimental tokens. This increases trust and usability but limits flexibility.
At the same time, regulatory pressure on stablecoins has accelerated the development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), as governments seek state-controlled digital alternatives.
7. Global Regulatory Fragmentation
Crypto is global, but regulation is local. Different countries take vastly different approaches, creating fragmentation.
Some embrace crypto as innovation
Some impose heavy restrictions
Some ban it outright
This creates regulatory arbitrage, where businesses move to friendlier jurisdictions. Capital, developers, and liquidity flow toward regions with clearer and more favorable rules.
Over time, this competition may push governments to refine policies or risk falling behind in financial innovation.
8. Market Volatility and Regulatory News
Regulation heavily influences crypto market psychology. Announcements related to bans, approvals, taxation, or enforcement actions often trigger sharp price movements.
Markets react because regulation affects:
Liquidity access
Institutional participation
Project survival
Legal risk
In this sense, regulation has become a macro driver for crypto markets, similar to interest rates or inflation data in traditional finance.
9. Investor Protection and Retail Confidence
Regulation improves investor protection by:
Reducing scams and fraud
Enforcing disclosures
Holding platforms accountable
This builds retail confidence and encourages broader participation. While speculative excess may decline, the market becomes more resilient and sustainable.
A regulated environment favors long-term investors over short-term hype cycles.
10. The Future: Coexistence, Not Conflict
Crypto regulation is no longer about suppression—it is about integration. Governments increasingly recognize that crypto is not disappearing. The challenge is to harness its benefits while managing its risks.
The future likely includes:
Regulated centralized platforms
Semi-compliant DeFi structures
Tokenized real-world assets
Blockchain-based financial infrastructure
Rather than killing crypto, regulation is shaping its evolution from rebellion to infrastructure.
Conclusion
Regulation is one of the most powerful forces shaping the crypto market. It determines who can participate, how businesses operate, and which innovations survive. While excessive regulation can slow progress, thoughtful frameworks create stability, trust, and long-term growth.
Crypto’s journey is no longer about avoiding regulation—but learning to grow within it. The projects and ecosystems that adapt intelligently will define the next phase of the digital financial revolution.
BTCUSD (1H) – Range Support Bounce | Bullish Reversal SetupBTCUSD (1H) – Range Support Bounce | Bullish Reversal Setup
Bitcoin is trading on the 1-hour timeframe after completing a corrective decline and forming a clear range structure. Price has recently reacted strongly from the lower demand/support zone, indicating buyer interest at this level.
Technical Breakdown:
Support Zone: Price bounced from a well-defined green demand area, aligning with a cyclical low and previous accumulation.
Structure Shift: After making a higher low, BTC is attempting to reclaim the mid-range, suggesting a short-term bullish reversal.
ALMA Indicator: Price is stabilizing around the ALMA, which often acts as a dynamic trend filter. Holding above it favors upside continuation.
Cycle Projection: The curved projection highlights a potential move toward the upper range resistance, following previous cyclical behavior.
Momentum: The oscillator shows recovery from oversold conditions, supporting the bullish bounce scenario.
Trade Idea:
Entry: Near current levels or on a minor pullback above the support zone
Target: Upper resistance / range high area
Invalidation: A clean break and close below the demand zone would invalidate the bullish setup
Bias:
📈 Bullish toward range high, as long as price holds above support.
⚠️ Always wait for confirmation and manage risk accordingly.
Bearish Continuation Setup After Dead-Cat Bounce (1H)
What the chart is saying:
Clear bearish trend: Price has been making lower highs and lower lows. The broader structure is decisively bearish.
Range breakdown: The blue box shows a consolidation range that broke to the downside, confirming continuation rather than accumulation.
Strong sell-off into demand: Price aggressively dropped into the red support zone (~62k–64k), where buyers stepped in hard, creating a sharp bounce.
Relief rally, not reversal: The current move up is a retracement, not a trend change. Momentum looks corrective, not impulsive.
Key resistance zone (~71k–72k):
This green area is previous support turned resistance
It aligns with the breakdown level → classic short opportunity
Planned trade idea (as drawn):
Entry: Into resistance (green zone)
Invalidation: Clean acceptance above resistance
Target: Prior support / liquidity pool around 63k
R:R: Favorable if rejection confirms
Bias:
📉 Bearish below resistance
Only a strong breakout + hold above 72k would weaken the short thesis
What to watch next:
Rejection wicks, bearish engulfing, or momentum divergence at resistance
Volume drying up on the push into the green zone
Failure to reclaim broken structure
⚠️ This setup assumes trend continuation, not a bottom. Until structure flips, rallies are sell-the-rip candidates.
