Chart Patterns
Part 3 Institutional Option Trading Vs. Techncal AnalysisOption Buyer vs Option Seller
Buyer pays premium, limited risk, unlimited profit.
Seller collects premium, limited profit, unlimited risk.
In real market volume, 80–90% of time sellers (institutions) dominate.
Expiry
Every option has a deadline (weekly, monthly).
On expiry day, option either:
ITM: Has value.
OTM: Becomes zero.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Moneyness of Options
ITM, ATM, OTM based on underlying price.
ATM options are most sensitive to price moves.
OTM options are cheap but decay fast.
Implied Volatility (IV)
Measures expected movement.
High IV = high premium.
IV crush happens after events (e.g., RBI meeting, Fed decision).
Part 5 Advance Option Trading Option Chain
Displays strike-wise premiums, open interest, volume, Greeks.
Traders read it to predict support/resistance and market structure.
Open Interest (OI)
Shows number of active contracts.
High call OI → resistance.
High put OI → support.
OI change indicates market sentiment shift.
Volume in Options
Measures trading activity at a price.
High volume = strong interest = better reliability.
Useful for volume profile and market structure analysis.
Part 2 Institutional Option Trading Vs. Techncal AnalysisTwo Types of Options
Call Option (CE): Right to buy at a chosen price.
Put Option (PE): Right to sell at a chosen price.
Strike Price
The fixed price at which you can buy/sell.
Example: Nifty 22,000 CE = option to buy Nifty at 22,000.
Premium
The price of the option contract.
Paid by the buyer, received by the seller (writer).
Part 1 Institutional Option Trading Vs. Techncal Analysis What Are Options?
Options are contracts that give you the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an asset at a fixed price before a certain date.
They are derivative instruments — their value comes from the underlying asset (index, stock, commodity, currency).
Options are mostly used for hedging, speculation, and income generation.
DAILY FOREX SCAN Session – 23 03 02 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
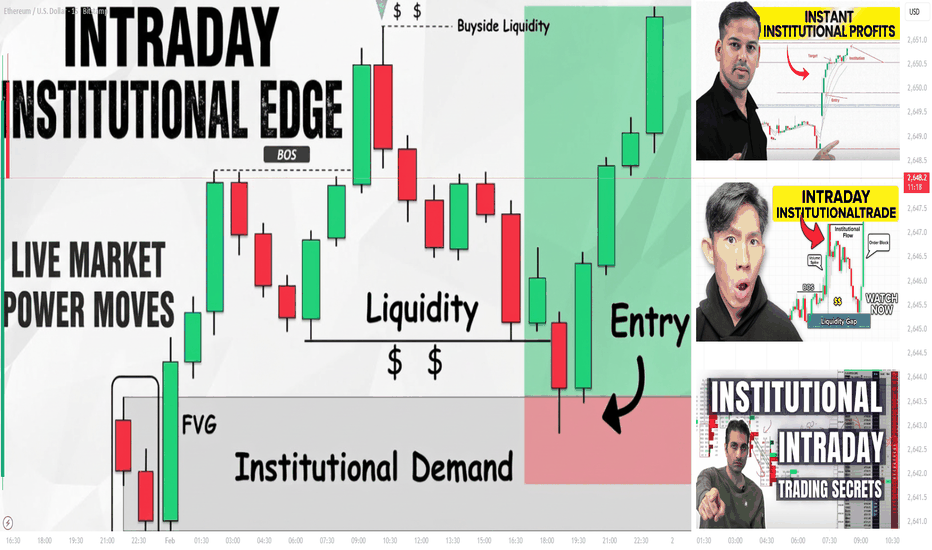
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingHedging with Options
Options are widely used for risk management.
Examples:
Buying put options to protect long equity portfolios
Using collars to limit upside and downside
Index puts for market crash protection
Hedging reduces returns slightly but protects capital, which is crucial for long-term survival.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Hedging with Options
Options are widely used for risk management.
Examples:
Buying put options to protect long equity portfolios
Using collars to limit upside and downside
Index puts for market crash protection
Hedging reduces returns slightly but protects capital, which is crucial for long-term survival.
Part 1 Technical Vs. Institutional Why Trade Options?
Option trading is preferred because it offers:
Leverage – Control large positions with small capital
Hedging – Protect portfolios against losses
Income Generation – Through option selling
Flexibility – Profit in bullish, bearish, and sideways markets
Defined Risk Strategies – With spreads and hedges
Divergence Secrets Option Buyers vs Option Sellers
Option Buyers
Pay premium
Limited risk
Unlimited or high reward
Affected negatively by time decay
Option Sellers (Writers)
Receive premium
Limited reward
Potentially unlimited risk
Benefit from time decay
This buyer–seller dynamic is the backbone of option trading.
