Part 1 Institutionaal Intraday Trading The Infrastructure: Speed and Connectivity
Institutional traders don’t use standard web-based brokers. They operate on direct market access (DMA) systems, connecting directly to stock exchange servers.
Co-location: Many firms pay premium fees to house their servers in the same data center as the exchange’s servers. This reduces "latency"—the time it takes for data to travel—to microseconds.
Dark Pools: To avoid moving the market price against themselves, institutions often trade in "Dark Pools." These are private exchanges where buy and sell orders are hidden from the public until the trade is executed.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): A subset of institutional trading where algorithms execute thousands of orders per second. These firms don't look for big price moves; they look for fractions of a cent across millions of trades.
Fundamental Analysis
Power Grid Purely a Buy on Dips trade.
We all know the company’s fundamentals remain strong . It holds MAHARATNA status and the majority stake is owned by GOI, which adds to long term confidence.
Option trading is NOT advised through this idea. Please consider it strictly as a Cash Swing Trade based on the levels mentioned below.
Before I share this trade idea, a small request to everyone:
💡 If you liked the idea, don’t forget to Boost 🚀
Your comments and views are always most welcome .
TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
What is plotted on the chart:
• Covid low connected to the recent low to understand the broader structure
• Sep 2024 ATH connected to the recent high to track the trend zone
• Major support level clearly marked
Trade Setup:
CMP: 300
Strategy: Add on dips till 250
SL (Closing Basis): 230
Expected Moves: 320 → 340 → 360 ATH & above
For more market insights & structured trade ideas,
📲 Visit my profile and hit Follow
Warm regards,
Naresh G
SEBI Registered Research Analyst
💬 Comment below if you want me to analyse any stock for you 🔍
JK Tyres - Rounding Bottom PatternJK Tyres is looking at 50-100% return on account of following:
Technical Parameters:
1. Breakout after consolidation for 2 years
2. Rounding Bottom Pattern
3. Breakout on a weekly time frame with good volume
Fundamental Parameters:
1. Best Quarterly top-line
2. Capacity expansion of INR 1000 crores
3. One of the top India & World Companies in Tyre Industry
Keep following @Cleaneasycharts as we provide Right Stocks at Right Time at Right Price!!
Cheers!!
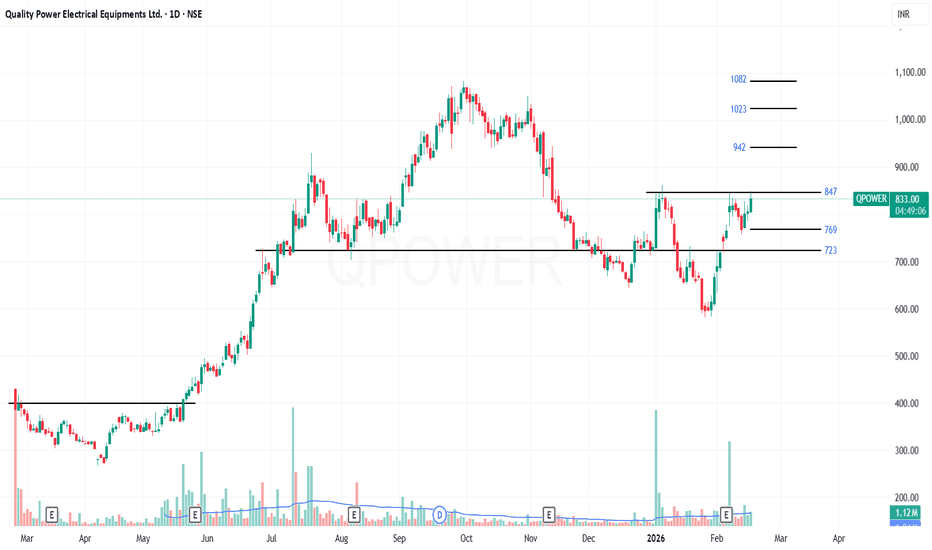
Quality Power: IPO Stock.Quality Power: IPO Stock. CMP 834
Resistance 847/942/1023/1082
Support 769/723
FY26-Q3: Strong Results
Quality Power Electrical Equipments – Q3 Results
• Net Profit: ₹38.92 cr ↑ 181% YoY, ↑ 60% QoQ
• Revenue: ₹283.99 cr ↑ 291% YoY, ↑ 38% QoQ
• EBITDA: ₹78.97 cr ↑ 354% YoY, ↑ 118% QoQ
• Margins: 27.81% vs 23.99% YoY, vs 17.60% QoQ
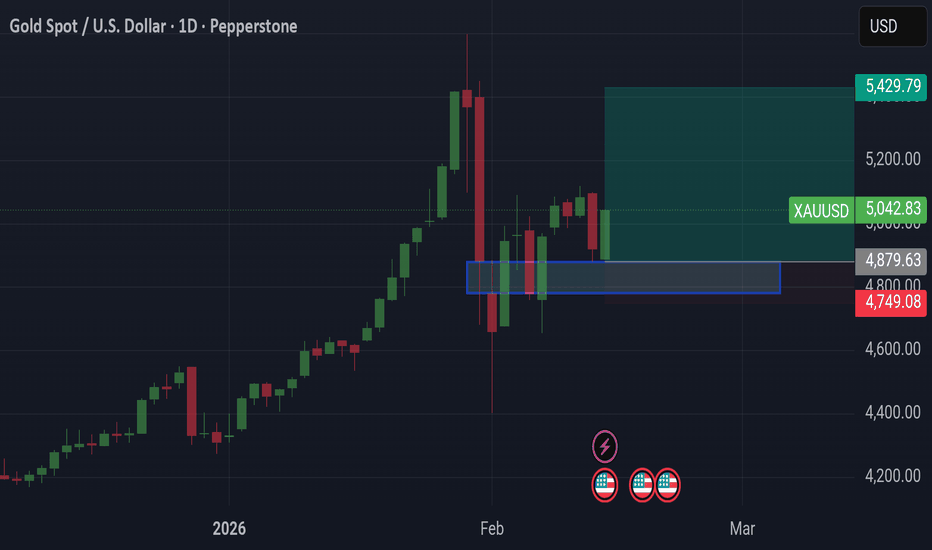
XAUUSD (H1) – Weekly Analysis | Geopolitical FactorsXAUUSD (H1) – Weekly Outlook | Geopolitics Back in Focus
Gold opens the week holding above short-term support after last week’s sharp sell-off and recovery. Price is now rotating beneath the 5,100 supply zone while geopolitical risk re-enters the narrative.