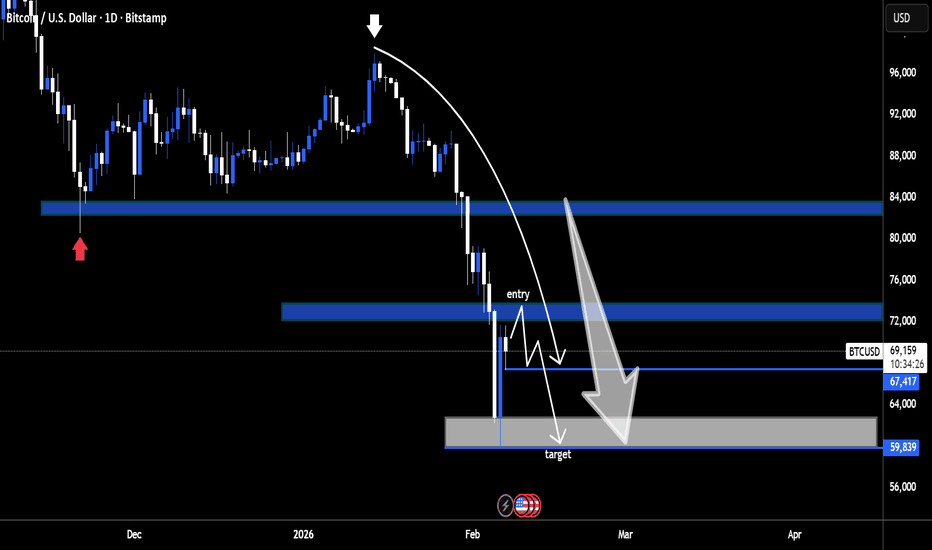
BTCUSD Daily – Bearish Breakdown & Sell-the-Retests Setup
Here’s what the chart is saying, clean and to the point:
Market Structure
Clear distribution → breakdown sequence on the daily.
Price topped near the mid-90Ks, rolled over, and lost the 83–84K demand zone (former support marked in blue).
That loss flipped market structure firmly bearish.
Key Levels
Major breakdown level: ~83–84K (prior demand → resistance)
Supply / entry zone: ~72–74K (blue zone labeled “entry”)
Current support: ~67.4K (thin blue line)
Primary target: ~60–62K (grey demand zone)
Price Action Logic
The vertical sell-off into ~67K suggests impulsive bearish strength, not exhaustion.
The projected path shows a dead-cat bounce / consolidation into ~72–74K.
That zone aligns with:
Prior consolidation
Bearish retest logic
Likely supply from trapped longs
Trade Thesis (as illustrated)
Bias: Short
Entry idea: Sell a rejection in the 72–74K zone
Invalidation: Strong daily close back above ~75K
Target: 60–62K demand (first meaningful higher-timeframe support)
Big Picture
Unless BTC reclaims the 80K+ region quickly, this chart favors continuation lower, not a V-shaped recovery. The structure says rallies are for selling, not buying.
BREV/USDT Crypto Futures – Buy Stop SetupBREV/USDT, a Buy Stop order is recommended at 0.1433, anticipating upward momentum. The trade targets are set at 0.1457 for TP1 and 0.1479 for TP2, offering potential profit zones as the price moves higher. To manage risk, a stop-loss is placed at 0.1397, ensuring controlled exposure in case of a market reversal. This setup suggests a bullish bias, and traders should monitor price action closely to confirm the momentum before entry.
BREV/USDT
Buy Stop
Entry: 0.1433
Target 1 (TP1): 0.1457
Target 2 (TP2): 0.1479
Stop Loss (SL): 0.1397
Bias: Bullish – expecting upward momentum
⚠️ Disclaimer:
This trade setup is for educational and informational purposes only. Trading cryptocurrencies involves high risk, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Always do your own research (DYOR) and trade responsibly. Never invest money you cannot afford to lose.
BTCUSD (1H) – Bearish Continuation | Trendline Breakdown IdeaMarket Structure
Bitcoin remains in a clear descending channel on the 1H timeframe. Price has consistently respected the downward sloping trendline, confirming a strong bearish structure with lower highs and lower lows.
