Institution Option TradingInstitutional options trading refers to the large-scale use of options by financial institutions such as hedge funds, mutual funds, pension funds, banks, insurance companies, and proprietary trading firms. Unlike retail traders, institutional participants possess significant capital, advanced technology, and deep market insight, enabling them to deploy complex options strategies for hedging, speculation, and arbitrage purposes.
Institutional options trading plays a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. These large entities can influence volatility, liquidity, and price movements due to the size and frequency of their trades. Understanding how institutional traders operate provides retail traders with key insights to align their strategies effectively.
The Foundation of Options Trading
1. Understanding Options
Options are derivative contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified time frame.
Types of Options:
Call Options: Provide the right to buy.
Put Options: Provide the right to sell.
2. Key Option Terminologies
Premium: Price paid to buy the option.
Strike Price: Predetermined price to buy/sell the underlying asset.
Expiration Date: Last date the option can be exercised.
In-the-Money (ITM): Option with intrinsic value.
Out-of-the-Money (OTM): Option with no intrinsic value.
Chart Patterns
Technical ClassCandlestick patterns are essential tools in technical analysis that help traders predict potential market movements based on price action. Each candlestick represents four key data points: Open, High, Low, and Close prices within a specific time frame.
Types of Candlestick Patterns:
1. Single Candlestick Patterns
Doji: Market indecision (Open ≈ Close)
Hammer: Bullish reversal, long lower wick
Shooting Star: Bearish reversal, long upper wick
Spinning Top: Market indecision, small body
2. Double Candlestick Patterns
Bullish Engulfing: Strong bullish reversal
Bearish Engulfing: Strong bearish reversal
Tweezer Bottom/Top: Reversal signals
3. Triple Candlestick Patterns
Morning Star: Bullish reversal (3 candles)
Evening Star: Bearish reversal (3 candles)
Three White Soldiers: Strong bullish continuation
Three Black Crows: Strong bearish continuation
✅ Importance in Trading:
Predict Trend Reversals
Identify Continuation Patterns
Spot Market Sentiment Early
Institutional TradingDefinition:
Institutional trading refers to the buying and selling of financial securities by large organizations such as mutual funds, pension funds, insurance companies, hedge funds, and investment banks.
Key Characteristics:
High-volume transactions
Lower transaction costs due to bulk orders
Direct access to market liquidity
Use of advanced trading algorithms and platforms
Example Institutions:
BlackRock
Vanguard
Goldman Sachs
Who are Institutional Traders?
Types of Institutional Traders:
Mutual Funds: Trade for large-scale portfolio diversification.
Pension Funds: Focused on long-term stable returns.
Hedge Funds: Seek high returns with complex strategies.
Insurance Companies: Invest premiums for steady growth.
Investment Banks: Trade for proprietary gains and clients.
How They Operate:
Work with large research teams
Utilize proprietary trading algorithms
Influence market prices significantly
Institutional TradingDivergence Trading
Divergence trading is a technical strategy based on the observation that asset prices and their related indicators (like RSI, MACD, etc.) sometimes move in opposite directions.
Types of Divergence:
Regular Divergence: Predicts potential trend reversals.
Hidden Divergence: Suggests trend continuation.
Tools Used:
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Stochastic Oscillator
How Divergence Works:
If prices are making new highs but the indicator isn’t, it signals weakening momentum and a possible reversal.
If prices are making new lows but the indicator isn’t, it could indicate that selling pressure is fading.
Benefits:
Early identification of potential trend changes.
Effective in volatile markets.
Risks:
False signals can occur, leading to premature trade entries.
Master Institutional TradingBenefits of Option Trading:
Leverage with less capital.
Hedging against market risks.
Income generation through premium collection.
Risks of Option Trading:
Complex pricing structures.
Potential for significant losses if not properly managed.
Divergence Trading
Divergence trading is a technical strategy based on the observation that asset prices and their related indicators (like RSI, MACD, etc.) sometimes move in opposite directions.
Institutional Master class
Option Trading Explained
Options are financial derivatives that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific period.
Types of Options:
Call Option: Right to buy the underlying asset.
Put Option: Right to sell the underlying asset.
Components of an Option Contract:
Strike Price: The agreed price to buy/sell.
Premium: Price paid to acquire the option.
Expiration Date: Date when the option contract ends.
Option Trading Strategies:
Buying Calls/Puts: Simple directional bets.
Covered Call: Holding stock while selling a call option to generate income.
Protective Put: Buying a put option to hedge a long stock position.
Spreads: Combining options to limit risk and cost.
Institutional Option TradingStock Market Participants:
Retail Investors: Individual traders and investors.
Institutional Investors: Mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, etc.
Market Makers: Provide liquidity by constantly quoting buy and sell prices.
Stock Trading Types:
Delivery Trading: Shares are purchased and held for longer periods.
Intraday Trading: Shares are bought and sold on the same day.
Importance of the Stock Market:
Helps in wealth creation.
Reflects economic health.
Provides investment and diversification opportunities.