Netanyahu’s firm stance on Iran’s nuclear infrastructure and visible tension ahead of US–Iran talks increase uncertainty. Historically, when geopolitical risk premiums rise, gold attracts defensive flows — especially when price is technically positioned near liquidity zones.
Right now, structure and macro are aligning at a decision point.
Technical Structure (H1)
Major supply: 5,080 – 5,105
Current price rotating around: 4,980 – 5,000
Intraday support: 4,930 – 4,950
Higher-timeframe demand: 4,658 – 4,685
After sweeping lows near 4,900, price reclaimed 5,000 but failed to break 5,100. This signals unfinished business on both sides of liquidity.
The market is compressing — and compression leads to expansion.
Weekly Scenarios
Scenario A – Liquidity Sweep Above 5,100 (Bullish Expansion)
If price accepts above 5,105, stops above range highs become fuel.
Upside continuation toward 5,150+ becomes likely.
Geopolitical headlines could accelerate this move.
Scenario B – Rejection From Supply (Corrective Rotation Lower)
Failure to reclaim 5,100 followed by weakness under 4,980 opens retracement toward:
4,930 liquidity
4,850 mid support
4,680 higher-timeframe demand
This would be a technical correction, not necessarily macro bearish.
Flow Perspective
Sell-side liquidity was cleared last week.
Now buy-side liquidity above 5,100 remains untouched.
Markets rarely leave equal highs untested for long.
Next week is likely a liquidity week — not a sideways week.
Execution Mindset
Watch reaction at 5,080–5,105.
Above it → expansion.
Rejection → rotation first, then reassess.
Trade the level.
Let structure confirm.
OBEROIRLTY 1 Week Time Frame 📍 Current Price (approx): ~₹1,560 – ₹1,565 on Feb 16 (based on latest exchange data)
📈 Weekly Support & Resistance Levels
1-Week (16 – 20 Feb 2026)
🔹 Immediate Resistance Levels
R1: ₹1,581.83 — near-term upside barrier
R2: ₹1,616.07 — next bullish test
R3: ₹1,649.33 — extended resistance if breakout sustains
🔸 Immediate Support Levels
S1: ₹1,514.33 — key near-term support
S2: ₹1,481.07 — secondary downside level
S3: ₹1,446.83 — deeper support range for weak price action
📊 Weekly Expected Trading Range:
₹1,447 – ₹1,649 (typical range without strong news impact).
📌 How to Use These Levels (Weekly Context)
Bullish Scenario
If Oberoi Realty closes above ₹1,581.83 on weekly basis → bullish continuation likely
Break above ₹1,616–₹1,649 increases probability of further upside momentum.
Bearish Scenario
If price breaks below ₹1,514.33 → downside might accelerate
Sustained weakness could target ₹1,481 then ₹1,447.
🧠 Intermediate Technical Context
Daily support/resistance (classic pivot method) also suggests shorter intraday levels (good for trade timing):
S1: ~₹1,545–₹1,550
S2: ~₹1,526–₹1,514
Pivot: ~₹1,558–₹1,560
R1: ~₹1,577–₹1,589
R2: ~₹1,589–₹1,608
This daily pivot cluster feeds into broader weekly zones.
📊 Technical Indicator Snapshot (Recent)
Moving averages (20/50/100/200) around current price — trading mostly neutral with slight resistance overhead.
Oscillators like RSI near neutral (~50), suggesting neither strongly overbought nor oversold conditions.
Nifty 15m – Follow-Up on Previously Shared Reference LevelsThe liquidity levels shared in the previous session continue to guide price action.
Price reacted and consolidated around these zones, confirming their importance.
Both upside and downside moves have respected these reference areas.
Sustained acceptance above the current balance may support continuation toward higher targets.
Failure to hold could invite a move back into lower liquidity zones.
These levels remain active — plan intraday trades with structure, confirmation, and risk control.
Understanding Arbitrage Opportunities Across World Exchanges What Is Arbitrage?
Arbitrage occurs when an identical or equivalent asset is priced differently in two or more markets. A trader simultaneously buys the asset at a lower price in one market and sells it at a higher price in another market, locking in a profit from the price discrepancy.
In theory, arbitrage is risk-free. In practice, however, transaction costs, execution delays, currency fluctuations, and regulatory constraints introduce risks.
Why Do Arbitrage Opportunities Exist?
Even in today’s highly connected global financial system, price discrepancies can occur due to:
Differences in supply and demand across regions
Currency exchange rate fluctuations
Market inefficiencies
Transaction delays
Regulatory or capital controls
Information asymmetry
While technology has reduced many arbitrage gaps, opportunities still arise—especially during periods of volatility or when markets open and close at different times.
1. Stock Market Arbitrage
One of the most common types of global arbitrage occurs between stock exchanges.
Example: Dual-Listed Companies
Some companies are listed on more than one exchange. For example:
Alibaba Group is listed on:
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX)
If Alibaba shares are trading at an equivalent of $80 in New York and $82 in Hong Kong (after currency conversion), a trader could:
Buy shares on NYSE
Sell shares on HKEX
Capture the $2 difference (minus fees)
This is known as cross-listing arbitrage.
However, settlement rules, capital movement restrictions, and time zone differences complicate the process.
2. Currency (Forex) Arbitrage
The foreign exchange market is the largest financial market in the world. Arbitrage in forex typically involves triangular arbitrage across three currencies.
For example:
USD → EUR
EUR → GBP
GBP → USD
If the implied exchange rates don’t perfectly align, traders can cycle through currencies and end up with more than they started.
Triangular Arbitrage Example
Suppose:
1 USD = 0.90 EUR
1 EUR = 0.80 GBP
1 GBP = 1.50 USD
If the mathematical relationships don’t perfectly match, a trader might exploit the imbalance.
These opportunities are extremely short-lived—often lasting milliseconds—and are usually captured by high-frequency trading systems.
3. Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
Cryptocurrency markets provide some of the most visible arbitrage opportunities due to fragmentation across global exchanges.