Technical Confluence
Trendline Resistance (Red): Multiple rejections validate seller dominance.
Auto Pitchfork: Price is trading below the median line, indicating continuation toward the lower parallel.
Dynamic Support (Green): The recent breakdown below channel support signals bearish continuation rather than a reversal.
Balance of Power (BoP): Reading around -0.38 reflects sustained selling pressure with no bullish divergence.
Price Action
A brief consolidation failed to hold, followed by a strong bearish impulse that broke key intraday support. The current move suggests momentum-driven continuation, not exhaustion.
Trade Idea
Bias: Bearish
Sell Zone: Pullback toward broken support / descending trendline
Targets:
First target: Previous minor low
Extended target: Lower pitchfork boundary / demand zone
Invalidation: Sustained close above the descending trendline
Conclusion
As long as BTC remains below the descending trendline and pitchfork median, the path of least resistance is downward. Any retracement into resistance is likely to be a selling opportunity unless market structure shifts.
Always manage risk and wait for confirmation.
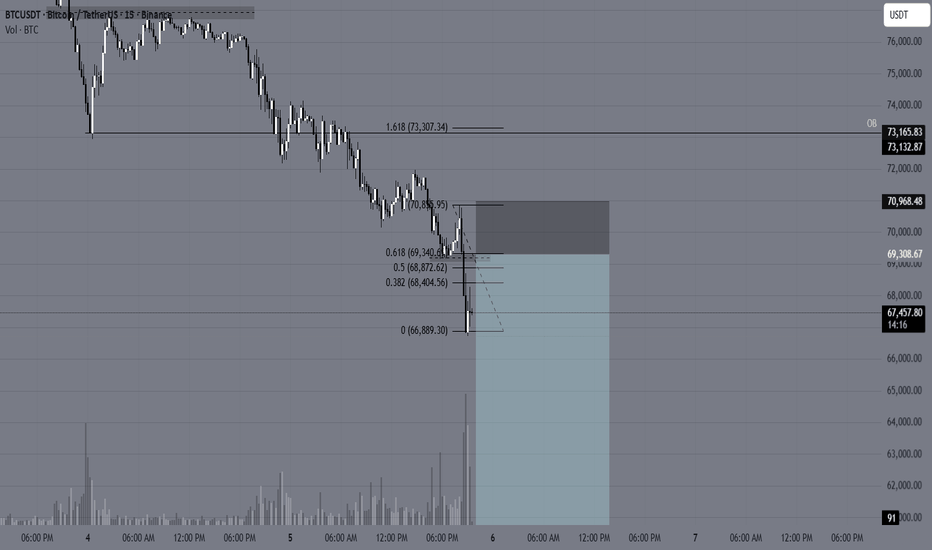
Bearish continuation for BTCUSD📍 Primary Plan — Short the Pullback
✅ Entry Zone (Sell)
69,800 – 70,800
Reason:
Previous breakdown area
Intraday supply
Likely retest zone after bounce
🛑 Stop Loss
Above 71,300
Why:
Above last lower-high cluster
Above pullback structure
If price gets here → bearish idea weakens
🎯 Targets
Target Level Logic
T1 68,000 intraday support
T2 66,500 recent sweep zone
T3 65,000 next liquidity pocket
T4 60,000 Final stoppage
Scale out — don’t hold full size to last target.
🚀 Alternate Plan — Breakout Long (Only If Structure Shifts)
Right now this is counter-trend — so only trade if confirmed.
✅ Breakout Confirmation (Must Have)
15m candle close + hold above 71,000–71,200
Not just a wick — a body close + small pullback hold.
📍 Long Entry Zone
On retest of 71,000–71,200 after breakout
🛑 Stop Loss (Long)
Below 70,200
🎯 Long Targets
Target Level
T1 72,300
T2 73,100
T3 74,200
⚠️ Quick Reality Check (Important)
Right now:
Momentum = bearish
Structure = lower highs / lower lows
Best edge = short pullbacks, not blind longs
Breakout longs only after reclaim — no anticipation trades here 😄
XAUUSD – Bullish Reversal from Demand Zone (H1)Gold (XAUUSD) was previously trading inside a well-defined ascending channel, indicating a strong bullish trend. After reaching the upper boundary, price faced a sharp bearish correction and broke down from the channel.