Option Trading The stock market is a platform where shares of publicly listed companies are bought and sold. It serves two primary functions: providing companies with capital to grow and giving investors the opportunity to share in the profits of publicly traded companies.
Key Components:
Stocks: Ownership shares in a company.
Stock Exchanges: Platforms like the NYSE, NASDAQ, and BSE where trading occurs.
Indices: Benchmarks like the S&P 500 or Nifty 50 that track the performance of groups of stocks.
Institutional Trading Trading is the act of buying and selling financial instruments like stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, and derivatives with the goal of making a profit. Traders operate in various markets, including stock markets, forex markets, commodity markets, and cryptocurrency markets. Trading is often contrasted with investing, which is generally focused on long-term wealth accumulation.
There are different types of traders:
Day Traders: Buy and sell securities within the same trading day.
Swing Traders: Hold positions from a few days to several weeks.
Scalp Traders: Execute dozens to hundreds of trades in a day, aiming for small profits.
Position Traders: Hold trades for months or even years, blending trading and investing.
Trading can be driven by technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both. Traders use a wide array of tools and strategies to analyze price movements and market trends.
Institutional Option Trading Part -xTrading Techniques
Block Trading: Large, privately negotiated trades.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Using algorithms for rapid-fire trades.
Algorithmic Trading: Automated trading based on predefined criteria.
Technology in Institutional Trading
Low Latency Networks: For speed advantage.
Advanced Algorithms: For market making, arbitrage, and execution.
Data Analytics: Real-time analysis to inform trading decisions.
Market Impact and Regulations
Institutional traders can move markets, prompting regulatory oversight.
Regulatory Bodies:
SEC (U.S.): Securities and Exchange Commission.
FINRA (U.S.): Financial Industry Regulatory Authority.
SEBI (India): Securities and Exchange Board of India.
Key Regulations:
Reporting Requirements: Large trades must be reported.
Fair Trading Practices: Prevent market manipulation.
Risk Controls: Institutions must manage trading risks appropriately.
Institutional TradingInstitutional Investment Process
Setting Objectives: Determining risk tolerance, return targets, and time horizons.
Asset Allocation: Dividing the portfolio among different asset classes.
Security Selection: Choosing individual investments.
Portfolio Monitoring: Continuously reviewing performance and risk.
Institutional Trading
Institutional trading refers to the buying and selling of securities in large volumes by institutions.
Types of Institutional Traders
Proprietary Traders: Trade with the institution's own money.
Agency Traders: Execute trades on behalf of clients.
Program Traders: Use algorithms to trade baskets of stocks.
Trading Venues
Exchanges: NYSE, NASDAQ, etc.
Dark Pools: Private exchanges for large orders.
Over-the-Counter (OTC): Direct trading without an exchange.
Advantages of Institutional Option TradingAdvantages of Institutional Option Trading
Institutional Investing
Institutional investing is the process of managing large-scale investment portfolios with long-term goals.
Investment Objectives
Capital Preservation: Maintaining the value of assets.
Capital Appreciation: Growing the portfolio over time.
Income Generation: Providing steady returns through dividends or interest.
Institutional Option Trading, Investing, and TradingInstitutional trading and investing significantly differ from retail activities. Institutions trade in large volumes, use complex strategies, and have access to exclusive information and tools. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of institutional option trading, investing, and general trading practices, detailing their methodologies, tools, and market impacts.
Understanding Institutional Investors
Institutional investors include mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, insurance companies, and large banks. These entities manage vast sums of money, often on behalf of others, and possess substantial market influence.
Key Characteristics:
Large Capital Base: Institutions trade in millions or billions.
Market Influence: Their trades can impact prices significantly.
Professional Resources: Access to cutting-edge research, proprietary algorithms, and high-speed trading platforms.