For example, Bitcoin might trade at:
$30,000 on one exchange
$30,400 on another
Bitcoin is traded globally across hundreds of platforms.
Why Crypto Arbitrage Exists
No centralized global pricing mechanism
Capital restrictions in certain countries
Differences in liquidity
Exchange withdrawal delays
A famous example is the “Kimchi Premium” in South Korea, where Bitcoin historically traded at significantly higher prices on Korean exchanges compared to U.S. exchanges.
Crypto arbitrage includes:
Spatial arbitrage (between exchanges)
Statistical arbitrage
Funding rate arbitrage (in futures markets)
Cross-border arbitrage
However, blockchain transfer times and transaction fees reduce profitability.
4. Commodity Arbitrage
Commodity arbitrage occurs across different exchanges or geographic locations.
For example, gold may trade on:
COMEX in the United States
London Metal Exchange in the UK
If gold prices differ beyond shipping and storage costs, traders can buy gold in one market and sell in another.
There are also:
Futures vs. spot arbitrage
Calendar arbitrage (between contract months)
Geographic arbitrage (physical commodities)
Physical commodity arbitrage requires logistics, storage, and insurance considerations.
5. Futures and Derivatives Arbitrage
Futures prices should theoretically reflect the spot price plus carrying costs (cost-of-carry model). When discrepancies occur, arbitrage becomes possible.
For example:
Buy underlying asset in spot market
Sell futures contract
Deliver asset at contract expiration
If futures are overpriced relative to spot, traders profit from the convergence.
This type of arbitrage is common in stock index futures and commodity futures markets.
6. ETF Arbitrage
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) track baskets of assets. If an ETF’s price deviates from its net asset value (NAV), authorized participants step in.
For example:
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust tracks the S&P 500 index.
If the ETF trades above its NAV:
Buy underlying stocks
Create new ETF shares
Sell ETF at higher price
This arbitrage mechanism helps keep ETF prices aligned with the underlying index.
Risks in Global Arbitrage
Though often described as risk-free, real-world arbitrage involves several risks:
1. Execution Risk
Price differences may disappear before trades complete.
2. Currency Risk
Exchange rate fluctuations can erode profits.
3. Regulatory Risk
Some countries restrict capital flows.
4. Transfer Delays
Crypto transfers or settlement cycles may take time.
5. Transaction Costs
Fees can eliminate thin profit margins.
Role of Technology
Modern arbitrage is dominated by:
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
Algorithmic trading
Low-latency infrastructure
Co-location servers
Large financial institutions invest heavily in infrastructure to capture microsecond-level opportunities.
Market Efficiency and Arbitrage
Arbitrage contributes to market efficiency. When traders exploit price differences:
Cheap markets see increased demand → price rises
Expensive markets see increased supply → price falls
This process quickly equalizes prices globally.
Thus, arbitrageurs serve as a stabilizing force in financial systems.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Arbitrage itself is legal in most jurisdictions. However:
Insider trading is illegal
Market manipulation is illegal
Certain cross-border capital movements may be restricted
Educational understanding should focus on the mechanics and risks rather than attempting unsophisticated real-world execution.
Conclusion
Arbitrage across world exchanges is a cornerstone of global finance. From stocks and currencies to cryptocurrencies and commodities, price differences arise due to market fragmentation, liquidity imbalances, and information delays.
While theoretically risk-free, practical arbitrage requires speed, capital, infrastructure, and deep market knowledge. Most opportunities are short-lived and dominated by institutional traders using advanced algorithms.
For educational purposes, arbitrage illustrates powerful economic principles:
Law of One Price
Market efficiency
Global financial integration
Risk management
Understanding arbitrage provides insight into how modern financial markets remain interconnected and how pricing discrepancies are corrected almost instantly in today’s digital world.
Trade Catalyst Series // Episode 3 // MOTHERSONI am back here with another episode of Trade Catalyst with another Stock -- Samvardhana Motherson International Ltd.
It is one of the world's Largest and most diversified auto component manufacturers.
In past one year the company has shown a strong financial recovery, aggressive acquisitions and significant re-rating of its stock.
last quarter - Q3Dec25 :-
Revenue Growth : +13.5% YOY
EBITA Margin : improved 9.7%
PAT : up 9% yoy
The growth was majorly fueled by acquisitions of Nexans Autoelectric and Atsumitec & SSCP Aero Topco (expanding its footprint in Aerospace sector).
Recent India-EU FTA will be a structural game-changer for this stock over long term view.
Direct Export Boost - EU eliminating the import duties of 3-4% on Indian auto components will help in boosting the export revenue.
China+1 Beneficiary - This is a important concept in almost all sectors, the recent FTA developments brings this in common. here as well india will now act as a strong counterweight to China for European Supply chains.
Domestic premium change - the lower cost of luxury cars, likely to increase their sales volume. Since Motherson supplies high-value content to these big brands, it is a win for them in Indian domestic Market.
Fundamental Projection : The order book is providing revenue visibility for the next 5-6 years. The FTA acts as a catalyst that could increase the win rate of new orders because Motherson can now quote lower prices to European clients by factoring in the zero-duty benefit from its Indian manufacturing base.
Technical Projection : On Weekly Chart the stock has already caught upto a good upward momentum since the news break. On the Fib level, last week candle has closed above the 78.6% level after taking a strong support on 50EMA, which is a very significant and promising move by the price.
The price range of 116 to 128 is a sweet spot to make an entry now in this stock, even current price isn't a bad price point to enter. with an re-entry if this setup fails at 89.
My personal Strategy :- Buy Now with the 50% allocation to it, if a good Dip again is seen, then buy it more with the remaining 50%.