Following this drop, price found strong support near the 5,000 demand zone, where buyers entered aggressively. From this area, price formed a V-shaped / rounded bottom recovery, signaling a shift in momentum from bearish to bullish.
Currently, price has reclaimed and is holding above the demand zone, showing strong bullish continuation. As long as price remains above this zone, the upside bias remains intact.
Trade Bias: Bullish above the demand zone
Entry Zone: Demand zone retest or bullish continuation
Targets:
Target 1: 5,120
Target 2: 5,198
Invalidation:
A strong break and close below the demand zone would invalidate the bullish setup.
This setup aligns with demand–supply dynamics, trend continuation, and a momentum shift, favoring buyers in the near term.
Cryptocurrency Trading: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Altcoins1. Understanding Cryptocurrencies
At its core, a cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual asset that uses cryptography for security. These assets are decentralized, meaning they are generally not controlled by a central authority like a government or bank.
Bitcoin (BTC): Launched in 2009 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is the first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency. It operates on a decentralized ledger called the blockchain and is often considered a “digital gold” due to its scarcity and store-of-value characteristics. Bitcoin’s price is highly sensitive to macroeconomic factors, investor sentiment, and adoption trends.
Ethereum (ETH): Created in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum introduced programmable smart contracts, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to run on its blockchain. Ethereum’s ecosystem supports DeFi (Decentralized Finance), NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), and other innovations. ETH’s price movements are influenced not only by market speculation but also by the adoption of its network and upgrades, such as the transition to Ethereum 2.0.
Altcoins: Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin and Ethereum is considered an altcoin. Examples include Ripple (XRP), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and Dogecoin (DOGE). Each altcoin may have unique use cases, consensus mechanisms, and communities. Traders often target altcoins for higher short-term gains due to their volatility, but they also carry higher risk and lower liquidity compared to BTC or ETH.
2. Types of Cryptocurrency Trading
Cryptocurrency trading can be categorized based on the duration and style of trading:
Spot Trading: This involves buying and selling actual cryptocurrencies on an exchange. Traders profit from price fluctuations without leveraging positions. Spot trading is straightforward and is ideal for beginners.
Margin Trading: Traders borrow funds to amplify their positions. For example, a 5x leverage allows you to trade five times your capital. While margin trading increases profit potential, it also magnifies losses, and liquidation risks are high during volatile market swings.
Futures and Derivatives Trading: Futures contracts allow traders to speculate on the price of cryptocurrencies without owning the underlying asset. Derivatives include perpetual contracts, options, and swaps. These instruments provide opportunities for hedging, arbitrage, and speculative trading but require strong risk management skills.
Algorithmic Trading: Some traders use bots and algorithms to execute trades automatically based on technical indicators, price patterns, or arbitrage opportunities. Algorithmic trading requires coding knowledge or access to trading platforms with prebuilt bots.
3. Key Trading Strategies
Successful cryptocurrency trading is a combination of research, strategy, and discipline. Some commonly used strategies include:
Day Trading: Traders open and close positions within the same day to profit from intraday price movements. This strategy requires constant monitoring of the market, quick decision-making, and a solid understanding of technical analysis.
Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on medium-term price trends. This strategy relies heavily on trend analysis, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns.
Scalping: Scalpers aim to make small profits from frequent trades, often holding positions for minutes or hours. Scalping demands high-speed execution, low transaction costs, and precise market timing.
HODLing: Derived from “hold,” HODLing involves buying and holding cryptocurrencies for the long term, believing in their future value appreciation. Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular choices for HODLers.
Arbitrage: Traders exploit price differences between exchanges by buying on one platform and selling on another. While theoretically low-risk, arbitrage opportunities are often short-lived and require fast execution and low fees.
4. Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Trading decisions are often informed by two primary approaches:
Technical Analysis (TA): TA involves studying price charts, volume, and market indicators to forecast future price movements. Common tools include moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Fibonacci retracements, and candlestick patterns. TA is crucial for short-term traders and day traders.
Fundamental Analysis (FA): FA focuses on the underlying value of a cryptocurrency. This includes network activity, adoption rates, developer activity, partnerships, regulatory news, and macroeconomic factors. For instance, Ethereum’s price is influenced by the growth of DeFi applications and the ETH 2.0 upgrade.
5. Risks in Cryptocurrency Trading
Cryptocurrency trading is inherently risky due to its volatility and lack of regulation in some jurisdictions. Key risks include:
Price Volatility: Cryptocurrencies can swing 10–20% in a single day. Sudden news events, market sentiment shifts, or regulatory announcements can trigger massive price movements.