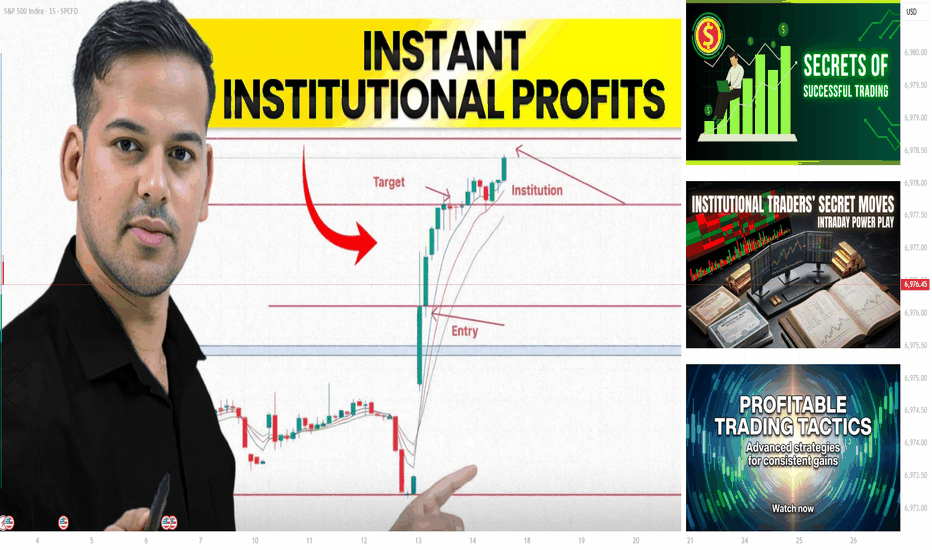
Part 1 Intraday Mater Class Introduction to Option Trading
Option trading is a derivative-based trading approach that allows traders and investors to profit from price movements, volatility, time decay, and even stagnant markets. Unlike equity trading—where profits depend largely on buying low and selling high—options provide multiple ways to make money, manage risk, and hedge portfolios.
An option is a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time period. The seller (writer) of the option has the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises it.
Options are widely traded in global markets and are extremely popular in India through NSE’s F&O segment, particularly in Index options (NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, FINNIFTY, SENSEX) and stock options.
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingOption Trading: Terms and Conditions
- Strike Price: Price at which option can be exercised.
- Expiry Date: Last day option can be exercised.
- Premium: Price paid for option.
- Lot Size: Number of shares/contracts per lot.
- Margin: Required for selling options.
- Exercise: Buyer chooses to buy/sell underlying asset.
- Assignment: Seller obligated to buy/sell if option exercised.
Part 1 Intraday Institutional Trading Who Should Trade Options?
People who:
- Understand options and risks.
- Have experience trading stocks/derivatives.
- Want to hedge existing positions.
- Are comfortable with potential losses.
Not suitable for:
- Beginners without knowledge.
- Risk-averse investors.
Part 5 Advance Trading Strategies Option Trading: Risks and BenefitsBenefits- Leverage: Control bigger positions with smaller capital.
- Limited Risk: Option buyers risk only the premium paid.
- Flexibility: Strategies for bullish, bearish, or neutral markets.
- Hedging: Protect portfolios with options.
Risks- Time Decay: Options lose value as expiry approaches.
- Volatility Risk: Options sensitive to changes in volatility.
- Loss of Premium: Buyers risk losing entire premium if wrong.
- Complexity: Strategies can be complex, require understanding.
Part 4 Technical Vs. Institutional Option TradingAdvanced Option Trading Strategies Explained1. Straddle/Strangle- Straddle: Buy call and put at same strike, profit from big price moves (volatility).
- Strangle: Buy call and put at different strikes, profit from big moves with lower cost.
2. Iron Condor- Sell OTM call and put spreads, profit from low volatility (price staying within range).
3. Butterfly Spread- Buy and sell options at multiple strikes, profit if price stays near middle strike.
4. Calendar Spread- Buy and sell options with same strike but different expiries, profit from time decay differences.
5. Ratio Spreads- Buy and sell options in different ratios, profit from volatility changes or direction.
Candle Patterns Basics of a Candlestick
Each candlestick represents price movement for a specific time period (1 minute, 1 day, 1 week, etc.). A candlestick has four key components:
Open – Price at the beginning of the period
Close – Price at the end of the period
High – Highest price during the period
Low – Lowest price during the period
Part 2 Technical Vs. Institutional Option Trading Types of Option Trading: Calls and Puts- Call Option:
- Gives buyer the right to BUY the underlying asset.
- Buyer expects price to RISE.
- Example: Buy Nifty Call at 22,000 strike, profit if Nifty goes above 22,000 + premium paid.
- Put Option:
- Gives buyer the right to SELL the underlying asset.
- Buyer expects price to FALL.
- Example: Buy Nifty Put at 22,000 strike, profit if Nifty goes below 22,000 - premium paid
DAILY FOREX SCAN Session – 22 30 01 26Scanning multiple forex pairs to filter high-quality trade setups. No trades are forced—only structure-based opportunities.
Note: There may be a delay in this video due to upload processing time.
Disclaimer: FX trading involves high leverage and substantial risk, and losses can exceed your initial investment. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trade at your own risk.
Part 2 Intraday Institutional TradingBest Practices for Retail Traders
1. Start with Buying Options
Risk is limited.
2. Prefer ATM or Slight ITM
Better stability, realistic probability.
3. Avoid Holding Overnight
Unless you understand IV, theta, and event risk.
4. Track Implied Volatility
Buy when IV is low, sell when IV is high.
5. Use a Trading Plan
Entry levels
Stop loss
Target
Position size
6. Don’t Chase Cheap OTM Options
They expire worthless most of the time.