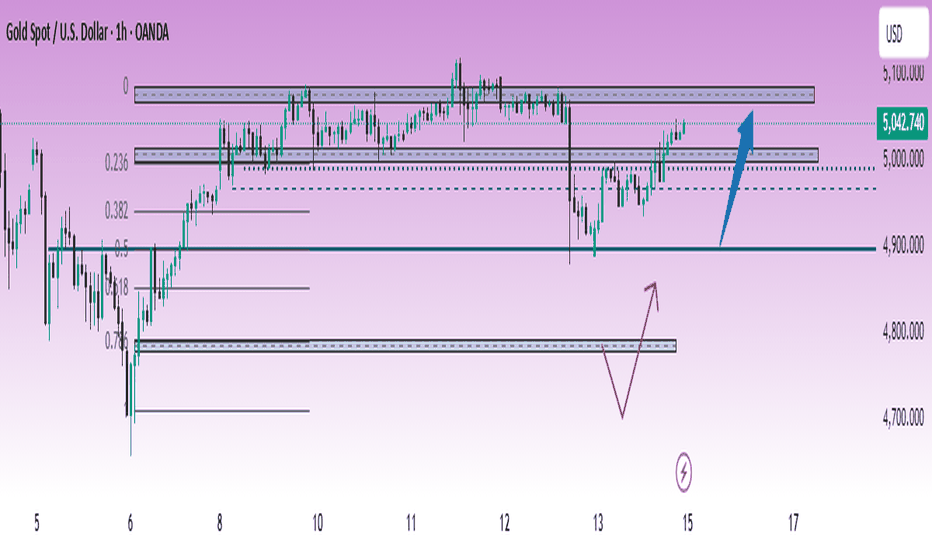
XAUUSD (H1) – Weekly Outlook | LiquidityXAUUSD (H1) – Weekly Outlook | Liquidity Rebuild Before Expansion
Gold has recovered strongly from the sharp sell-off into 4,900 and is now rotating back toward the upper range. The current structure shows a classic liquidity rebuild phase after a stop run — and next week will likely decide whether this becomes continuation or distribution.
Structure Overview (H1)
Strong reaction from 4,900 – 4,880 demand.
Price reclaimed the 0.5 Fibonacci / 5,000 psychological level.
Currently trading just below the 5,060 – 5,090 supply band.
Prior equal highs remain intact above.
Momentum is constructive, but price is now approaching decision territory.
Key Levels To Watch Next Week
Immediate Resistance / Supply
5,060 – 5,090 (range high / distribution zone)
Breakout Target
5,120 – 5,150 (liquidity above highs)
Mid Support
5,000 – 4,980 (flip zone)
Major Demand
4,900 – 4,880
4,780 – 4,750 (deep liquidity pocket)
Weekly Scenarios
Scenario A – Continuation Break (Bullish Bias While Holding 5,000)
If price accepts above 5,060 and holds above 5,000 on pullbacks, upside liquidity becomes the magnet.
Expansion toward 5,120+ is likely once equal highs are taken.
Scenario B – Rejection From Supply (Rotation Lower)
Failure to hold above 5,060 followed by strong rejection could send price back toward 5,000 and possibly 4,900 liquidity.
A clean loss of 4,900 reopens deeper downside into 4,780.
Context & Flow
The recent drop appears to have cleared sell-side liquidity.
Now price is rebuilding structure beneath resistance.
This is not random movement — it is positioning.
Next week will likely be an expansion week.
Compression under highs usually does not last long.
Execution mindset:
Let price confirm at 5,060–5,090.
Trade reaction, not prediction.
Structure first. Emotion last.
Tech Bubble vs Value Rotation DebatesThe Tech Bubble Argument
The term “tech bubble” immediately evokes memories of the late 1990s and the collapse of the dot-com boom. During that period, companies with little revenue and no profits achieved astronomical valuations. The Nasdaq Composite rose nearly fivefold between 1995 and early 2000 before crashing dramatically. Many firms disappeared entirely.
In current debates, those warning of a new tech bubble point to:
1. Elevated Valuations
Technology companies often trade at high price-to-earnings (P/E) and price-to-sales ratios. Critics argue that expectations for perpetual high growth are unrealistic. When valuations stretch far beyond historical norms, even small disappointments in earnings can trigger sharp corrections.
2. Concentration Risk
Modern indices are heavily weighted toward a handful of mega-cap tech firms. For example, companies like Apple Inc., Microsoft, and NVIDIA have, at times, accounted for an unusually large portion of index performance. Skeptics argue this narrow leadership resembles past speculative periods.
3. Narrative-Driven Investing
Technological revolutions—cloud computing, artificial intelligence, electric vehicles—generate powerful stories. Investors may extrapolate long-term disruption too aggressively, bidding up stocks based on future dominance rather than current cash flows.
4. Monetary Policy Tailwinds
Periods of low interest rates tend to boost growth stocks because their future earnings are discounted at lower rates. When central banks such as the Federal Reserve maintain accommodative policy, capital flows more freely into higher-risk, high-growth assets. Bubble theorists argue that ultra-low rates artificially inflate tech valuations.
In short, the tech bubble thesis claims that excessive optimism, easy money, and crowd psychology have pushed valuations beyond sustainable levels.
The Value Rotation Argument
In contrast, the “value rotation” narrative focuses on cyclical market dynamics. Instead of viewing tech as irrationally inflated, proponents argue markets move in multi-year cycles between growth and value leadership.
1. Growth vs. Value Defined
Growth stocks: Companies expected to grow earnings faster than the broader market, often reinvesting profits.
Value stocks: Companies perceived as undervalued relative to fundamentals, often with stable cash flows and dividends (e.g., banks, energy firms, industrials).
Historically, these styles alternate in performance dominance.
2. Interest Rate Sensitivity
Growth stocks are more sensitive to interest rates because their valuations depend heavily on future earnings. When rates rise, the present value of distant cash flows falls, often hurting tech stocks. Conversely, value sectors such as financials may benefit from higher rates.
For example, when U.S. Treasury yields climb, sectors like banking often outperform because higher rates can widen lending margins. Thus, a rise in rates can trigger capital flows from growth into value—what investors call a “rotation.”
3. Economic Cycles
During early recoveries from recession, cyclical sectors (industrials, materials, energy) often outperform as demand rebounds. In contrast, during slow-growth or low-rate environments, investors favor scalable, asset-light tech firms.
The value rotation argument suggests that market leadership changes are not necessarily bubbles bursting but rational reallocations in response to macro conditions.
4. Post-Pandemic Dynamics
After the 2020 pandemic shock, massive fiscal stimulus and ultra-low interest rates fueled tech outperformance. However, as inflation rose and the Federal Reserve tightened policy, value stocks temporarily gained relative strength. Some analysts framed this not as a tech collapse, but as a cyclical shift.