Regulatory Risk: Governments may introduce regulations that impact trading, taxation, or even the legality of cryptocurrencies in certain regions.
Security Risk: Exchanges and wallets are targets for hackers. Using hardware wallets, enabling two-factor authentication, and avoiding unregulated platforms can reduce exposure.
Liquidity Risk: Low-volume altcoins may be difficult to buy or sell at desired prices, leading to slippage or losses.
Psychological Risk: Emotional trading can result in impulsive decisions, chasing losses, or FOMO-driven buying. Maintaining discipline is essential for long-term profitability.
6. Choosing the Right Exchange
Selecting a cryptocurrency exchange is critical. Traders should consider:
Security: Look for exchanges with strong security protocols, insurance funds, and a track record of handling breaches.
Liquidity: Higher liquidity ensures better execution of trades with minimal slippage.
Fees: Trading, withdrawal, and deposit fees can significantly impact profits, especially for frequent traders.
Features: Advanced charting tools, leverage options, staking, and futures trading can influence your trading style.
Regulation and Reputation: Exchanges registered in reputable jurisdictions with clear KYC/AML policies offer better reliability.
7. Portfolio Management and Diversification
Even in cryptocurrency trading, diversification is key. Allocating funds across multiple coins, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and promising altcoins, can reduce risk. Position sizing, stop-loss orders, and taking profits at predefined levels help manage volatility and protect capital.
8. Trends Shaping Cryptocurrency Trading
Several trends are transforming cryptocurrency trading:
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms like Uniswap and PancakeSwap allow peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, promoting decentralized finance.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies, such as USDT and USDC, offer traders a safe haven during market downturns.
NFTs and DeFi: Non-fungible tokens and decentralized finance applications are creating new trading opportunities beyond conventional crypto assets.
Institutional Adoption: Increasing interest from hedge funds, banks, and corporations provides greater liquidity and legitimacy to the market.
9. Regulatory Considerations
Regulations vary by country. In India, cryptocurrencies are legal but heavily monitored, and taxation applies to gains. Traders must stay updated on government policies, tax obligations, and exchange compliance requirements to avoid legal pitfalls.
10. Conclusion
Cryptocurrency trading is a blend of art and science, combining technical skills, fundamental research, risk management, and emotional discipline. While Bitcoin and Ethereum dominate the market due to their liquidity and established networks, altcoins provide opportunities for higher returns—and higher risk.
Traders should approach this market with caution, continuous learning, and a well-defined strategy. Whether engaging in short-term trades or long-term HODLing, understanding market dynamics, technology trends, and risk management practices is essential to navigate the volatile and exciting world of cryptocurrency trading.
In summary, cryptocurrency trading is not just about chasing profits but about understanding the technology, analyzing market behavior, and making informed decisions in an ever-evolving financial landscape.
Cryptocurrency & Digital Asset MarketsIntroduction
The rise of cryptocurrencies and digital assets represents one of the most significant innovations in financial markets over the last decade. Originating with Bitcoin in 2009, cryptocurrencies have evolved from a niche technology experiment into a multi-trillion-dollar ecosystem encompassing thousands of digital assets, decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), stablecoins, and blockchain-based applications. These markets challenge traditional financial structures by providing decentralized, borderless, and programmable forms of money and value transfer. Understanding the structure, dynamics, and risks of cryptocurrency markets is crucial for investors, traders, and policymakers alike.
Cryptocurrency and Digital Asset Basics
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security, making them resistant to counterfeiting. Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, primarily using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger that records all transactions transparently and immutably.
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency, designed as a decentralized digital alternative to traditional currency.
Altcoins: Other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and Ripple (XRP) with specific use cases beyond payment, including smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and finance.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to traditional currencies like USD (e.g., USDT, USDC) to minimize volatility and serve as a medium of exchange in digital markets.
Tokens: Digital assets built on existing blockchains, representing assets, access rights, or utilities within ecosystems.
Digital assets encompass a broader category beyond cryptocurrencies. They include NFTs, tokenized securities, and digital representations of real-world assets. Digital assets are programmable, tradable, and often interoperable across blockchain networks.
Market Structure
Cryptocurrency markets differ from traditional financial markets in several key aspects:
Decentralization: Unlike stock or bond markets, many cryptocurrency markets operate without a central exchange or authority. Peer-to-peer trading, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and blockchain protocols allow transactions without intermediaries.