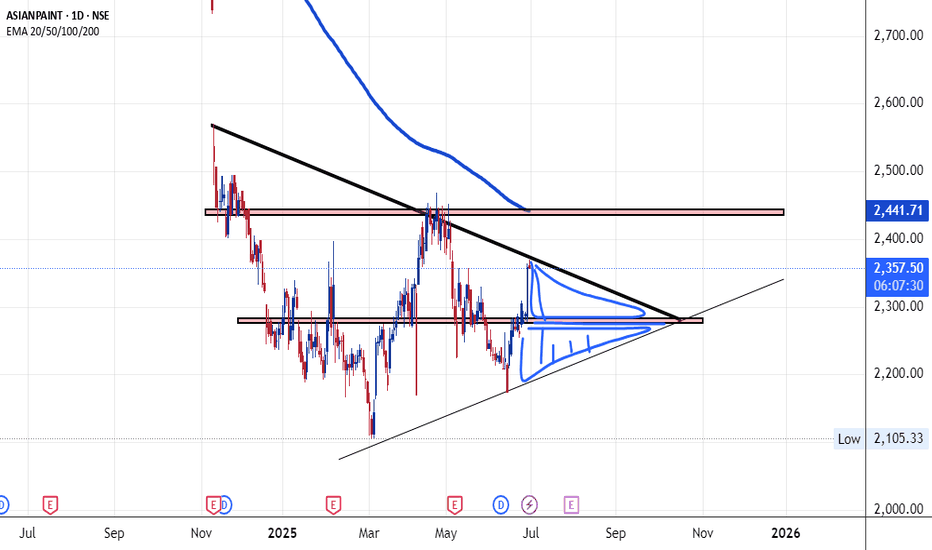
Asian Paints Chart Move Update **Asian Paints Business Model**:
---
## 🏢 **Asian Paints Ltd – Business Model Overview**
### 1. **Company Overview**
* **Founded:** 1942
* **Headquarters:** Mumbai, India
* **Founders:** Champaklal H. Choksey, Chimanlal Choksi, Suryakant Dani & Arvind Vakil
* **CEO & MD:** Amit Syngle (as of 2024)
* **Industry:** Paints and Coatings, Home Décor, Bath Fittings
* **Market Position:** India's largest and Asia’s third-largest paint company
---
### 2. **Core Business Segments**
| Segment | Description |
| ---------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Decorative Paints** | Wall paints, enamels, wood finishes, distempers, primers, etc. |
| **Industrial Coatings** | Automotive and powder coatings in partnership with PPG Inc. |
| **Home Improvement & Décor** | Kitchen, bath fittings (via Sleek and Ess Ess), waterproofing |
| **International Operations** | Presence in 15+ countries, strong in South Asia and Middle East |
---
### 3. **Key Revenue Streams**
* **Retail Sales** (B2C): Via large dealer and distributor networks across India.
* **Institutional/B2B Sales**: Projects, contractors, automotive OEMs.
* **Premium Product Lines**: Royale, Ultima, Tractor Emulsion.
* **Services**: Home painting services, waterproofing, colour consultancy.
---
### 4. **Distribution Network**
* Over **70,000+ dealers** in India
* **Robust supply chain** with over 30+ manufacturing facilities globally
* Digital tools like **Colour Visualizers, SmartCare App** for consumer engagement
---
### 5. **Digital & Technology Integration**
* **ColourNext** trend forecasting platform
* Use of **AI/ML in demand forecasting** and inventory management
* E-commerce platforms for paints & décor
* CRM systems for improved customer service and feedback
---
### 6. **Business Strategy**
* **Backward Integration**: Manufacturing of raw materials like emulsions & pigments
* **Innovation**: Focus on eco-friendly and long-lasting paints
* **Brand Building**: Iconic advertising (e.g., “Har Ghar Kuch Kehta Hai”)
* **Customer-Centric Services**: Safe Painting Service, Colour Consultancy, etc.
---
### 7. **Competitive Advantages**
* **Strong Brand Loyalty**
* **Pan-India Dealer Network**
* **In-house R\&D** and innovation capabilities
* **Diverse Product Portfolio** for all price points and segments
* **Agile supply chain and logistics**
---
### 8. **Recent Initiatives**
* Expansion into **home décor** through **Beautiful Homes platform**
* Entry into **furnishings & lighting**
* Strengthening of **waterproofing solutions**
* Focus on **sustainable paints** (low VOC, green-certified)
---
### 9. **Challenges**
* Raw material price volatility (e.g., crude oil-based inputs)
* Competitive pressure from **Berger Paints, Nerolac, Akzo Nobel**
* Seasonal demand patterns
* Margin pressure in low-end segments
---
### 10. **Conclusion**
Asian Paints is not just a paint company; it’s evolving into a **comprehensive home improvement brand**. With its innovation-driven strategy, strong retail presence, and digital transformation efforts, it continues to lead the Indian market and expand globally.
---
thanks & regards
the golden farms of equity
Institutional Option Trading Part -3Institutional Investment Process
Setting Objectives: Determining risk tolerance, return targets, and time horizons.
Asset Allocation: Dividing the portfolio among different asset classes.
Security Selection: Choosing individual investments.
Portfolio Monitoring: Continuously reviewing performance and risk.
Institutional Trading
Institutional trading refers to the buying and selling of securities in large volumes by institutions.
Types of Institutional Traders
Proprietary Traders: Trade with the institution's own money.
Agency Traders: Execute trades on behalf of clients.
Program Traders: Use algorithms to trade baskets of stocks.
Trading Venues
Exchanges: NYSE, NASDAQ, etc.
Dark Pools: Private exchanges for large orders.
Over-the-Counter (OTC): Direct trading without an exchange.
Institutional Option Trading Part -10Investment Strategies
Active Management: Constantly buying and selling assets to outperform benchmarks.
Passive Management: Tracking indices like the S&P 500 to match market performance.
Value Investing: Identifying undervalued stocks.
Growth Investing: Focusing on companies with high growth potential.
Quantitative Investing: Using mathematical models to guide investment decisions.
Risk Management
Diversification: Spreading investments across various sectors and assets.
Hedging: Using derivatives to offset risks.
Liquidity Management: Ensuring enough cash to meet obligations.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to financial regulations.