Structural Differences from the Dot-Com Era
A key dimension of the debate centers on whether today’s tech giants resemble speculative startups of the late 1990s.
Profitability and Cash Flow
Unlike many dot-com companies, modern technology leaders are highly profitable, generate enormous free cash flow, and hold significant balance sheet strength.
Infrastructure and Adoption
Technologies like cloud computing and AI are deeply embedded in global business operations. This contrasts with the earlier internet era, when adoption rates were uncertain.
Market Dominance
Large firms such as Alphabet Inc. and Amazon operate diversified ecosystems with recurring revenue streams. Supporters argue this makes them fundamentally stronger than speculative dot-com ventures.
Thus, value rotation proponents contend that while valuations may fluctuate, labeling the sector a “bubble” ignores structural profitability and economic centrality.
Behavioral Finance and Market Psychology
The debate also reflects behavioral biases:
Recency Bias: Investors extrapolate recent performance trends.
Herding Behavior: Capital clusters around recent winners.
Overconfidence: Belief in technological inevitability may overshadow risks.
At the same time, pessimism can overshoot. During sharp corrections, tech valuations sometimes fall below historical averages, contradicting bubble claims.
Markets often oscillate between enthusiasm and caution. The bubble narrative gains traction during rapid price appreciation, while rotation narratives dominate when leadership broadens.
The Role of Inflation and Policy Regimes
Inflation and monetary policy are central to this debate. Low inflation and stable growth tend to favor technology stocks due to predictable discount rates. High inflation and aggressive rate hikes compress valuations of long-duration assets (like growth stocks).
For instance, during tightening cycles led by the Federal Reserve, investors may shift capital toward sectors with near-term cash flows and pricing power. Energy and commodities often benefit in such regimes.
Thus, the tech bubble vs value rotation debate often reduces to differing expectations about:
Long-term interest rates
Inflation persistence
Economic growth trajectories
Concentration and Systemic Risk
Another layer involves market structure. Passive investing and index funds amplify flows into mega-cap stocks. If a few companies dominate benchmarks, inflows mechanically push their prices higher, reinforcing momentum.
Critics argue this dynamic can inflate valuations regardless of fundamentals. Supporters counter that dominance reflects superior business models and network effects.
The question becomes: Is concentration a symptom of bubble behavior or of economic winner-take-most dynamics?
Long-Term Perspective
Historically, style leadership has rotated over decades. In the 1970s, energy dominated. In the 1980s and 1990s, technology surged. In the early 2000s, value outperformed growth for several years after the dot-com crash. In the 2010s, growth regained dominance.
Neither growth nor value permanently wins.
Investors who frame the debate as binary—bubble or rotation—may overlook that both dynamics can coexist. Valuations can be stretched in certain subsectors while broader performance shifts reflect macro cycles.
Conclusion
The tech bubble vs value rotation debate is fundamentally about interpretation:
Bubble thesis: Prices reflect speculative excess, driven by easy money and over-optimistic narratives.
Rotation thesis: Performance shifts reflect rational adjustments to interest rates, inflation, and economic cycles.
Reality often lies between extremes. Some segments of the market may experience speculative fervor, while broader movements represent structural change or macro-driven reallocations.
For investors, the key questions are less about labeling the environment and more about assessing valuation discipline, earnings durability, macro sensitivity, and risk tolerance. Whether one views tech as overheated or structurally dominant depends largely on assumptions about future growth, policy regimes, and innovation trajectories.
Ultimately, markets are cyclical, narratives evolve, and leadership changes. Understanding both perspectives equips investors to navigate uncertainty rather than react to headlines.
Robotics and Automation StocksWhat Are Robotics and Automation?
Robotics refers to programmable machines capable of carrying out complex actions automatically. Automation is broader—it includes the use of control systems, software, and technologies to operate equipment and processes with limited human input. Together, they power “smart factories,” autonomous logistics systems, robotic surgery, and even AI-driven customer service platforms.
The industry spans multiple sectors:
Industrial robotics – robotic arms used in automotive, electronics, and heavy manufacturing.
Service robotics – robots for healthcare, hospitality, cleaning, and agriculture.
Warehouse automation – robotic picking systems and automated guided vehicles.
Autonomous vehicles and drones – self-driving transport and aerial inspection systems.
AI and software automation – robotic process automation (RPA) and machine learning platforms.
Major Companies in Robotics and Automation
1. ABB Ltd
ABB is a Swiss-Swedish multinational corporation specializing in robotics, electrification, and automation. Its robotic arms are widely used in automotive assembly lines and electronics manufacturing. ABB focuses heavily on collaborative robots (“cobots”), which safely work alongside humans, making automation accessible to small and medium enterprises.
2. Fanuc
Fanuc is a Japanese leader in factory automation and computer numerical control (CNC) systems. Recognizable for its bright yellow robots, Fanuc serves industries ranging from automotive to electronics. It is known for high reliability and a large installed base worldwide.
3. KUKA
KUKA, based in Germany, is a major supplier of industrial robots and smart factory solutions. Its automation systems are widely used in automotive production. KUKA emphasizes digital manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
4. Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation focuses on industrial control systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and factory software. Rather than producing robots themselves, Rockwell provides the digital backbone that enables automated production systems to operate efficiently.
5. NVIDIA
Although primarily known for graphics processing units (GPUs), NVIDIA plays a significant role in robotics and automation through AI chips and simulation platforms. Its hardware powers autonomous machines, robotic vision systems, and AI-driven automation in warehouses and vehicles.
Why Investors Are Interested
Several structural trends drive investor interest in robotics and automation stocks:
1. Labor Shortages and Rising Wages
Aging populations in developed countries and rising labor costs globally push companies to automate tasks. Robots can operate continuously without fatigue, reducing dependency on human labor.
2. Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing. Smart sensors, cloud computing, and AI enable predictive maintenance and real-time production monitoring.
3. E-commerce Growth
The rapid expansion of online shopping increases demand for automated warehouses and robotic fulfillment systems.
4. Artificial Intelligence Integration
Modern robots are increasingly intelligent. Machine learning enables robots to recognize objects, adapt to new tasks, and improve performance over time.
5. Government Support
Many governments promote automation to boost productivity and competitiveness, offering incentives for advanced manufacturing adoption.