24/7 Trading: Cryptocurrency markets never close. Trading occurs continuously, globally, providing high liquidity opportunities but also exposing participants to constant market risk.
Market Participants: Participants include retail investors, institutional investors, miners, validators, and algorithmic trading bots. Institutional adoption has grown in recent years, introducing products like cryptocurrency ETFs, futures, and custody services.
Exchanges: Cryptocurrencies trade on centralized exchanges (CEXs) like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken, which provide liquidity, custody, and compliance. Decentralized exchanges like Uniswap and Sushiswap operate without intermediaries, using smart contracts to facilitate trades.
Price Determinants
Cryptocurrency prices are influenced by multiple factors:
Supply and Demand: Fixed supply (e.g., Bitcoin’s 21 million cap) versus demand from investors, institutions, and retail users.
Market Sentiment: News, social media, and macroeconomic events can significantly impact crypto prices due to market psychology and herd behavior.
Regulation: Legal frameworks in different countries affect adoption and trading. Positive regulation encourages investment, while bans or restrictions can trigger sell-offs.
Technological Developments: Upgrades to blockchain protocols, new network features, or innovations in scalability and security can drive price appreciation.
Macro Factors: Inflation, interest rates, and currency depreciation indirectly influence crypto adoption as an alternative store of value.
Key Market Segments
Spot Market: The direct buying and selling of cryptocurrencies at current prices. Spot trading is the foundation of crypto markets.
Derivatives Market: Includes futures, options, and perpetual contracts allowing traders to hedge, speculate, or leverage positions. Derivatives markets add liquidity but increase systemic risk.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): A rapidly growing sector offering lending, borrowing, yield farming, and automated market-making without traditional banks. DeFi uses smart contracts to automate financial services.
NFT Market: Non-fungible tokens represent unique digital assets such as art, collectibles, or virtual real estate. NFTs are changing the way ownership and creativity are monetized.
Tokenized Assets: Traditional assets like real estate, commodities, or stocks are increasingly tokenized to enable fractional ownership, faster settlements, and cross-border liquidity.
Trading and Investment Strategies
Cryptocurrency markets offer diverse opportunities, but they are highly volatile and risky. Common strategies include:
HODLing: Long-term holding of cryptocurrencies based on belief in their future adoption and value appreciation.
Day Trading: Short-term trading to exploit price volatility within intraday movements.
Swing Trading: Capturing medium-term price trends over days or weeks.
Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between exchanges or markets.
Staking and Yield Farming: Earning rewards by locking cryptocurrencies in networks or DeFi protocols.
Market Risks and Challenges
Cryptocurrency and digital asset markets are exposed to several unique risks:
Volatility: Price swings of 10–20% in a single day are common. Extreme volatility can lead to significant gains or catastrophic losses.
Security Risks: Hacks, scams, phishing, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts or exchanges have historically caused large financial losses.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still defining legal frameworks. Sudden regulations can restrict access or impact asset values.
Liquidity Risk: Smaller cryptocurrencies may have low trading volume, making it difficult to enter or exit positions at desired prices.
Technological Risk: Blockchain bugs, network forks, and software vulnerabilities can disrupt trading and asset functionality.
Market Manipulation: Low liquidity and lack of regulation in some areas make cryptocurrencies susceptible to pump-and-dump schemes and price manipulation.
Adoption and Institutional Participation
Institutional adoption has accelerated the growth of cryptocurrency markets:
Major financial institutions now offer crypto custody, trading, and investment products.
Hedge funds, pension funds, and insurance companies are allocating portions of their portfolios to digital assets.
Payment companies like PayPal and Mastercard facilitate crypto transactions.
Central banks are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), potentially integrating digital assets with traditional monetary systems.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulation remains a defining factor in the future of crypto markets:
Countries like the United States and the European Union are working on clear regulatory frameworks covering taxation, anti-money laundering (AML), and investor protection.
Some nations, such as El Salvador, have adopted cryptocurrencies as legal tender.
Others, like China, have banned crypto trading and mining, illustrating the wide divergence in global policies.
Regulatory clarity is expected to increase market legitimacy, attract institutional capital, and reduce systemic risks.
Future Trends
DeFi Expansion: Decentralized finance is expected to grow, providing more sophisticated financial services without intermediaries.
