Nifty Intraday Analysis for 30th January 2026NSE:NIFTY
Index has resistance near 25625 – 25675 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach near 25875 – 25925 range.
Nifty has immediate support near 25225 – 25175 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 24975 – 24925 range.
The market is expected to remain range-bound on this pre-budget trading day, driven by a mix of budget expectations, cautionary fears, and geopolitical uncertainty.
Trend Analysis
Banknifty Intraday Analysis for 30th January 2026NSE:BANKNIFTY
Index has resistance near 60350 – 60450 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach near 60850 – 60950 range.
Banknifty has immediate support near 59550 - 59450 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 59050 - 58950 range.
The market is expected to remain range-bound on this pre-budget trading day, driven by a mix of budget expectations, cautionary fears, and geopolitical uncertainty.
Finnifty Intraday Analysis for 30th January 2026NSE:CNXFINANCE
Index has resistance near 27725 - 27775 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach near 28000 - 28050 range.
Finnifty has immediate support near 27275 – 27225 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 27000 – 26950 range.
The market is expected to remain range-bound on this pre-budget trading day, driven by a mix of budget expectations, cautionary fears, and geopolitical uncertainty.
Midnifty Intraday Analysis for 30th January 2026NSE:NIFTY_MID_SELECT
Index has immediate resistance near 13550 – 13575 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach 13700 – 13725 range.
Midnifty has immediate support near 13300 – 13275 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 13150 – 13125 range.
The market is expected to remain range-bound on this pre-budget trading day, driven by a mix of budget expectations, cautionary fears, and geopolitical uncertainty.
XAUUSD – M30 Technical AnalysisMild Pullback Before the Next High | Lana ✨
Gold has extended sharply and is now trading into a high-resistance zone, where price often needs a light correction or consolidation to rebuild liquidity before attempting higher levels again. The broader trend remains bullish, but the next clean opportunity is more likely to come from a pullback into structure, not from chasing the highs.
📈 Market Structure & Trend Context
Price is still respecting the broader bullish structure, but the current leg is stretched after a strong impulsive run. The market is now reacting under the highest resistance zone, which typically creates short-term profit-taking and liquidity reactions before continuation.
As long as price holds above key structural support, the bullish trend remains intact.
🔍 Key Technical Zones
Highest resistance zone: 5585 – 5600 This is a premium area where price may hesitate or reject in the short term.
First support zone: 5508 A key decision level where price can rebalance before choosing direction.
Buy liquidity zone: 5446 – 5450 A strong liquidity pocket where buyers are more likely to step back in.
Long-term support zone: 5265 – 5285 A deeper base area if volatility expands into a broader correction.
🎯 Trading Scenarios
Gold may correct modestly from resistance and retest structure before pushing higher.
Buy Entry: 5446 – 5450 Stop Loss: 5438 – 5440
Take Profit targets:
TP1: 5508
TP2: 5538 – 5545
TP3: 5585 – 5600
TP4: 5650+
A shallower pullback toward 5508 could also be enough to reset momentum before another attempt higher, but repeated rejection at the top would increase the risk of deeper consolidation.
🧠 Lana’s View
Gold remains bullish, but the market is now at a level where patience matters more than speed. Rather than chasing price near resistance, the focus should stay on how price reacts during pullbacks into key structural zones.
✨ Respect the structure, manage risk, and let price come to your level.