Financial Characteristics of Robotics Stocks
Robotics and automation companies typically show:
High research and development (R&D) spending
Strong intellectual property portfolios
Cyclical revenue patterns tied to industrial investment
Global customer bases
Their performance often correlates with capital expenditure trends in manufacturing and technology sectors.
Risks and Challenges
Despite strong growth potential, robotics stocks carry risks:
Economic Cyclicality – During recessions, companies reduce capital spending, affecting automation sales.
High Valuations – Many automation stocks trade at premium price-to-earnings ratios due to growth expectations.
Technological Disruption – Rapid innovation means current leaders could be displaced.
Supply Chain Issues – Semiconductor shortages or geopolitical tensions can disrupt production.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Investors seeking diversified exposure often choose robotics and automation ETFs. Examples include:
Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF
ARK Autonomous Technology & Robotics ETF
These funds hold baskets of companies involved in robotics, AI, automation software, and autonomous vehicles, reducing single-company risk.
Future Outlook
The robotics and automation industry is expected to expand significantly in the coming decades. Key growth areas include:
Healthcare robotics – Surgical robots and rehabilitation devices.
Agricultural automation – Autonomous tractors and harvesting robots.
Autonomous transportation – Self-driving trucks and delivery robots.
Humanoid robots – Emerging systems designed to operate in human-centric environments.
AI integration will likely transform robotics from rigid, pre-programmed systems into adaptive, collaborative machines capable of learning in real time.
Conclusion
Robotics and automation stocks represent companies at the forefront of technological transformation. From industrial robot manufacturers like ABB, Fanuc, and KUKA to digital automation providers like Rockwell Automation and AI hardware leaders like NVIDIA, the sector covers a broad spectrum of innovation.
Investing in this space offers exposure to long-term themes such as labor efficiency, artificial intelligence, and smart manufacturing. However, it also requires understanding economic cycles, competitive pressures, and valuation risks. For long-term investors who believe in the continued digitization and automation of the global economy, robotics and automation stocks provide a compelling opportunity to participate in the next wave of industrial evolution.
AI Infrastructure & Data Center Bullish Flows1. What Do “Bullish Flows” in AI Infrastructure & Data Centers Mean?
“Bullish flows” refers to strong capital inflows and positive sentiment from investors, corporations, and lenders into AI infrastructure — particularly data centers. This includes:
Equity investments (stock purchases, venture capital into AI and infrastructure firms),
Corporate capital expenditures (CapEx) by hyperscalers building facilities,
Debt financing issuance to fund construction and operations,
M&A transactions in the data-center sector,
Institutional commitments by funds and strategic investors.
These flows signal belief in long-term demand growth and expected returns from owning or servicing AI infrastructure.
2. Why Is AI Infrastructure a Bullish Investment Theme?
AI Workloads Require Massive Compute
Unlike traditional workloads, AI — especially large language models, generative AI, and deep learning systems — requires enormous computational power. These workloads:
Rely on dense GPU, TPU, and custom silicon clusters,
Consume orders of magnitude more energy and cooling capacity,
Demand high bandwidth networking and low latency.
This fundamentally changes the economics and scale of data centers — they are no longer just storage and general compute facilities; they are AI compute factories.
3. A Supercycle of CapEx: Hyperscalers Leading the Charge
Capital expenditure on AI infrastructure has entered what many analysts call a “supercycle” — an extended, accelerating wave of spend:
Analysts project 2026 AI infrastructure CapEx worldwide at ~$602 billion, a ~36% increase from 2025.
Hyperscalers like Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet (Google), and Meta are dramatically increasing AI spend — often hundreds of billions annually.
In some cases, infrastructure spend constitutes 45–57% of revenue for major cloud providers, reflecting a strategic pivot to AI.
This scale of spend is historically unprecedented: capital flows into both building and equipping data centers dwarf most past tech infrastructure waves.
4. Market and Investment Growth Metrics
Market research firms project dramatic expansion in both market size and economic importance:
The AI data center market could grow from ~$13.7 billion in 2024 to ~$78.9 billion by 2032 at ~24.5% CAGR.
Other projections put the longer-term market above $197 billion by 2035 at ~27% CAGR.
Some analyses forecast trillions of dollars in capex by 2030, driven largely by generative AI demand.
These figures illustrate why investors are bullish — they are betting on exponential growth in AI compute demand over the next decade.
5. Data Center Investment Record Levels
Investment flows are being reflected in deal activity and acquisition volumes:
A consortium including BlackRock, Nvidia, and Microsoft agreed to acquire Aligned Data Centers for ~$40 billion, signaling massive strategic bets on owning physical infrastructure.
Global data center M&A and transactions reached near record highs (~$61 billion in 2025), as companies and funds compete for AI-ready facilities.
Private equity and infrastructure funds are particularly active, drawn by the long-term returns and recurring revenue profiles from leased data center capacity.
6. Debt Markets Fuel Expansion
Not all capital comes from equity or corporate cash flows. Debt markets have expanded sharply:
Data center-specific debt issuance jumped ~112% year-over-year in 2025 (~$25 billion), as firms leverage borrowing to build costly facilities that might otherwise strain operating cash flows.
Morgan Stanley estimates AI data center spending could reach ~$2.9 trillion between 2025–28, with roughly half financed externally.
These debt flows reveal investor confidence but also risk — heavy leverage increases exposure to economic cycles and interest rate environments.
7. Structural Drivers of the Bullish Trend
Several structural (not cyclical) forces are driving bullish flows:
AI Model Complexity Growth
As models grow from millions of parameters to billions or trillions, compute requirements increase non-linearly, fueling sustained demand for specialized, large-scale infrastructure.
Hyperscale Cloud Leadership
Major cloud providers race to build multi-gigawatt AI campuses — each requiring massive power, cooling, networking, and land — creating a competitive arms race.
Data Center Evolution
Modern data centers are becoming AI-optimized, with advanced cooling (liquid immersion), renewable energy integration, and modular or edge deployment models, which further attracts capital.
Network & Connectivity Buildouts
AI demand is also driving fiber and interconnect investments, as high throughput and low latency become essential.
8. Sustainability and Operational Constraints
The bullish narrative often comes with sustainability, energy, and power challenges:
AI data centers could consume up to ~10–12% of U.S. electricity by 2030.