Web3 Integration: Blockchain technology will underpin digital identity, social networks, and decentralized applications, creating new ecosystems for value exchange.
Layer-2 Scaling: Solutions like Ethereum’s layer-2 protocols aim to reduce transaction costs and increase network speed.
Interoperability: Cross-chain solutions will enable seamless asset transfers between blockchain networks.
Sustainable Practices: Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) will gain traction over energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) models.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency and digital asset markets represent a paradigm shift in how value is created, transferred, and stored. They combine technological innovation with financial markets, providing opportunities for speculation, investment, and new financial services. However, these markets remain highly volatile, technologically complex, and subject to regulatory uncertainty. Successful participation requires a strong understanding of blockchain fundamentals, market dynamics, risk management, and strategic foresight. As adoption grows and regulation matures, digital assets are likely to become a mainstream component of global finance, reshaping economies, investment strategies, and the financial system itself.
ETHUSD 45-Min Chart — Counter-Trend Long From Demand After Major
Chart Analysis:
Market Structure:
Ethereum broke decisively below the 2,855 resistance zone, confirming a bearish structure shift. The move down was impulsive, followed by weak consolidation — classic distribution → continuation behavior.
Support / Demand Zone:
Price is reacting around 2,485–2,520, a highlighted demand area. This zone aligns with the first strong base formed after the sell-off, making it a high-interest reaction level.
Current Price Action:
ETH is printing long lower wicks into support, suggesting seller exhaustion and early dip-buying. However, structure is still bearish until a reclaim occurs.
Entry Logic:
The marked entry near ~2,490–2,510 assumes:
Support holds
A short-term higher low forms
Momentum flips on lower timeframes
Upside Targets:
TP1: ~2,690 (range equilibrium / liquidity grab)
TP2: ~2,740 (previous consolidation + minor resistance)
Final Target: ~2,855 major resistance (breakdown origin)
Invalidation:
A clean breakdown and close below 2,480 invalidates the long bias and opens continuation toward lower liquidity.
Bias Summary:
Trade Type: Counter-trend bounce
Risk Profile: Higher risk, higher R:R
Trend Context: Bearish until 2,855 is reclaimed
BTCUSD 45-Min Chart — Support Reclaim Setup After Sharp Breakdow
Chart Analysis:
Market Structure:
Clear bearish break from the prior range near 87k resistance, followed by a strong impulsive sell-off → confirms a bearish market shift.
Support Zone (Key Area):
Price is reacting around 80,600–81,000, a marked demand/support zone. This is the first meaningful base after the dump.
Current Price Action:
BTC is testing support after a lower high, suggesting sellers are losing momentum. Wicks into support show buying interest, but confirmation is still needed.
Entry Logic:
The marked entry near 80.6k assumes:
Support holds
A bounce + reclaim of minor structure (above ~82k)
Targets:
TP1: ~83.2k (range midpoint / liquidity)
TP2: ~83.7k (previous consolidation)
Final Target: ~87.1k resistance (major supply zone + breakdown origin)
Bias Summary:
Short-term: Tactical long from support
Invalidation: Clean break and close below 80.6k
Overall trend: Still bearish until 87k is reclaimed
Takeaway:
This is a counter-trend long setup — high reward, but only valid if support holds and momentum flips. Conservative traders should wait for a confirmed reclaim above 82–83k before committing.
Introduction to Cryptocurrency and Digital AssetsBlockchain Technology: The Backbone
At the heart of cryptocurrencies is blockchain technology, a distributed ledger system that records all transactions across a network of computers. A blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, each containing transaction data, timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This design ensures:
Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants.
Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect against fraud and unauthorized alterations.
Decentralization: No single entity controls the ledger, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be changed or deleted.
Beyond just financial transactions, blockchain enables smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded into the blockchain—which expand the utility of digital assets into areas like decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and digital identity verification.
Types of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
1. Cryptocurrencies:
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies designed to work as a medium of exchange. They include:
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, used as a store of value and medium of exchange.
Ethereum (ETH): A platform cryptocurrency that enables smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies like USD (e.g., USDT, USDC), designed to reduce volatility.
Altcoins: Alternative cryptocurrencies with varied purposes, such as Ripple (XRP) for cross-border payments or Cardano (ADA) for sustainable blockchain operations.
2. Digital Tokens:
These are blockchain-based units that can represent a variety of assets:
Utility Tokens: Provide access to a platform or service, like Binance Coin (BNB) for exchange fee reductions.