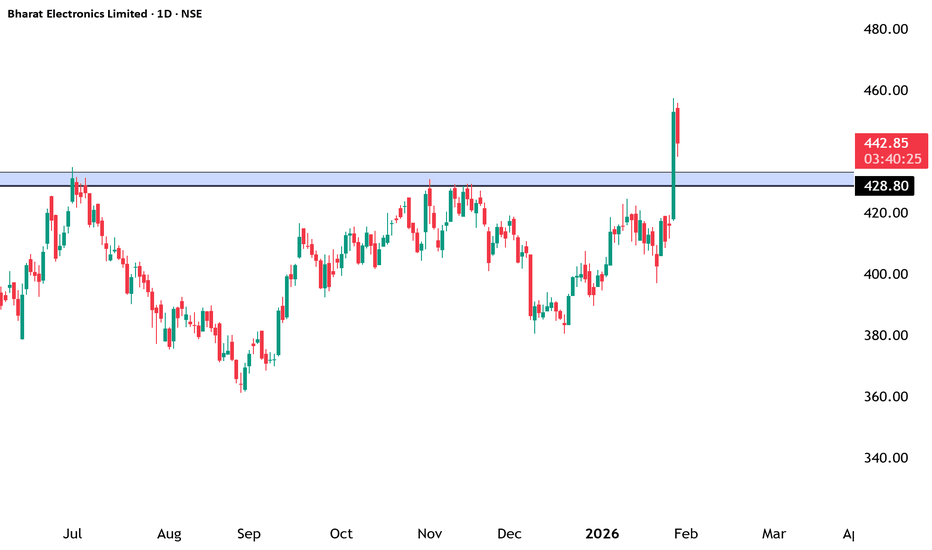
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) – Bullish Structure BreakoutNSE:BEL
🔹 Technical View
Price has decisively broken above a major supply / resistance zone (~₹428–432) after multiple rejections in the past.
Strong bullish momentum candle indicates institutional participation and demand dominance.
Previous resistance now likely to act as strong support on any pullback.
Structure shows higher highs & higher lows, confirming an ongoing uptrend.
Immediate levels to watch:
Support: ₹428–420
Upside potential: ₹460 → ₹480 (positional)
🔹 Volume & Price Action
Breakout supported by healthy volume expansion, validating the move.
No major selling pressure visible near breakout zone so far.
🔹 Fundamental View
BEL is a Navratna PSU and a key player in defence electronics.
Strong order book driven by:
Defence modernization
Indigenous manufacturing (Make in India / Atmanirbhar Bharat)
Consistent revenue visibility, healthy margins, and improving ROE.
Virtually debt-free balance sheet adds financial stability.
🔹 Future Growth Prospects
Long-term beneficiary of India’s rising defence spending.
Increasing focus on:
Radar systems
Electronic warfare
Missile & naval electronics
Export opportunities and private-defence collaboration act as additional growth triggers.
Well-positioned for sustainable compounding over the next few years.
🔹 Conclusion
Technically strong breakout + fundamentally robust business.
Suitable for positional & long-term investors on dips near support.
Trend remains bullish as long as price sustains above ₹420–428 zone.
==============
⚠️ Disclaimer:
==============
This content is shared strictly for educational and informational purposes.
We are not SEBI-registered investment advisors or analysts.
The views expressed are personal opinions, based on publicly available data and market observations.
Please consult a SEBI-registered investment advisor before taking any investment or trading decisions.
Any actions taken based on this content are entirely at your own risk and responsibility.
========================
Trade Secrets By Pratik
========================
BANKNIFTY Levels for Today
Here are the BANKNIFTY’s Levels for intraday (in the image below) today. Based on market movement, these levels can act as support, resistance or both.
Please consider these levels only if there is movement in index and 15m candle sustains at the given levels. The SL (Stop loss) for each BUY trade should be the previous RED candle below the given level. Similarly, the SL (Stop loss) for each SELL trade should be the previous GREEN candle above the given level.
Note: This idea and these levels are only for learning and educational purpose.
Your likes and boosts gives us motivation for continued learning and support.
Nifty Intraday Analysis for 29th January 2026NSE:NIFTY
Index has resistance near 25550 – 25600 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach near 25800 – 25850 range.
Nifty has immediate support near 25150 – 25100 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 24900 – 24850 range.
Markets are expected to react at the opening to the outcome of tonight's US Fed FOMC decision. A rate cut typically weakens the Dollar, providing a bullish signal for equities and metals. Meanwhile, with the Economic Survey set to be tabled on January 29, 2026, investors will also be closely monitoring the survey data for further direction.
Technical vs. Fundamental AnalysisIntroduction
In the world of investing and trading, understanding the value and timing of financial instruments is crucial. Investors and traders often rely on two primary methods to guide their decisions: technical analysis and fundamental analysis. While both aim to inform decisions about buying, holding, or selling securities, they differ fundamentally in approach, methodology, and application. Understanding the strengths, limitations, and appropriate use cases of each is vital for anyone participating in financial markets.
1. Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a security’s intrinsic value. It attempts to determine whether a stock, bond, or other asset is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced based on the underlying economic and financial factors.
1.1 Core Principles
At its core, fundamental analysis is about understanding the “health” of a company or asset. Analysts examine various factors, including:
Financial Statements: Income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements are analyzed to assess profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. Key metrics include earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on equity (ROE).
Industry Conditions: The sector in which a company operates affects its potential. Market share, competitive advantages, regulatory environment, and industry growth trends are critical considerations.
Macroeconomic Factors: Interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, and fiscal policies can significantly influence asset prices.
Management Quality: Leadership decisions, corporate governance, and strategic vision often determine long-term success.
1.2 Methods
There are two primary approaches to fundamental analysis:
Top-Down Approach: Analysts first study macroeconomic conditions, then industry trends, and finally specific companies.
Bottom-Up Approach: Focuses on analyzing individual companies, often ignoring broader economic conditions, to identify investment opportunities.
1.3 Example
Suppose an investor evaluates Company X, a technology firm. By analyzing its revenue growth, profit margins, R&D spending, and competitive position, the investor determines the intrinsic value of the stock to be $150. If the current market price is $120, the stock may be considered undervalued, presenting a potential buying opportunity.
1.4 Advantages of Fundamental Analysis
Long-Term Perspective: Helps investors identify securities that may generate sustainable returns over years.
Value Identification: Can reveal undervalued or overvalued assets relative to intrinsic value.
Economic Insight: Offers a comprehensive understanding of industry and macroeconomic impacts on investments.
1.5 Limitations of Fundamental Analysis
Time-Consuming: Requires deep research, data collection, and analysis.
Subjectivity: Estimating intrinsic value involves assumptions that may differ among analysts.
Less Effective for Short-Term Trading: Market prices may diverge from fundamental values for extended periods.
2. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis, on the other hand, focuses on price movements and trading patterns rather than the underlying business. It assumes that all relevant information is already reflected in the asset’s price, and that historical patterns tend to repeat over time.
2.1 Core Principles
Technical analysis is based on three key assumptions:
Market Action Discounts Everything: Prices reflect all available information, including fundamentals, market sentiment, and news.
Prices Move in Trends: Once established, trends are more likely to continue than reverse, at least until proven otherwise.
History Tends to Repeat Itself: Human psychology leads to recurring price patterns.
2.2 Tools and Techniques
Technical analysts use charts, patterns, and indicators to forecast price movements:
Charts: Line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts visualize price action over different time frames.
Indicators: Moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), MACD, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracement levels help identify trends and momentum.
Patterns: Head-and-shoulders, double tops/bottoms, triangles, and flags signal potential reversals or continuations.
Volume Analysis: Helps confirm trends or warn of potential reversals.
2.3 Example
A trader observes that Stock Y has formed a “double bottom” pattern on its daily chart, signaling a potential upward reversal. Using this information, the trader may enter a long position, anticipating a price increase based on historical pattern behavior rather than the company’s earnings or fundamentals.
2.4 Advantages of Technical Analysis
Timing and Short-Term Opportunities: Helps traders make decisions based on market trends and entry/exit points.
Quantitative Approach: Uses measurable price data and mathematical indicators.
Market Sentiment Insight: Captures emotions and behaviors that drive short-term price movements.
2.5 Limitations of Technical Analysis
Does Not Measure Intrinsic Value: Focuses purely on price action without regard to a company’s financial health.
False Signals: Patterns and indicators can fail, leading to losses.
Short-Term Focus: Often unsuitable for long-term investment strategies.
3. Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis: Key Differences
Feature Fundamental Analysis Technical Analysis
Focus Intrinsic value of the asset Price movements and trends
Time Horizon Long-term Short- to medium-term
Basis Financial statements, economic indicators, industry trends Price charts, volume, technical indicators
Assumption Market prices eventually reflect true value History tends to repeat; price trends continue
Tools Ratios, financial models, macroeconomic data Charts, trend lines, moving averages, oscillators
Decision Making Buy undervalued, sell overvalued Buy when patterns signal upward trend, sell on reversal signals
Use Case Investment (long-term) Trading (short-term or swing trading)
4. Integrating Both Approaches
Many successful investors and traders combine both fundamental and technical analysis:
Long-Term Investors: Use fundamental analysis to identify undervalued stocks, then apply technical analysis to optimize entry points.
Swing Traders: May rely primarily on technical analysis but consider fundamental news (earnings, economic data) to anticipate volatility.
Portfolio Management: Combining both can improve risk management and timing of trades.
Example of Integration
Consider a tech company showing strong earnings growth (fundamental analysis). A technical analyst may wait for a price breakout above a resistance level before entering a trade. By combining both approaches, the investor aligns value with optimal timing.
5. Market Psychology and Behavioral Insights
Fundamental Analysis: Relies on rational evaluation of financial health, assuming markets are logical over the long term.
Technical Analysis: Captures human psychology, fear, and greed, which often dominate short-term market behavior.
This difference reflects the broader tension between value investing and trend trading. Technical analysis often thrives in volatile, sentiment-driven markets, whereas fundamental analysis provides a grounded assessment during stable, growth-oriented periods.
6. Conclusion
Both fundamental and technical analysis offer valuable insights, but they serve different purposes. Fundamental analysis is ideal for long-term investors seeking intrinsic value, focusing on company performance, industry trends, and economic conditions. Technical analysis suits short-term traders aiming to exploit market trends and price patterns, focusing on timing and market sentiment.
While some purists favor one approach over the other, the most successful market participants often blend the two. Fundamental analysis provides the “why” behind an investment, while technical analysis provides the “when.” By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, investors and traders can make more informed, strategic, and disciplined financial decisions.
In today’s dynamic financial markets, a holistic approach that considers both fundamentals and technical signals can enhance profitability, reduce risk, and provide a robust framework for navigating complexity. Knowledge of both allows market participants to adapt to changing conditions, combine long-term insight with short-term strategy, and ultimately make more confident decisions in the face of uncertainty.
Possibility of some cooldown on GOLD for few months.Possibility of some cooldown on GOLD for few months.
Gold after Rally to ATH of 165000+ looks reached on top end of the Channel ... Possibilities are it can consolidate near 170-175K Level for few weeks before providing new direction to the commodity.
LTP - 164K
Range 150K to 175K.
View - Cautious / Consolidation
Technicals:
Crude is seen moving in upward direction ... Crude / Equities & Gold / Silver are seen moving in opposite directions in past ... With Equities market looking to bottomed out we can see big money moving from Metals to Equity in near months.
Happy Investing.
XAUUSD Upside Potential with Important Trade ZonesXAUUSD shows a clear swing-trade structure with defined trend, momentum, and supply-demand alignment. Price remains bullish, forming higher highs and higher lows, supported by steady bullish candles. The recent impulsive rally began from the demand zone near 5,000–5,030, which acted as a base for further continuation.
A supply zone around 5,100–5,120 has now flipped into support after a breakout retest. As long as price holds above this level, the bullish outlook remains valid. Immediate resistance is near 5,300–5,320, which may act as a stop-loss liquidity area. RSI suggests momentum is slowing near highs, indicating possible consolidation or a corrective pullback.
Potential buying opportunities can appear on pullbacks into 5,120–5,100 (support flip) or deeper toward the demand zone near 5,030–5,000. Traders should wait for price action confirmation in these areas. A rejection from resistance could trigger a healthy correction, while a clean breakout above 5,320 may extend the bullish move.
This analysis focuses purely on structure, key zones, and risk-aware trading.
Massive crash in the market⚠️ Massive sell-off across global markets ⚠️
A sharp wave of panic hit both metals and equities within the last hour, wiping out trillions in market value:
• Gold plunged 8.2%, erasing nearly $3 trillion in market capitalization
• Silver crashed 12.2%, losing around $760 billion
• S&P 500 slipped 1.23%, wiping out $780 billion
• Nasdaq dropped over 2.5%, cutting roughly $760 billion
Heavy risk-off sentiment is clearly dominating as investors rush to reduce exposure across asset classes.