This surge heightens environmental and policy considerations around energy sourcing, water usage, and carbon footprints.
Investors and planners are increasingly factoring green energy commitments and efficiency technologies into decisions, which affects both cost and community acceptance.
9. Risks and Counterweights to Bullishness
While bullish flows are strong, there are legitimate risks:
1. Potential Overcapacity
Executives in China and elsewhere warn of potential idle AI data center capacity if buildouts outpace actual demand.
2. Cost Inflation and Memory Price Effects
Rising memory prices have inflated capex figures, suggesting actual unit count growth may be slower than nominal spend indicates.
3. Financing and Leverage Risk
Heavy debt issuance increases financial stress and refinancing risks if interest rates rise or demand slows.
4. Regulatory and Geopolitical Factors
Data localization laws and geopolitical strategies could redirect investment flows regionally, changing risk profiles for global investors.
10. Why Investors Are Still Bullish
Despite risks, several factors sustain bullish sentiment:
Long-term secular growth in AI compute demand across industries.
Dominant positions of key players (e.g., Nvidia in GPUs, hyperscalers with deep pockets).
Recurring revenue models from leased capacity and cloud services.
Infrastructure as critical backbone to future digital economies.
Bullish flows reflect consensus that AI capabilities will underpin future innovation in automation, enterprise software, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and much more — all requiring vast computational infrastructure.
Conclusion
AI infrastructure and data center investment flows have become one of the biggest themes in global technology and finance:
Massive capex by Big Tech,
Record M&A and transaction activity,
Significant debt and equity capital pouring into specialized builds,
Market growth projections into the tens or hundreds of billions globally.
This bullish trend isn’t merely about short-term hype; it’s grounded in the fundamental technological requirements of modern AI systems, the competitive dynamics among hyperscalers, and the strategic positioning of infrastructure as a long-duration, high-barrier asset class.
However, risks around capacity, financing, sustainability, and geopolitical fragmentation mean that while flows are bullish, they require careful analysis and monitoring.
AI-Powered Algorithmic Trading Tools1. What Is AI-Powered Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading (also called algo-trading) uses predefined rules and mathematical models to execute trades. When artificial intelligence (AI) is integrated, these systems become adaptive—they can learn from data, adjust to new market conditions, and improve performance over time.
Traditional algorithms:
Follow fixed rule-based logic
Example: Buy when 50-day moving average crosses above 200-day moving average
AI-powered algorithms:
Learn from historical and real-time data
Detect nonlinear patterns
Continuously optimize strategies
AI trading systems are widely used by hedge funds, investment banks, proprietary trading firms, and increasingly by retail traders.
2. Core Technologies Behind AI Trading
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning models identify patterns in historical price data, order flow, macroeconomic indicators, and alternative datasets.
Common techniques:
Supervised learning (price prediction)
Unsupervised learning (clustering market regimes)
Reinforcement learning (adaptive strategy optimization)
Popular ML frameworks:
TensorFlow
PyTorch
These frameworks allow developers to build neural networks that predict price movement probabilities.
Deep Learning
Deep learning uses multi-layer neural networks to analyze:
High-frequency tick data
News sentiment
Options flow
Order book microstructure
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and LSTMs are often used for time-series forecasting.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP analyzes unstructured text data such as:
Earnings reports
Financial news
Social media sentiment
Central bank speeches
For example, AI systems may scan headlines to react to earnings surprises faster than human traders.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning models simulate trading as a game:
The model takes an action (buy/sell/hold)
Receives a reward (profit/loss)
Adjusts strategy to maximize long-term returns
This approach is particularly powerful for dynamic portfolio management.
3. Types of AI Trading Strategies
1. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
4
HFT uses AI models to:
Execute thousands of trades per second
Exploit micro price discrepancies
Provide market liquidity
These strategies rely on ultra-low latency infrastructure and co-located servers near exchanges.
2. Quantitative Long/Short Strategies
AI models analyze large stock universes and:
Rank securities based on predictive signals
Go long on top-ranked stocks
Short bottom-ranked stocks
Firms like Renaissance Technologies have famously used advanced mathematical and AI models to achieve consistent performance.
3. Sentiment-Based Trading
4
AI analyzes:
Twitter/X posts
Reddit discussions
Financial news feeds
Earnings transcripts
The rise of retail trading communities on platforms like Reddit has made sentiment-driven models increasingly relevant.
4. Statistical Arbitrage
AI detects temporary mispricings between correlated assets such as:
ETF vs. underlying basket
Futures vs. spot prices
Pairs trading opportunities
Models continuously retrain to adapt to changing correlations.
5. Portfolio Optimization
AI systems dynamically rebalance portfolios by:
Minimizing risk
Maximizing Sharpe ratio
Adjusting exposure to volatility regimes
Robo-advisors like Betterment use AI-driven optimization to provide automated investment management.
4. Leading AI Algorithmic Trading Platforms
Several platforms provide AI-driven tools for institutions and individuals:
Institutional Platforms
BlackRock – Uses AI in its Aladdin risk management system
Two Sigma – A data-driven quantitative hedge fund
Citadel – Employs advanced quantitative models
Retail & Developer Platforms
QuantConnect – Open-source algorithm development platform
MetaTrader – Popular retail trading platform with automated trading support
TradeStation – Offers advanced automation tools
5. How AI Trading Systems Work (Step-by-Step)
Data Collection
Market prices
Macroeconomic data
News and alternative data
Data Cleaning & Feature Engineering
Removing noise
Normalization
Creating predictive indicators
Model Training
Split into training/testing sets
Backtesting on historical data
Strategy Optimization
Parameter tuning
Risk constraints
Transaction cost modeling
Live Deployment
Real-time execution
Continuous performance monitoring
Risk Management
Stop-loss mechanisms
Position sizing rules
Drawdown limits
6. Benefits of AI-Powered Trading
Speed
AI systems react in microseconds, capturing opportunities humans cannot.
Data Processing Scale
They analyze:
Millions of data points per second
Global markets simultaneously
Complex multi-asset relationships
Emotion-Free Execution
AI eliminates fear, greed, and cognitive bias.
Adaptability
Advanced models adjust to changing volatility and macroeconomic conditions.