Security Tokens: Represent ownership of real-world assets such as shares, bonds, or real estate, regulated under securities laws.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Unique tokens representing ownership of digital or physical items like art, music, or collectibles.
3. Tokenized Assets:
Blockchain allows real-world assets—stocks, real estate, commodities—to be converted into digital form, making them easier to trade, fractionalize, and secure.
Use Cases of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Financial Transactions and Remittances:
Cryptocurrencies enable peer-to-peer payments without intermediaries, reducing fees and transaction times for international transfers.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DeFi platforms use smart contracts to offer banking services like lending, borrowing, and yield farming without traditional banks.
Digital Ownership and NFTs:
NFTs revolutionize digital ownership, allowing artists, gamers, and content creators to monetize their digital creations and maintain provable ownership.
Investment and Speculation:
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets are increasingly seen as investment vehicles, attracting both retail and institutional investors seeking diversification and high returns.
Cross-Border Payments and Financial Inclusion:
Cryptocurrencies provide access to financial systems for unbanked populations, offering secure and cost-effective cross-border transactions.
Supply Chain and Identity Verification:
Blockchain’s transparency ensures traceability of goods, anti-counterfeiting measures, and secure digital identities.
Advantages of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
Decentralization reduces reliance on central banks and financial institutions.
Transparency and security make financial operations more trustworthy.
Efficiency in cross-border transactions and settlements.
Innovation potential with smart contracts and tokenization.
Financial inclusion, particularly in regions with limited access to banking.
Challenges and Risks
Despite their promise, cryptocurrencies and digital assets face significant challenges:
Volatility: Prices can fluctuate wildly, making them risky for investors and unstable as currencies.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments vary in their approach to regulation, ranging from outright bans to active adoption.
Security Concerns: Hacks, scams, and loss of private keys pose risks to users.
Scalability Issues: Popular networks like Ethereum have faced congestion and high transaction fees.
Environmental Impact: Proof-of-work-based cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, consume enormous amounts of energy.
Adoption Barriers: Limited understanding, technological literacy, and infrastructure issues slow mainstream adoption.
Regulation and Legal Landscape
Governments worldwide are exploring how to regulate cryptocurrencies and digital assets to prevent fraud, money laundering, and market manipulation while enabling innovation. Regulatory approaches include:
Licensing cryptocurrency exchanges.
Taxation on transactions and holdings.
Oversight of stablecoins and digital banking platforms.
Creating central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as regulated alternatives.
Countries like Japan and Switzerland have embraced crypto-friendly regulations, whereas others like China have restricted trading and mining activities.
Future of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
The future of digital assets is promising but uncertain. Key trends include:
Integration with traditional finance: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly exploring crypto custody, trading, and payment systems.
Expansion of DeFi: More financial services may migrate to decentralized networks.
Tokenization of assets: Ownership of real-world assets will become more flexible, liquid, and transparent.
CBDCs and hybrid models: Central banks are exploring digital currencies that combine regulation with blockchain efficiency.
Greater mainstream adoption: Merchants, consumers, and enterprises may increasingly accept cryptocurrencies for payments and investments.
The evolution of cryptocurrency and digital assets could redefine how value is stored, transferred, and created globally, challenging traditional financial systems while opening new opportunities for innovation, inclusion, and efficiency.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies and digital assets represent a revolutionary shift in the way people perceive and interact with money, ownership, and digital ecosystems. While they bring enormous opportunities for financial innovation, inclusion, and efficiency, they also carry inherent risks related to volatility, security, and regulation. The continued development of blockchain technology, smart contracts, tokenization, and decentralized finance is likely to shape the future of global finance, making it more transparent, accessible, and efficient. As adoption grows, understanding the fundamentals, potential, and pitfalls of cryptocurrencies and digital assets is essential for investors, policymakers, and the general public alike.
#ETH ON THE EDGE DELTAIN:ETHUSD.P
ETH is on the edge of the cliff. If it breaks below this level, we can see a significant downward move to $2200 easily and worst case of $1500 & $1400.
Long term investors can accumulate on the supports. Follow me for more.
This indicator is provided for educational and informational purposes only.
It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or trade signals.
The creator and Systematic Traders Club are not responsible for any financial losses resulting from the use of this indicator.
Trading and investing involve risk. Always do your own analysis and use proper risk management.