Midnifty Intraday Analysis for 29th January 2026NSE:NIFTY_MID_SELECT
Index has immediate resistance near 13500 – 13525 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach 13650 – 13675 range.
Midnifty has immediate support near 13250 – 13225 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 13100 – 13075 range.
Markets are expected to react at the opening to the outcome of tonight's US Fed FOMC decision. A rate cut typically weakens the Dollar, providing a bullish signal for equities and metals. Meanwhile, with the Economic Survey set to be tabled on January 29, 2026, investors will also be closely monitoring the survey data for further direction.
GOLD (XAU/USD) – Bullish Continuation Toward Higher Highs🔍 Technical Analysis (H1):
Market Structure:
Gold remains in a strong bullish structure with clear higher highs & higher lows ✔️, firmly respecting the ascending trendline 📈.
Breakout & Momentum:
Multiple clean breakouts above previous resistance zones confirm strong buying pressure 💪. Each breakout is followed by healthy pullbacks, showing controlled bullish momentum.
POI → Pivot Support:
Previous POI zones have successfully flipped into support 🔄, and price is currently holding above the Pivot Point zone, which strengthens bullish continuation bias 🟢.
Current Price Action:
Price is consolidating above the pivot area, suggesting a brief pause before the next impulsive move higher ⏳➡️⬆️.
🎯 Upside Targets:
Target 1: 5,300 🎯
Target 2: 5,330 🎯🎯
Extended Target: 5,360+ 🚀 (if bullish momentum accelerates)
🛡️ Invalidation / Support to Watch:
Bullish bias remains valid as long as price holds above the Pivot Point zone. A break below may trigger a deeper pullback, not trend reversal ⚠️.
📌 Conclusion:
Overall trend is bullish, structure is healthy, and price action favors a continuation toward the marked target zone after minor consolidation 📦➡️🚀.
✨ Trade with the trend & manage risk wisely! 💼📊
XAUUSD – Bullish trend, focus on Buy pullbacks to 5,700Market Context (M30)
Gold continues to trade in a strong bullish continuation after a clean impulsive leg higher. The recent consolidation above former resistance shows acceptance at higher prices, not exhaustion. This behavior suggests the market is rebalancing liquidity before the next expansion leg.
On the macro side, USD remains under pressure, while safe-haven demand stays firm. Even though bond yields are relatively stable, capital flows continue to favor gold, keeping the upside bias intact.
➡️ Intraday bias: Bullish – trade with the trend, not against it.
Structure & Price Action
• Market structure remains bullish with Higher Highs – Higher Lows
• Previous resistance has flipped into demand and is being respected
• No bearish CHoCH or structural breakdown confirmed
• Current pullbacks are corrective moves within an active uptrend
Key takeaway:
👉 As long as price holds above key demand, pullbacks are opportunities for continuation.
Trading Plan – MMF Style
Primary Scenario – Buy the Pullback
Patience is key. Avoid chasing price into extensions.
• BUY Zone 1: 5,502 – 5,480
(Minor demand + short-term rebalancing zone)
• BUY Zone 2: 5,425 – 5,400
(Trendline support + deeper liquidity zone)
➡️ Only execute BUYs after clear bullish reaction and structure confirmation.
➡️ No FOMO at highs.
Upside Targets
• TP1: 5,601
• TP2: 5,705 (upper Fibonacci extension / expansion target)
Alternative Scenario
If price holds above 5,601 without a meaningful pullback, wait for a break & retest to join the next continuation leg.
Invalidation
A confirmed M30 close below 5,400 would weaken the bullish structure and require reassessment.
Summary
Gold remains in a controlled bullish expansion supported by both structure and macro flow. The edge lies in discipline — buying pullbacks into demand while the trend stays intact, not predicting tops.
➡️ As long as structure holds, higher prices remain the path of least resistance.