7. Risks and Challenges
Overfitting
Models may perform well in backtests but fail in live markets.
Black Box Problem
Deep learning models can be difficult to interpret.
Market Regime Shifts
Unexpected events (e.g., pandemics, geopolitical crises) can break models.
Regulatory Risks
Financial authorities increasingly scrutinize AI trading systems.
Flash Crashes
Highly automated systems can amplify volatility.
8. Infrastructure Requirements
Institutional AI trading systems require:
High-performance computing clusters
GPU acceleration
Low-latency data feeds
Co-location with exchanges
Robust cybersecurity
Cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure offer scalable AI infrastructure for trading firms.
9. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Governments and regulators monitor:
Market manipulation risks
Insider data misuse
Systemic stability threats
Algorithm transparency
As AI becomes more autonomous, regulatory frameworks are evolving to ensure financial stability.
10. The Future of AI in Trading
Emerging trends include:
1. Generative AI for Strategy Design
Large language models assist in coding trading strategies and analyzing market reports.
2. Quantum Computing Integration
Future quantum-enhanced optimization may improve portfolio construction.
3. Alternative Data Expansion
Satellite imagery, credit card data, and supply chain analytics are becoming key predictive signals.
4. Fully Autonomous Trading Agents
Reinforcement learning agents that continuously adapt in real time.
Conclusion
AI-powered algorithmic trading tools represent one of the most sophisticated applications of artificial intelligence in finance. By combining machine learning, big data analytics, and automated execution systems, these tools enhance speed, scalability, and decision-making precision.
However, they also introduce complexity, regulatory challenges, and systemic risks. As computing power increases and AI models become more advanced, algorithmic trading will likely grow even more dominant in global financial markets.
Whether used by large institutions like Renaissance Technologies or retail traders through platforms like QuantConnect, AI-driven trading is reshaping the future of investing—moving markets closer to a fully automated, data-driven financial ecosystem.
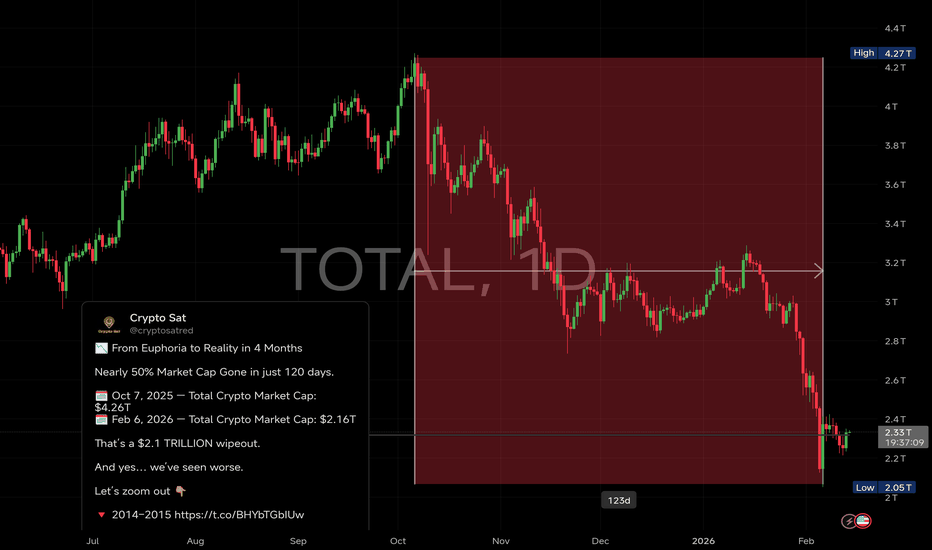
Nearly 50% Market Cap Gone in just 120 days📉 From Euphoria to Reality in 4 Months
Nearly 50% Market Cap Gone in just 120 days.
🗓 Oct 7, 2025 — Total Crypto Market Cap: $4.26T
🗓 Feb 6, 2026 — Total Crypto Market Cap: $2.16T
That’s a $2.1 TRILLION wipeout.
And yes… we’ve seen worse.
Let’s zoom out 👇
🔻 2014–2015 Bear Market
• Market cap fell ~-86%
• From ~$15B → ~$2B
Mt. Gox collapsed.
70% of Bitcoin volume vanished overnight.
Trust was shattered. Exchanges failed.
Crypto was declared “dead” for the first time.
🔻 2018 Bear Market
• Market cap crashed ~-84%
• From ~$830B → ~$130B
The ICO bubble imploded.
Projects with no product evaporated.
BTC fell from $20K to $3K.
ETH dropped ~94% at the lows.
Leverage got annihilated. Retail disappeared.
🔻 2022 Bear Market
• Market cap dropped ~-77%
• From ~$3T → ~$760B
VIE:LUNA collapsed in days.
Three Arrows Capital liquidated.
Celsius froze withdrawals.
FTX went bankrupt.
Contagion spread across the entire industry.
That was maximum fear.
📉 Current Drawdown
We’re sitting around ~49% down from the peak.
Painful? Absolutely.
Historic? Not yet.
True crypto bears didn’t stop at 30–40%.
They:
• Crushed sentiment
• Broke leverage
• Forced capitulation
• Made people swear they’d “never touch crypto again”
So here’s the uncomfortable question:
Is this just a violent mid-cycle reset?
Or is the deeper capitulation still ahead?
The market just erased $2.1T in value.
Now we watch carefully.
Because every brutal reset in history
eventually became the foundation
for the next expansion.
EURUSD BUY Breakout + Retest Entry
➡️ Break & Buy Above: 1.18956
When price decisively breaks above key resistance and holds, this signals bullish continuation.
📌 Stop-Loss: 1.1372
📌 Targets:
• TP1: 1.20888
• TP2: 1.21500
Why this works: Breakouts that retest previous resistance as support can unleash strong up moves.
NZD/JPY – Buy Entry Points📈 NZD/JPY – Buy Entry Points (Structured Plan)
Since you prefer clear trading levels, here is a clean buy setup plan.
🟢 1️⃣ Aggressive Buy (Trend Continuation)
Condition: Price holding above short-term support
Entry: 92.534 (on small pullback)
Stop Loss: 91.937
Target 1: 93.70
Target 2: 94.20
Target 3: 94.90