SbinThe daily time frame chart shows that the price is bouncing from the trend line support. In the lower time frame, the price has formed a rounding bottom.
Buy above 1048 with the stop loss of 1040 for the targets 1054, 1060, 1068 and 1076.
A rounding bottom pattern can form a candle if it has a pullback. At the same time, in the daily chart, the price should hold the trend line support.
Always do your analysis before taking any trade.
25500 might cause some trouble for NIFTY As we can see NIFTY has shown great upmove after getting rejected from important demand zone as analysed in the analysis. Moreover we ca see NIFTY forming more like an W kinda pattern in smaller time frame but there can be seen an immediate SUPPORT turned RESISTANCE so until and unless NIFTY manages to sustain itself above that demand zone every rise can be sold so plan your trades accordingly and keep watching everyone
Finnifty Intraday Analysis for 29th January 2026 NSE:CNXFINANCE
Index has resistance near 27550 - 27600 range and if index crosses and sustains above this level then may reach near 27825 - 27875 range.
Finnifty has immediate support near 27125 – 26075 range and if this support is broken then index may tank near 26850 – 26800 range.
Markets are expected to react at the opening to the outcome of tonight's US Fed FOMC decision. A rate cut typically weakens the Dollar, providing a bullish signal for equities and metals. Meanwhile, with the Economic Survey set to be tabled on January 29, 2026, investors will also be closely monitoring the survey data for further direction.
Oil Supply and Demand Balances1. Understanding Oil Supply
Oil supply refers to the total quantity of crude oil and petroleum products available for consumption at a given time. It can be categorized into several sources:
a) Crude Oil Production:
Crude oil production is the primary component of oil supply and is influenced by geological availability, technological capabilities, investment in exploration, and political factors. Major oil-producing countries such as Saudi Arabia, the United States, Russia, and members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) play a pivotal role in global production levels.
b) Inventories and Stockpiles:
Strategic and commercial oil reserves contribute to supply. Strategic reserves are maintained by governments to stabilize domestic markets in times of disruption, while commercial stockpiles are held by oil companies to meet demand fluctuations. Changes in inventory levels can signal either oversupply or shortages, impacting market prices.
c) Refinery Output:
Oil supply also depends on the capacity of refineries to process crude oil into usable products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and heating oil. Refinery utilization rates, maintenance schedules, and technological improvements can affect the amount of refined products available in the market.
d) Geopolitical Factors:
Supply is highly sensitive to geopolitical events. Conflicts in oil-producing regions, sanctions, or trade restrictions can constrain supply, while agreements among producers to cut or increase output (such as OPEC+ decisions) directly influence global supply levels.
e) Technological Advances and Unconventional Sources:
The development of unconventional sources, such as shale oil and oil sands, has significantly expanded supply options. Advances in hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling, particularly in the U.S., have shifted the global supply landscape by increasing production flexibility.
2. Understanding Oil Demand
Oil demand represents the quantity of crude oil and petroleum products that consumers are willing and able to purchase at prevailing prices. It is shaped by multiple factors:
a) Economic Activity:
Oil is a critical input for industrial production, transportation, and power generation. Economic growth drives higher energy consumption, especially in emerging economies such as China and India, which have rapidly growing industrial sectors and expanding transportation networks.
b) Transportation Sector:
The transportation sector accounts for the largest portion of oil demand. Demand for gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel is highly correlated with vehicle ownership, freight movement, and air travel. Shifts toward electric vehicles and public transportation can gradually reduce oil demand growth.
c) Seasonal Variations:
Oil demand fluctuates seasonally. For example, gasoline consumption typically rises during the summer driving season, while heating oil demand peaks in winter in colder regions. These seasonal patterns create temporary imbalances in supply and demand.
d) Energy Policy and Substitutes:
Government policies, such as fuel efficiency standards, carbon taxes, and subsidies for renewable energy, can affect oil demand. Increased adoption of alternative energy sources, biofuels, and electric mobility reduces reliance on oil and shifts the demand curve downward.
e) Population Growth and Urbanization:
Long-term oil demand trends are influenced by population growth and urbanization. Growing populations increase energy consumption, while urbanization often leads to higher transportation fuel usage, expanding the overall demand for oil.
3. Balancing Supply and Demand
The balance between oil supply and demand is crucial for maintaining price stability. When supply exceeds demand, inventories build up, leading to falling prices. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, inventories decline, creating upward pressure on prices. This balance can be analyzed in several ways:
a) Global Oil Market Equilibrium:
Oil markets aim to reach an equilibrium where the quantity supplied matches the quantity demanded at a certain price. This equilibrium is rarely static due to continuous changes in production, consumption patterns, and external shocks.
b) Short-term vs Long-term Balances:
Short-term balances are influenced by seasonal fluctuations, weather events, refinery outages, and geopolitical crises. For instance, hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico can temporarily disrupt U.S. production, tightening supply and pushing prices higher.
Long-term balances are determined by structural factors such as new oil field developments, technological innovation, energy transitions, and long-term economic growth trends.
c) Market Signals:
Oil prices serve as a signal for both producers and consumers. High prices incentivize increased production and energy efficiency, while low prices can reduce exploration investment and promote consumption. Futures markets also reflect expectations about future supply-demand balances.
4. Factors Disrupting the Balance
Oil supply-demand balances are highly sensitive and prone to disruption. Key disruptive factors include:
Geopolitical Tensions: Wars, sanctions, and political instability in oil-producing regions can reduce supply unpredictably.
Natural Disasters: Hurricanes, earthquakes, and other natural events can damage infrastructure, affecting both production and transportation.
Technological Changes: Breakthroughs in extraction or renewable energy can shift the balance. For example, the shale revolution dramatically increased U.S. oil production.
Economic Shocks: Global recessions reduce industrial activity and transportation, causing oil demand to fall sharply.
Policy Shifts: Regulatory changes, carbon pricing, and subsidies for alternative energy can either suppress or stimulate oil consumption.
5. Measurement of Supply-Demand Balances
Organizations such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), and OPEC regularly monitor oil supply-demand balances. Key metrics include:
Supply Figures: Crude oil production, refinery output, and stock changes.
Demand Estimates: Consumption data across sectors and regions, including transportation, industrial, residential, and power generation.
Inventory Levels: Changes in crude and product stocks, signaling tightness or oversupply in the market.
Market Indicators: Futures prices, backwardation/contango structures, and spreads between crude grades.
These metrics allow analysts to forecast potential shortages or surpluses and anticipate price trends.
6. Implications for the Oil Market
The supply-demand balance has profound implications:
Price Volatility: Imbalances lead to sharp fluctuations in oil prices, affecting energy costs globally.
Investment Decisions: Producers rely on supply-demand forecasts to plan new exploration, production, and refining capacity.
Policy Formulation: Governments monitor the balance to ensure energy security, manage strategic reserves, and design energy policies.
Global Economic Impact: Oil prices influence inflation, trade balances, and economic growth worldwide. Surplus supply tends to lower prices, benefiting consumers, while shortages raise prices and strain economies.
7. Future Trends in Supply-Demand Balances
Several emerging trends are reshaping oil supply-demand dynamics:
Energy Transition: Shift toward renewables, electric vehicles, and energy efficiency may reduce long-term oil demand growth.
Peak Oil Demand: Some analysts project a peak in global oil demand in the next few decades, driven by technological innovation and policy shifts.
Geopolitical Realignments: Changes in OPEC+ strategies and new producers entering the market will influence future supply levels.
Climate Policies: Decarbonization commitments and emission reduction targets are likely to constrain fossil fuel consumption.
Conclusion
Oil supply and demand balances form the foundation of global energy markets. Supply is shaped by production levels, inventories, refinery capacity, technology, and geopolitics, while demand is influenced by economic activity, transportation, policies, population growth, and energy alternatives. Maintaining equilibrium is critical for price stability and economic planning. Disruptions in either supply or demand can lead to volatility, affecting markets worldwide. As the world moves toward cleaner energy sources, the dynamics of oil supply-demand balances will continue to evolve, making careful monitoring and analysis increasingly vital for stakeholders across the energy sector.